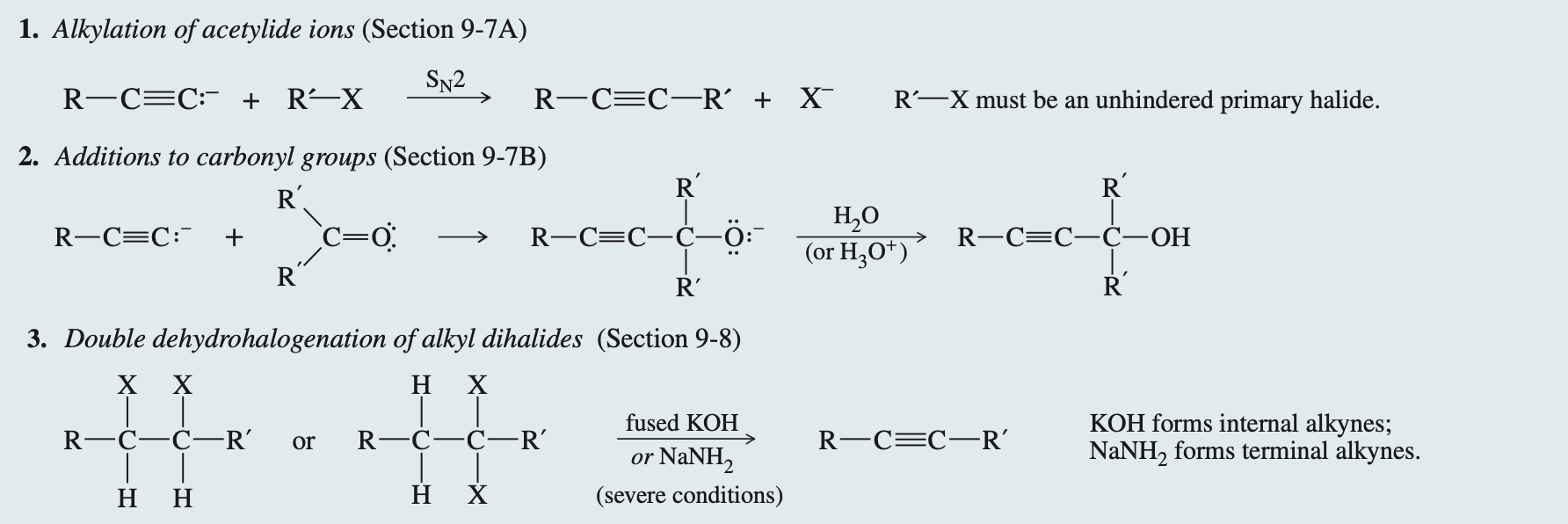
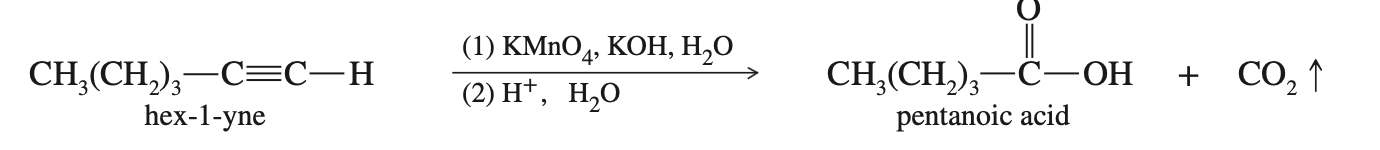Alkyne Reactions
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Alkene Elongation
Create a Acetylide ion with NaNH2
Acetylide Ions are strong nucleophiles and thus can do SN2 substitution to unhindered alkyl-halide
