World history unit 5
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/83
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
1
New cards
What was the Minoan civilization
the first Aegean civilization centered on the Island of Crete with its capital at Knossos
2
New cards
What was the Minoan civilization like?
* Women had a High Status
* Influential in Later Greek Culture
* Powerful Seafaring People- Dominated Trade
* Loved Sports! Bull Jumping, Wrestling, Boxing
* Linear A as the language
* Influential in Later Greek Culture
* Powerful Seafaring People- Dominated Trade
* Loved Sports! Bull Jumping, Wrestling, Boxing
* Linear A as the language
3
New cards
What did the palace at Knossos look like?
Open, more peaceful, had lots of art mostly containing bulls, had black and red columns
4
New cards
What is a possible end to the Minoan civilization?
Volcanic Explosion
5
New cards
What were the Myceneans like?
* Begin to trade with Minoans
* language- Linear B.
* **Began to build fortresses on the Peloponnesus**
* **City-States with citadels: fortified palaces centered on hills, civilians live outside the walls.**
* **Warrior People:**
* **Raiders/pirates**
* **Mercenaries**
* **Conquerors (Crete)**
* **Traders and merchants**
* **Minoan Influence**
* language- Linear B.
* **Began to build fortresses on the Peloponnesus**
* **City-States with citadels: fortified palaces centered on hills, civilians live outside the walls.**
* **Warrior People:**
* **Raiders/pirates**
* **Mercenaries**
* **Conquerors (Crete)**
* **Traders and merchants**
* **Minoan Influence**
6
New cards
What was the Mycenean involvement in the trojan war?
* c. 1250 possible trade war against Troy
* weakened strength of Kings at homeWH
* weakened strength of Kings at homeWH
7
New cards
What was Mycenae like?
* More war focused
* Had walls around the city
* Fortress was built on a hilltop
* Had walls around the city
* Fortress was built on a hilltop
8
New cards
Who was Agamemnon and what did he do?
He was the king of Mycenae and commanded the Greeks during the trojan war
9
New cards
Dark Ages – Dorian Age
c. 1110-750 BCE
c. 1110-750 BCE
* **Everything decreased:**
* **food production**
* **population**
* **writing**
* **art**
* **Trade**
* **Dorians settled in Peloponnesus.**
* **Weak Kings ruled small territories with aristocratic councils (clans).**
* Homer’s poems revealed what life in the Dark Ages was like
* **food production**
* **population**
* **writing**
* **art**
* **Trade**
* **Dorians settled in Peloponnesus.**
* **Weak Kings ruled small territories with aristocratic councils (clans).**
* Homer’s poems revealed what life in the Dark Ages was like
10
New cards
What are the column names for the most simple, the somewhat simple and somewhat complex, and the fancy one
Doric, Ionic, Corinthian (in order)
11
New cards
After Athens and Sparta were left weakened from the Peloponnesian War, THIS KING conquered Greece but passed away before he was able to conquer anything further.
Philip 2 of macedon
12
New cards
What was the capital of the Persian Empire established by Darius?
Persepolis
13
New cards
What is a famous Greek structure involving columns called?
The Parthenon
14
New cards
List the art eras and the differences between them.
Archaic - very simple people standing up straight
Classical- More movement, including people throwing things and sports “moment before movement”
Hellenistic- extremely detailed impressive sculptures and the wet drape style
Classical- More movement, including people throwing things and sports “moment before movement”
Hellenistic- extremely detailed impressive sculptures and the wet drape style
15
New cards
What is a path associated with the Persian empire?
The Persian Royal Road
16
New cards
While greatly outnumbered in most battles, the Greeks were partially successful in the Persian Wars because of their use of __**this**__ formation pictured below
Phalanx
17
New cards
What led immediately to the Dark Ages in Greece, a time of reduced art, trade, and population growth.
Dorian invasion
18
New cards
In the Republic, Plato believed that the best form of government is one ruled by …
Philosopher kings
19
New cards
Greek Mythology was often used to do what two things
1. Explain natural phenomena
2. Teach us morals and values
20
New cards
Why were the Olympics important for Greek Society, and even today?
Notable because even if these city-states were in conflict, they put down their arms for this competition
21
New cards
Why was Greek city-state unification difficult?
Because of their geography! Mountainous terrain physically prevented Greek unification, leading to different cultural city states.
22
New cards
He wanted to punish the Greeks for their support of the Ionian Revolt, thereby reigniting the war between Greece and Persia for the final time.
Xerxes
23
New cards
Which Polis is being discussed in this source?
“The ability to read and to write was important to their people – reading and writing was needed in order to be a citizen, and to carry out their duty. Their citizens needed a basic knowledge of reading and writing in order to be a member of the government. Education was made available by the government. Only male citizens were sent to school. There they would learn about poetry, literature, math, and science. It was all about preparing citizens to be in the government. Slaves were not awarded these same rights but did attain limited education in the household.”
“The ability to read and to write was important to their people – reading and writing was needed in order to be a citizen, and to carry out their duty. Their citizens needed a basic knowledge of reading and writing in order to be a member of the government. Education was made available by the government. Only male citizens were sent to school. There they would learn about poetry, literature, math, and science. It was all about preparing citizens to be in the government. Slaves were not awarded these same rights but did attain limited education in the household.”
Athens
24
New cards
What does the Acronym MOAT-D stand for?
Monarchy → Oligarchy → Aristocracy → Tyranny → Democracy
25
New cards
This system devised by Darius divided the Persian Empire into administrative districts, led by governors, that made life easier for the government and daily life. People were able to access their government easier if they needed anything, and the government was able to tax and rule the people easier.
Satrapies (Leaders are Satraps)
26
New cards
What did Cleisthenes do?
* Known as the “Father of Democracy,” he instituted democratic reforms in Athens that allowed male citizens to participate in government instead of a government that was simply ruled by a King or Emperor.
* Established a democratic court system with trial by jury.
* Established a democratic court system with trial by jury.
27
New cards
This Philosopher was sentenced to death by Athens for “corrupting the youth.” He spent his time pushing us to question the basic assumptions we are taught in society, and to always ask questions of authority figures.
Socrates
28
New cards
What is an Oligarchy/Aristocracy?
Rule by wealthy individuals, they control the state’s resources and military. There are typically a small number of them.
29
New cards
What is one of Alexander the Great’s greatest legacy?
Spreading and blending cultures and ideas
30
New cards
One of Alexander the Great’s greatest legacy was the assimilation and blending of cultures within the boundaries of his Empire. This was known as the beginning of a new era, the spread of _______________ culture.
