microeconomics exam 2 hw
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
This is unlikely to be true. In general, demand elasticity increases as prices drop and quantities increase, so we would expect the second 10% decrease in price to be met with a larger than 8% increase in quantity.
If a 10% decrease in the price of one product that you buy causes an 8% increase in quantity demanded of that product, will another 10% decrease in the price cause another 8% increase (no more and no less) in quantity demanded?
is maximizing utility.
When Marietta chooses to only purchase a combination of goods that lie within her budget line, she:
is decreasing utility.
is maximizing utility.
must reduce the quantity.
likely has negative savings.
To integrate the insights of psychology into economics to enrich our understanding of decision-making.
What is the goal of behavioral economics?
To shift economic theory from a mathematical base to more of a psychological study.
To eliminate the consumers’ state of mind from consideration in economic analysis.
To integrate the insights of psychology into economics to enrich our understanding of decision-making.
To study consumer behavior over time rather than behavior in the moment and integrate these insights in economic analysis.
income effect; higher price
The term _____________ describes a situation where a ________________ causes a reduction in the buying power of income, even though actual income has not changed.
income effect; higher price
intertemporal budget; lower price
substitution effect; lower price
intertemporal budget; higher price
The tendency to focus more on the loss than the gain.
What is loss aversion?
The tendency of an individual to invest all of their resources to avoid losing.
The ability of humans to exercise complete self control in high stakes situations to avoid losing.
The temptation company’s face to invest in questionable techniques to avoid losing money.
The tendency to focus more on the loss than the gain.
The change in total utility / the change in quantity
Marginal utility is defined as the increment to total utility that results from the consumption of one more unit of some good or service. The equation for marginal utility is:
The change in quantity / the change in total utility
The change in total utility / the change in quantity
The change in total utility / the change in total revenue
Total revenue / quantity demanded
The price of designer jeans has increased, so the buying power of your income has been reduced. You purchase 2 new pairs of new jeans instead of 3 that year.
Which of the following best describes the income effect?
The price of designer jeans has increased, so you have less of an incentive to purchase new jeans. You purchase 3 pairs of chinos instead that year.
The gap between the rich and everyone else has gotten bigger.
The bank increases interest rates on savings accounts from .04% to 5%, so you start placing more of your monthly income in that savings account.
The price of designer jeans has increased, so the buying power of your income has been reduced. You purchase 2 new pairs of new jeans instead of 3 that year.
The degree to which concerts and overnight getaways are normal goods or inferior goods.
Kimberly has $1,000 per year to spend between $50 concert tickets and $200 per night getaways. Her utility maximizing combination is 8 concerts and 3 overnight getaways.
She recently received a promotion on her job and now she can spend up to $2000 per year on these two items. Her new utility maximizing combination will depend in part on what?
The degree to which concerts and overnight getaways are normal goods or inferior goods.
The fact that concerts and getaways are fungible goods.
The substitution effect.
The income effect.
(The marginal utility associated with good 1 / the price of good 1) = (the marginal utility associated with good 2 / the price of good 2)
You were presented with a utility maximizing rule which states: If you always choose the item with the greatest marginal utility per dollar spent, when your budget is exhausted, the utility maximizing choice should occur where the marginal utility per dollar spent is the same for both goods.
That rule is expressed as follows:
(The marginal utility associated with good 1 / the price of good 1) = (the marginal utility associated with good 2 / the price of good 2)
The marginal utility per dollar of good 1 > the marginal utility per dollar of good 2.
(The marginal utility associated with good 1 / the price of good 2) = (the marginal utility associated with good 2 / the price of good 1)
% change in price / % change in quantity
In general, greater consumption of a good brings higher total utility. However, the additional utility received from each unit of greater consumption tends to decline in a pattern of diminishing marginal utility
Briefly discuss how greater consumption of a good affects utility.
Mental accounting is the notion of putting dollars in different mental categories where they take different values.
Explain the idea of mental accounting.
Mental accounting is the way people keep track of their mental assets and liabilities.
Mental accounting refers to the way we emotionally account for ups and downs of our lives.
Mental accounting is the notion of putting dollars in different mental categories where they take different values.
Mental accounting refers to the interest rate we use when we calculate the present value of future mental assets.
2400
Jimmy saves part of his income to entertain himself once a year. He spends some of these savings on vacation and buying new clothes.
He spent $200 on his new clothes, his marginal utility from new clothes purchases is 300 utilis and his marginal utility from the vacation he went on is 3600 utilis. This means that his vacation must cost:
$4500
1600
3000
2400
8
Jed's weekly budget for lunch is $24. He eats only pizza and burgers. Each pizza costs $6 and each burger costs $3. Jed knows that 2 pizzas and 4 burgers will give him a utility of 8. At his utility-maximizing point, Jed's utility is:
6
4
8
10
utility
In microeconomic terms, the ability of a good or a service to satisfy wants is called:
profit potential
opportunity cost
utility
utility maximization
diminishing marginal utility
The term ___________________ is used to describe the common pattern whereby each marginal unit of a consumed good provides less of an addition to utility than the previous unit.
diminishing marginal utility
decreasing marginal utility
marginal utility pattern
marginal income utility
8
Rick eats only french fries and burgers at his office cafeteria. His weekly lunch budget is $24. Each burger costs $6 and each order of fries costs $3. When deciding how much of each good to buy, Rick knows that 2 burgers and 4 orders of French fries will give him a utility of 8. At his utility-maximizing point, Rick's utility is:
48
40
24
8
his tax on alcohol only impacts supply and demand trends within the liquor industry.
