Anatomy 1 lab skull, spine, rib, & sternum bones
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
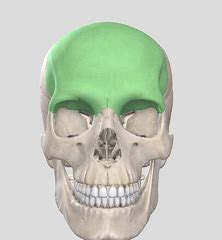
Frontal bone
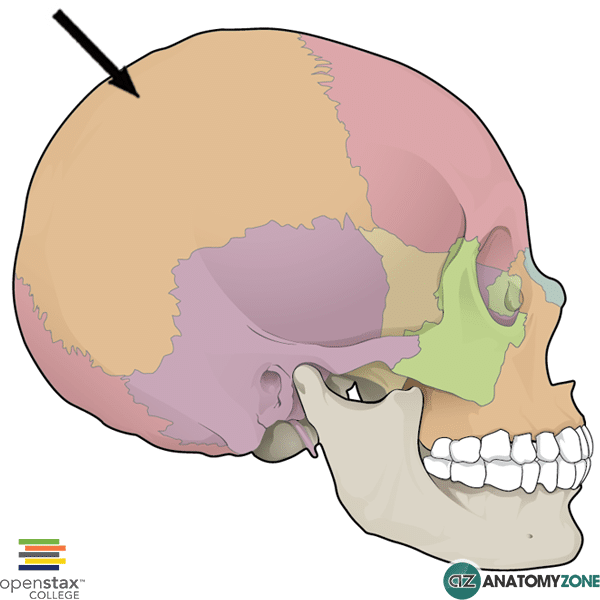
Parietal bone
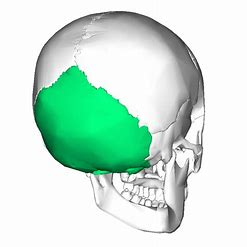
Occipital bone
Coronal suture
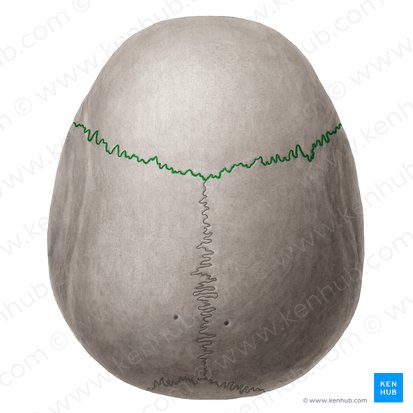
Sagittal suture
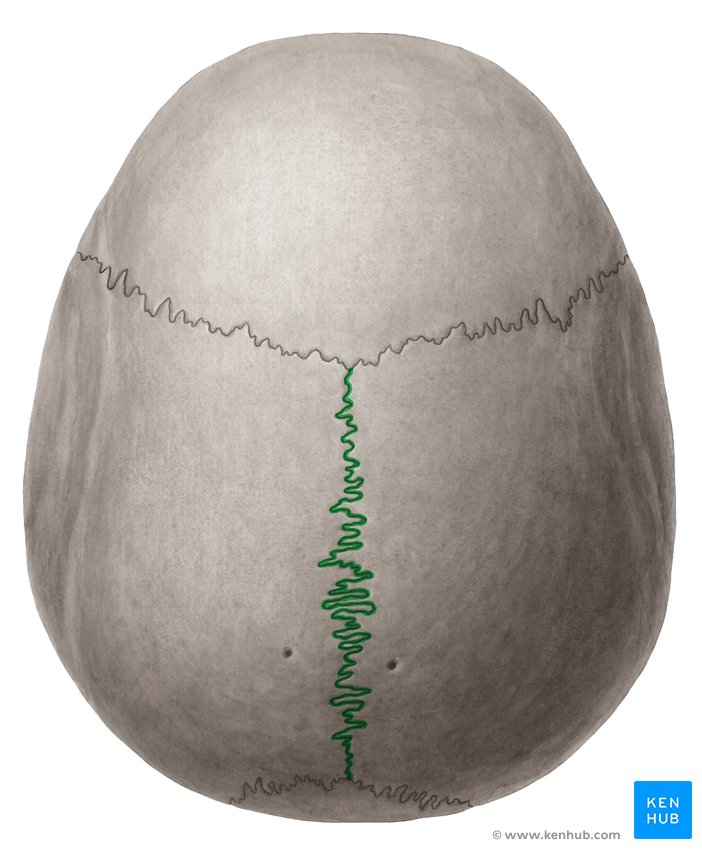
Lambdoid suture
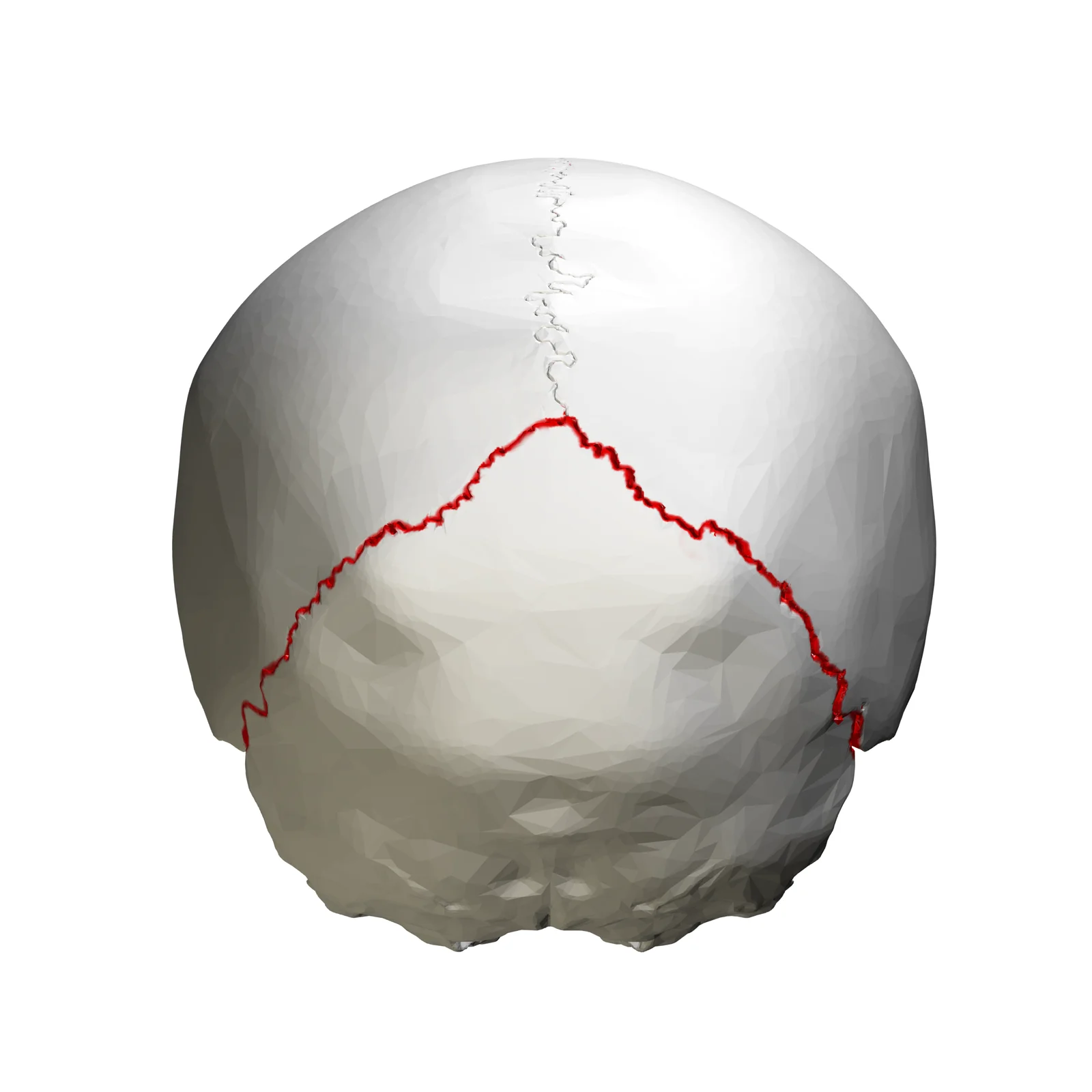
Squamous suture
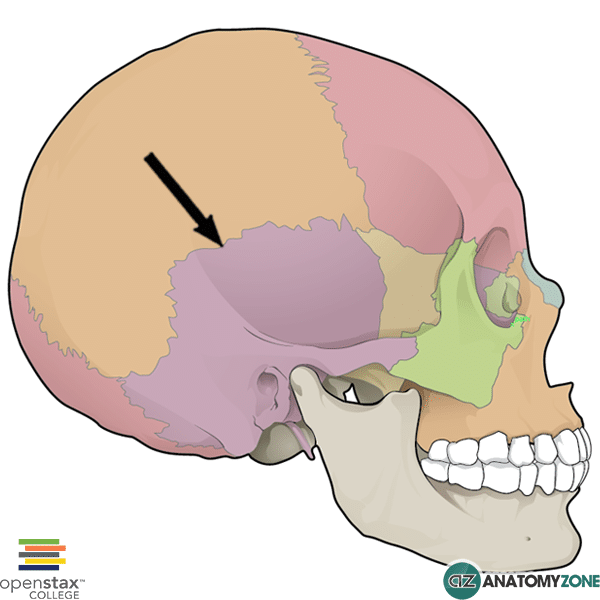
Zygomatic process (helps form zygomatic arch with the zygomatic bone)
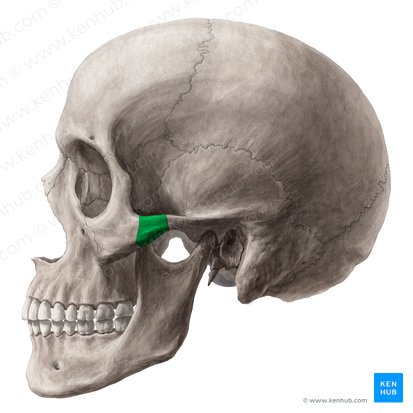
Mandibular fossa (receives the condyle of the mandible (lower jaw)
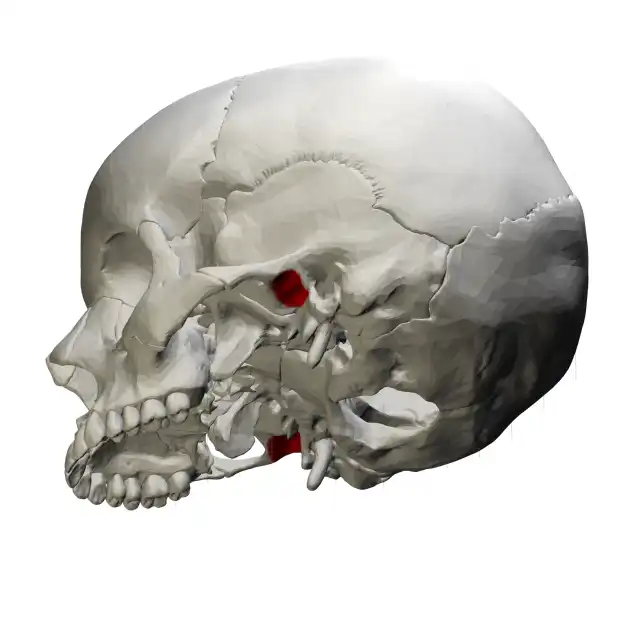
External auditory meatus (external ear canal)