Hellenistic
31
New cards
Put the battles of the Persian Wars in order
Marathon, Thermopylae, Salamis, Platea
32
New cards
Battle of Marathon
Importance: myth of Persian invincibility is broken
occurred under Darius’s rule
occurred under Darius’s rule
33
New cards
Battle of Thermopylae
The Persians burn Athens to the ground.
Outcome: Persians win, but Persian army is delayed.
Important Consequence: this allows Greeks time to reorganize.
Outcome: Persians win, but Persian army is delayed.
Important Consequence: this allows Greeks time to reorganize.
34
New cards
Battle of Salamis
Athenians fake retreat and lure Persians into the strait.
Athenian navy victorious
(This battle was fought in the water)
Athenian navy victorious
(This battle was fought in the water)
35
New cards
Battle of Platea
This was the final battle of the Persian War, a decisive Greek victory and the Persian Empire was never able to conquer Greece.
36
New cards
Order the following:
Athenian Golden Age
Dark Ages Greece
Macedonian Conquest
Mycenaean/Minoan Greece
Greco-Persian War
Peloponnesian War
Athenian Golden Age
Dark Ages Greece
Macedonian Conquest
Mycenaean/Minoan Greece
Greco-Persian War
Peloponnesian War
Mycenaean/Minoan Greece
Dark Ages Greece
Greco-Persian War
Athenian Golden Age
Peloponnesian War
Macedonian Conquest
Dark Ages Greece
Greco-Persian War
Athenian Golden Age
Peloponnesian War
Macedonian Conquest
37
New cards
Skepticism
This Greek School of Thought teaches us to never take strong positions on political, moral, and social issues because they doubted the possibility of anyone knowing everything.
38
New cards
Stoicism
This Greek School of Thought was very influential on the later Romans, and taught logic, respecting the natural order of things, and the value in seeking a virtuous life.
39
New cards
Epicureans
Identified pleasure as the greatest good. By pleasure they did not mean unbridled hedonism but, rather, a state of quiet satisfaction that would shield them from the pressures of the Hellenistic world
40
New cards
Cyrus the great
* This Persian King is highly regarded in Hebrew culture because he freed the Jews during their Babylonian Captivity
* **Tolerant** Ruler
* He allowed conquered people to keep their leaders, religions, and other cultural practices.
* Cyrus the Great began the dynasty and wrote that he wanted to, *“Conquer the world.”*
* Formed the largest army the world had ever known
* Made Pasargadae the capital and his tomb was there
* **Tolerant** Ruler
* He allowed conquered people to keep their leaders, religions, and other cultural practices.
* Cyrus the Great began the dynasty and wrote that he wanted to, *“Conquer the world.”*
* Formed the largest army the world had ever known
* Made Pasargadae the capital and his tomb was there
41
New cards
This Greek Scientist first theorized the atom was the singular entity that makes up all living beings
Democritus
42
New cards
This Athenian leader established a permanent, written, law code for Athens that helped solidify the power of the Aristocracy.
Draco
\
\
\
\
(malfoy ?!?)
\
\
\
\
(malfoy ?!?)
43
New cards
Plato’s philosophy pushes us to question the world around us, and notably, to consider what is truly meant by ‘beauty’, ‘truth,’ and even the ideal government. He discusses his theory of ‘Forms’ and these aforementioned ideas in THIS story.
Allegory of the Cave
44
New cards
What was Plato’s most famous book?
The Republic
45
New cards
This Greek Scientist reformed medicine by dedicating his medical texts and practices based directly on anatomy instead of religious or spiritual beliefs.
Hippocrates
46
New cards
What did Solon do?
This Athenian leader made citizen classes based on income not birth, thus allowing poorer classes a chance in holding power. His reforms helps transition Athens away from an Aristocracy towards a Democracy. He also cancelled debt and forbade debt slavery.
47
New cards
Known as the “Father of Tragedy” his plays and creation of this genre have influenced movies, art, theatre, and literature to this day.
Aeschylus
48
New cards
Socrates → Plato → _____________ → Alexander the Great
Aristotle
49
New cards
________ the Great began the _____________ Dynasty and set the stage for the rest of their Empire’s history by declaring that he wanted to, “Conquer the World.”
Cyrus, Achaemenid
50
New cards
Cleisthenes reformed this government body, composed of male citizens, that operated like a direct democracy. Many say that this government body officially made Athens a Democracy.
The Assembly
51
New cards
Who was Pisistratus?
* This Tyrant took power by force in Athens, but beloved by the Athenian people for his reforms that helped the lower classes, reduced taxation, and introducing festivals for the city.
* Helped the lower classes by exiling nobles, seizing their lands and giving them to the poor Provided new jobs for the poor
* Helped the lower classes by exiling nobles, seizing their lands and giving them to the poor Provided new jobs for the poor
52
New cards
4 Overall Effects of the Persian War
* Increased sense of Greece Nationality and Unity (only temporary)
* Athenian Navy dominates the Aegean Sea, leading to greater colonization and wealth from trade which Sparta resents
* Athens enters a Golden Age and creates Democracy
* Creation of the Delian and Peloponnesian League which in turn further leads to the Peloponnesian War
* Athenian Navy dominates the Aegean Sea, leading to greater colonization and wealth from trade which Sparta resents
* Athens enters a Golden Age and creates Democracy
* Creation of the Delian and Peloponnesian League which in turn further leads to the Peloponnesian War
53
New cards
The causes of the Peloponnesian war
* Many city-states resented growing Athenian power
* Especially when Athens became leader of Delian League
* To counter the Delian League, Sparta and other enemies form the Peloponnesian League
* Both cities press for war as each thought they had the advantage-- **Athens = navy & Sparta = army**
* Especially when Athens became leader of Delian League
* To counter the Delian League, Sparta and other enemies form the Peloponnesian League
* Both cities press for war as each thought they had the advantage-- **Athens = navy & Sparta = army**
54
New cards
Who was Pericles
* Leader during the golden age of Athens
* Supported the arts and the government paid for large scale public works, theaters, and monuments
* Extended gov. jobs to all free males in society
* Ostracism: Could expel a citizen for 10 years
* Pericles died in the Peloponnesian war and that ended the golden age
* Supported the arts and the government paid for large scale public works, theaters, and monuments
* Extended gov. jobs to all free males in society
* Ostracism: Could expel a citizen for 10 years
* Pericles died in the Peloponnesian war and that ended the golden age
55
New cards
What is Important about the Peloponnesian War?
* Sparta wins (with some $$ from Persians)
* Ends Athenian Golden Age
* Democratic government suffers- Philosophers Start to Question
* Greece becomes vulnerable to Macedonian invasion.
* Ends Athenian Golden Age
* Democratic government suffers- Philosophers Start to Question
* Greece becomes vulnerable to Macedonian invasion.
