Health Psych Midterm 2
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
immune system
Lymphatic system mature and are stored in immune system organs
Tissues, organs, and processes that protect the body from invasion
Locates foreign microorganisms, mutant cells, or damaged cells and activates processes to eliminate them
inflammation in the immune system response
Phagocytosis and inflammation involving granulocytes and macrophages
Works to restore tissue damaged by invaders.
Blood vessels in area of injury dilate causing redness and warmth.
Damaged cells release enzymes that help destroy invaders.
Granulocytes & macrophages migrate to site of injury to help destroy invaders.
secondary immune response
Some sensitized T-cells and B-cells (called memory lymphocites) replicate and are held in reserve for next time pathogen invades
Nonspecific response
works great for general, minor threats to our immune system
Specific response
works great for more serious threats to our immune system (i.e. fungi, viruses, parasites, and mutations of cells)
Primary immune response initiated at first exposure
every exposure afterwards initiates secondary immune response
“suppression” of the immune system
weaker (i.e. Blood samples from those highly hostile couples or PTSD)
How can we create immunity to a virus?
Vaccination: weakened form of virus or bacterium is introduced into body, stimulating production of antibodies. Small pox eradicated through vaccine
Autoimmune diseases
Immune system doesn’t recognize that own body is SELF
Immune system treats own body like a virus, infection, germ
Includes lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis
Adler and Cohen
Shaped by 1975 experiment using classical conditioning
Taught rat to associate sweet tasting water with chemical that suppressed the immune system
Rats rank solution and were injected with immunosuppressive drug
Immune system was suppressed with just water after removing injection
psychoneuroimmunology
Multidisciplinary field focusing on interactions among behavior, the nervous system, the endocrine system, and the immune system
Janice Kiecolt-Glaser’s research
Exam Stress
Medical students had more symptoms of infectious disease before and after exams
Drew blood and found evidence that immune system functioning was suppressed (less antibodies)
Heterosexual couples come in for 2 visits. Each visit the couple got eight tiny uniform blisters on their arms
Wounds took a day longer to health after arguments
Couple who showed high levels of hostility needed two days longer for wound healing compared with low hostile
Blood samples from high hostile couples → suppress immune system?
diathesis-stress model
Some individuals are vulnerable to stress-related diseases because either genetic weakness or biochemical imbalance inherently predisposes them to those diseases. These diseases may not occur without environmental stress
health behaviors
Diet, exercise, and no smoking
Sheldon Cohen’s research
Higher the stress → higher likelihood of getting aq cold
Duration matters more than severity
Acute severe stress < 1 month didn’t lead to cold
Severe chronic stress > 1 month led to substantiation increase in colds
People who are more sociable developed fewer colds
How is stress related to HIV?
Stress affects both the progression of HIV infection and the affected person’s immune response to antiviral drug treatment
Stress & Heart disease
increases heart rate
Stress & Asthma
Proinflammatory cytokines may a fundamental or even causal role in development of disorder
Stressors, such as emotional events & pain can trigger asthma attack
Kids living in inner-city with parents who have mental problems showed sharply heightened risk
Stress & Arthritis
Occur when immune system attacks body; not well understood
Stress & Ulcers
Stress is not a major factor
Stress & Headaches
causes muscle tension
Stress & Pregnancy
Mothers who are stressed are more likely to deliver preterm babies and babies with lower birth weights
Chronic stress more damaging than acute stress
Stress later in pregnancy more damaging than earlier stress
What is the link between stress and psychological disorders?
Stress and Depression:
Stress contributes to development of depressive symptoms
Rumination may increase stress and depression
Kindling hypothesis – major life stress provides a “kindling
experience that prompts the development of depression
Some types of stress (chronic workplace stress, health problems) produce greater risk of depression.
Stress and PTSD
PTSD produces long-lasting suppression of the immune system and an increase in proinflammatory cytokines.
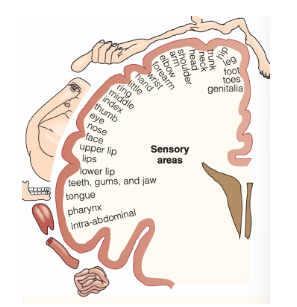
What parts of the brain are involved in the sensory and emotional aspects of pain?
