Lec 18 - Feeding & Drinking
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Herbivore
General plant vegetation
Rabbit
Cows
Carnivores
Animal protein
Lion
Wolves
Insectivores
Insects
Shrews
Bats
Browsers
Shrubs and herbaceous vegetation
Deer
Giraffes
Folivores
Leaves
Howler monkeys
Koalas
Frugivores
Fruits
Primates
Bats
Nectarivores
Pollen and nectar
Bats
Marsupials
Granivores
Seed eaters
Rodents
Sanguinivores
Blood
Vampire bats
What are some cranial modifications for consumption and retention of nutrients and water?
Dentition (e.g., aquatic baleen loss of teeth, dolphin homodont dentition)
Jaw muscles (e.g. Masseter size of rodents, shearing of carnassials carnivores)
Digestion (e.g. ruminant cattle)
Digestive enzymes
Digestive tract modifications
Digestive Enzymes
Secreted in:
Oral cavity - splits starch into sugar
Stomach - Splits protein chains into polypeptides
Small intestine - breakdown polypeptides to amino acid
Pancreas - neutralize gastric acid
Liver - disperse far and water-insoluble substances
Name some examples of digestive tract modifications
Insectivores - short intestine, no cecum
Carnivores - short intestine and colon, small cecum
Nonruminant herbivores - simple stomach, large cecum
Ruminant herbivore - four-chambered stomach, large ramen, long small and large intestine
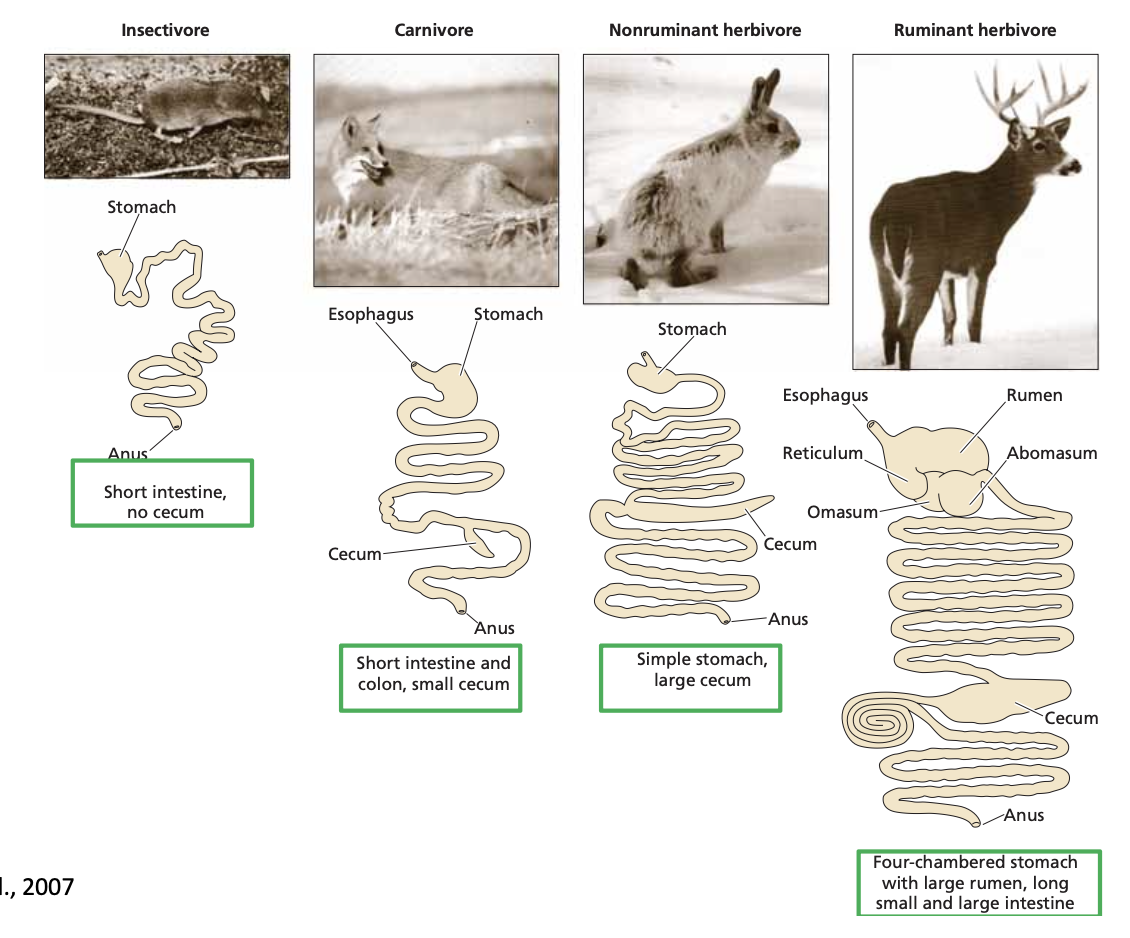
Mammals that consume plant material have a special challenge to process large amounts of difficult to digest material like cell walls and ….