56
New cards
Famous Greek historian that detailed the Persian War
Herodotus (Thucydides detailed the *Peloponnesus* war)
57
New cards
Socrates
* Question everything!
* “Socratic Method”
* Sentenced to death by the state
* “Socratic Method”
* Sentenced to death by the state
58
New cards
Plato
* Allegory of the Cave (Forms)
* Question everything (from his teacher)
* Rule by Philosophers (Philosopher kings)
* *The Republic*
* Question everything (from his teacher)
* Rule by Philosophers (Philosopher kings)
* *The Republic*
59
New cards
Aristotle
* Logic
* Taught Alexander the Great
* Founded Lyceum (hall for public discussions)
* Taught Alexander the Great
* Founded Lyceum (hall for public discussions)
60
New cards
Philip II of Macedon’s legacy
* United Greece by force
* Cultural diffusion and syncretism of the places within his Empire
* Founded more than 20 significant cities, including Alexandria in Egypt
* Cultural diffusion and syncretism of the places within his Empire
* Founded more than 20 significant cities, including Alexandria in Egypt
61
New cards
Hellenistic Era
* Time in between Alexander’s death (323 BC) and emergence of the Roman Empire (31 BC)
* Name derived from the name for Greece: Hellias
* Period saw the rise of art, trade, literature, theatre, music, mathematics, philosophy, and science throughout Greece and the old Empire
* Name derived from the name for Greece: Hellias
* Period saw the rise of art, trade, literature, theatre, music, mathematics, philosophy, and science throughout Greece and the old Empire
62
New cards
What is Athens after the Dark Ages
Athens emerges from a **monarchy** after the Dark Ages
63
New cards
What is an Oligarchy
Oligarchy is when wealthy hereditary nobles (landowners) control the military and state resources
64
New cards
What did Darius the Great do?
* Extended the Persian Empire from Egypt to India
* Invested in building and public works projects:
* notably building a **canal** in Egypt (Suez canal)
* Built the Capital of **Persepolis**
* Built the **Royal Road**
* Centralization! Connected the empire and made life easier for the Persian people
* Created a massive army and network of spies
* Established the __**Satrap system**__
* Invested in building and public works projects:
* notably building a **canal** in Egypt (Suez canal)
* Built the Capital of **Persepolis**
* Built the **Royal Road**
* Centralization! Connected the empire and made life easier for the Persian people
* Created a massive army and network of spies
* Established the __**Satrap system**__
65
New cards
What were Satraps and Satrapies?
