Thermal Properties
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MEE1004: Mechanics of Materials - Lecture 8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Thermal properties
Quantify the response of materials to heat.
Two important reference termperature
Melting temperature Tm
Glass transition temperature Tg
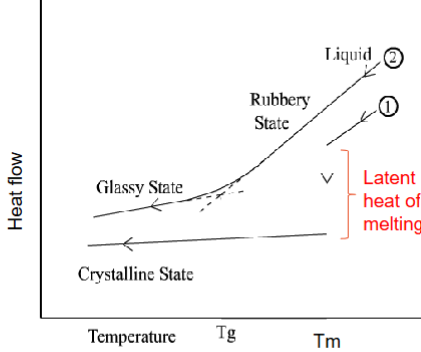
Crystalline and non crystalline thermal properties
Crystalline materials: defined T at which they melt (Tm)
Non-crystalline solids: transition T from a true solid to a very viscous liquid (Tg)
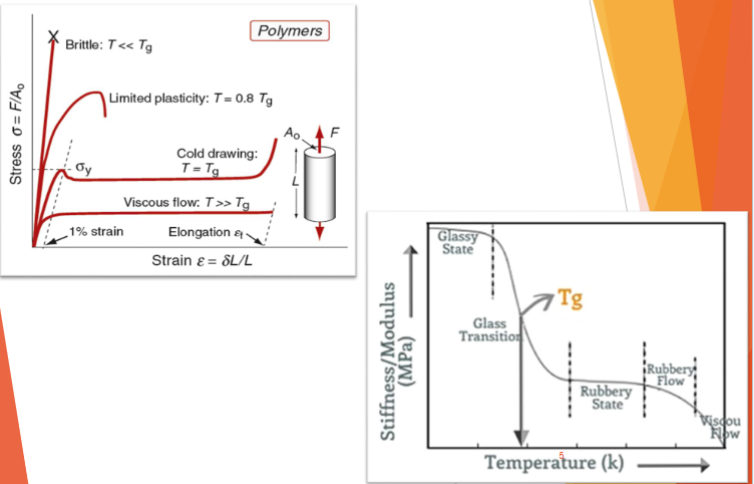
Stiffness of Polymers
Thermal Conductivity (λ)
Heat conduction rate through a solid at steady-state (temperature profile does not change with time)
Unit: W/m.K
Thermal Diffusivity (a)
Conduction rate of a temperature pulse (transient, non-constant flow of energy)
Unit: m2/s
Thermal diffusivity equation
λ: thermal conductivity
Cp: specific heat capacity
ρCp: volumetric heat capacity
ρ: density
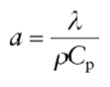
Solids thermal properties
λ/a is a constant
Foams thermal properties
Low λ, do not transmit much heat
Change T relatively quickly
Good for insulating applications
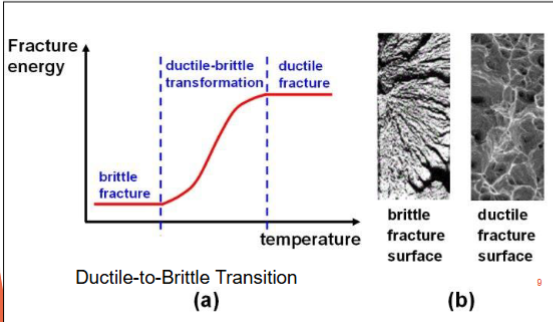
Temperature dependence and material properties
At low temperatures most metals and all polymers become brittle.
Exceptions: FCC metals such as copper, stainless steel.
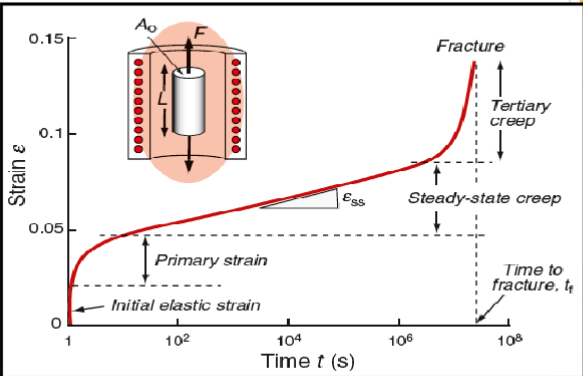
Creep
Slow and continuous deformation of a material that occurs as a stress less than σ generally at elevated temperatures.
Creep factors
Time, load, (temperature)
Creep curves
Creep v diffusion
Creep requires relative motion of atoms
Diffusion is the spontaneous intermixing of atoms over time
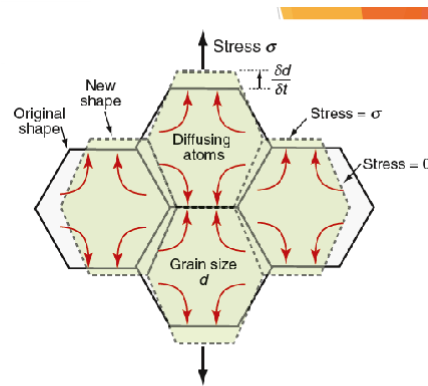
Creep in polycrystalline materials by diffusion
Grain boundaries act as sources and sinks for vacancies
If a vacancy joins a boundary, an atom must leave it (crystal eaten away)
If a vacancy leaves a boundary, an atom must joint it (face grows)
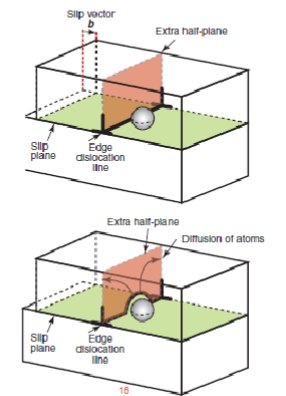
Creep by dislocation climb
The diffusion can unlock dislocation from obstacles
Half plane of atom diffused away - dislocation climb
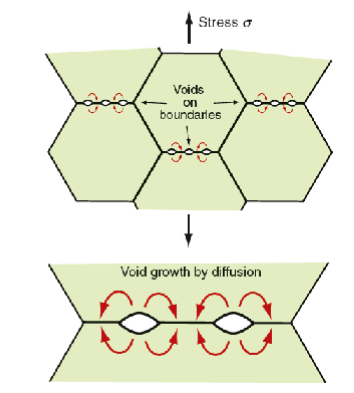
Creep fracture
Fracture occurs due to creep (tertiary creep stage) by creating voids that nucleate on grain boundaries
Thin walled pressure vessel hoop stress equation
σ: hoop stress or circumferential stress
p: internal pressure
R: radius
t: wall thickness
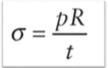
Thermal conductivity
Rate at which heat is conducted through a solid a steady state (temperature profile does not change with time).
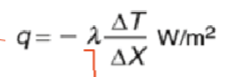
Thermal diffusivity
How quickly a temperature pulse can transverse a material of known thickness when a heat source is applied briefly on one side. Governs transient heat flow.
How strengthening processes affect thermal conductivity
Strengthening mechanisms such as solid solution and precipitation increase the yield strength of metals but introduce scattering sites for phonons which can reduce thermal conductivity.