Cellulose. In addition, protein content in plants is generally lower and difficult to access.
What are modifications found in digestive tracts to better consume cellulose?
Hindgut fermentation
Rumination
Hindgut Fermentation
Initial digestion with chewing.
Digestion continues in the stomach through enzyme activity but moves rapidly to the small intestine.
Nutrients are observed in the small intestine.
Small food particles enter cecum, the principal fermentation chamber.
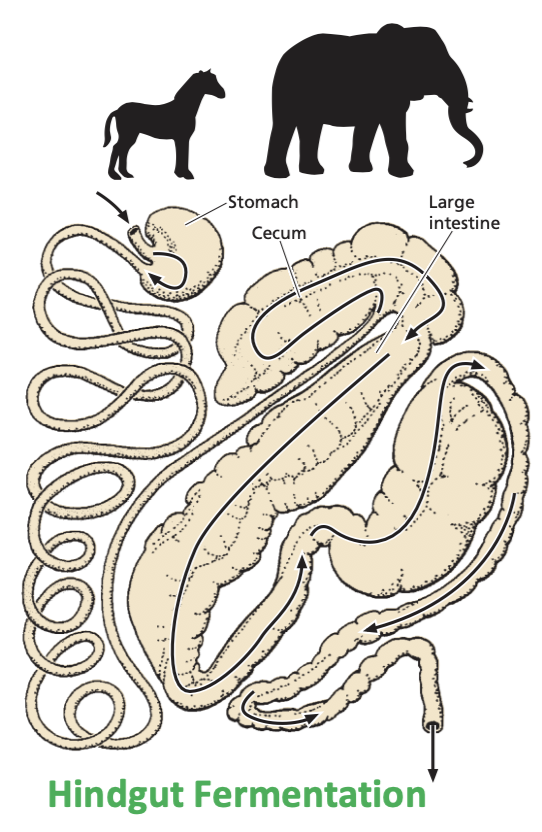
Where is cellulose broken down in Hindgut Fermentators?
Cecum & Large intestine. Already past the point of being able to absorb much energy.
Rumination (or Foregut Fermentation)
Have multi-chambered stomach with cellulose digesting microorganisms.
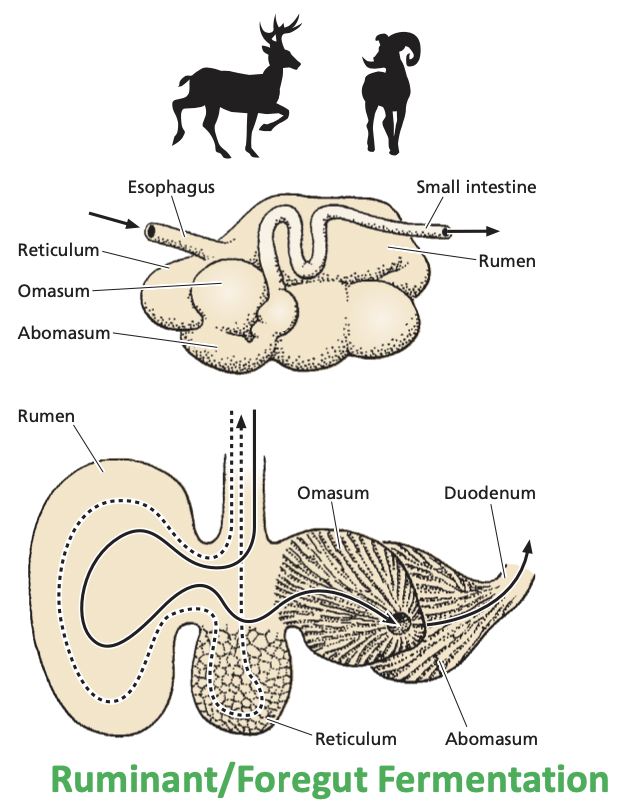
What are the four chambers of the ruminant digestion?