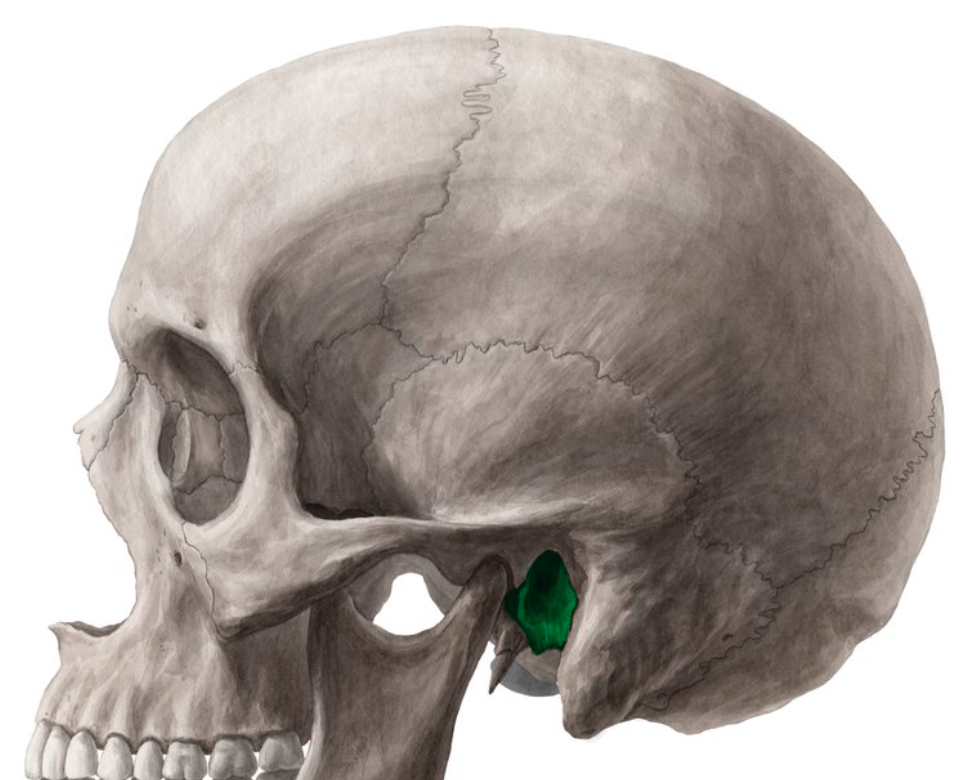
Styloid process (“stake like” point of attachment for several tongue and neck muscles)
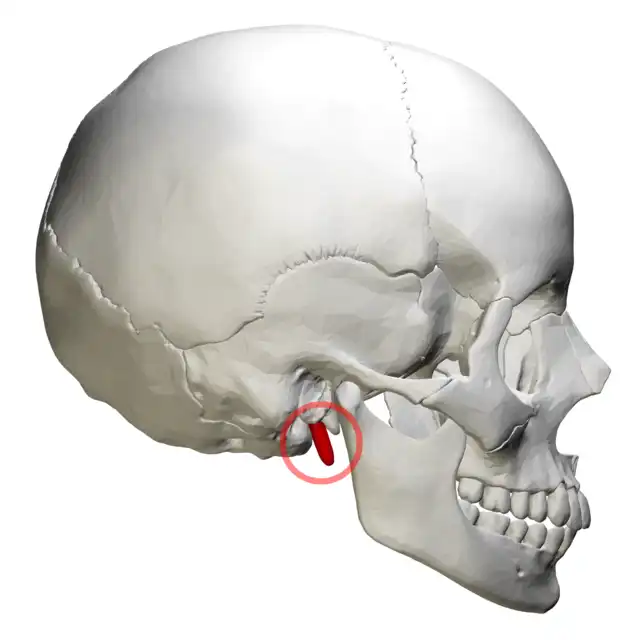
Mastoid region of the temporal bone
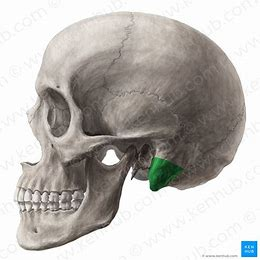
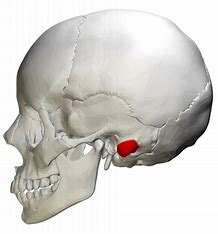
Mastoid process (anchoring site for several neck muscles)
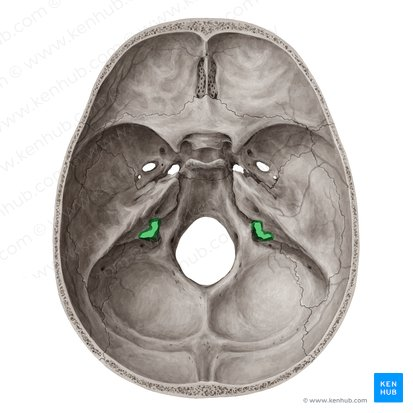
Jugular foramen (for internal jugular vein and nerves)
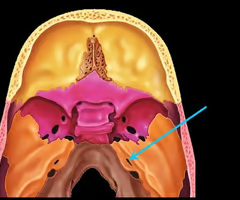
Internal acoustic meatus (for passage of the auditory nerve)
Maxilla bone
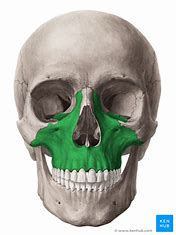
Zygomatic bone
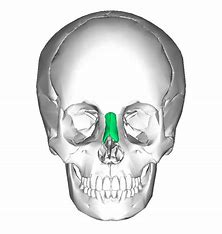
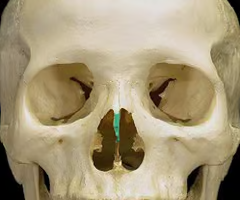
Nasal bone
Lacrimal bone
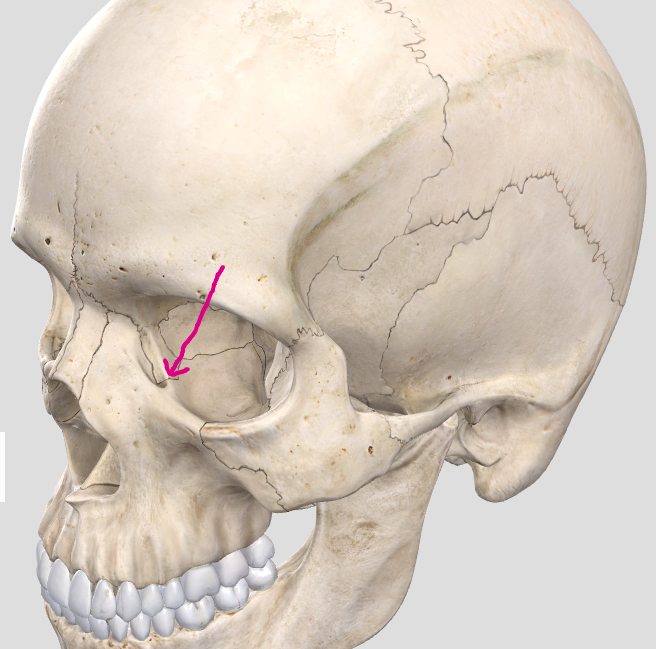