Say that a tax on alcohol leads to a higher price at the liquor store. Which of the following is NOT likely to occur?
Consumers spend less on other food items to compensate for this expense.
his tax on alcohol only impacts supply and demand trends within the liquor industry.
Alcoholic beverage consumption is likely to decrease.
The higher price of alcohol causes the budget constraint to pivot left.
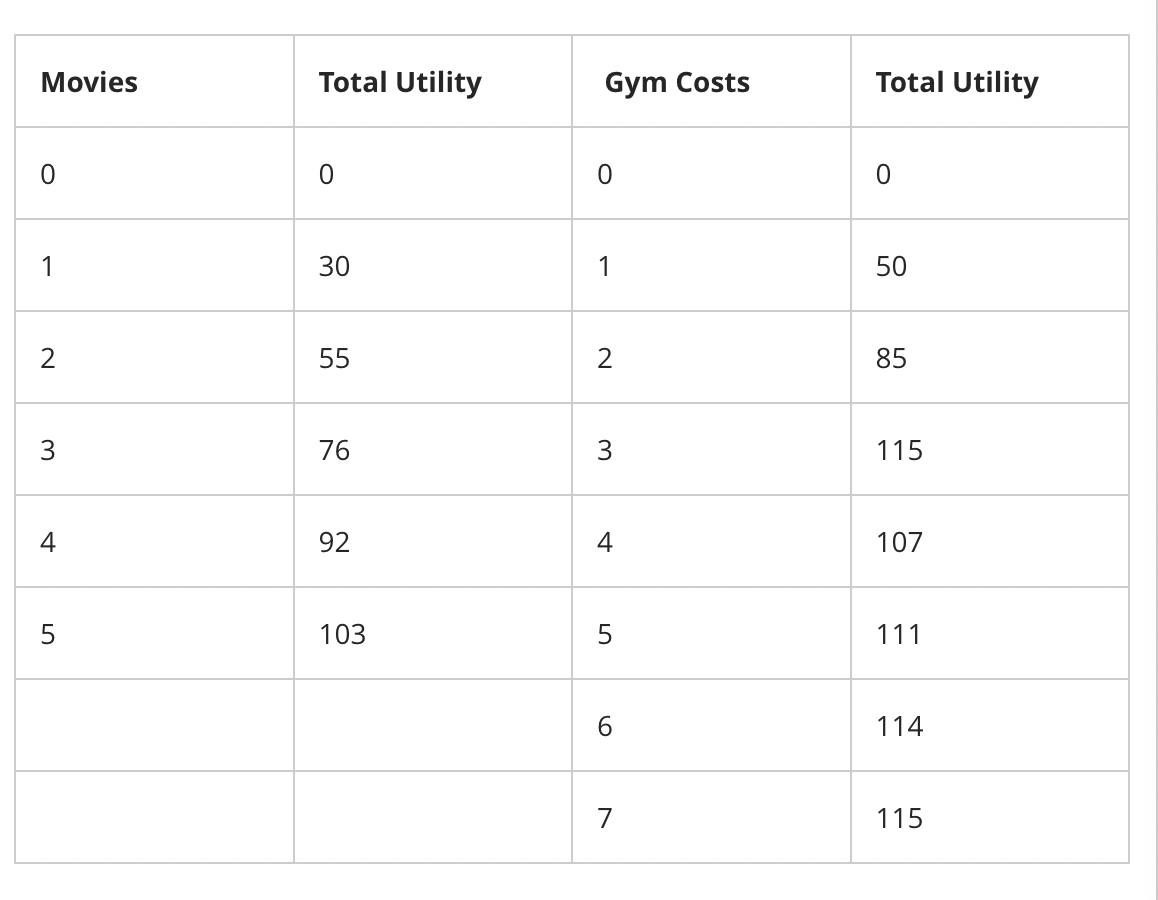
3 movies; 3 gym workout sessions
Bob budgets $18 a week for entertainment. He splits his time between going to the movies and going to the gym. Each movie costs $3 and each session at the gym also costs $3. The total utility from each of these activities is shown in the table below. Bob’s utility maximizing point is:
4 movies; 2 gym workout sessions
1 movie; 5 gym workout sessions
3 movies; 3 gym workout sessions
4 movies; 0 gym workout sessions
3 salads, 6 vegetarian burgers
For lunch, Maria eats only salads or vegetarian burgers. Her weekly food budget is $36. Each salad costs $6 and each vegetarian burger costs $3. When deciding how much of each good to buy, Maria knows that 2 salads and 4 vegetarian burgers will give her a utility of 8. Maria’s utility-maximizing point is:
2 salads, 8 vegetarian burgers
3 salads, 6 vegetarian burgers
6 salads, 1 vegetarian burger
4 salads, 6 vegetarian burgers
Examine the following diagram. With this information, what kind of curve could you derive?
Marginal Cost Curve
Supply Curve
Marginal Revenue Curve
Demand Curve
elective surgery due to its lower marginal return rate.
The government wants to make medicare benefits available to more people, but to achieve this goal, it needs to make cuts in the existing medicare budget. The two areas where they are considering cuts are non-essential elective surgery and 6-12 month mental health care programs. Applying the concept of diminishing marginal utility, the budget cuts should be made for spending on:
both programs, which have the same marginal return rate.
elective surgery due to its lower marginal return rate.
neither can be compared by measuring marginal utility.
mental health therapy due to its higher marginal return rate.