The somatosensory system (nerves, sensory surfaces on our organs & skin)
All sensory information from the body to the brain
Nociceptors: the specific receptors
Henry Beecher’s study
Soldiers more cheerful and optimistic vs normal surgical patients experience more pain and request more drugs
Intensity of suffering is largely determined by pain perception to the patient
Size of wound bears only a small relationship to how much pain is experienced
What are pain behaviors and how can they be affected by other people?
The brain (somatosensory Cortex)
Signals from thalamus from afferent nerves
The spinal cord
Nerves responsible for spinal reflexes (immediate reflexes to noxious stimuli, like a hot stove)
specificity theory of pain
Body used to be viewed as a machine → not always the case!!
Pain = results of the transmission of specific signals
Experience of pain is approximately equal to the amount of tissue damage or bodily injury
Linear model of pain
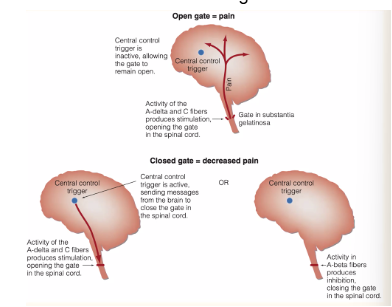
gate control theory of pain
Pain is only PARTLY controlled by bottom-up processes: afferent neurons (neurons that go from the body/spinal cord to the brain)
It is ALSO controlled by the top-down processes - the brain and spinal cord decide how much of the messages from the afferent neurons affect the brain
What factors open or close the pain gate?
Open gate = Pain
Closed gate = decreased pain
Physical
Extent of injury
Inappropiate activity level
Cognitive
Focusing on the pain
Boredom
Emotional
Anxiety, worry
Depression, anger
Ronald Melzack’s theory
Focused on how different parts of the brain are involved in the increasing or decreasing the experience of pain.
What methods have been used to measure pain?
Self-report, Behavioral assessment, and Physiological measures
Self-report
Pain intensity on a scale of 1-10 and Pain unpleasantness or on Visual Analogue Scale where you draw a line
Behavioral assessment
Watching to see if they exhibit pain behaviors: Guarded movement, Bracing, Position shifts, Partial movement, Grimacing, Limitation statements, Emitting pain sounds (Good for kids, older adults )
Physiological measures
Researchers have tried muscle tension and autonomic nervous system response. However, they don’t show sufficient reliability or validity.
Migraine headaches
recurrent, throbbing, very painful headache, happens on or worse one side
Tension headaches
is dull and happens on both sides of the head
Acute pain
short period of time (i.e. pain from cuts, burns)
Chronic pain
enduring beyond normal healing time, constant (i.e. lower back pain)
What conditions contribute to low back pain?
chronic low back pain usually resulting from injury and or structural vulnerabilities.
percentage of people with low back pain have an identified cause
20%
How well do physicians and nurses do in estimating the pain of patients?
Doctors and nurses underestimate the pain of patients.
They may prescribe or administer too little pain medication
What do we know about the risk of opiate drugs for pain patients?
the most effective analgesic drugs, have the potential to produce tolerance and dependence, making health care professionals reluctant to prescribe adequate doses.
The recent increase in prescription analgesic drugs was due mostly to the demand for oxycodone (Oxycontin) and Hydrocodone
Alternative medicine
used instead of conventional medicine
Complementary medicine
used along with or as a complement to conventional medicine
how are alternative and complementary medicine different from conventional medicine?
Neither practice is used in western medicine
Integrative medicine
mixture of both conventional medicine and CAM
main limitations of alternative and complementary medicine
Limited research examining effectiveness or comparing to placebo
Natural products not regulated
Some herbal remedies and botanical products have dangerous interactions with each other
Limited avaliability and high cost
Individuals with some conditions should avoid some treatments
People may use CAM instead of more effective treatments
What are the main ancient systems of medicine?
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM: unblocking Qi) and Ayurveda (Origins in India; balance of body, mind, & spirit)
Naturopathy
diseases can treated or prevented without the use of drugs through diet, exercise and massage
Homeopathy
Based on principle of “like cures like” – substances have curative power when they produce symptoms like those of disease.