Lacrimal fossa (for lacrimal sac, part of tear drainage system into nasal cavity)
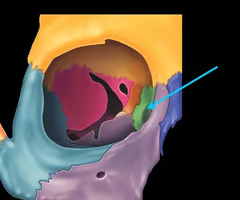
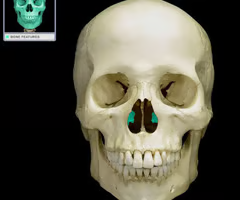
Inferior nasal conchae
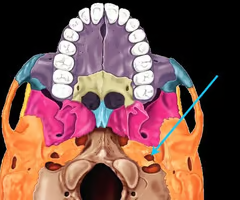
Carotid canal (for internal carotid artery)
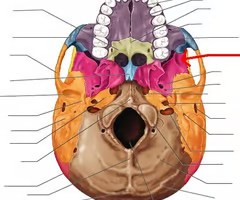
Greater wing of the sphenoid bone (“sphen”=wedge)
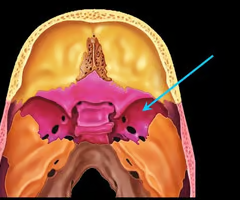
Greater wing of the sphenoid bone (“sphen”=wedge)
Lesser wing of the sphenoid bone
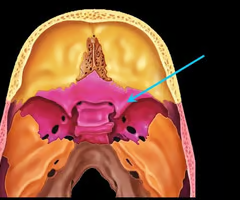
Sella turcica (holds pituitary gland - “Turk’s saddle”)
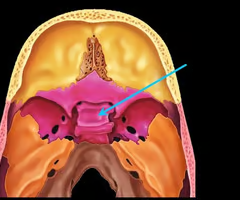
Pterygoid processes of sphenoid bone (trough - shaped anchor for chewing muscles)
Cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone (notice olfactory formina in it - for olfactory nerves. Crista galli “rooster’s comb” dura mater attaches here)