Use utils as a measure of utility, assigning a specific number to T-shirts and movies, and then add those together.
The goal of the consumer is to maximize the total utility or satisfaction derived from their purchase choices, given the unique budget constraint. To calculate total utility of a given combination of T-shirts and movies, one would use the following approach:
For a given combination of T-shirts and movies, survey a group of individuals to determine an average for utils to be assigned to the number of T-shirts and movies.
Use utils as a measure of utility, assigning a specific number to T-shirts and movies, and then add those together.
For a given combination of T-shirts and movies, assign a number of utils to that combination.
For a given combination of T-shirts and movies, use Google to identify the number of utils associated with the number of T-shirts and movies and then sum them.
the marginal utility per dollar is the same for both goods
Which of the following is considered to be a tell-tale signal that the point with the highest total utility has been found?
the demand curves are flatter reducing quantity
the marginal utility per dollar is the same for both goods
the quantities demanded change so total utility rises
the marginal utility per dollar is controlled by trade-of
substitution effect
Which of the following occurs simultaneously with an income effect?
substitution effect
preferences effect
Giffen good effect
backward-bending supply curve
market demand to shift to the left.
a decrease in consumer preference for a product, other things being equal, will cause:
market demand to shift to the left.
market demand to shift to the right.
quantity demanded is not a price function.
a decrease in supply.
$50
In May and June, Tammy spent all her clothing budget on bathing suits and beach bags. Each bathing suit cost $75. At Tammy’s optimal choice, her marginal utility from the last bathing suit purchased is 300 and her marginal utility from the last beach bag purchased is 200. This means that each handbag must cost
$150
$100
$25
$50
substitution effect
The ________________ arises when a price changes because consumers have an incentive to consume less of the good with a relatively higher price and more of the good with a relatively lower price.
preferences effect
income effect
substitution effect
backward-bending supply curve
economies of scale; a larger factory can produce at a lower average cost than a smaller company.
When __________________ exist, doubling of all inputs will result in more than doubling output, which means __________________________________________.
low labor inputs; larger scale of production leads to higher costs.
labor inputs; economies-of-scale curve is U-shaped
economies of scale; a smaller factory can produce at a lower average cost than a larger company
economies of scale; a larger factory can produce at a lower average cost than a smaller company.
35%
Approximately what percentage of the US labor force is employed by firms that have fewer than 100 employees?
45%
50%
35%
63%
inputs and outputs
A production function is a mathematical expression or equation that explains the engineering relationship between:
inputs and outputs
Capital and labor
The size of the factory and the rate of production
New technology and its application
physical space for the gallery
Marcella operates a small, but very successful art gallery. All but one of the following can be classified as a variable cost arising from the physical inputs Marcella requires to operate her business. Which is it?
physical space for the gallery
wages paid to three part-time employees
costs of purchasing art work to sell in the gallery
accountant's fees for preparing tax returns
the building where the assembly takes place.
We can describe inputs as either fixed or variable. Thinking about a company that assembles cars, which of the following would be an example of a fixed input that could not be changed in the short run?
The robots that help assemble the cars.
The electricity required to support the assembly activity.
The building where the assembly takes place.
The employees that work for the company.
Q1/ Production Method 1 (50 units of labor, 10 units of capital) should be used since the total cost of $9,000 is significantly lower than the cost using the other methods.
Q2/ Production Method 1 is still the best option if the cost of labor rises to $200/unit, since $14,000 is less than the total cost for the other methods.
A small company that shovels sidewalks and driveways has 100 homes signed up for its services this winter. It can use various combinations of capital and labor: lots of labor with hand shovels, less labor with snow blowers, and still less labor with a pickup truck that has a snowplow on front. To summarize, the method choices are:
Method 1: 50 units of labor, 10 units of capital
Method 2: 20 units of labor, 40 units of capital
Method 3: 10 units of labor, 70 units of capital
Q1/If hiring labor for the winter costs $100/unit and a unit of capital costs $400, what production method should be chosen?
Q2/ What method should be chosen if the cost of labor rises to $200/unit?
total costs
___________ include all spending on labor, machinery, tools, and supplies purchased from other firms.
Total revenues
Total costs
Total profits
Total profit margins
$2.43
I’MABigCorp. produces and sells kitchen wares. Last year, it produced 7,000 can openers and sold each one for $6. To produce the 7,000 can openers, the company incurred variable costs of $28,000 and a total cost of $45,000. I'MABIGCorp.'s average fixed cost to produce the 7,000 can openers was
$1.50
$1.23
$2.25
$2.43
the change in total cost divided by the change in output.
Mathematically, marginal cost is expressed as..
Unit production costs times the change in output
Unit production costs times the number of workers employed
The change in total cost divided by the change in output.
Total cost divided by output.
interest and dividends
The factor payment for the use of financial capital (loans and equity investments) is called...
Profit.
Interest and dividends.
Wages.
Rent.
when the number of bakery staff increases from 2 to 3 bakers, 5 additional loaves are made.
Which of the following best describes marginal product?
The total number of loaves a bakery can create with 5 workers and a fixed amount of capital
When the number of bakery staff increases from 2 to 3 bakers, 5 additional loaves are made.
Leftover output - the loaves a bakery makes but does not sell and that goes unused.
