Pupil assessment (9)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
what is the pupil
an aperture in the iris
regulates retinal illumination
very small (miotic) in brightly lit conditions and large (mydriatic) in dim illumination
covered by a membrane up to the 8th month gestation
what 2 muscles does the iris contain
sphincter pupillae
dilator pupillae
both innervated by thr autonomic nervous system : controlled by the central neural pathways that are influenced by retinal illumination , viewing distance, attention and alertness
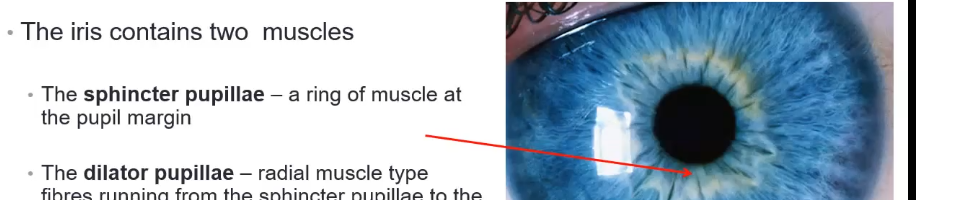
what is the sphincter pupillae
a ring of muscle at pupil margin

what is the dilator pupillae
a radial muscle type fibres running from the sphincter pupillae to the iris root
sphincter muscle
circular muscle
anchored to adjacent stroma and retains its function even if severed
contraction of the sphincter causes pupil to constrict in miosis.
muscle is innervated by the parasympathetic system
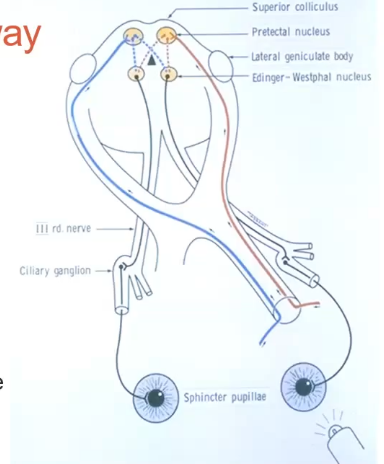
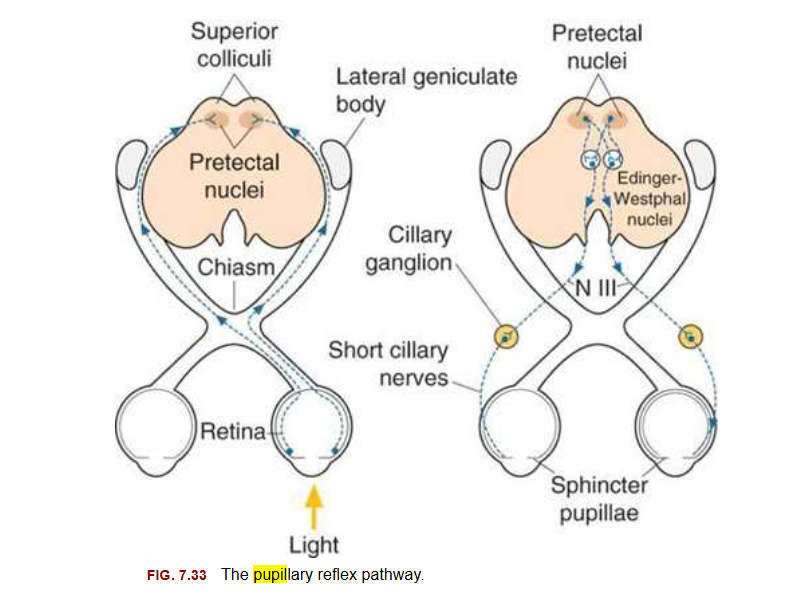
Afferent: to the brain - optic nerve → chiasm → optic tract → pretectal nucleus
Efferent: from the brain - ciliary gaglion → 3rd nerve → sphincter pupillae
section of iris: shows sphincter
dilator: myoepithelium which is muscle and epithelial properies

Afferent pathway
going from retina down the optic nerve, half goes into the brain on one side, other goes to the brain on the opposite side
fibres of sphincter muscle doesnt go too far into the brain . hits pre tectal nucleus
crosses over- so any light shon on one eye should affect both
efferent pathway
ciliary ganglion from the brain, passes the 3rd nerve then to the sphincter pupillae
dilator - innervation pathway
dilator pupillae
innervated by sympathetic system
arises from the superior cervical ganglion
lack of stimulation of sphincter causes pupils to get bigger
starts from the central nervous system in the neck ( cervical ganglion)
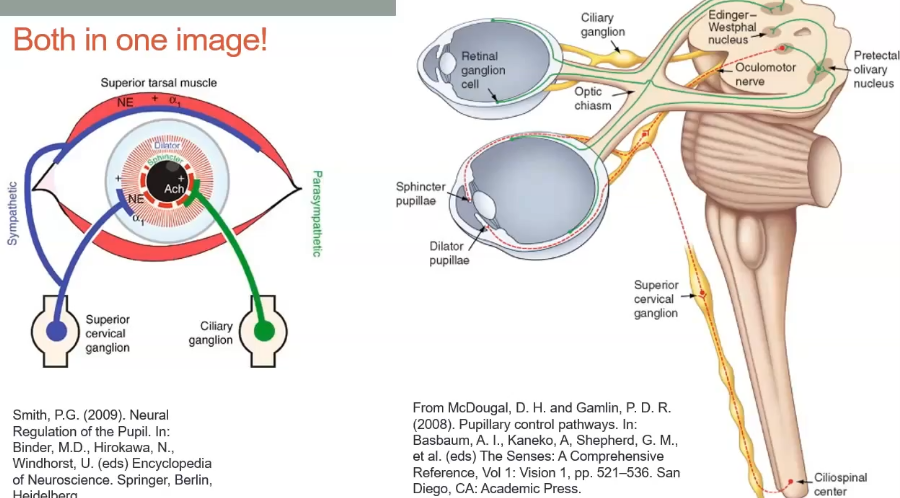
both pathways in the eye
pupillary reflec pathway
pupil responses
pupil response- dilation
this is when pupil gets larger
called dilation/mydriasis
stimulated by sympathetic nervous system or lack of stim from sphincter
associated with low light
associated with mydriatic drugs eg tropicamide or phenylphrine , or amy sympathetic NS stimulant
associated with excitement or fear
pupipl response- constriction
pupil gets smaller
miosis
induced by the parasympatheic action on the sphincter muscle
associated with bright light
miotic drugs
what are the 2 types of pupil responses
direct- seen when the light enters the eye
consensual- seen when light falls in the fellow eye
pupils should react as a pair
