Pharmaceutics & DDS - Exam 2 - Physiochemical Properties of Solids, Liquids, & Gases
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
what is sublimination?
what a substance converts directly from a solid to a gas

what is lyophilization?
freeze drying
due to the random and rapid collisions of gas molecules, gas often exerts ____________
pressure
according to the Ideal Gas law, what is the relationship between P, V, and T?
- T is directly proportional to both P and V (as T increases, P increases; as T increases, V increases)
- P and V are inversely related (as P increase, V decreases)
the Ideal Gas law is a combination of what 3 other laws?
- Boyle's law
- Charles' law
- Gay-Lussac's law
what is Boyle's law?
relates the V and P of a given mass of gas at a constant T
P ∝ 1/V, or PV = k
what is Charles' law?
relates the V and absolute T of a given mass of gas at a constant P
V ∝ T, or V = kT
what is Gay-Lussac's law?
relates the P and absolute T of a given mass of gas at constant V
P ∝ T, or P = kT
what are the assumptions made by the Ideal Gas law?
- no intermolecular forces exist
- collisions are perfectly elastic
- no energy exchange occurs
P1V1 / T1 = P2V2 / T2
REFRESHER - what is the Ideal Gas law equation?
PV = nRT
what is the relationship between the Ideal Gas law and molecular weight of a gas?
remember moles = g/mw
substitute g/mw in for "n" in PV = nRT
mw = (gRT)/PV
T/F: cooling a gas reduces its kinetic energy
TRUE
what happens when you pressurize a gas?
applying pressure to a gas leads to increased contact between the gas molecules
- this encourages van der Waals interactions, passing the gas into its liquid state (liquids are denser than gas!)
T/F: both gases and liquids can assume a definite volume
FALSE
- liquids can assume a definite volume, but gases cannot
what is vapor pressure of a liquid?
pressure at dynamic equilibrium between a liquid and its vapor, when molecules escape into the gas phase

how does temperature affect vapor pressure?
vapor pressure increases as temperature increases
solids can be classified as either...?
crystalline or amorphous
what are crystalline solids?
solids arranged in a fixed geometrical pattern known as lattice
- ex: diamonds, NaCl, ice
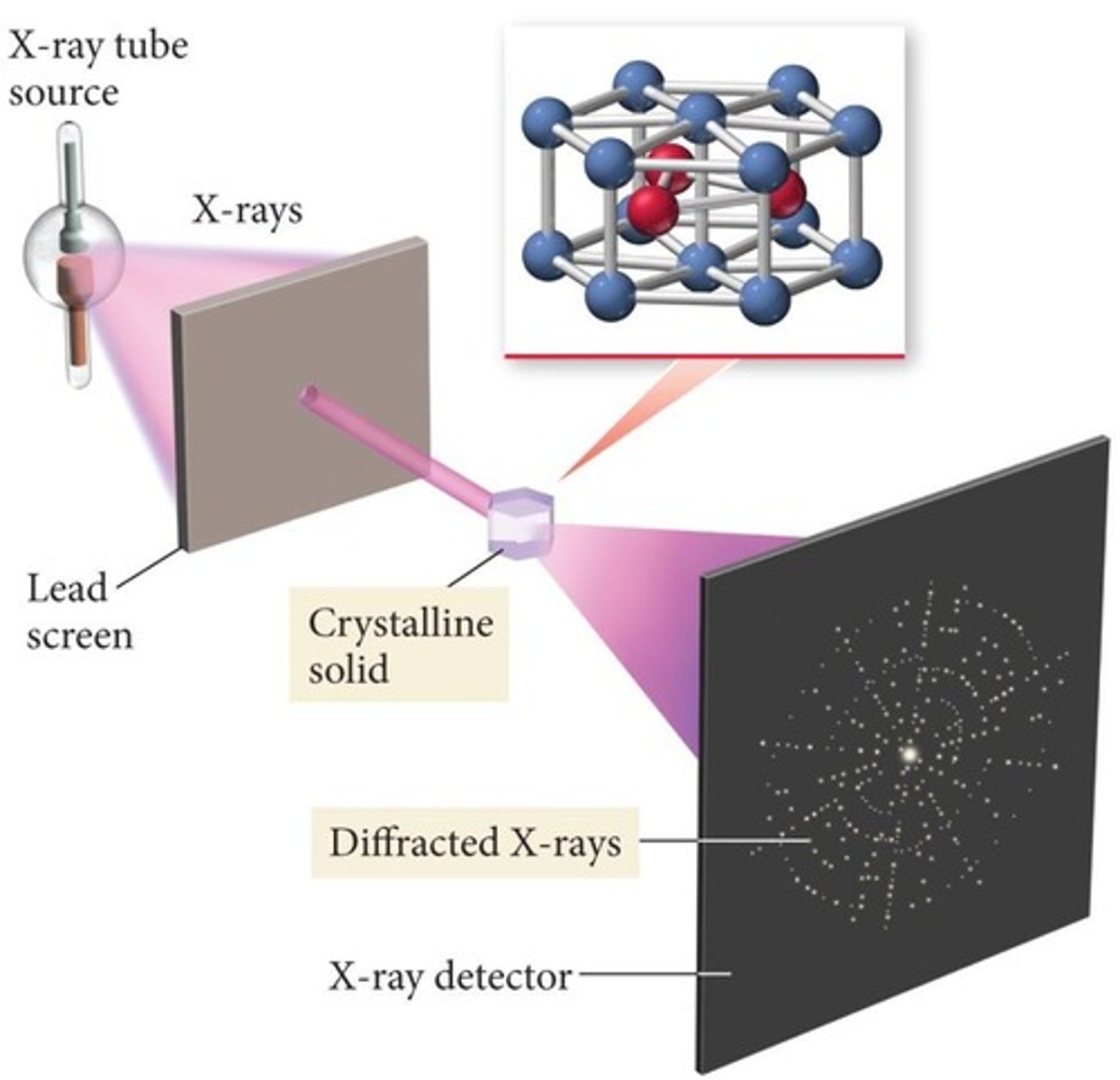
what is polymorphism?
when a crystalline solid occurs in >1 crystal form
- polymorphs have difference physical properties (melting point, solubility)
- ex: albuterol
what are amorphous solids?
solids that lack a definite arrangement
- molecules are arranged randomly (no lattices) and are not as stable as crystals
- aka super-cooled liquids
- ex: graphite
T/F: amorphous solids exhibit polymorphism
FALSE
- amorphous solids do NOT exhibit polymorphism