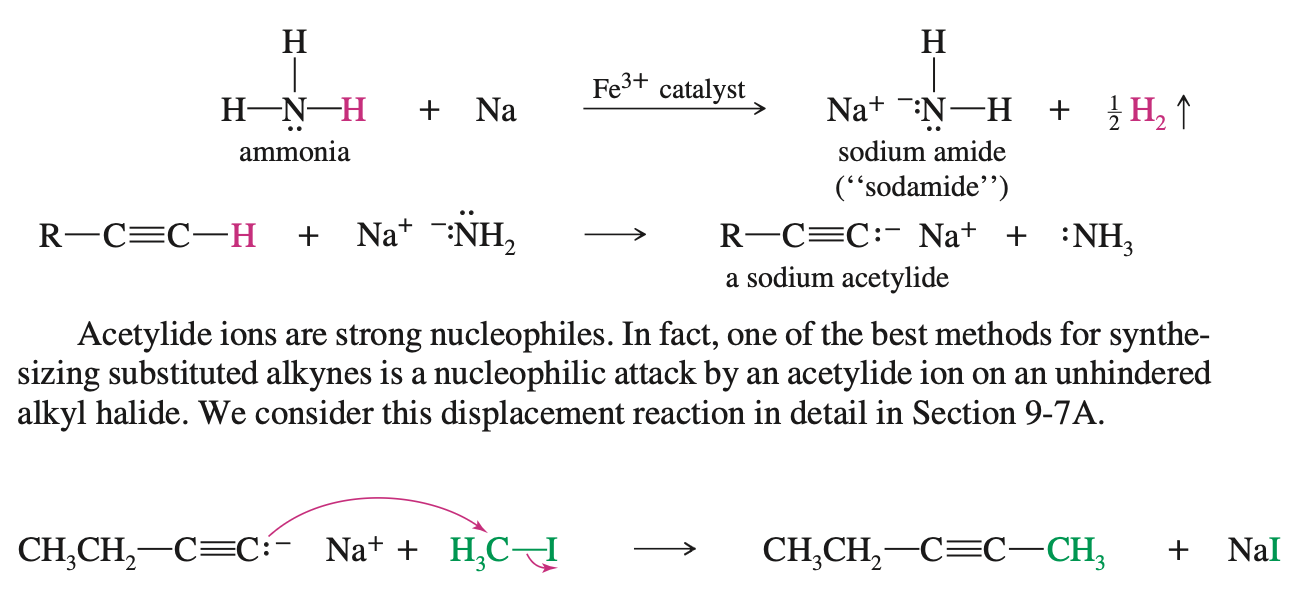
Addition of Acetylide Ions to Carbonyl Groups
When an acetylide Ion performs a backside attack on a carbonyl group it results in the formation of an alkoxide anion
This alkoxide anion then becomes a alcohol by taking a proton from water
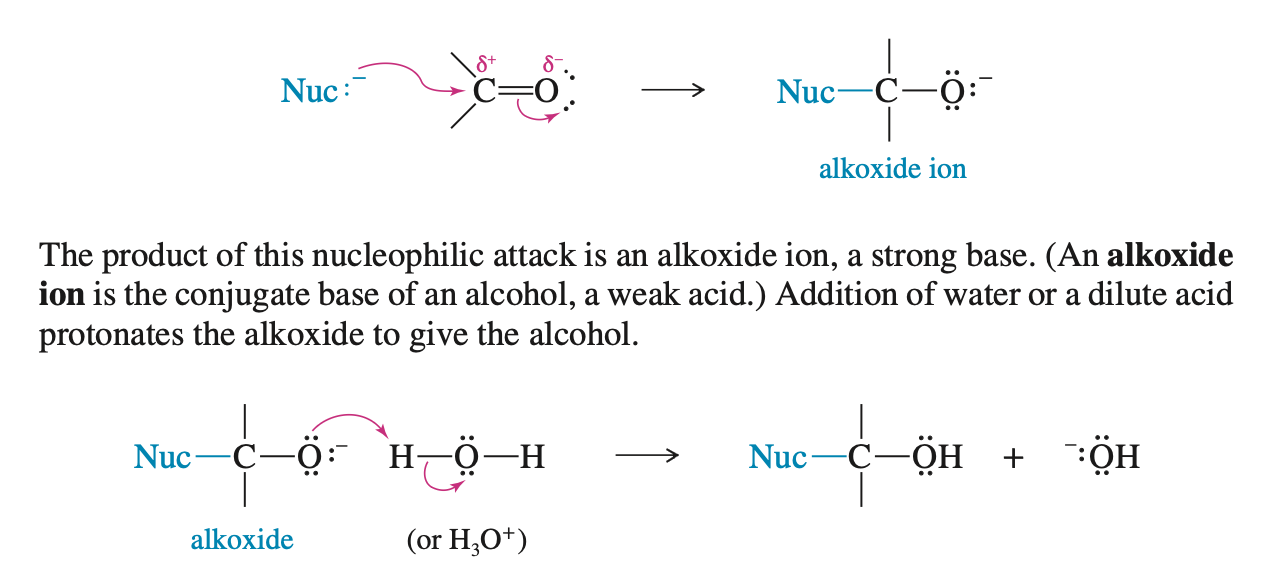