The loaves made by a bakery using a substandard quality flour that ultimately harms business profits.
average cost
In order to determine ____________, the firm's total costs must be divided by the quantity of its output.
average cost
variable cost
fixed costs
diminishing marginal returns
total revenue
Whatever the firm’s quantity of production, _____________ must exceed total costs if it is to earn a profit.
marginal costs
total revenue
average costs
variable costs
government economic subsidies protect firms from competition to avoid losses.
Economies of scale may arise from all but one of the following. Which one is it?
doubling promotional expenses to expand sale more than proportionately
having a larger retail space can expand sales more than proportionately
government economic subsidies protect firms from competition to avoid losses.
spreading the fixed-costs of administration over more customers holds average costs down
mortgage or rent
factor payment for land
wages or salary
factor payment for labor
a monopoly
In economics, a firm that faces no competitors is referred to as _________________.
an oligopoly
an oligopolizor
a perfect competitor
a monopoly
costs incurred in the act of producing
Which of the following falls outside of the classification of business expenses that fall into the category of fixed costs?
costs that vary according to specific line of business
costs incurred in the act of producing
costs incurred as advertising expenses
costs that must be made before production starts
divide total costs into two categories: fixed costs that can’t be changed in the short run and variable costs that can be
If a solar panel manufacturer wants to look at its total costs of production in the short run, which of the following would provide a useful starting point?
divide the total costs of production by the quantity of output
divide total costs into two categories: fixed costs that can’t be changed in the short run and variable costs that can be
divide total costs into two categories: variable costs that can't be changed in the short run and fixed costs that can be
divide the variable costs of production by the quantity of output
the sum of the materials ($100), website charge ($10), and 4% payment processing charge (4%)
Mirtha owns an online jewelry store that specializes in earrings. In March, she sells 50 pairs of earrings priced at $15. The cost of materials to create the 50 pairs of earrings was $100. The website she uses to sell her wares costs her $10 a month, and she is also charged 4% on each sale by the company that processes debit/credit card purchases.
Which of the following best represents Mirth’s total cost?
The costs of materials minus the costs it takes to run her business through the online store, in this case the $10 website charges and the 4% payment processing charge
The cost of all the materials used to create the earrings, $100
The sum of the materials ($100), website charge ($10), and 4% payment processing charge (4%)
The $750 Mirtha earned from earring sales minus the materials ($100), online website charge ($10), and payment processing charge (4%)
decreasing and diminishing returns to scale
A situation where the level of output, scale and average costs are all rising is called
decreasing returns to scale
diminishing returns to scale
both a and b are correct
diseconomies of scale
do so regardless of what type of competition exists in a market.
According to the definition of profit, if a profit-maximizing firm will always attempt to produce its desired level of output at the lowest possible cost, then it will
take a long-run perspective on costs, when such costs cannot be adjusted
take a short-run perspective on labor costs which cannot be immediately changed.
breakdown its cost structure according to short-run adjustments.
do so regardless of what type of competition exists in a market.
20,000
continuing the firm Exercise the firm’s factory sits on land owned by the firm that could be rented out for $30,000 per year. What was the firm’s economic profit last year?
30,000
10,000
20,000
50,000
A firm had sales revenue of $1 million last year. It spent $600,000 on labor, $150,000 on capital and $200,000 on materials. What was the firm’s accounting profit?
50,000
A firm had sales revenue of $1 million last year. It spent $600,000 on labor, $150,000 on capital and $200,000 on materials. What was the firm’s accounting profit?
50,000
35,000
70,000
85,000
all factors are variable
The long run is the period of time during which...
All factors are variable.
Some outputs are variable.
All outputs are variable.
At least some factors of production are fixed.
the $40,000 in rental income an entrepreneur no longer receives after converting the rental space to their new storefront.
Which of the following is an example of an implicit cost?
$60,000 spent to purchase the lumber needed to create a product.
The $40,000 in rental income an entrepreneur no longer receives after converting the rental space to their new storefront.
Federal taxes paid by the firm.
$25 hourly wage paid to a seasonal clerk that a firm employs on a contract basis.
economies of scale
The portion of a long run average cost curve that is downward sloping is called the range of:
Constant returns to scale.
Diseconomies of scale.
Economies of scale.
Unit returns to scale.
variable costs
If a paper mill shuts down its operations for three months so that it produces nothing, its __________________ will be reduced to zero?
fixed costs
opportunity costs
variable costs
total cost
variable costs
______________ include all of the costs of production that increase with the quantity produced.
Variable costs
Fixed costs
Average costs
Average variable costs
if marginal costs exceed marginal revenue, then the firm will reduce its profits for every additional unit of output it produces.
Why a profit-maximizing firm will not choose to produce at a quantity where marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue
Profit would be greatest if it reduces output to where MR = MC.
The firm may produce when MC exceed MR because their profit will increases.
If marginal costs exceed marginal revenue, then the firm will reduce its profits for every additional unit of output it produces.
price > average total costs
The profit maximizing condition for a purely competitive firm is when...
Price elasticity of demand is positive.
Price < average total costs
Price > average total costs
Price = average total costs
consider shutting down or stopping production
A strawberry farm operating in a perfectly competitive market is operating below the break-even point. What is the best thing to do in the short run?
Borrow money and buy more capital equipment.
consider shutting down or stopping production
Increase the price of its strawberries.
Hire more workers.
the average product of labor is always equal to the marginal product of labor.
