CH6: Opioid (narcotic analgesics and antagonists)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Learning objectives

Who are they for?
patients in whom NSAIDs are contraindicated
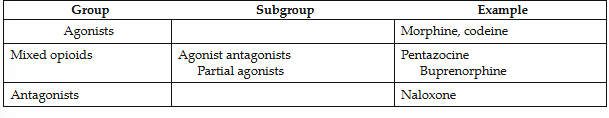
Classification
by mechanism of action at receptor sites:
agonists
mixed opioids
antagonists
Mechanism of action
Bind to the receptors in the CNS and the spinal cord producing an altered perception of reaction to pain
Substances with opioid like actions → enkephalins, endorphins,
dynorphins
★ These naturally occurring peptides possess analgesic action and have addiction potential
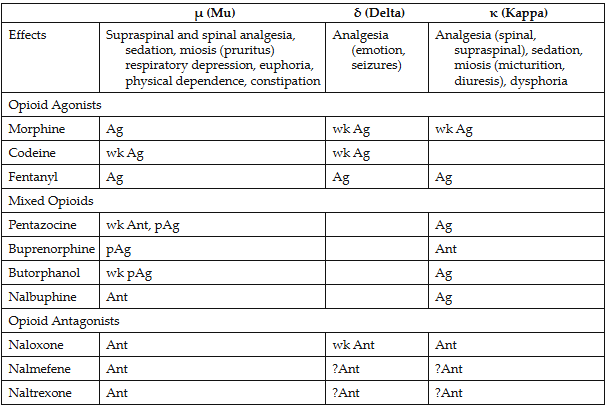
Important receptors
mu-analgesia
kappa(k)- dysphoria
delta-
- Differences in affinity for and action of different opioids at these and other specific receptors explain some of the distincitoons among the different opioids adverse reactions
Other:
sigma (O)-hallucinations, nightmare, anxiety
epsilon (e)-
Pharmacokinetics
● Absorption → oral, nasal, skin mucous membranes
● Distributioon → first-pass metabolism in the liver or intestinal wall, bound to plasma proteins and distributed throughout the body
● Metabolism → conjugated in the liver with glucuronic acid
● Excretion → excreted in the urine
● Onset = 1 hour (4-6 hour dosing)
Pharmacologic effects
★ The severity of the side effects is proportional to the agents efficacy (strength)
-efficacy is variable among opiods
★ They provide varying degrees of analgesia depending on the
strength of the agent
● U receptor → analgesia (inability to feel pain)
● K receptor → dysphoria and analgesia (dissatisfaction with
life)
● Opioids alter the patients reaction to painful stimuli by altering the release of certain central neurotransmitters
● Cough suppression
● GI effects → decrease propulsive contractions and motility
making them useful in treatment of diarrhea
Sedation & euphoria: generally produce sedation by the K receptor stimulation which may potentiate their analgesic effect and relieve anxiety
Adverse reactions
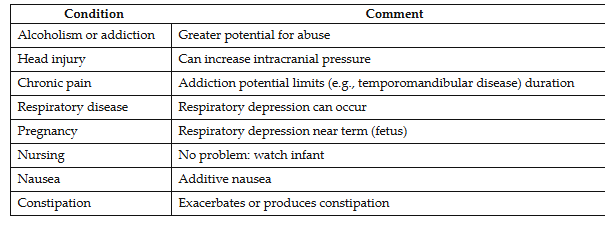
● Respiratory depression-not a problem with usual doses in normal patients; death if overdose
Head injury
Chronic pain
Respiratory disease
Alcoholism or addiction
● Nausea and emesis (vomiting)
● Constipation
★ Miosis → pinpoint pupils, overdose or sign of addiction
● Urinary retention
● CNS → stimulation as anxiety, restlessness, or nervousness
● Dysphoria
● Cardiovascular effects → syncope, bradycardia, postural
hypotension
● Biliary tract constriction (pain associated with gallstones)
● Histamine release → itching and urticaria at site of injection
● Pregnancy & nursing → prolong labor and depress fetal
respiration. Therapeutic doses pose no problem to normal infant
● Addiction
Addiction
a disease of the brain involving both physical and psychological dependence of the drug.
Two major signs:
- cravings (intense desire for the drug) and a loss of control of the ability to stop using the drug or the amount
- Total loss of control
tolerance is normally not a problem for those who take it no more than 1-3 days
Overdose symptoms and treatment
MAJOR- RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION
Pinpoint pupils and coma
NALOXONE (ANTAGONIST)
Treatment for addiction
1) Methadone substitution: substituting the equivalent amount of an oral opioid (methadone) for the injectible form the addict has
been using → gradual withdrawal
2) Cold turkey: abruptly withdrawing the opioid and using adjunctive medicine to alleviate symptoms of withdrawl
3) Methadone maintenance: maintaining a patient on high doses of
methadone taking large supervised oral doses on a daily basis
4) Naltrexone (Trexan): orally effective long acting antagonist
blocking the action of usual doses of opioids administered
illicitly
Withdrawal
abrupt disruption of an opioid
- Yawning
- Lacrimation
- Perspiration
- Gooseglesh (cold turkey)
- Irritability
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Chills
Shoppers
addicts who will try to find a physician or dentist to prescribe the drug of their choice