Acupuncture
inserting needles into specific points on skin and continuoslty stimulating needles to unblock qi
Better for neck pain, shoulder, or elbow pain and tension-type headaches vs migraines
Reduction of arthritis
Chiropractic Treatment
Adjustments to spine and joints to correct misalignment
Covered by many insurance plans
Most used for back and neck paikn and somewhat effective for both of those conditions
How are demographic factors related to the use of alternative and complementary medicine?
Ethnic stereotypes of recent immigrants using CAM is incorrect
CAM use is associated with being European American, well educated, wealthy, and female.
Chinese Americans’ use of CAM depends on how strongly they identify with Asian heritage
integrative medicine
mixture of both conventional medicine and CAM
“Best of both worlds”
Faces challenge of melding very different philosophies of treatment but offers benefits of both approaches.
Two areas in which integrative medicine is advancing most rapidly are pain management and cancer treatment.
mindfulness meditation
origins in buddhist practices
Sitting in a relaxed, upright posture
8 wk course, 2 hrs per day, intensive retreat. Works by altering brain function
transcendental meditation
Usually sit with eyes closed and muscles relaxed, focusin on breathing, and silently repeat a sound, such as an “om”
Repetition of mantra meant to distract from outside thoughts
Brain imaging results of mindfulness meditation
During mindfulness meditation, left frontal lobe of brain becomes more active and right lobe less so
Consistent with an increase in the experience of positive emotions
What problems are mindfulness meditation and transcendental meditation effective for?
Meditation and mindfulness have proven effective for people with anxiety, stress-related problems, and relapse into depression
Guided imagery
people conjure up a calm, peaceful image which can divert attention away from the painful experience
Effective with chronic pain, quality of life in cancer patients, hypertension, obesity, headaches
Hypnosis
an altered state of consciousness that boosts relaxation and suggestibility vs. a more generalized trait of some individuals
Biofeedback
Patients gain awareness and alter physiological responses by viewing their measure of biological responses
Effective with lower back pain, tension headache, migraines
What problems are guided imagery, hypnosis, and biofeedback effective for?
Meditation and guided imagery have been shown to be very effective in managing chronic pain. Less suggestible subjects respond no better to hypnosis than to a placebo.
Biofeedback- shows limited benefits for pain management
Coronary Arteries
Supply blood to the myocardium (heart muscle)
Atherosclerosis
cholesterol and lipids build up plaque that restricts and partially blocks blood flow in the artery - blood can’t get to the heart muscle
Arteriosclerosis
hardening or loss
Heart/myocardium
a muscle that pumps blood throughout the body
the strongest predictors of heart attacks and stroke
Hypertension number one risk factor for CVD
Our systolic blood pressure over our diastolic blood pressure
Force exerted during ventricular contractions over pressure between the contractions
Inflammation: stress influences low grade, chronic inflammation
Low density lipoprotein
marked as “bad” cholesterol because it accumulates in our arteries as plaque and is a risk factor for heart disease
High density lipoprotein
good cholesterol because it absorbs other cholesterol in our bodies
kinds of foods offer protection against heart disease
HDL – high density lipoprotein (“good cholesterol”) (i.e. oil, nuts, fruit, oats)
Type A personality
is someone who is outgoing, ambitious, rigidly organized, highly status-conscious, impatient, anxious, proactive, and concerned with time management
what part of Type A personality puts people at the greater risk for heart disease?
Someone who is impatient, aggressive, and very competitive, often called a Type A personality, has a higher risk of heart disease
marital status and gender related to heart disease
Poor marriages and men have slightly higher risk of death from CVD than women
What racial / ethnic groups have higher rates of heart disease and why?
African Americans have higher risk – may be related to discrimination
anti-inflammatory drugs elated to lower risk of heart disease
Taking low-dose aspirin
How have health psychologists contributed to heart health?
Health psychologists develop and test interventions to encourage behaviors that reduce the risk of heart disease, such as:
Quitting smoking, Eating a balanced diet, Exercising regularly, Reducing alcohol intake, Adhering to medications
Balloon angioplasty
A small balloon is inserted into a narrowed or blocked artery. The balloon is inflated to compress the plaque against the artery walls, widening the artery. Then the balloon is removed, and nothing is left behind.