* Satrapies were administrative districts within the Persian Empire, like states or counties
* Satraps were leaders of these districts
* These districts were established for localized and decentralized control and tax collecting
* Inspired the system established by the Greeks and possibly influencing the way many countries today set up their local and state governments
* Satraps were leaders of these districts
* These districts were established for localized and decentralized control and tax collecting
* Inspired the system established by the Greeks and possibly influencing the way many countries today set up their local and state governments
66
New cards
What is Zoroastrianism?
* Founded by Zarathustra / Zoroaster (Prophet)
* One of the oldest World Religions
* Dates: 6th Century B.C.
* Location: Middle East, notably Iran
* May have influence over Judaism, Christianity, and Islam (much older than them!)Message: “Good thought, good deeds, good word.”
* Dualistic battle of Good vs. Evil
* May be first religion to create the concept of a Heaven vs. Hell
* Ahura Mazda (good spirit) vs. Ahriman (bad spirit)
* The “Sacred Fire” (pictured below)
* Ethical Monotheism
* One of the oldest World Religions
* Dates: 6th Century B.C.
* Location: Middle East, notably Iran
* May have influence over Judaism, Christianity, and Islam (much older than them!)Message: “Good thought, good deeds, good word.”
* Dualistic battle of Good vs. Evil
* May be first religion to create the concept of a Heaven vs. Hell
* Ahura Mazda (good spirit) vs. Ahriman (bad spirit)
* The “Sacred Fire” (pictured below)
* Ethical Monotheism
67
New cards
Who was King Leonidas?
* A Spartan King that fought with his people
* In a story of Herodotus, portrayed as very loyal to his people and as being a good king
* In a story of Herodotus, portrayed as very loyal to his people and as being a good king
68
New cards
Who created the Delian League and who created the Peloponnesian League?
Athens-Delian
Sparta-Peloponnesian
Sparta-Peloponnesian
69
New cards
Flip cards
😎
70
New cards
C
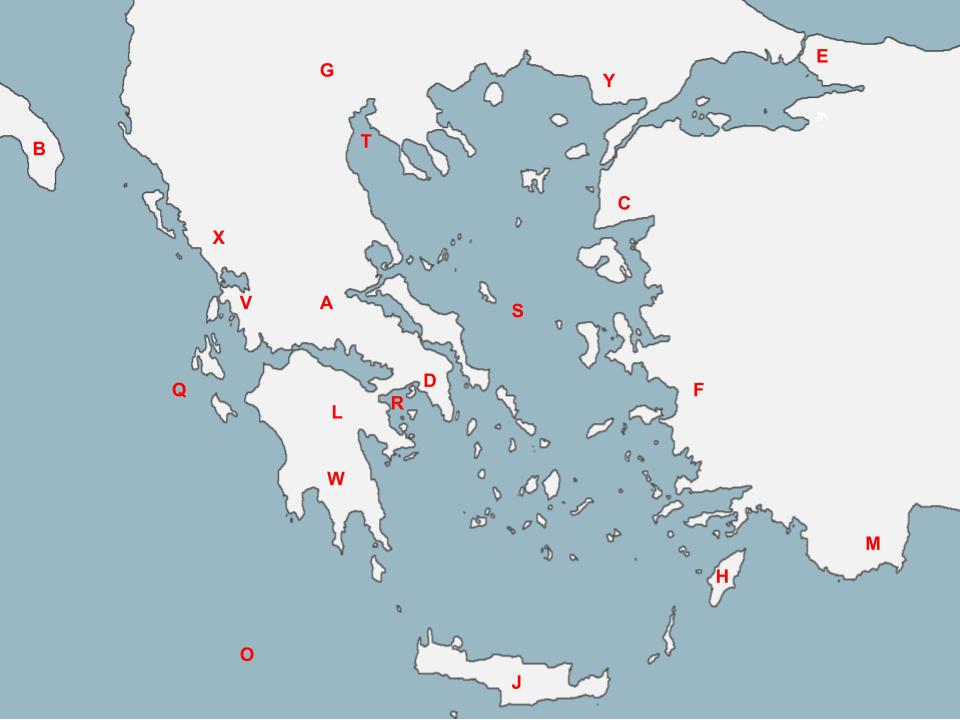
According to Homer, the Mycenaeans crafted a plan to hide their soldiers in a wooden horse to surprise attack this enemy civilization located here
71
New cards
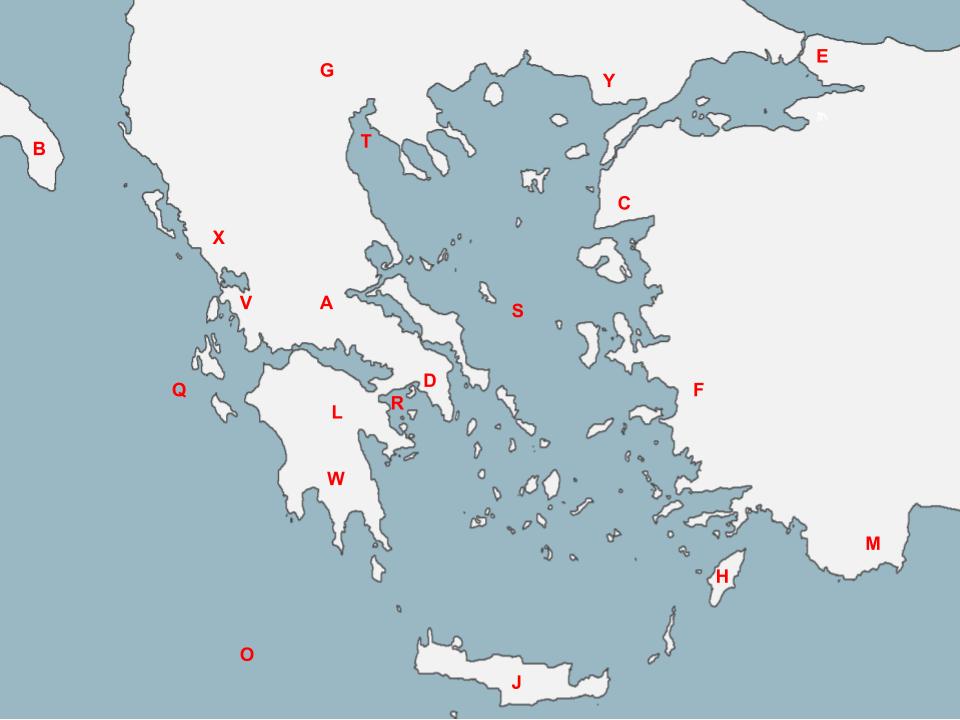
W
This polis was victorious in the Peloponnesian War
72
New cards
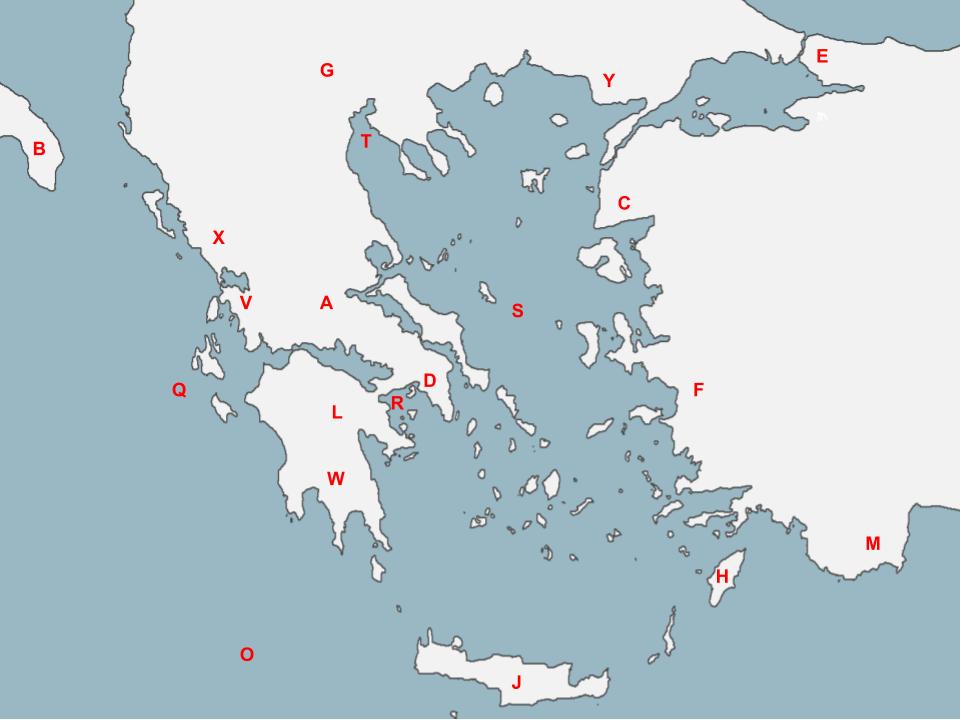
D
The Delian League was led by the city-state located here.
73
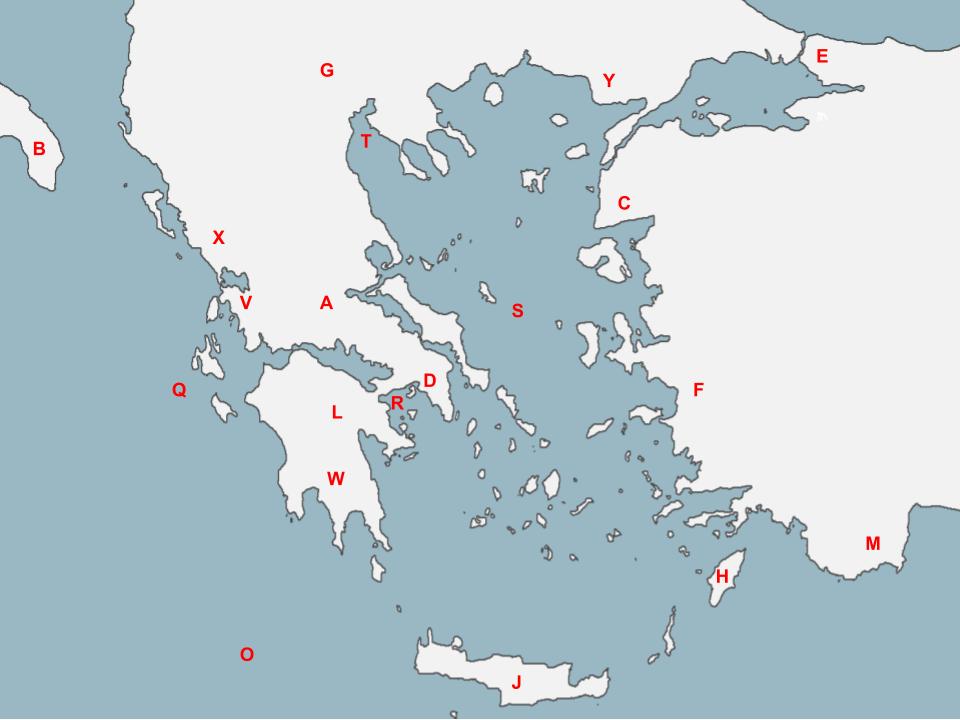
New cards
G
Alexander the Great led the Macedonian people, which originated __**here**__.