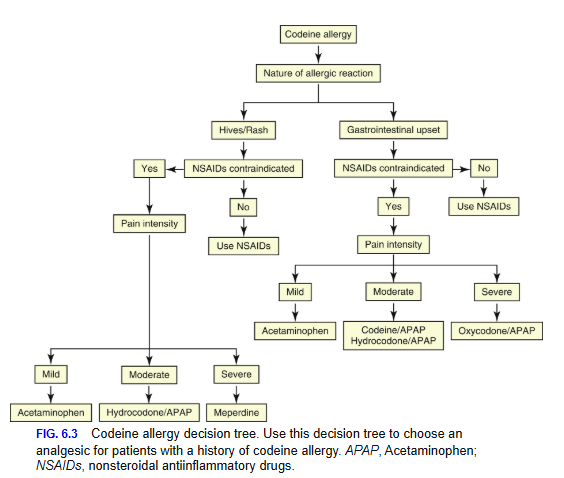
Allergic reactions
● Opiod allergy is uncommon
● Most common allergy is dermatologic in nature (skin rashes)
● Contact dermatitis
● If an allergy, an opioid from a different chemical class should be chosen
★ Severe pain → allergies to morphine and codeine → use meperidine or fentanyl
★ Mild to moderate pain → acetaminophen or NSAID drugs

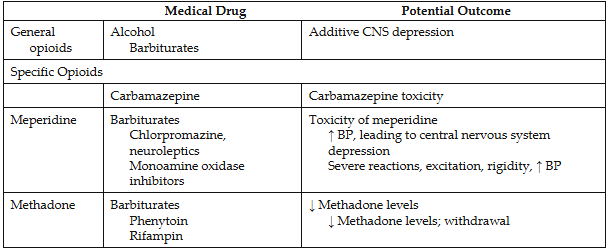
Drug interactions
alcohol or sedative-hypnotic agents=potentiate
Antihistamine=opodiod dose should be reduced
MAOIs (monoamine oxidase inhibitors)=for depression; CNS excitation, hypertension, hypotension
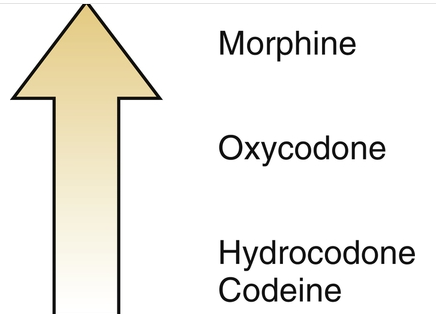
Opioid agonists
- U and K receptors
- Morphine → 10mg, terminal illness and post-op care
- Oxycodone → combined with aspirin or acetaminophen to
relieve moderate to severe pain; chronic pain from cancer
-Oxymorphone-more potent than morphine; pain from cancer
- Hydrocodone → many combo products (ibuprofen or
acetaminophen)
- Codeine → the most commonly used opioid in dentistry and
is combined with acetaminophen (Tylenol #3). It is a WEAK
analgesic, often NSAID drugs produce better results for
dental pain
- Meperidine → Demerol, acute management of moderate to
severe pain. Has a rapid onset of action but is short-acting
- Hydromorphone → Dilaudid, management of severe pain.
Effective orally and is more potent than morphine
- Methadone → Dolophine, used for treatment for opioid
addicts (either for withdrawl or maintenance). Since it is
an opioid analgesic, the RISK for dependence still exists
- Fentanyl Products → Duragesic, Sufenta, Alfenta. Used
perioperatively or during general anesthesia. Sold as
patches as well for constant pain relief for the
terminally ill
-Abuse-deterrent opioids-help deter against substance abuse; reduced doctor shopping for OxyContin
Mixed opioids
- Pentaxocine (Talwin) → available in oral form or with Naloxone (Talwin-NX), reverses opioid overdose
- Butorphanol (Stadol) → nasal spray
- Denzocine (Dalgan), Nalbuphine (Nubain), Butorphanol
(Stadol), → all available paenterally
- Buprenorphine (Buprenex, Subutex) → oral and parenteral,
suppresses withdrawl
Opioid antagonists
- Naloxone (Narcan) → drug of choice for agonist or mixed opioid overdose
- Nalmefene (Revex) → reverses opioid overdose
- Naltrexone (ReViam Vivitrol) → acute hepatitis and liver failure, maintenance in detoxification, used to prevent opioid and alcohol use in addicts
Full agonist/reuptake inhibitors
Tapentadol-oral opioid receptor agonist and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor; II drug=abuse, misuse, dependence
Tramadol: inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin
- Adverse reactions include... dizziness, headaches, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, seizures
- Associated with physical dependency and withdrawal symptoms
Dental use of opioids
● Can use when NSAIDs are contraindicated
● Not for chronic pain
● Prescription writing

Chronic dental pain and opioid use
chronic orofacial pain
dentist only one who can prescribe long-term opioid therapy
prescriptions=only for small amts without refills and only if dental treatment has been performed
TMJ disease
Patient concerns regarding opioid use
remind that short term use shouldn’t cause problems with addiction or dependence and the proper use of opioid analgesic will provide needed pain management
DH considerations
• If opioid analgesics are necessary, the dental hygienist should conduct a thorough medication/health history of the patient to determine whether there are any contraindications or drug interactions.
• The dental hygienist should be aware that many opioid analgesics are combined with nonopioid analgesics. Remind patients to not supplement with over-the-counter (OTC) analgesics if a combination nonopioid/opioid analgesic is prescribed.
• The most common side effect of the opioid analgesics is sedation. Other sedating drugs should be avoided or used with caution if they are essential.
• Patients should avoid anything that requires thought or concentration while taking an opioid analgesic.
• If patients complain of gastrointestinal adverse effects, they may require a semisupine chair position during dental treatment.
• The dental hygienist should be aware of the signs of opioid addiction and how to identify an addict.
• Consult Box 6.2 for patient instructions regarding opioid analgesics.