In Sam's greenhouse operation, labor is the only short term variable input. After completing a cost analysis, if the marginal product of labor is the same for each unit of labor, this will imply that
as more labor inputs are used, the average product of labor inputs will fall.
the average product of labor is always greater that the marginal product of labor
the average product of labor is always less than the marginal product of labor.
the average product of labor is always equal to the marginal product of labor.
short run; the quantity of output where profits are highest
In the _______________, the perfectly competitive firm will seek out _______________.
long run; methods to reduce production and shut down
short run; the quantity of output where profits are highest
short run; profits by ignoring the concept of total cost analysis
long run; the quantity of output where profits are highes
firms set different prices for their product, either at or above the equilibrium price.
Which of the following characteristics does NOT describe a perfectly competitive market?
Companies are able to enter and exit the market without any restrictions.
Firms set different prices for their product, either at or above the equilibrium price.
There are many people who desire and have the ability to purchase the product.
Many firms are producing identical products
they sell each package of strawberries for $5, and the average variable cost is $4.75.
In the short run, a strawberry farm operating in a perfectly competitive market would produce strawberries at a profit if...
Their fixed costs are less than their variable costs.
They sell each package of strawberries for $5, and the average variable cost is $4.75.
They sell each package of strawberries for $5, and the average cost is for each package is $5
Set the price for each package of strawberries above the prevailing equilibrium price.