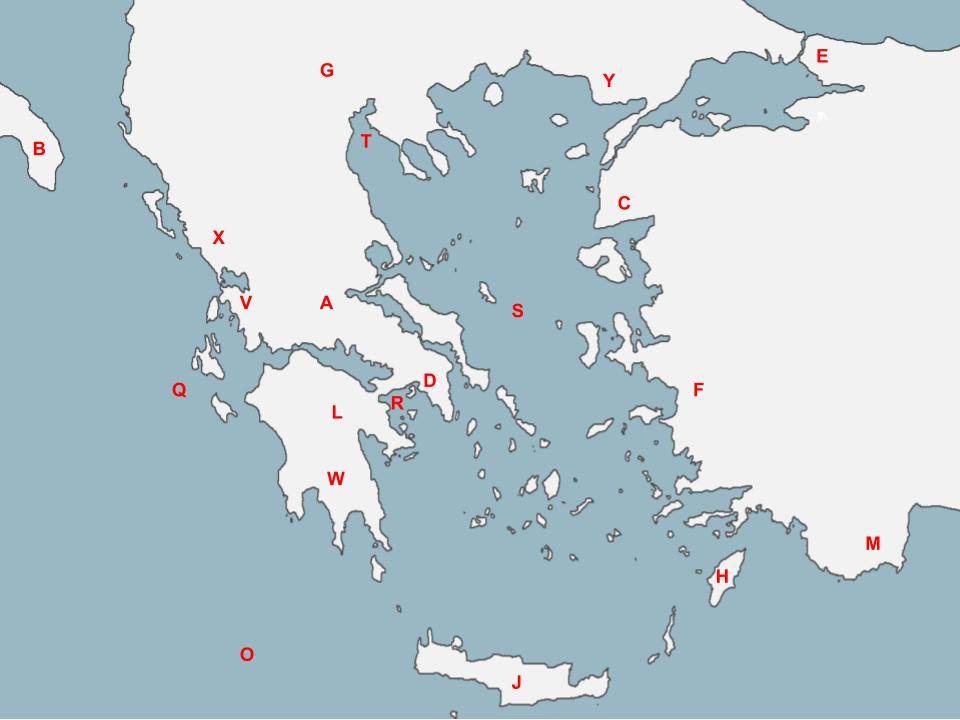
74
New cards
S
After the Persian War, Athenians freely colonized numerous territories in this body of water
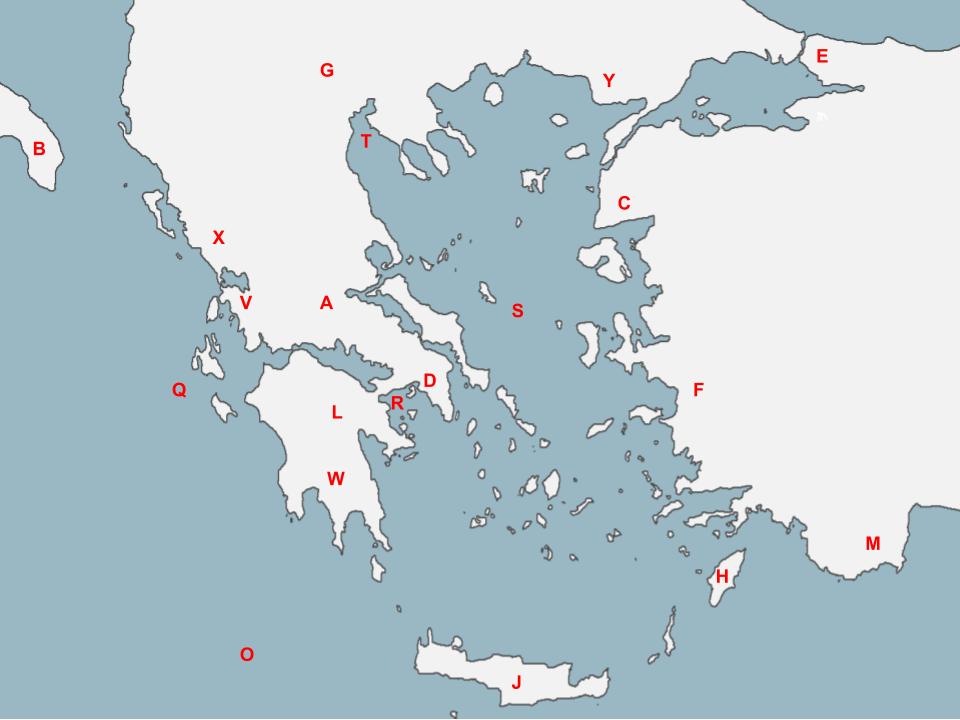
75
New cards
L
(Mycenae!)
(Mycenae!)
This structure, known as the Lion’s Gate, was built as an entrance to the city located here.
