Triple Sugar Iron Agar, Oxidase Test, Malonate Utilization Test, MacConkey Agar, Gram Staining Test, Urea Hydrolysis, Citrate Utilization Test, MIO Test, Catalase Test, Lysine Iron Agar, Blood Agar, 10% Tryptone Test, Carbohydrate Fermentation Test
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
TSIA Testing For
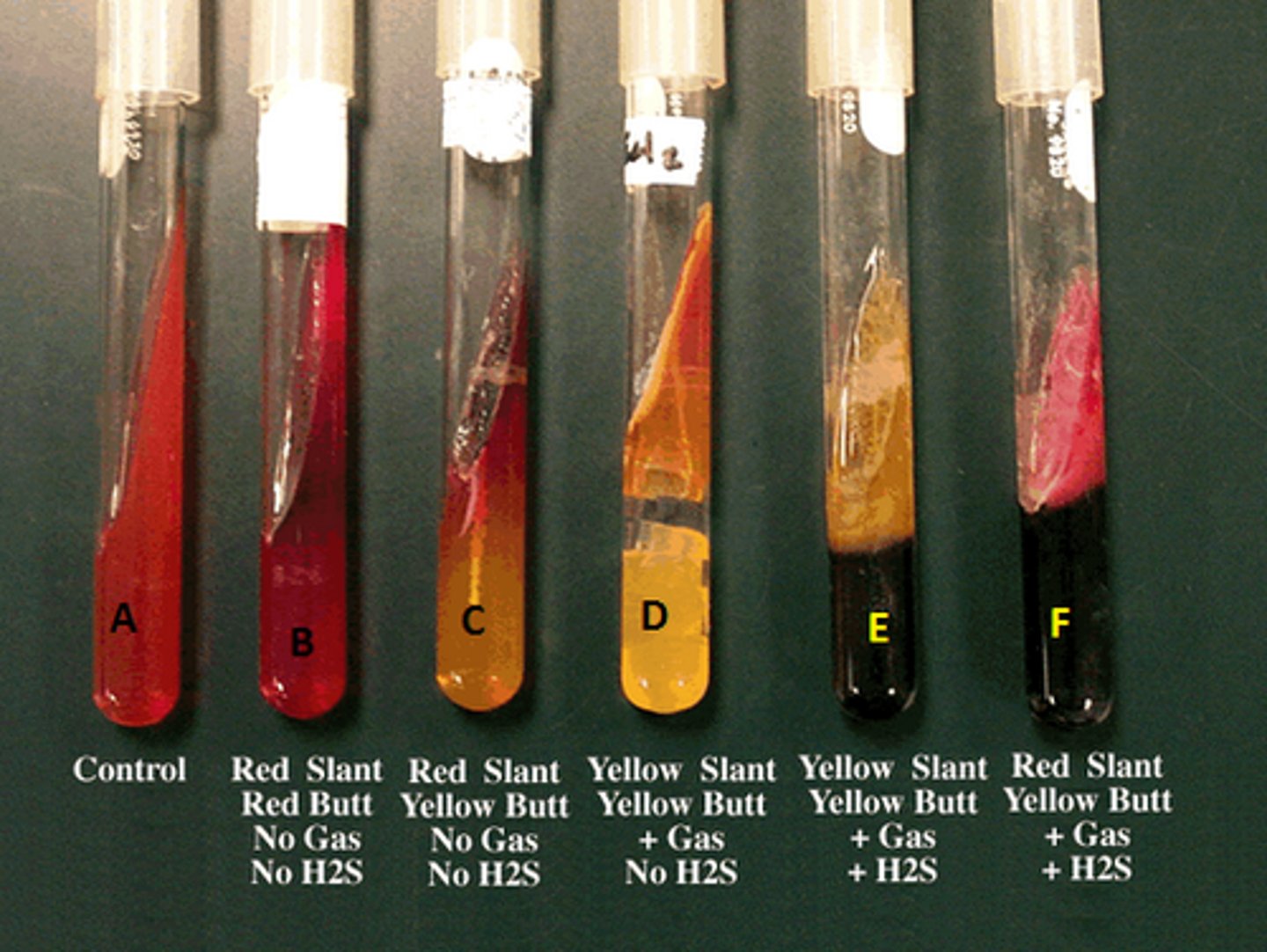
• Glucose Fermentation • Sucrose/Lactose Fermentation • Gas Production • Sulfur Reduction
TSIA Glucose Fermentation Reagent
Phenol Red
TSIA Sucrose/Lactose Fermentation Reagent
Phenol Red
TSIA Gas Production Reagent
N/A
TSIA Sulfur Reduction Reagent
Iron in Ferrous Sulfate
TSIA Glucose Fermentation Postive Result
Red Slant/Yellow Butt
TSIA Glucose Fermentation Negative Result
Red Slant/Red Butt
TSIA Sucrose/Lactose Fermentation Positive Result
Yellow Slant/Yellow Butt
TSIA Sucrose/Lactose Fermentation Negative Result
• Red Slant/Red Butt
• Red Slant/Yellow Butt
TSIA Gas Production Positive Result
Bubbles Present
TSIA Gas Production Negative Result
No Bubbles Present
TSIA Sulfur Reduction Positive Result
Black Precipitate
TSIA Sulfur Reduction Negative Result
No Black Precipitate
TSIA Test: How to read the interpretation.