Elimination to synthesize alkynes
Using either KOH or sodium amide at these elevated temperatures implies brutal
reaction conditions, encouraging side reactions and rearrangements. Yields are often
poor
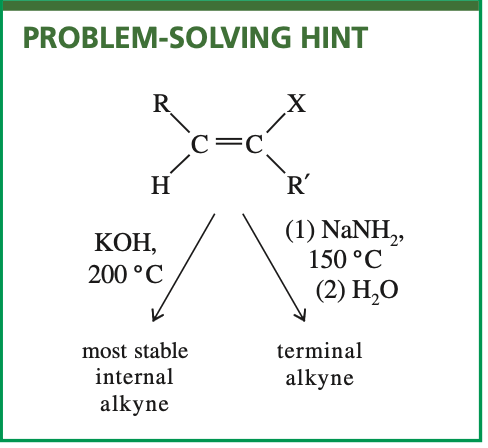
Mega question all 3 ways to synthesize alkyne
Catalytic Hydration of Alkenes
Use a metal catalyst to add hydrogen to Alkynes
Using a catalysts such as pure Pd or platinum or whatever results in reduction to alkane
Using a poison catalyst like Lindlar’s catalyst (aka quinoline) or Ni2B will result in SYN hydration alkene
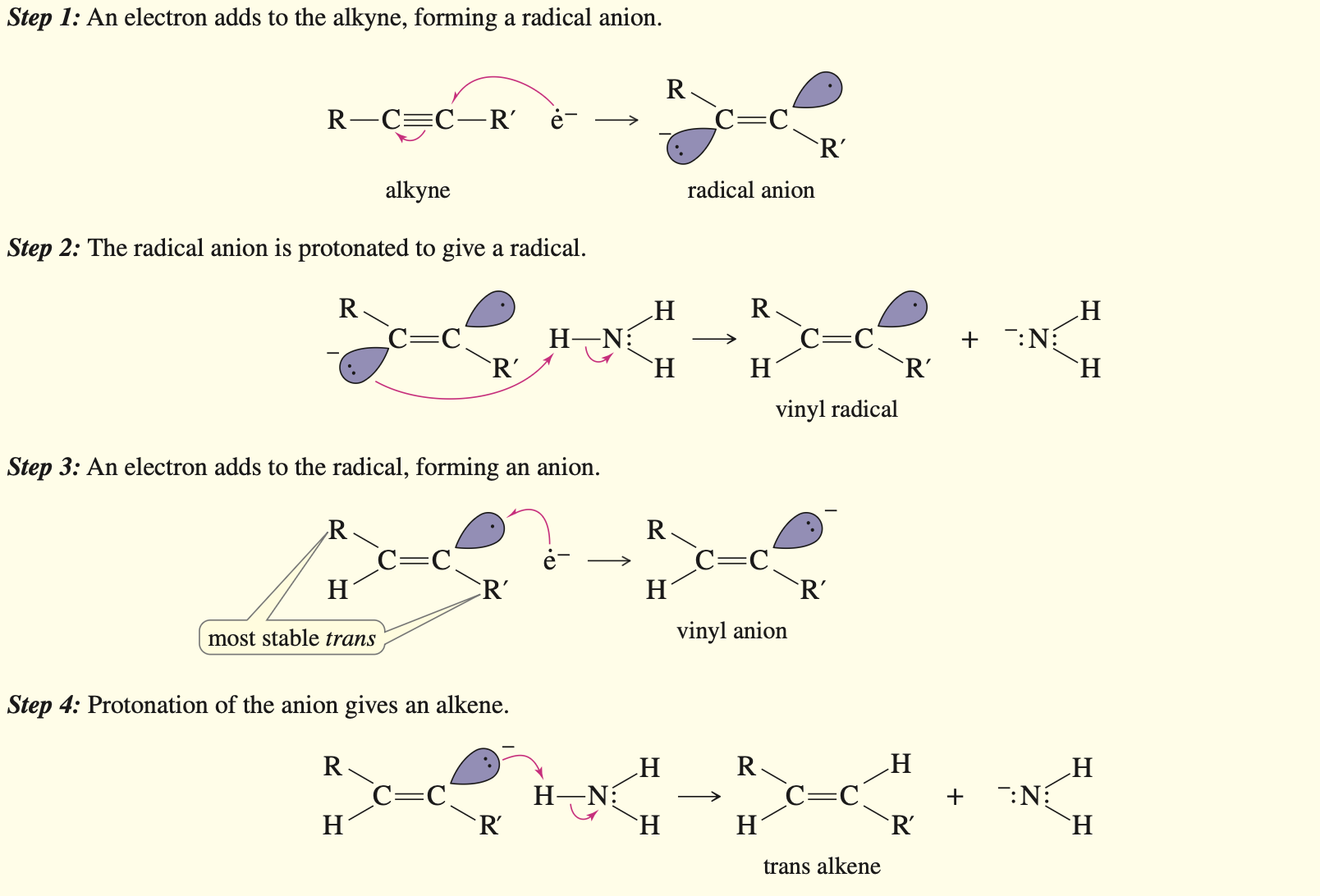
Anti Reduction of an alkene