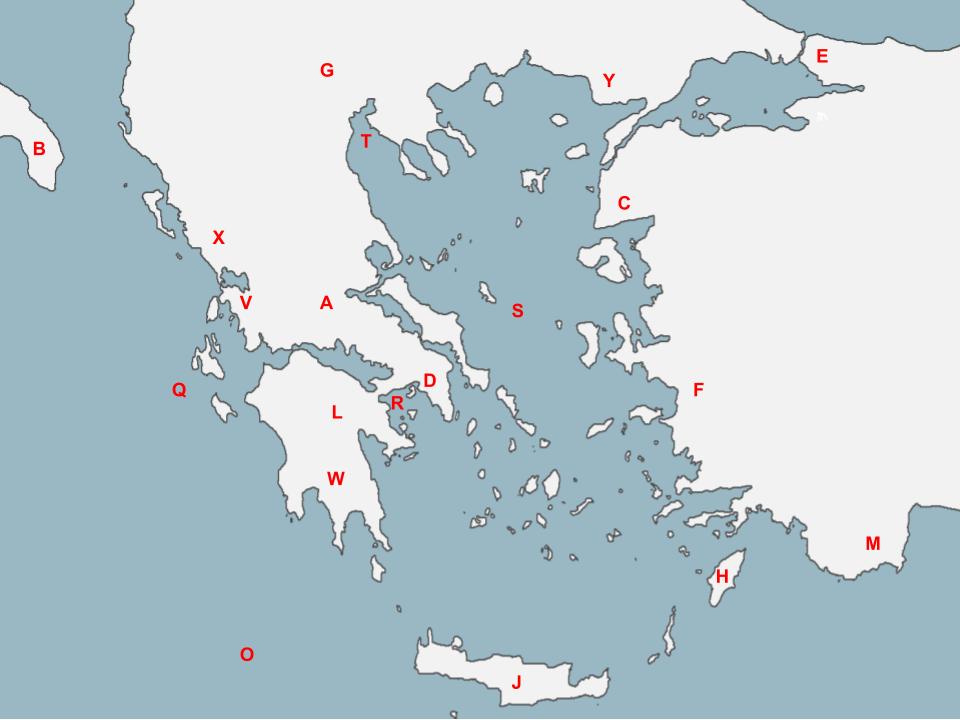
76
New cards
A
Sparta bravely defended Athens from the Persian Invasion, sacrificing their lives in order to successfully stall the Persians at this battle located here
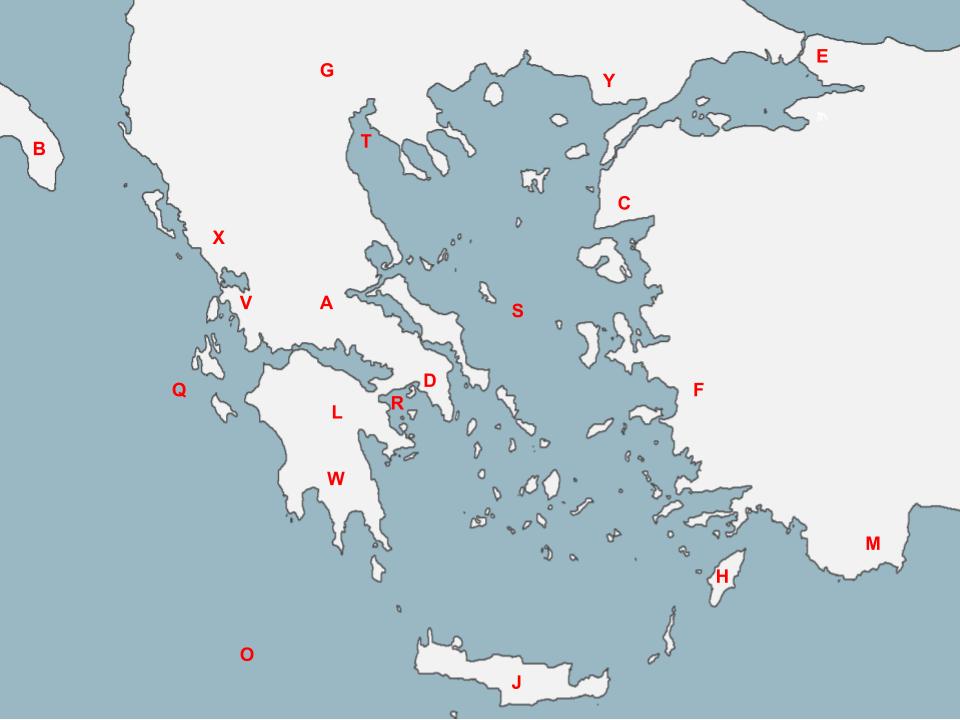
77
New cards
D
Pericles created numerous public works projects, such as the Acropolis, and further reformed his government towards a more true Democracy in this city.
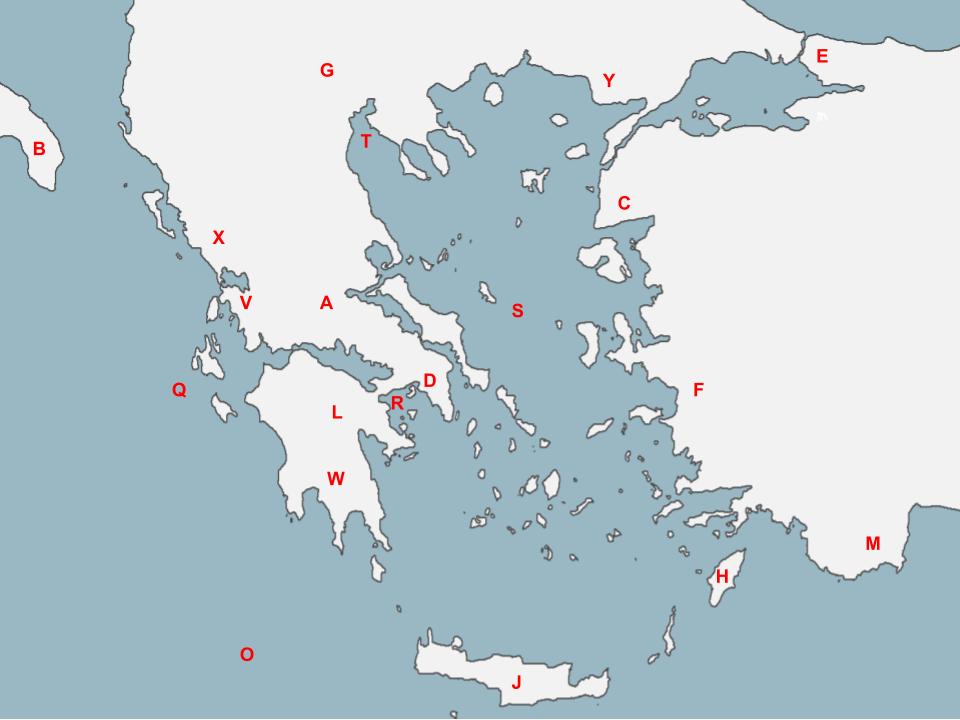
78
New cards
Q
The Ionian Sea
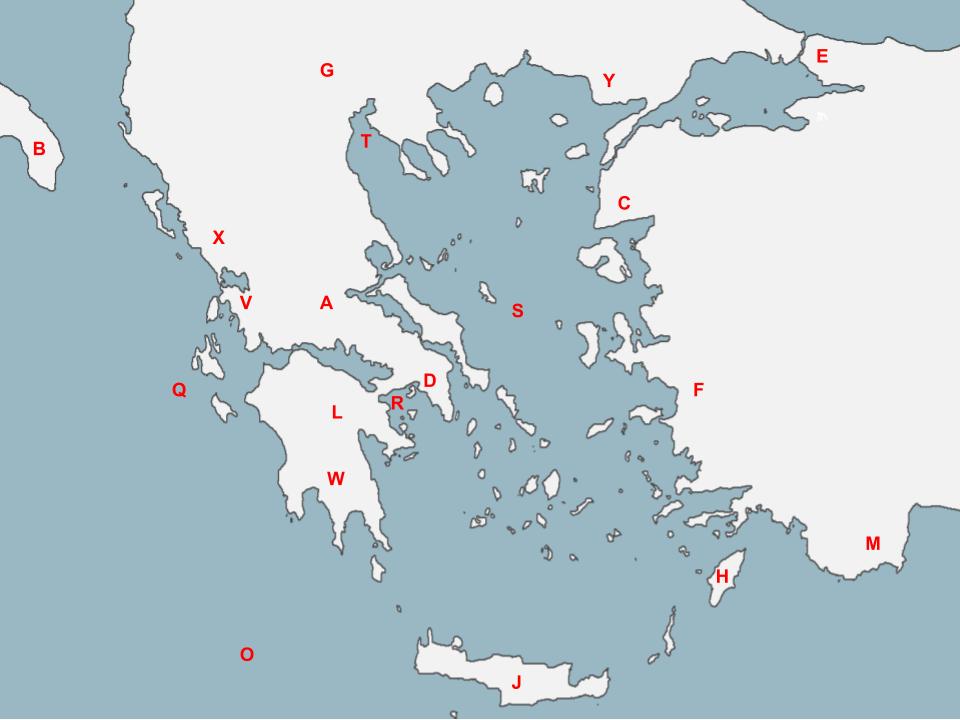
79
New cards
F