Stent Angioplasty
same process as ballon, except a stent (a small metal mesh tube) is placed in the artery.
Bypass surgery
Replaces blocked portion of the coronary artery called CABG -coronary artery bypass graft or coronary bypass surgery.
Expensive and risky but usually relieves angina and improves quality of life
Cardiac rehabilitation
Helps cardiac patients (e.g. those with CAD or who have had MI or heart surgery) adjust lifestyle to minimize risk factors
Programs can be very effective.
But only 15-35% of patient follow through with such programs.
Perhaps as low as 10% who have heart attacks enter them
Cancer
Group of disease characterized by the occurence of new cells that grow and spread beyond control
Benign tumors
remain localized, less threatening
Malignant tumors
spread, more dangerous
biggest reasons for declining death rates due to cancer
Declined in the 1990s
Early detection and treatment
Lifestyle factors (better diets, less smoking)
Strongest inherent risk factors for cancer
Ethnic Background
Black people have higher incidence for most cancers, due to later diagnoses in later stages
Asians generally have lower total cancer death than other ethnic groups
Stomach cancer is highly correlated with diet and chronic H. pylori bacterial infection
Liver cancer highly correlated with infection and hepatitis C infection
Family History
Only a small genetic component to getting cancer
Women who have a mutated form of BRCA1 are much as 7 times as likely to develop one form of breast cancer
However, the forms of cancer related to BRCA1 and BRCA2 are responsible for no more than 10% of breast cancer cases. BRCA 18
Advancing Age
strongest behavioral risk factors for cancer
Behavioral
• Smoking
Stomach
Bladder
Upper digestive tract
Esophagus, Colon, Prostate cancer
23.3 moe times likely to die of lung cancer than men who have never smoked
• Diet
• Foods that may cause cancer are called carcinogenic
• Foods with no preservatives or high level of
preservatives
• Foods high in fat
Preserved meats and red meat increase risk of colorectal cancer
Overweight and obesity account for 14-20% of all cancer-related deaths – strong link to colorectal, esophageal, breast, endometrial, and kidney cancer
• Alcohol
Increases risk for mouth, esophageal, breast, and liver cancers
People who abuse alcohol are more likely to die from other causes before they develop liver cancer.
Women who drink alcohol daily have higher risk for breast cancer
• Sedentary Lifestyle
Increases risk of colon, endometrial, breast, lung, and pancreatic cancer
• UV light exposure
One form of skin cancer – malignant melanoma, has high death rate
Strong genetic component for skin cancer – fair-skinned, blue-eyed people at higher risk
Can decrease risk by wearing sunscreen and sun-protective clothing
• Sexual behavior
HPV increases risk for cervical and oral cancer
Can decrease risk by practicing safe sex
most common cancer for women
breast cancer
most common cancer for men
prostate cancer
most deadly cancer for men and women
Lung & Bronchus Cancer
What factors may account for the different cancer death rates across ethnic backgrounds?
Ethnic background
African Americans have greater incidence
NOT biological
Family history
BRCA1 & BRCA2 mutations (breast cancer)
Advancing age
Environmental
Radiation
Abestos
Pesticides & chemicals
risk factors for cervical cancer
HPV (70% of cervical cancer by this)
behavioral factors are most important for preventing cancer
Behavioral
Smoking, Diet, & Alcohol
Sendentary Lifestyle
UV light exposure
Sexual behavior (HPV)
Treatments for Cancer
Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy
Side effects of treatments for cancer
Fear, anxiety, loss of hair, fatigue, depression
How do people adjust to a diagnosis and learn to live with cancer, including finding support and psychological interventions?
More than a million Americans are diagnosed with cancer each year
Most of these people will experience feelings of fear, anxiety, and anger as a result of their diagnosis
About 25% may have major depression
Optimism
Helps reducting negative affect and social inhibitions
Not for a long term cancer survival
Social Support
Health care professionals: instrumental
Family and friends: emotional
Psychological interventions
Shirt-term benefits
No evidence on prolonging the life span
How have health psychologists been most involved in treating people with cancer?
Individual and group techniques to help cancer patients:
Cognitive behavioral stress management skills
Providing social support
Opportunities to express emotions