long run; increasing its production
In the _____________, the perfectly competitive firm will react to profits by
__________________.
long run; tailoring their quality controls
long run; increasing its production
short run; increasing quality of products
short run; reducing its labor inputs
provided each is willing to accept the prevailing market price.
Idaho farmers can sell as large a quantity of their potato crop as they wish,
provided each is willing to accept the prevailing market price.
provided quality is perceptible and determines the market price.
if they set their own price in the long run, but in the short run, the market sets the price.
if they set their own price in the short run, but in the long run, the market sets the price.
Shifts to the right with new firms’ entry and stops at the point where the new long-run equilibrium intersects at the same market price as before.
For a constant cost industry in a purely competitive market structure, whenever there is an increase in market demand and price, then the supply curve
The supply curve becomes unstable. and firms leave the market because management costs become very high
Shifts to the right with new firms’ entry and stops at the point where the new long-run equilibrium intersects at a lower market price.
Shifts to the right with new firms’ entry and stops at the point where the new long-run equilibrium intersects at the same market price as before.
Shifts to the left as some firms leave the market and the market price rises to a new level.
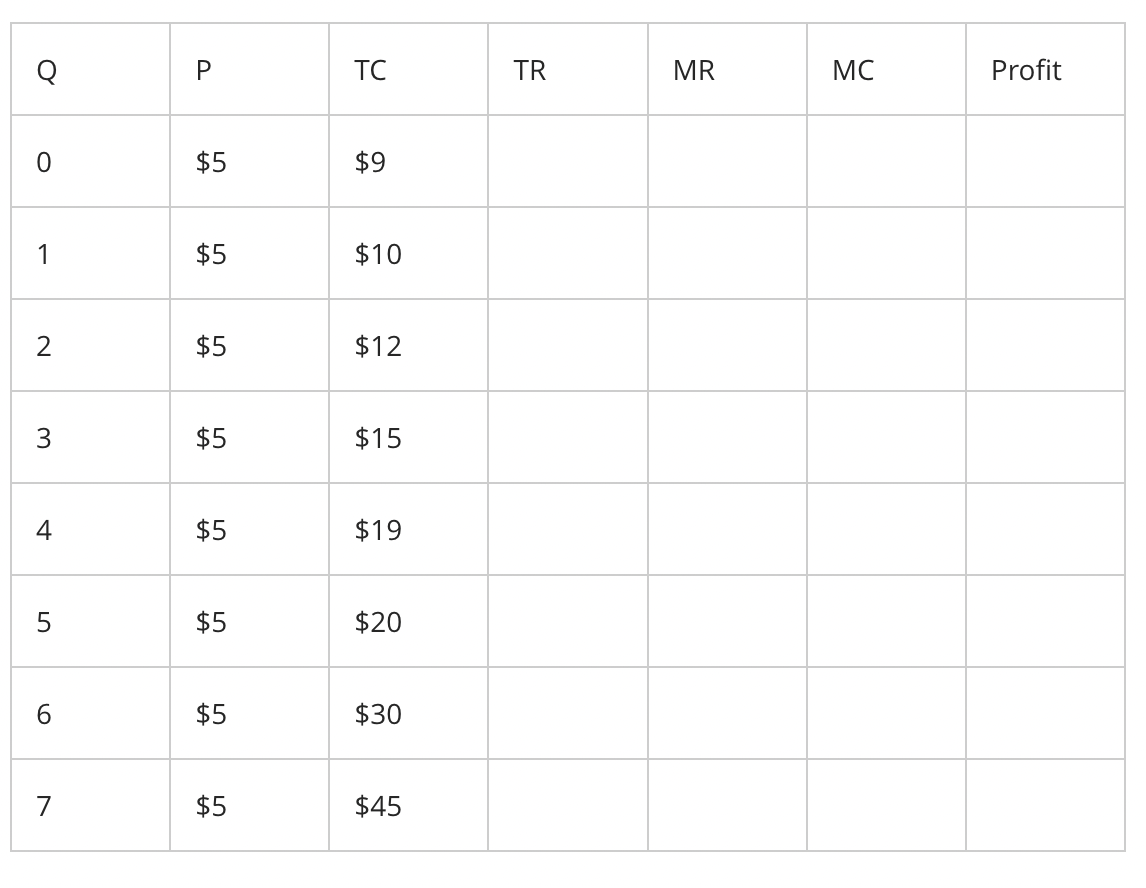
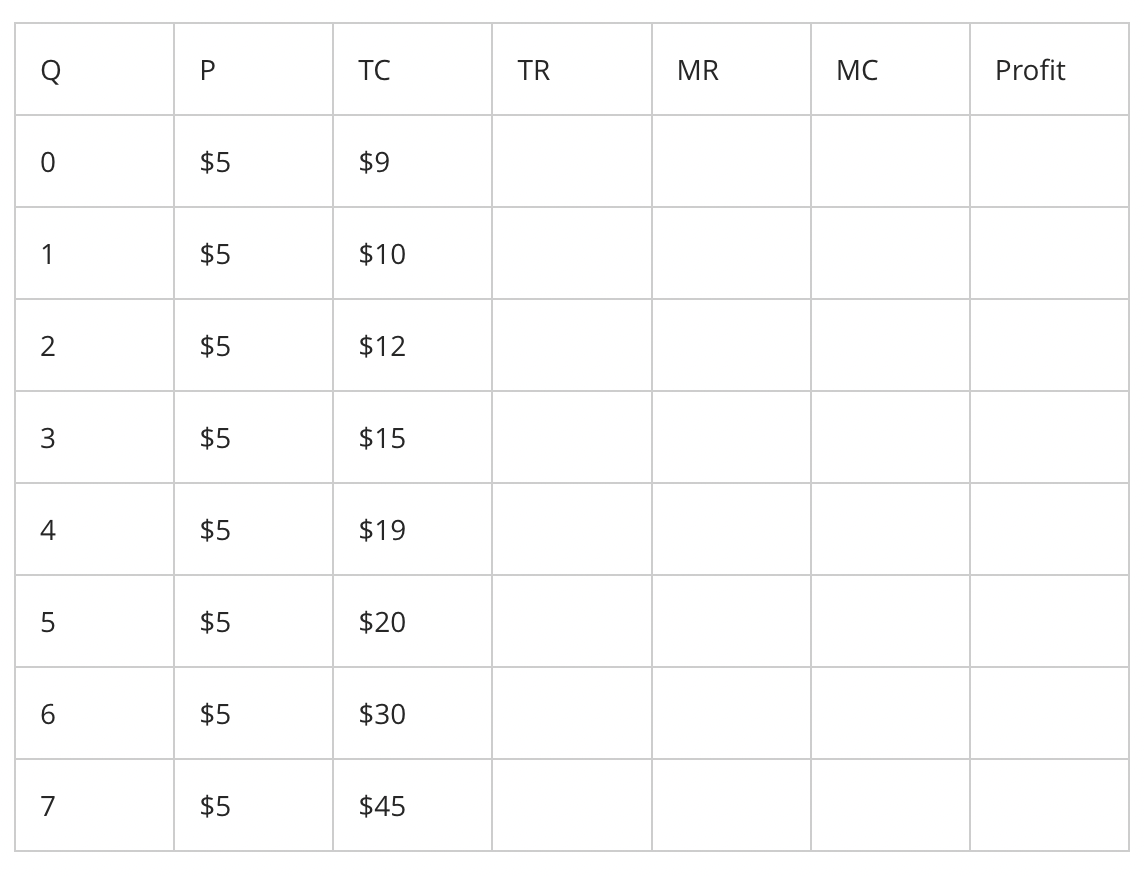
$9.00
what will the fixed costs equal for production at quantity (Q) level 4?
$35.00
$4.00
$9.00
$36.00
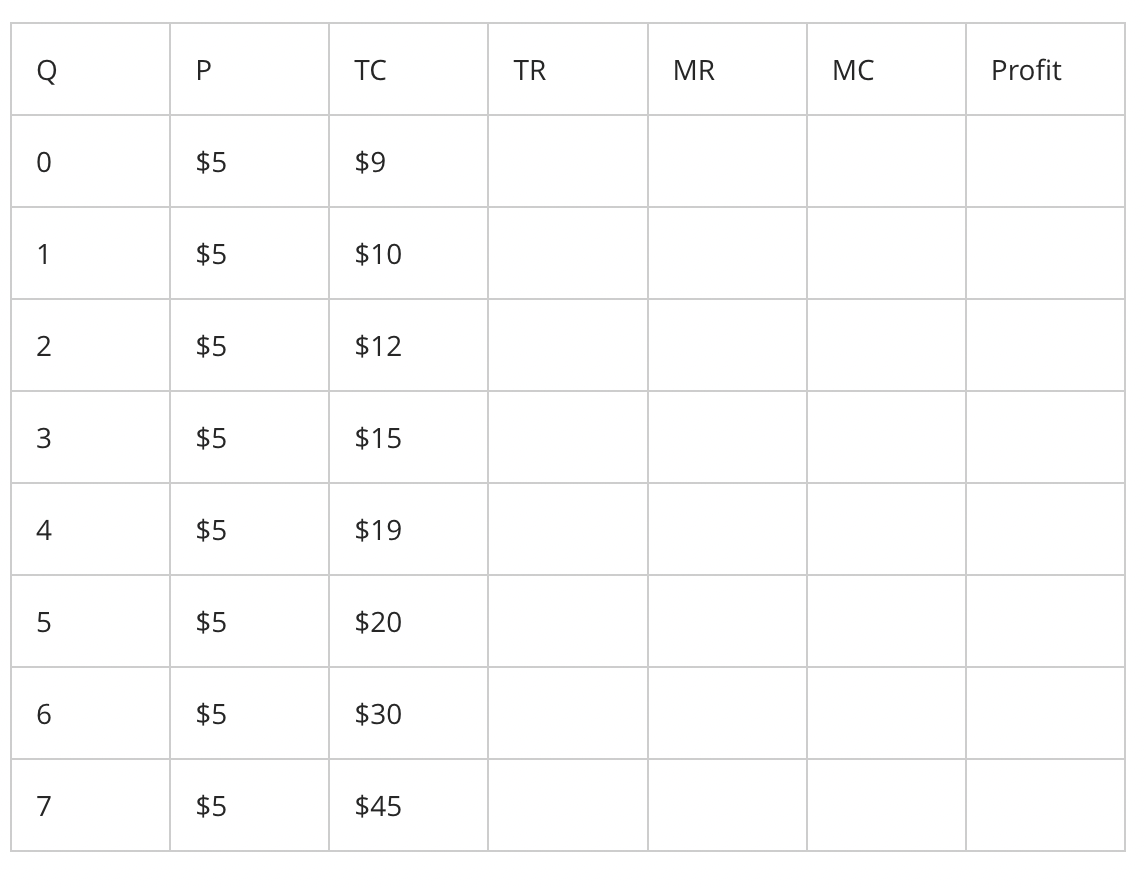
$4.00
what will the marginal cost equal for production at quantity (Q) level 4?