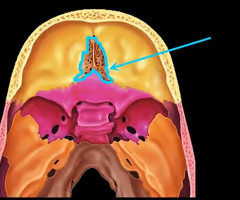
Perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone (helps form bony nasal septum with vomer)
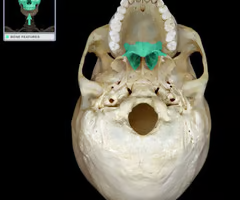
Palatine process of maxilla (helps form hard palate with palatine bones)
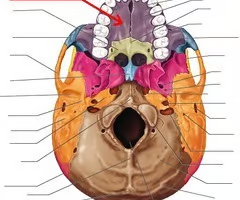
Palatine bones
Vomer
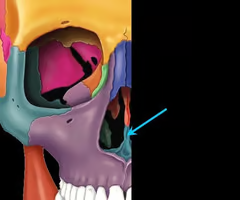
Vomer
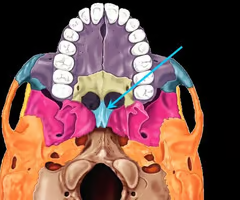
Occipital condyles (articulates with superior articular surfaces of atlas)
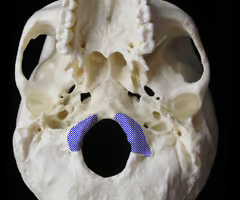
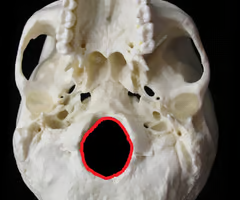
Foramen magnum (“big hole” for the spinal cord)
Optic canals (optic nerve)
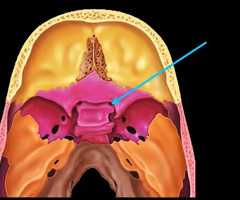
Optic canals (optic nerve)