Reagents: Na NH3
Neither Mark nor AntiMark
Anti-Addition
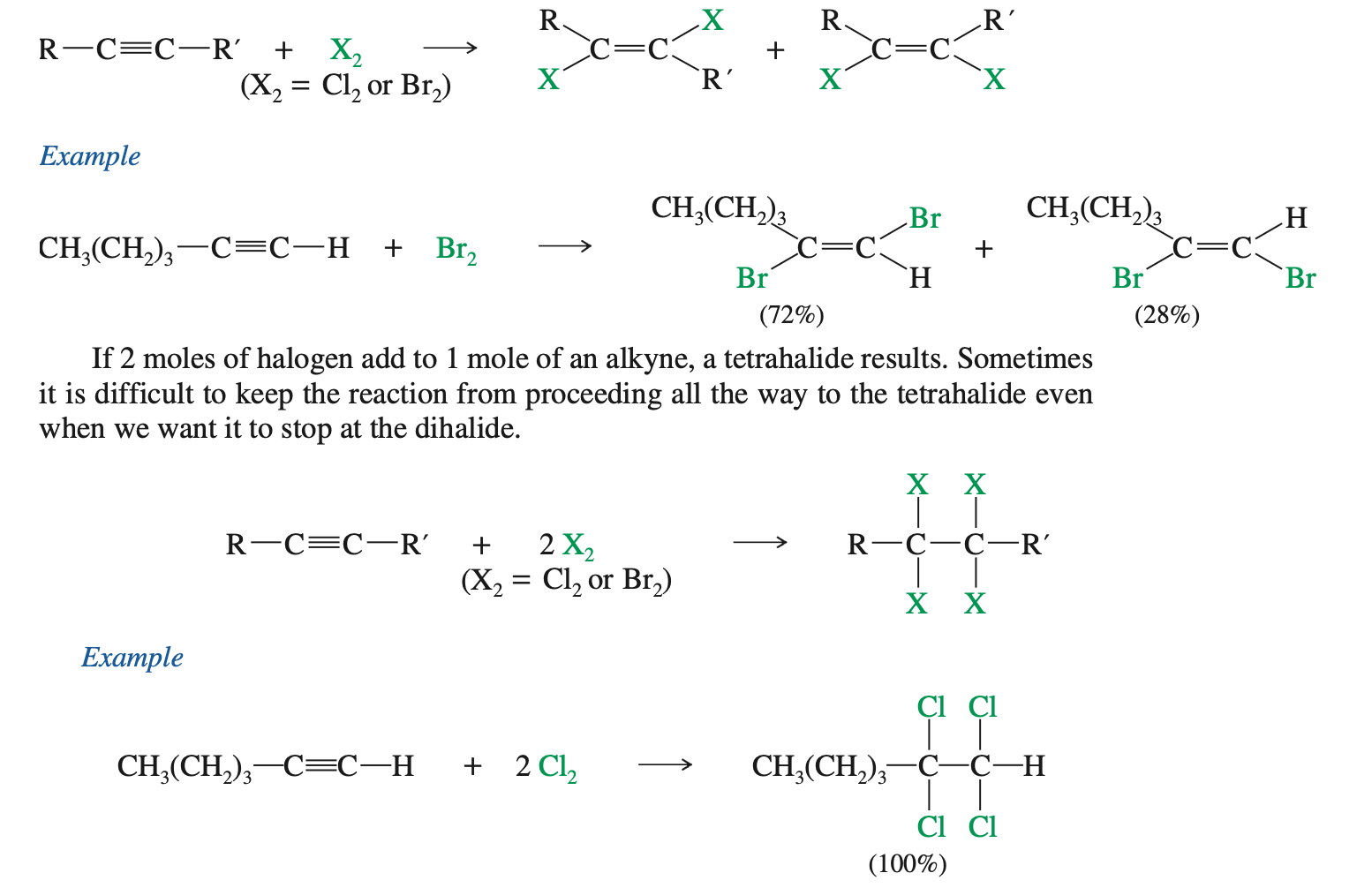
Addition of halogen
Just need to know that X2 ands anti in equimolar and completely in 2 Molar
Addition of Hydrogen Halide
Reagents: H—X
Mark orientation (geminal halide if double)
Both Syn and Anti
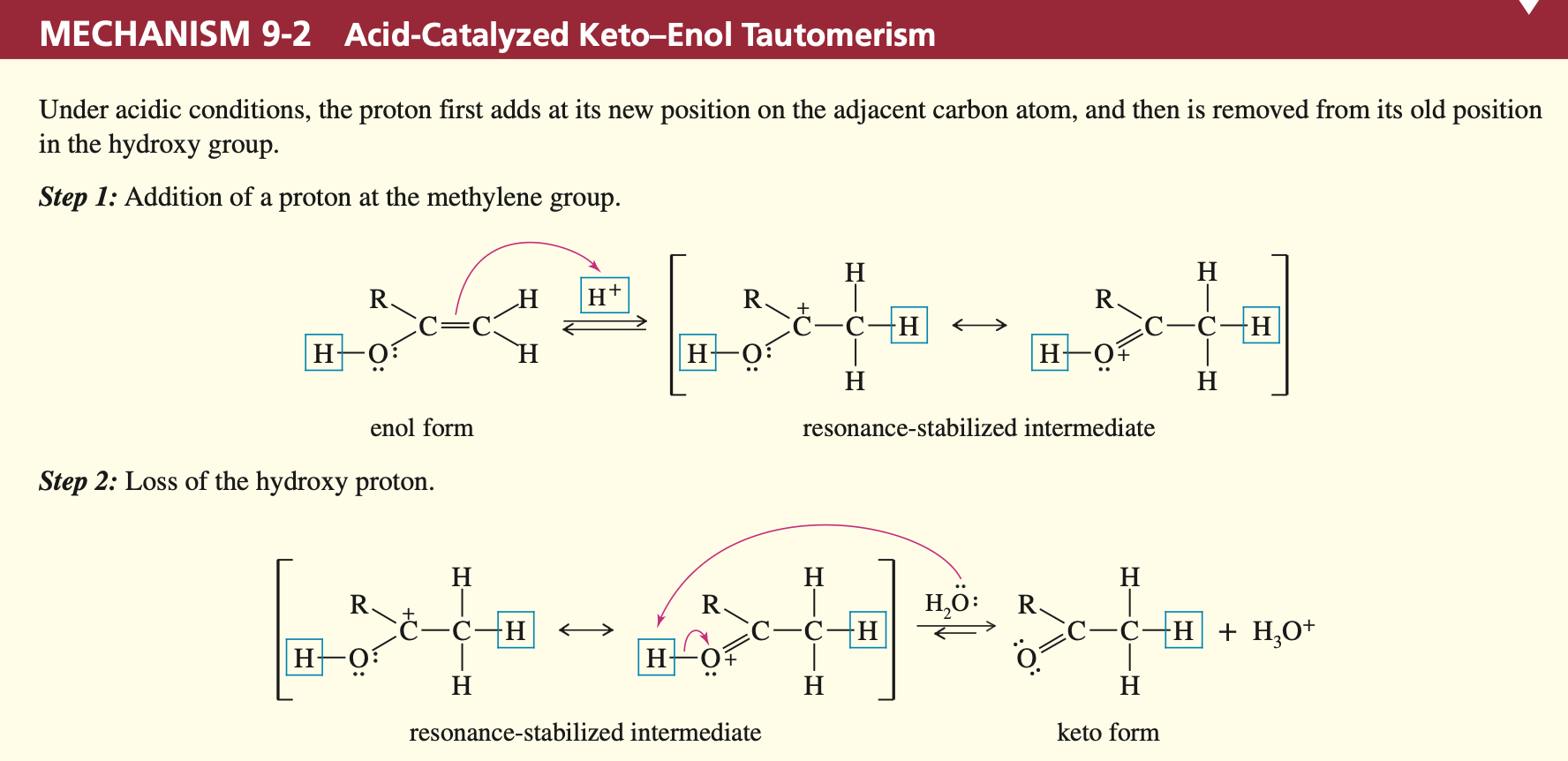
