Chemistry: Crude Oil, Fractionating column, Alkanes
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What is crude oil a mixture of?
hydrocarbons
What is fuel?
A Fuel is a substance which when burnt (combusted) releases heat energy
What is complete combustion and it’s product?
Fires with enough oxygen, Product is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) + Water
What is incomplete combustion and it’s product?
Fires without enough oxygen, Product is Carbon Monoxide (CO) + Water
What does refinery do to compound in oil?
separates them into simpler groups called fractions.
What are fractions?
mix of compound with similar number of carbon atoms.
What do refineries do to crude oils?
Monetize crude oil by transforming it into finished products
What are the fractions that crude oil are transformed into?
LPG, petenem feeds, gasoline, kerosene, jet fuel, diesel fuel, heating oil, asphalt, pet coke.
What does carsenogenic mean?
cancer-causing
Describe the process of a fractionating column
Oil is heated to about 370 degrees celcius and pumped into bottom of tall tower, where it vapourises.
As vaporised oil rises, it cools and condenses.
Heavy factions (contains large molecules), have high boiling pts and condenses near bottom of column. More bonds to break.
Lighter fractions (contains small molecules) have lower boiling pts and condenses further up. Less bonds to break.
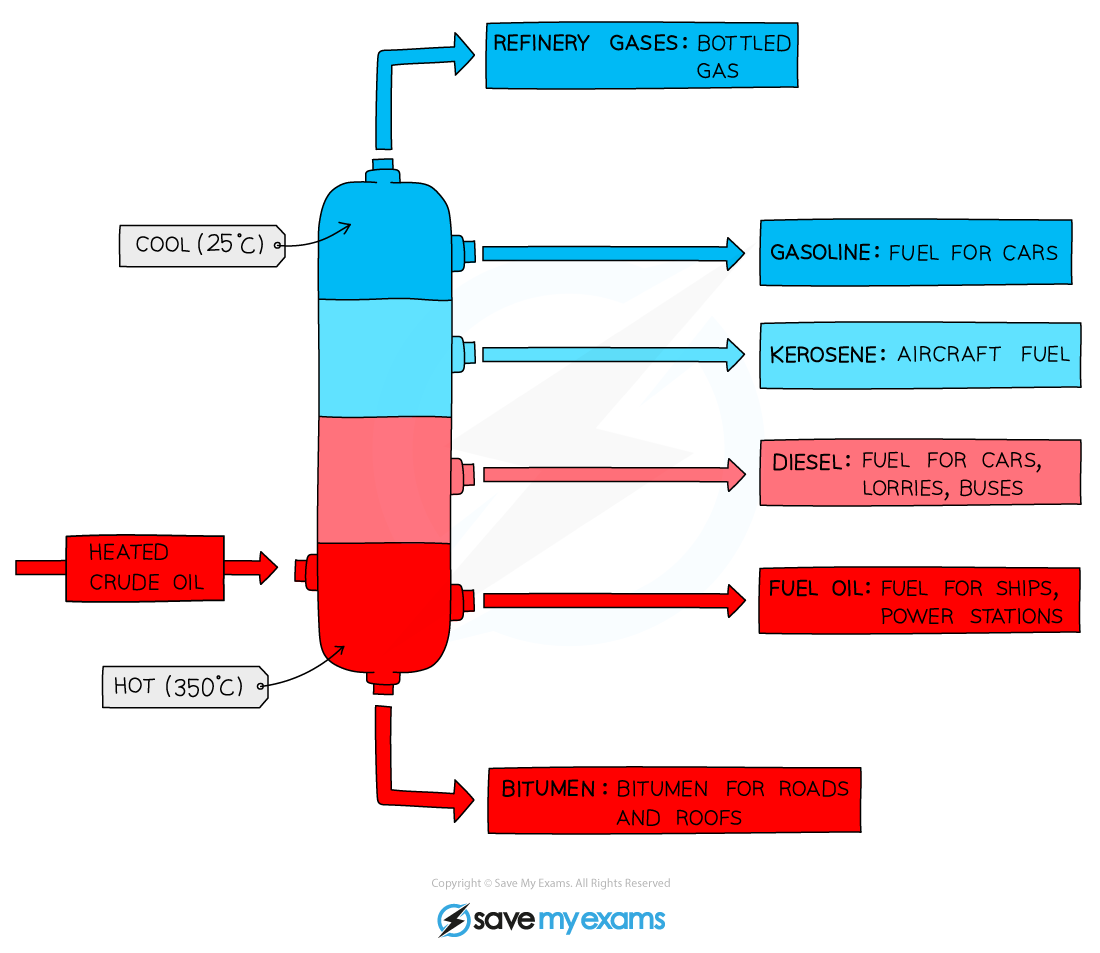
Where is it hottest in the fractionating column?