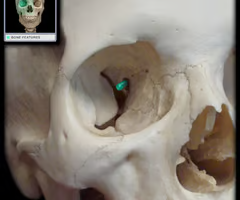
Hyoid bone (only bone that does not articulate directly with any other bone)
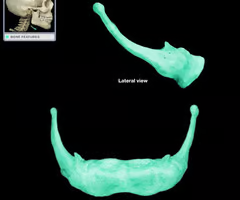
Maxilla bone
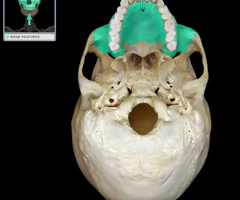
Mandibular condyle (forms TMJ)
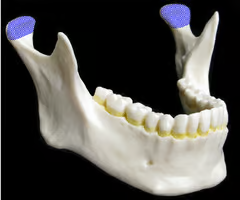
Coronoid process
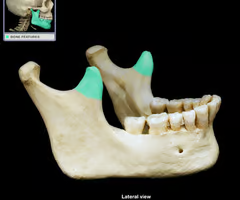
Mandibular notch
Ramus (“rami” = branches)
Mandibular angle (where ramus and body meet)
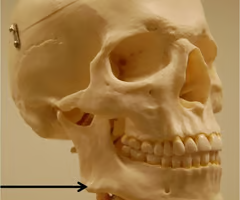
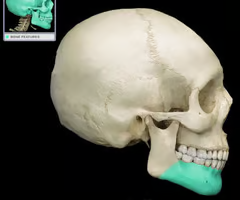
Body (forms the chin)
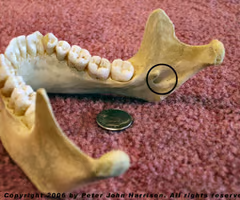
Mandibular foramen (nerves involved in tooth sensation - pass to lower jaw teeth - dentists inject Novocain to numb lower teeth)
skull, vertebral column, ribs, sternum
What is the axial skeleton composed of?