if shine light in one eye and that pupil constricts its called direct
when shine light in one pupil and look at the other eye, thats consensual
the pupil- the near triad
accomodation - pupil constriction change when looking at distance vs near
convergence
pupil constriction
pupil size
it is governed by a balance between the sypathetic and parasympathetic input
methods of assessment of the pupil
done in normal room illumination
px remove glasses
look at a letter on the chart
use a spotlight if they have a vision of less than 6/18 or theyre hyperopic , to avoid stimulating accom
sit in front of the patient, dont block their view
check for size shape and location
checkng pupil size
both pupils should be equal in size
bright light: 3-6 mm in da=iameter
dim light: 4-8mm in diameter
the pupil size will show normal fluctuations known as hippus
pupil size nomally decreases with age
pupil shape
both pupils should be round or even slightly oval
location of pupils
both pupils should be central in the iris
measuring pupil size
can use a ruler or pupil gauge
have ruler on forehead and as close to thr px eye as possible
reduce the room illumination but keep emough light to se the pupil margin
use a UV burton lamp if eyes are dark
do in bright and dark
repeat the pupil measurements
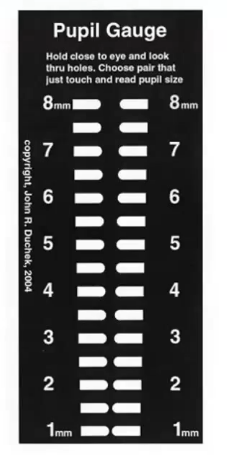
duchek pupil gauge
peoce or plastic, cardboard with holes in it
distance between holes get larger
start from bottom
hold the gauge as close to the eye as possible
look through the bottom pair of holes
the holes appear to overlap through which you can see the distance target
move the card down. As you lool through the holes that are further apart the images will overlap less
at some point the images will only just touch ( no black in between them) ,and youll only be able to see the distance target . this is the pupil size
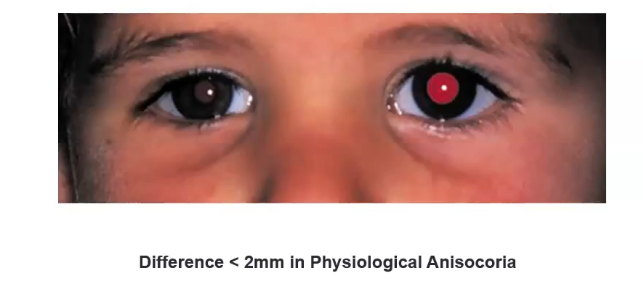
anisocoria
unequal pupil size in normal room illumination
down to physiology
direct and consensual reflexes
px fixates ahead at the chart or spot of light
shine a pen torch into the right eye (5-10cm)
position the light at the inferior temporal side
watch the right eye for constriction
note down speed and degree of response
this is direct response
do the same but watch the left pupil for constriction : consensual response
may need a burton lamp
repeat with light entering the left eye
observing the direct and consensual dilation
shine the light in the right eye as before
observe the pupil response in both eyes when the light is removed
it should be equal
now repeat shining the light in the left eye
observe the diation when the light is removed
should be equal and smooth