Hydration of Alkynes (Ketone)
Reagents: HgSO4/H2SO4
Mark Orientation of the OH
REARANGEMENT TO KETONE
Mechanism (Acid catalyzed)
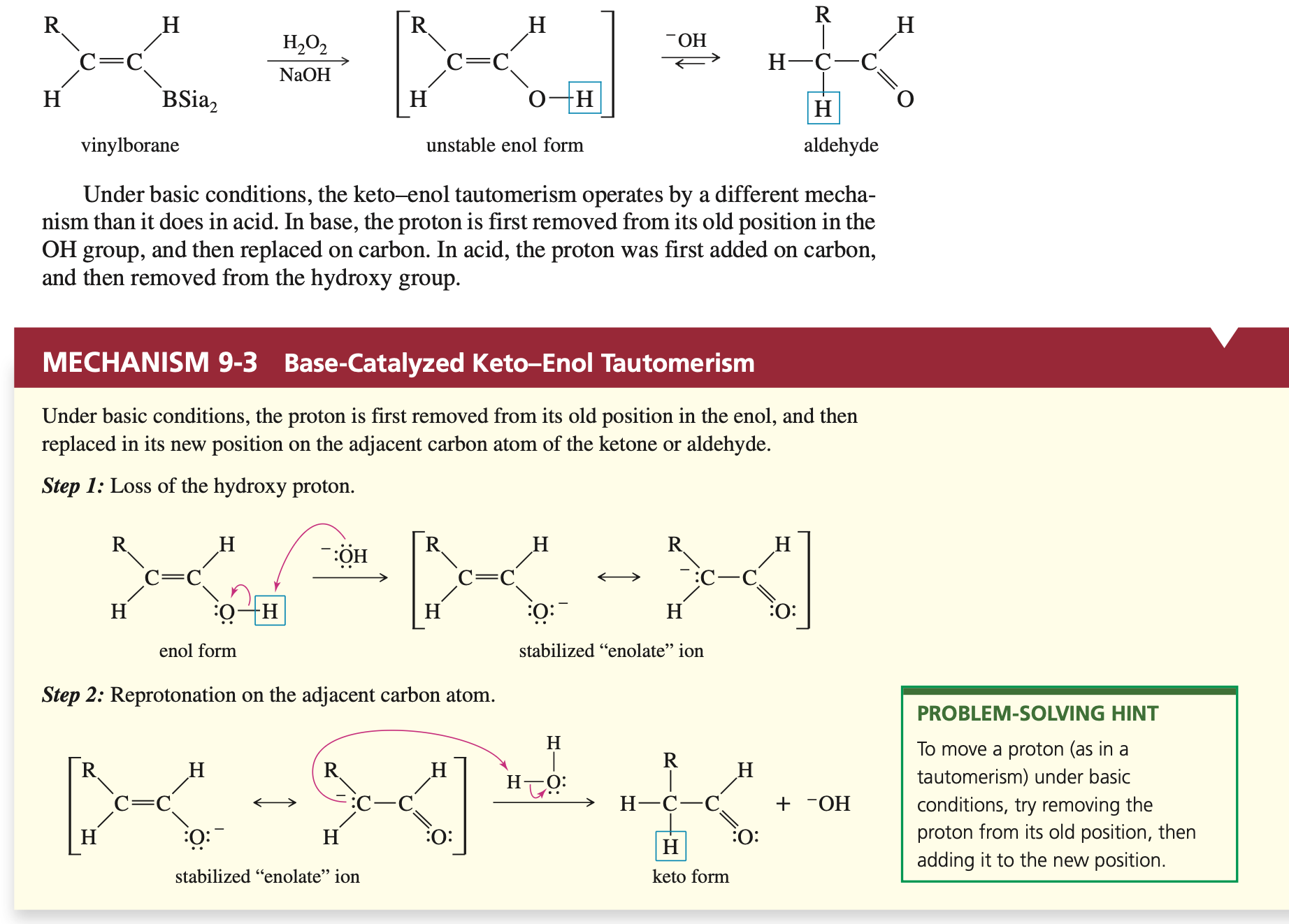
Hydration of Alkynes (Aldehyde)
Reagents: Sia2BH followed by H2O2/NaOH
Anti Mark Orientation
Base Catalyzed Keto-Enol Transformation
Oxidation of Alkynes
You only need to know cold KMnO4 adds 2 carbonyls (one to each carbon in a triple bond). Also if there are any spare H its make that an alcohol
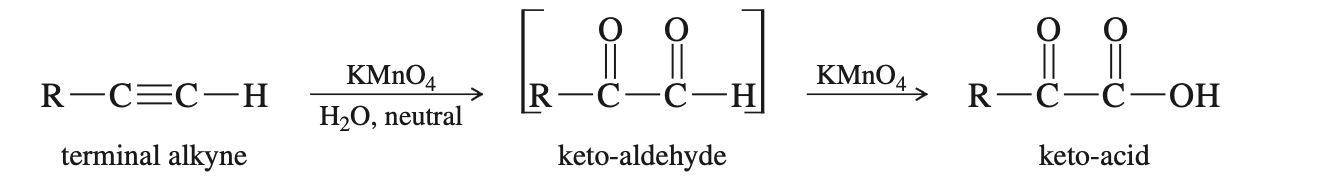
Clevage of Alkanes
Reagents:
KMnO4/KOH
O3 + H2O
Results: Cleavage and creation of Carboxylic acid (or CO2)