The people located here revolted against the Persians, and when Athens and Sparta supported this revolt the Persian War began…
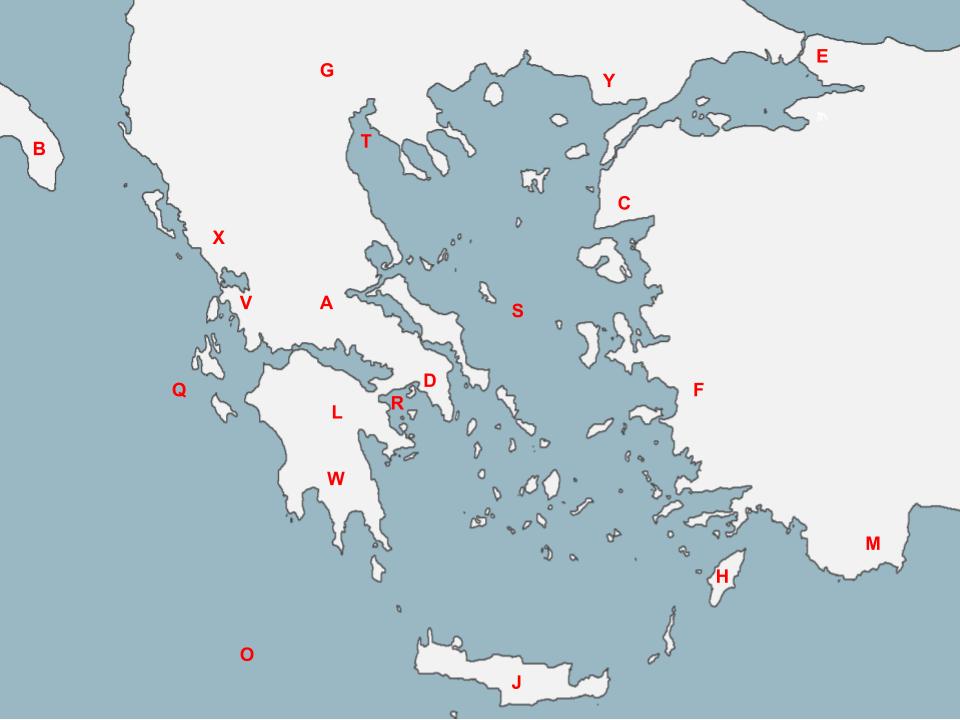
80
New cards
D
The first battle of the Persian War was a surprise attack from King Darius I approximately located here.
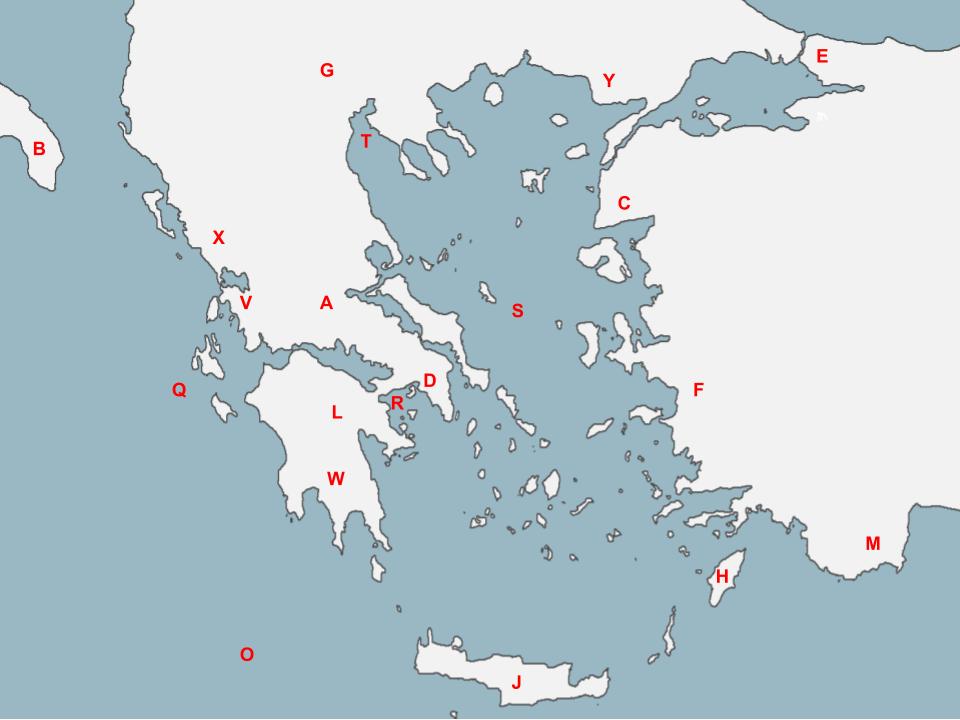
81
New cards
G
The Dorians probably migrated from approximately here before they ‘invaded’ Greece
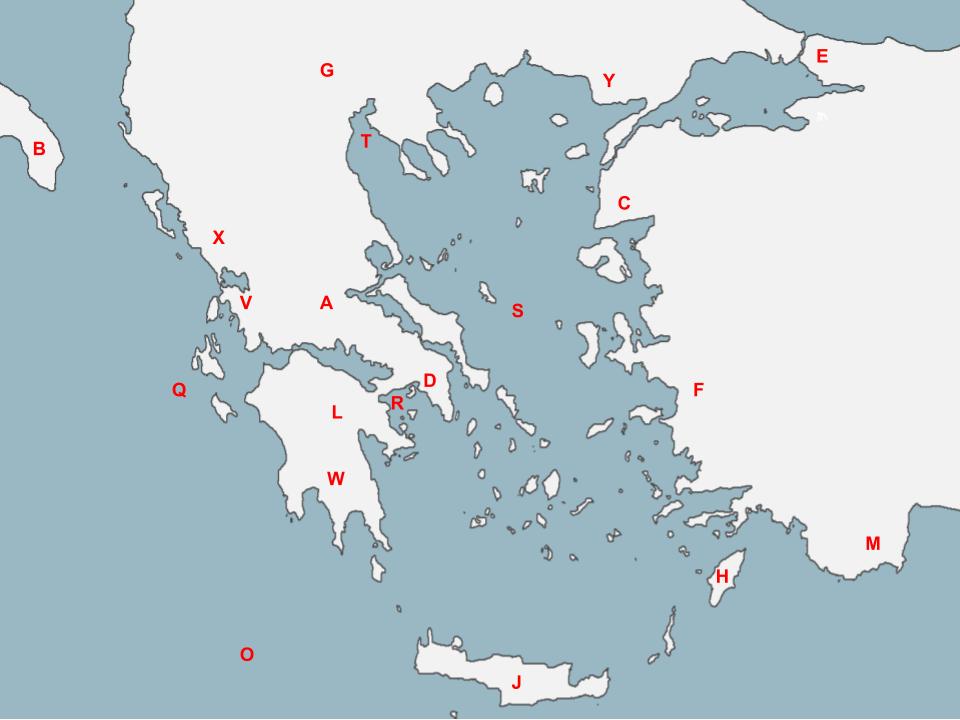
82
New cards
J
The Palace located here left behind many artifacts that tell us of a peaceful, artistic, wealthy, and sea-faring people that valued trade and the beauty in nature.