$1.00
$5.00
$3.00
$4.00
can also be interpreted as shifts of their respective marginal cost curves.
Temperatures have persisted below freezing levels in Florida throughout the months of December and January. As a result, demand for electricity sharply increased and the price of electricity rose sharply. The price of coal also rose. In these circumstances, any resulting shifts in the supply curves for coal miners and electricity producers
will determine what price to produce at given the market demand.
at all levels of output shifts marginal costs to the right.
can also be interpreted as shifts of their respective marginal cost curves.
shifts marginal costs to the right enabling both to produce more at any given market price
$20.00
Given the data provided in the table below, the total revenue (TR) for production at quantity (Q) level 4 equals to
$zero
$15.00
$1.00
$20.00
at first, all firms would achieve economic profit, but eventually economic profit would fall back to zero as new firms enter the market.
Assume the purely competitive market is in long-run equilibrium. For some reason market demand increases. What would happen?
At first, all firms would achieve economic profit, but eventually economic profit would fall back to zero as new firms enter the market.
Market price would increase, and producers would band together to prevent new entrants to the market.
Market prices would fall, causing producers to reduce output. All economic losses are incurred, firms start leaving the market.
An increase in market demand would not produce any change in price, production, or the movement of firms in and out of the market.
could likely result in a notable loss of sales to competitors
It is said that in a perfectly competitive market, raising the price of a firm's product from the prevailing market price of $179.00 to $199.00, ________________________.
will cause the firm to recover some of its opportunity costs
will likely cause the firm to reach its shutdown point immediately
could likely result in a notable loss of sales to competitors
is a sure sign the firm is raising the given price in the market
what quantity to produce
In a free market economy, firms operating in a perfectly competitive industry are said to have only one major choice to make. Which of the following correctly sets out that choice?
what quantity of labor is needed
what quantity to produce
what quality to produce
what price to charge
firms produce that quantity where the price consumers pay equals the cost to society to produce it.
how would you explain allocative efficiency in a purely competitive market structure?
Allocative efficiency is a concept involving only two goods, so it cannot be applied to a perfectly competitive market..
Firms produce the quantity where the price consumers pay is less than the cost to society to produce it.
Firms ensure that they produce enough quantity so that everyone who wishes to buy the product can do so.
Firms produce that quantity where the price consumers pay equals the cost to society to produce it.
$5.00
what will the marginal revenue equal for production at quantity (Q) level 4?
$20.00
$15.00
$5.00
$1.00
quantity (Q) level 5
At what quantity (Q) level the profit will be maximized?
quantity (Q) level 2
quantity (Q) level 7
quantity (Q) level 5
quantity (Q) level 4
price taker
The term _______________ refers to a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market that must take the prevailing market price for its product.
trend setter
business entity
price taker
price setter
It will eventually reach long-run equilibrium.
In a perfectly competitive market...
It will eventually reach long-run equilibrium.
Firms will compete for business by setting different prices at or above the prevailing equilibrium price
A few firms will dominate the market share.
Economic profits will be driven down to zero in the short run
$200.00
in order to produce 100 pairs of oven gloves, Marcia incurs an average total cost of $2.50 per pair. Marcia’s marginal cost is constant at $1.00 for every pair of oven gloves produced. The total cost to produce 50 pairs of oven gloves is
$300.00
$200.00
$250.00
$500.00
-$10.00
what will the amount of profit be for production at quantity (Q) level 7?
zero
$1.00
-$5.00
-$10.00
$20
in order to produce 100 oatmeal cookies, GoodieCookieCo incurs an average total cost of $0.25 per cookie. The company’s marginal cost is constant at $0.10 for all oatmeal cookies produced. The total cost to produce 50 oatmeal cookies is
$60
$50
$20
$25
marginal revenue
____________ refers to the additional revenue gained from selling one more unit.
Total revenue
Accounting profit
Economic profit
Marginal revenue
is dictated by the forces of demand and supply.