• Slant/Butt/Gas/H2S
• K - Alkaline
• A - Acidic
• Bubbles or cracks in the tube indicate gas production
• Black precipitate indicates H2S production
TSIA Test: Be able to describe the meaning of K/A, A/A, A/K, and K/K.
-A/A (yellow butt and slant): glucose and lactose/sucrose fermenter with acid accumulation
-K/A (red slant/yellow butt): glucose fermenter only, alkaline products due to reversion
-K/K (red slant and butt): no fermentation; peptone catabolized, not enteric
-A/K (yellow slant red butt?): You should never get, if you do, improper inoculation
-H2S (black precipitate in agar): sulfur reduction and fermentation
TSIA Test: Can you get a A/K reaction?
No, if you do you did not inoculate correctly. You must stab AND streak.
TSIA Test: What causes the change in color of the butt of the tube?
Acid Production and Alkaline Products
TSIA Test: What causes the change in color in the slant?
glucose, lactose, and sucrose fermenter
TSIA Test: What butt reaction will you see for all enterics?
Yellow Butt
TSIA Test: What are the three sugars and what is the purpose of their concentrations?
• Glucose
• Sucrose
• Lactose
TSIA
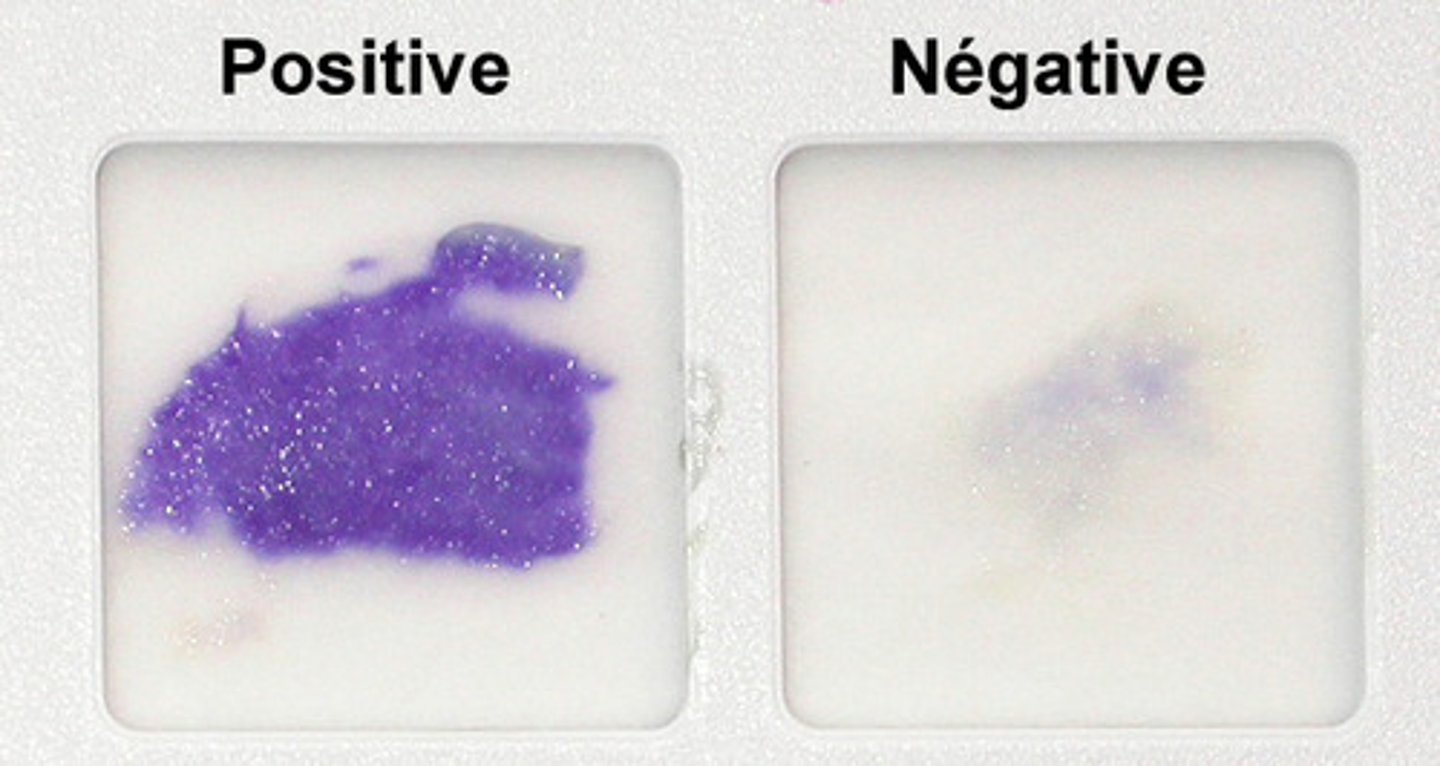
Oxidase Testing For:
Presence of Cytochrome C oxidase
Oxidase Reagent Used:
Tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine (Oxidase)
Oxidase Positive Result:
Dark blue or purple in 30 seconds
Oxidase Negative Result:
No color change within color changes
Oxidase Test: How is the test performed?