2
The skull is divided into how many regions?
cranium (brain case) and facial bones
What are the regions of the skull?
8
How many bones are in the cranium?
1 frontal bone, 2 parietal, 1 occipital, 2 temporal, 1 ethmoid, 1 sphenoid
What are the bones in the cranium?
Ethmoid bone
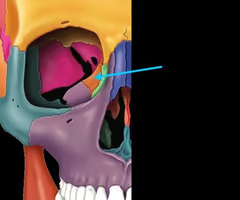
14
The facial bones are made up of how many bones?
1 mandible, 2 maxilla, 2 zygomatic, 2 nasal, 2 lacrimal, 2 palatine, 1 vomer, 2 inferior nasal conchae
What bones are in the facial bones?
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
The only moveable joint of the skull
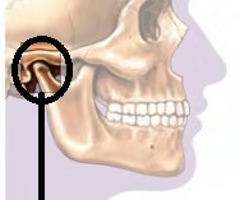
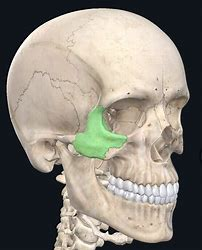
Temporal bone
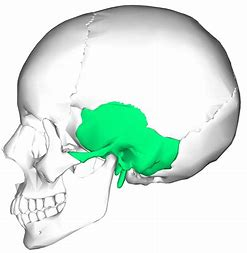
7
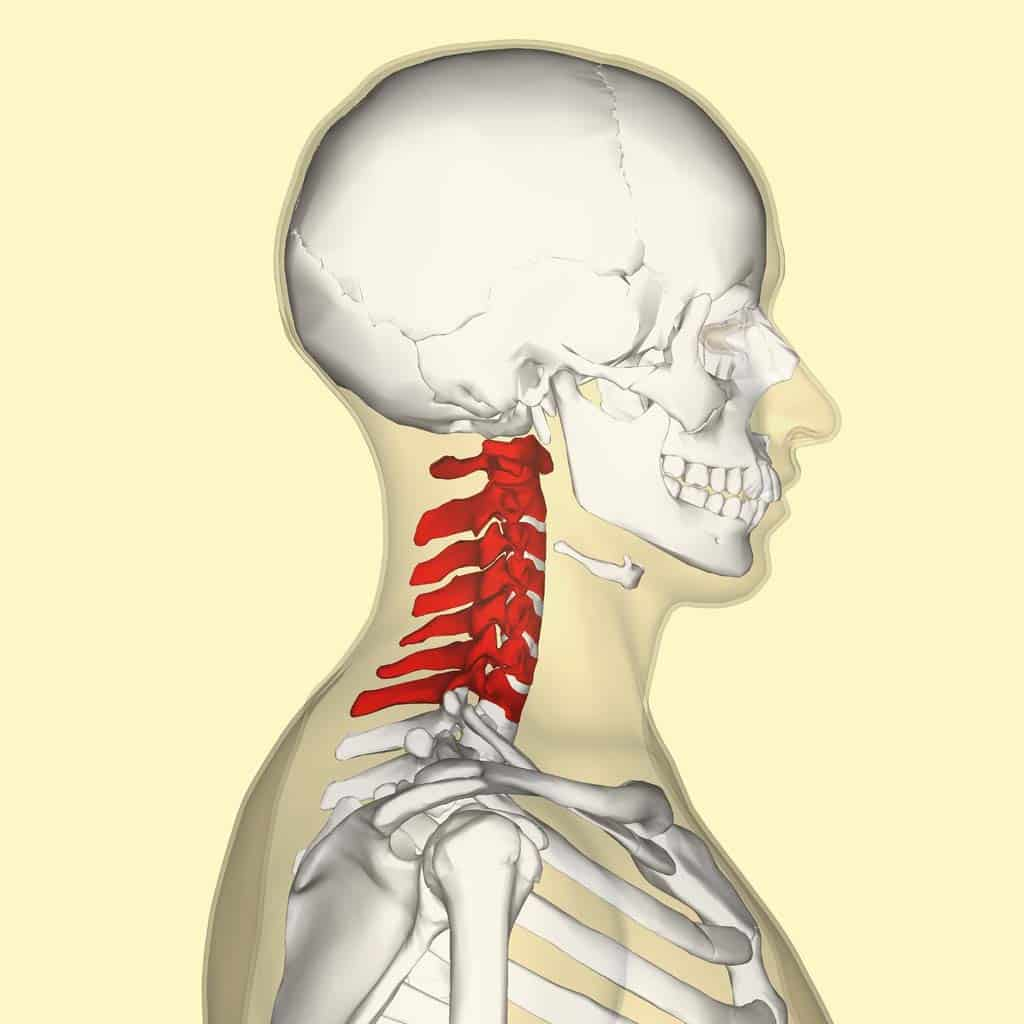
How many vertebrae make up the cervical division?
12
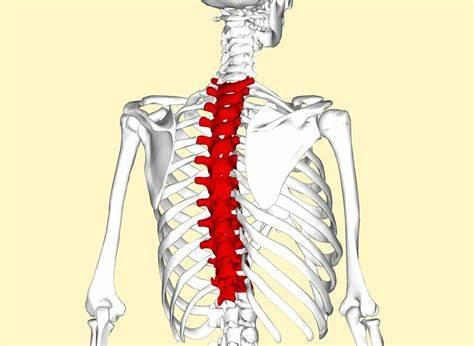
How many vertebrae make up the thoracic division?
5
How many vertebrae make up the lumbar division?
5 fused
How many vertebrae make up the sacrum division?
3-5 fused (tailbone)