Rumen
Reticulum
Omasum
Abomasum
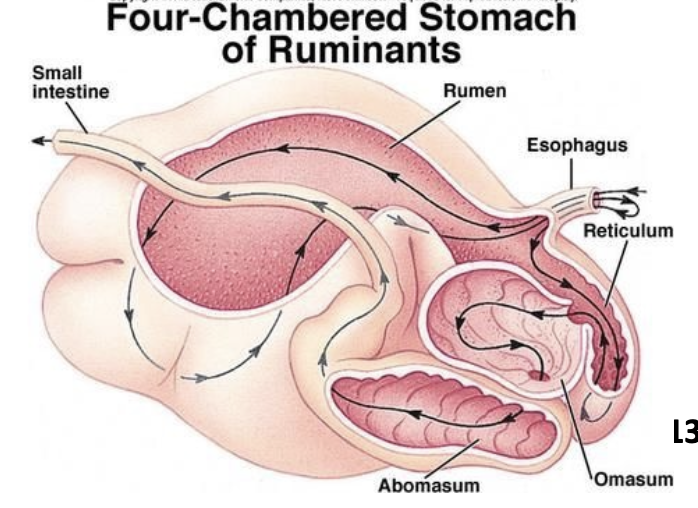
Rumen
Moisten food mix with microorganisms, initiates fermentation.
Reticulum
Receives larger particles of food, forms a softened mass (cud) and fermentation continues. Cud can be regurgitated to chew again where salivary amylase if added.
Omasum
Food bolus smashed by muscular walls.
Abomasum
The true stomach where digestive enzymes are added.
Why do ruminants tend to chew longer and regurgitate, while Hindgut Fermentators do not?
Ruminants have microorganisms in their saliva which help breakdown cellulose.
What are some characteristics of hindgut fermentation?
Ancestral condition
Process food rapidly
Digest protein well, and move indigestible material quickly
Don’t get all nutrients from food.
Eat large and varied foods
Plant toxins not digested/detoxified
What are some characteristics of foregut fermentation?
Derived condition
Slow digestion
Protein and fibers processed slow
Efficient digestion - microorganisms, help provide essential amino acids.
Plant toxins detoxified
Size limitations
Coprophagy
Feeding on feces.
Rodents, shrews, lagomorphs, marsupials
Produce soft and hard feces. Soft feces are immediately re-consumed to maximize nutrient extraction
Hindgut fermentation
Name an example of a blood-feeder (sanguinivores)
Vampire bats
Stores blood in enlarged, narrow stomach that absorbs water to concentrate the blood. water is excreted to reduce weight for flight.
Name an example of unique feeding specialization of a nectar diet.
Some bats have coevolved tongue morphology with certain flower species.
Name an example of unique feeding specialization of a gum diet.
Marmoset
Modified incisors with enamel only on the outer surface. Teeth wear into chisels which they use to gouge grooves into tree bark to stimulate the flow of plant gums which they consume.
Water balance
Not losing more water than taken up. Water and retention of moisture in terrestrial homeotherms is critical to survival.
What are physiological threats in hot environments?
Heat stress
Water stress
Need to maintain a positive water balance to not overheat.
What are potential sources for water loss?
Evaporation
Respiration
Excretion (urine/feces)
Lactation
What are potential sources for water gain?
Drinking free water
Dietary water
Metabolic water
What are examples of solutions to limit water loss and enhance water gain?
Loss of sweat glands
No panting
Fur coat
Live in burrow systems
Long snout/rostrum
Reduction of water content in urine and feces
Lactate only during favorable season
Increase concentration of milk
Feed at night when humidity is higher
Drink free water
Structure of Mammalian Kidney
Metabolizes protein waster into ammonia, toxic, into urea, less toxic and more soluble. Urea accumulates and releases as urine. The kidney can concentrate urine through Nephron.
Nephron
The functional unit of the kidney. Together with the glomerulus, urine is formed and concentrated.
Which hormone regulates permeability (or thirst)?
ADH
causes the kidneys to release less water, decreasing the amount of urine produced.
Alcohol suppresses ADH production, why more water loss.
Name an examples of a water balance adaptation in desert rodents
Nocturnal behavior - minimizes respiration water loss.
Dietary water - seeds at night absorb moisture.