Bottom, cooler at top.
List the order of the crude oils from the bottom to the top in fractionating column.
Bitumen, fuel oil, diesel oil, kerosene, gasoline, refinery gases
Which crude oils are most likely to use as fuel?
Lower carbon atoms fractions as little heat is needed.
What are the properties of the fractions at the top?
High flammability
Low viscosity
Low boiling points
Light colour
What are the properties of the fractions at the bottom?
Low flammability
High viscosity
High boiling points
Dark colour
What is viscosity?
how thick and runny a substance is
What is volatility?
How easily a substance changes from liquid or solid to a gas
What is energy content?
amount of heat energy released by fuel.
What are alkanes?
Saturated hydrocarbons
What does saturated mean?
they only have single carbon-carbon bonds.
Why can’t alkanes undergo additional reactions?
Since all bonds are taken, cannot add any more atoms to them and have no single bonds to react.
What alkanes examples of?
homologous series, which are group of organic compounds with the same functional group or chemical properties.
What is the molecular and structural formula of methane?
Molecular formula: CH4
Structural formula: CH4
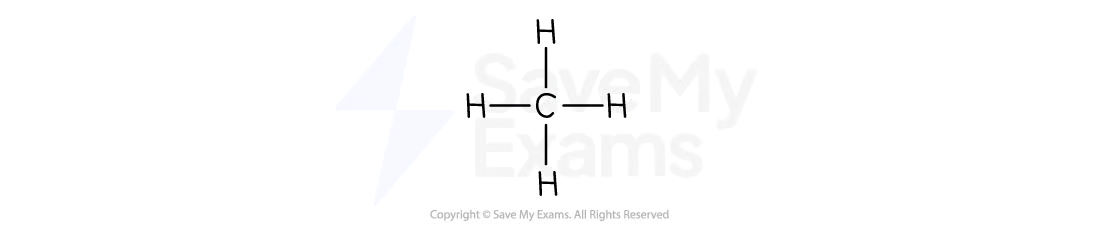
What is the molecular and structural formula of ethane?
Molecular formula: C2H6
Structural formula: CH3 CH3

What is the molecular and structural formula of propane?
Molecular formula: C3H8
Structural formula: CH3 CH2 CH3

What is the molecular and structural formula of butane?
Molecular formula: C4H10
Structural formula: CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3
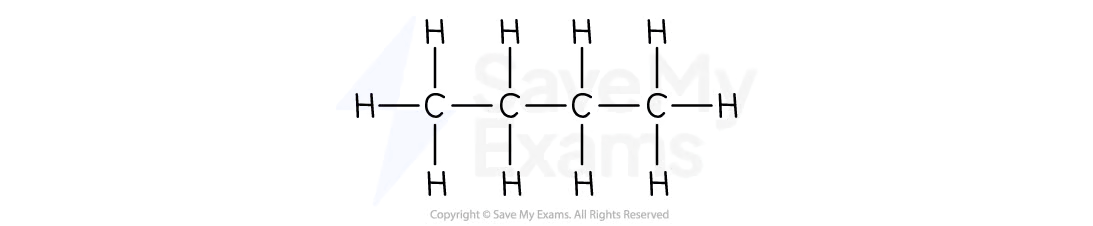
What is the general formula for alkanes?
The general formula of the alkanes is CnH2n+2
Which two reactions can alkanes only undergo?
Combustion and substitution with halogens
What is the formula for combustion in alkanes?
Alkane + oxygen → carbon + water
What is substitution?
When one atom (or group of atoms) is replaced by another atom (or group of atoms)
How can substitution only happen?
One at a time and only one hydrogen gets replaced at a time.
What need to be present in substitution with halogens?
Ultraviolet radiation
How and why do you substitute an alkane?
Because alkanes are saturated, you must replace (substitute) a hydrogen with a halogen, such as chlorine
What are these products called from substituting an alkane?
Haloalkane
What is the prefix in substitution reactions of alkanes?
Added to the name of the alkane depending on what halogen are attached.
Name the prefix of all the halogens
Florine: Fluoro
Chlorine: Chloro
Bromine: Bromo
Iodine: Iodo
Name the prefixes by numbers
2 = di
3 = tri
4 = tetra
5 = penta
What is an isomer?
Molecules with the same molecular
formula but different structure