How many vertebrae make up the coccyx division?
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacrum
Coccyx
Intervertebral foramen (“between-vertebral hole”; spinal nerves pass thru)
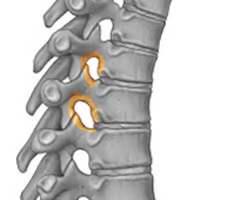
Body
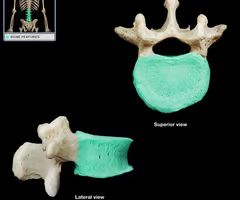
Pedicles (“little feet”)
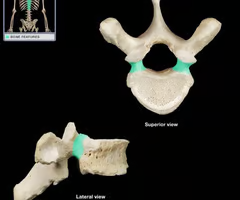
Lamina
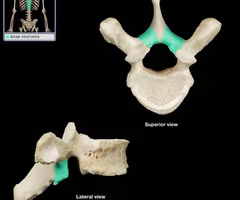
Transverse process
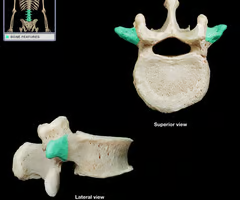
Spinous process
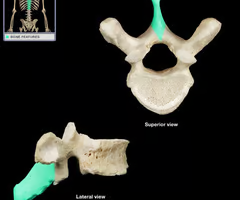
Superior articular process
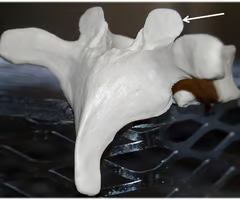
Inferior articular process
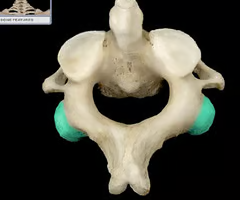
Vertebral foramen (spinal cord passes thru)
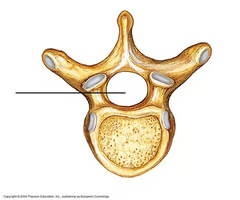
Intervertebral disc (cushion-like pad made of 2 parts)
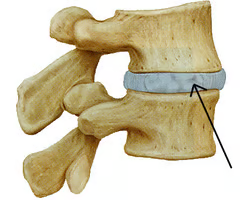
Nucleus pulposus
Inner gelatinous material that acts like a rubber ball to give disc elasticity and compressibility
Annulus fibrosus
Strong collar surrounding nucleus pulposus; made of fibrocartilage and collagen fibus.