I'maSolarPanelCo. manufactures and distributes solar panels in the US market. Two years ago, it had 5 US competitors, but government stimulus in the industry has encouraged 7 new US competitors to enter the market. In these circumstances, I'maSolarPanelCo.'s price for its output
can be tailored to exceed the price of its inputs.
can be set by management to maximize profits.
can be tailored to meet the price of its inputs.
is dictated by the forces of demand and supply.
it provides a useful comparison to markets that operate in more complex, real-world conditions.
Why is the perfect competition often used as a benchmark?
It provides a useful comparison to markets that operate in more complex, real-world conditions.
The perfect competition model is more frequently observed in the real world compared to other market models
In the real world, all markets are perfectly competitive, so this model allows us to compare them to one another.
It accounts for a variety of issues like pollution, inventions of new technology, poverty, and government programs that other models do not account for.
profit = total revenue – total cost
A firm in a purely competitive market structure calculates profit using the following equation:
Profit = average total cost
Profit = total revenue – total cost
Profit = price times quantity sold
Profit = total revenue divided by output
predatory pricing
A large airline provides most of the flights between two particular cities. A new, small start-up airline decides to offer service between these two cities. The large airline immediately slashes prices on this route to the bone, so that the new entrant cannot make any money. After the new entrant has gone out of business, the incumbent firm raises prices again. We would call the behavior of the large airline...
Predatory pricing
Aggressive marketing
Competitive pricing
Multi-level marketing
completely inelastic
For a monopolistic firm, the demand for its product is
completely inelastic
completely elastic
neither b or c
unitary elastic
copyright legislation, as well as all of the above
Intellectual property law is a body of law that includes
the right of inventors to produce their inventions
the right of inventors to sell their inventions
trademark, patent and trade secret legislation
copyright legislation, as well as all of the above
price is between average total cost and average variable cost.
The profit maximizing monopolist would achieve loss minimization when...
Price is above average total cost.
Price is below average variable cost.
Price is between average total cost and average variable cost.
Total cost equals total revenue.
during the author's life plus 70 years
Copyright protection legislation provides protection for original works
during the author's life plus 20 years
until the author is 75 years of age
until the author is 70 years of age
during the author's life plus 70 years
start low, rise, and then decline.
The total revenue curve for a monopolist will
start high, rise, and then decline.
start low, decline, and then rise.
start high, decline, and then rise.
start low, rise, and then decline.
demand curve and its cost structure
The two primary factors determining monopoly market power are the firm's
demand curve and its cost structure
demand curve and level of wealth within its market
revenues and size of its customer base
variable cost curve and its fixed cost structure
By determining where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
How does the monopoly determine the level of output that maximizes profit?
By determining where total revenue equals marginal cost.
By multiplying price by marginal cost.
By determining where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
A monopoly does not need to calculate where maximum profit occurs because they have no competition and can set any price they want for their product.
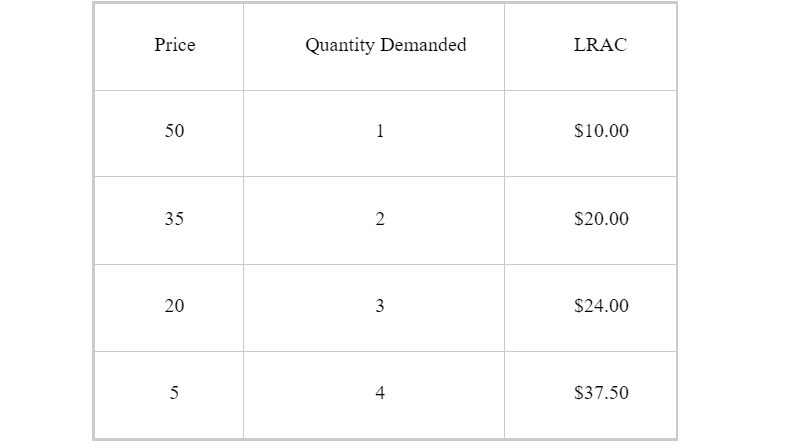
50
At what price Long run average cost were the lowest?
20
50
5
35
20 years
In the United States, a pharmaceutical company's exclusive patent rights last for
70 years.
25 years.
20 years.
10 years.
$3.40 or less
If a firm holds a pure monopoly in the market and is able to sell 5 units of output at $4.00 per unit and 6 units of output at $3,90 per unit, it will produce and sell the sixth unit if its marginal cost is
$3.50 or less
$3.40 or less
$4.00 or less
$3.90 or less
the profit-maximizing level of output will be where marginal revenue intersects marginal cost.
How can a monopolist identify the profit-maximizing level of output if it knows its marginal revenue and marginal costs?
The profit-maximizing level of output will be where marginal revenue larger than marginal cost.
The profit-maximizing level of output will be where marginal revenue smaller than marginal cost.
The profit-maximizing level of output will be where marginal revenue intersects marginal cost.
predatory pricing
The use of sharp, temporary price cuts as a form of ________ would enable traditional US automakers to discourage new competition from smaller electric car manufacturers.
oligopolistic competition
predatory pricing
monopolistic competition
natural monopoly
that firm could set up barriers to entry to discourage competition.
If it was possible for one company to gain ownership control all of the uranium processing plants in the US, then
government will deregulate to ensure the company's monopoly.
they will strive to reach efficiencies only they know how to make.
the factors of market demand and supply will set the price.
that firm could set up barriers to entry to discourage competition.