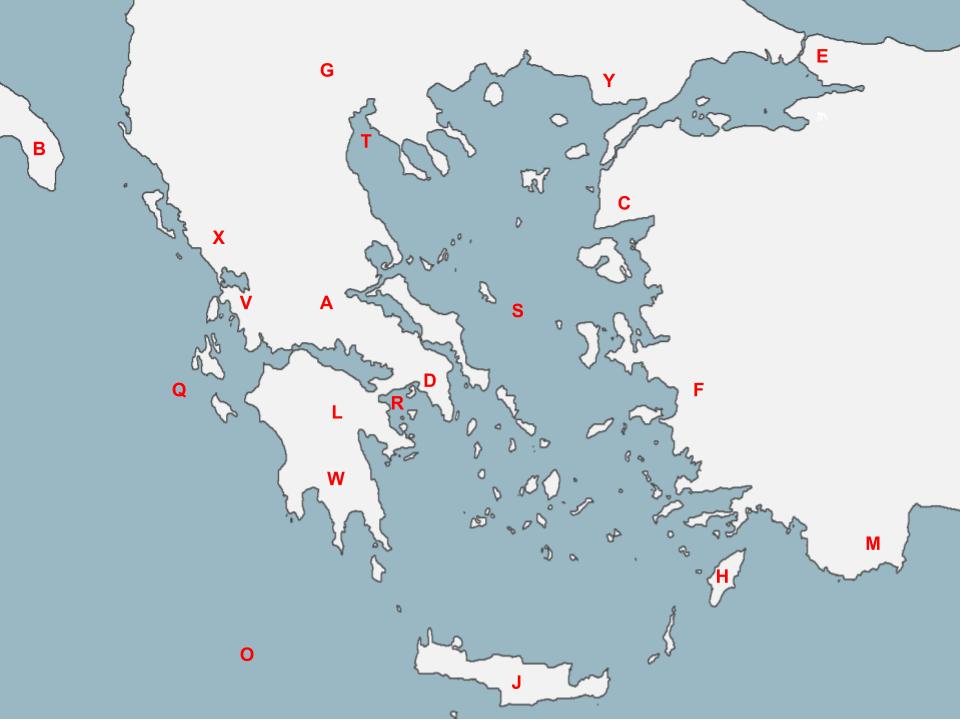
83
New cards
R
The naval battle located here was a genius ambush planned by the Athenians to draw in the Persian ships before soundly destroying them, demonstrating the might of the Athenian navy to the world.
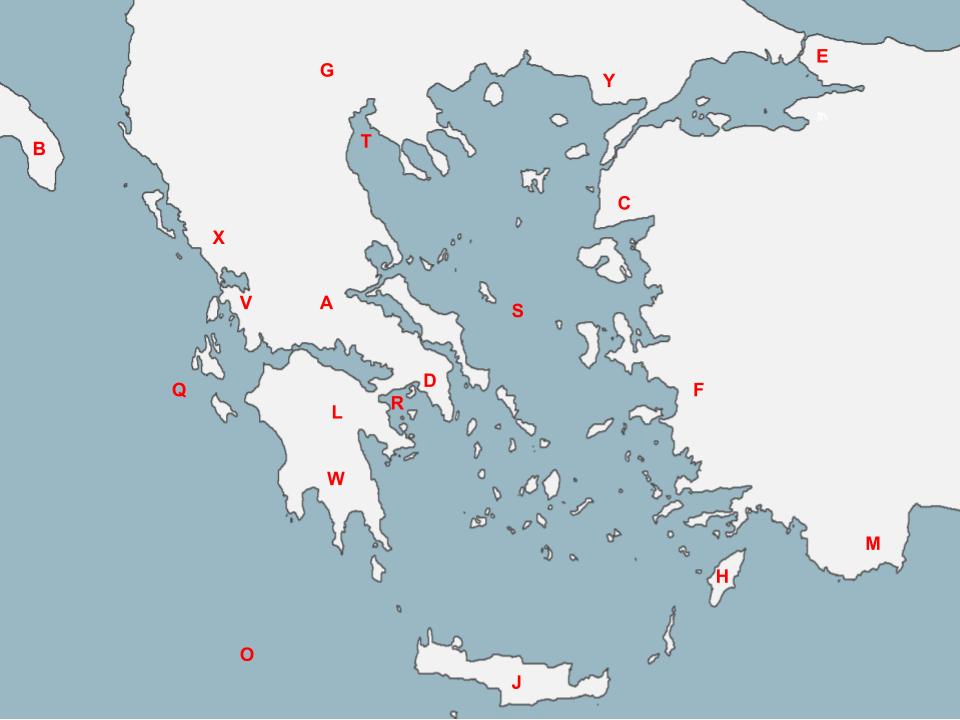
84
New cards
W
The People located here valued strength, military might, hard work, and equality in society. They were often criticized for their aggressive military training for their youth.