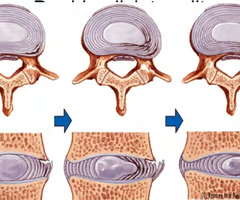
Herniated (slipped) disc
Occurs when spongy nucleus pulposus protruded thru a rupture in annulus fibrosus and presses on the spinal cord or spinal nerves.
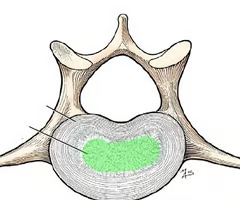
Nucleus pulposus
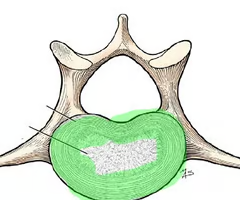
Annulus fibrosus
Herniated (slipped) disc
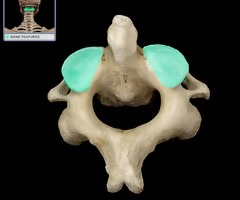
Atlas (is first cervical vertebrae)
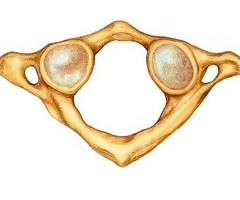
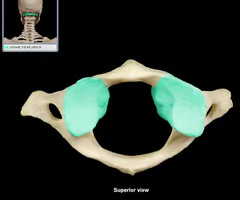
Lateral mass
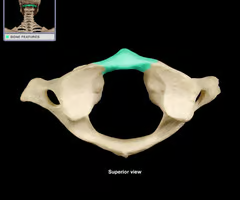
Anterior arch
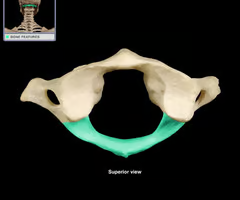
Posterior arch
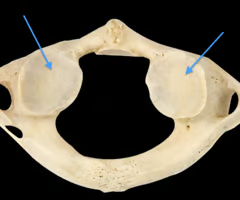
Superior articular process of axis
Inferior articular process
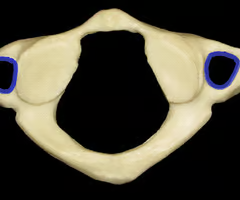
Transverse foramen (for passage of the vertebral arteries to the brain)
Axis (is second cervical vertebrae)
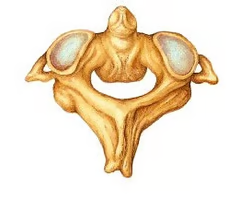
Dens (odontoid process - acts as a pivot for rotation of Atlas to make “no” motion)
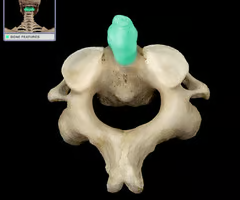
Transverse Foramen
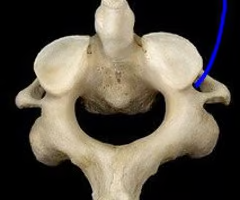
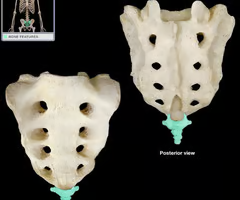
Sacrum
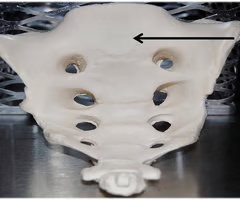
Alae (wing like processes)
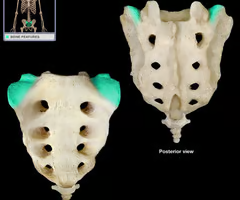
Sacral promontory
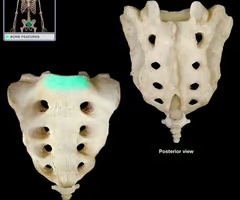
Sacral foramina
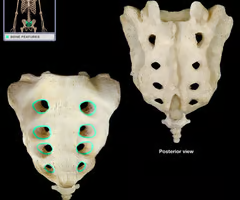
Median sacral crest (remnant of spinous processes)
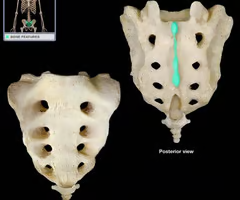
Kyphosis
“Hunchback,” is an exaggerated thoracic curvature.
Lordosis
“Swayback,” is an accentuated lumbar curvature.
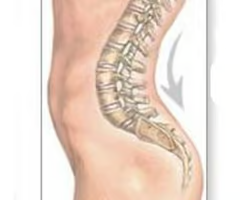
Scoliosis
Abnormal lateral curvature, usually in thoracic region.