1. Place culture on filter paper
2. Add drops of reagent
3. View color change in 30 secs.
Oxidase Test: Why should you read the results within 30 seconds?
Reagents used for this test are unstable and may oxidize independently shortly after they become noise.
Oxidase look like
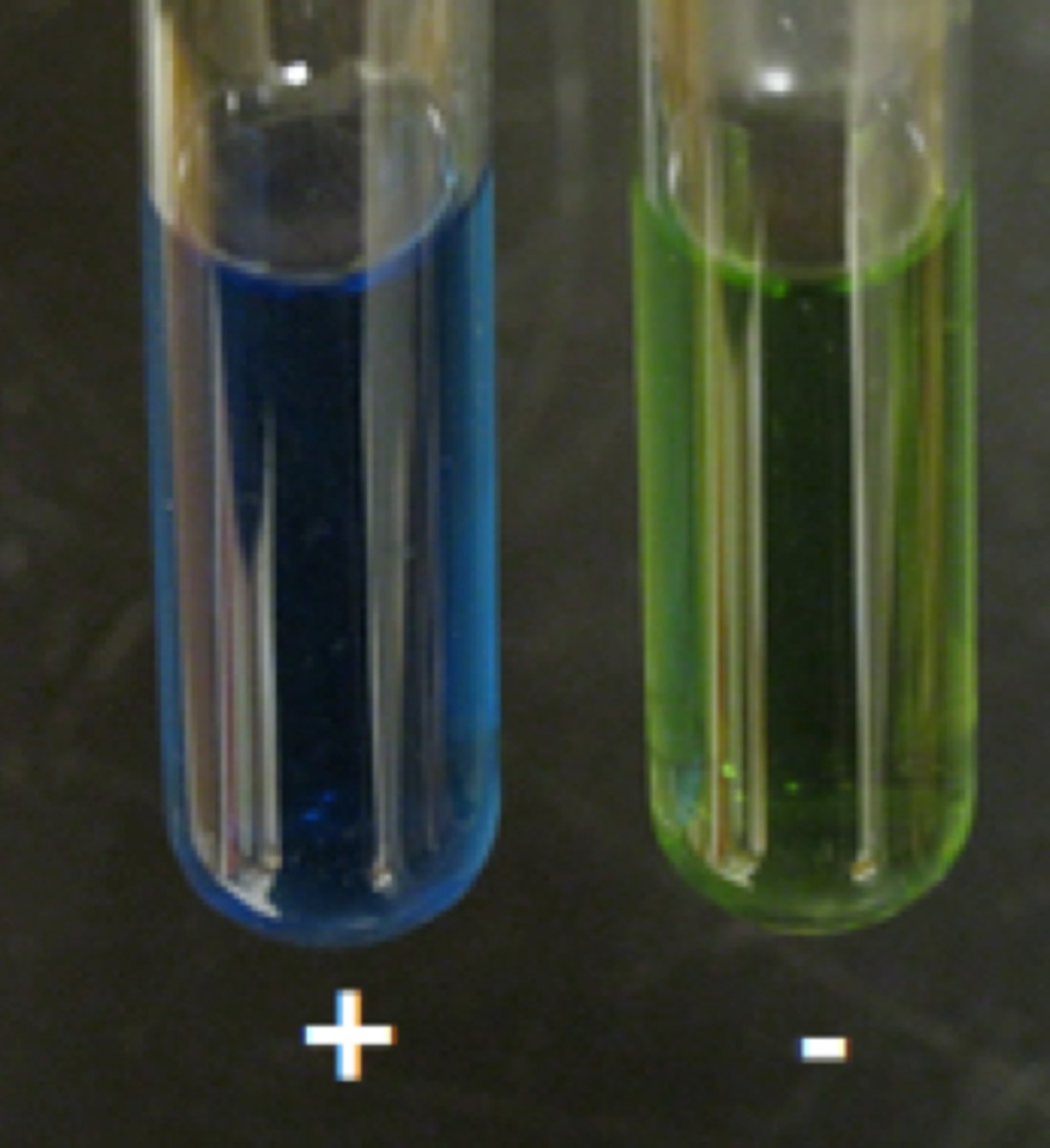
Malonate Testing For:
Utilization of Malonate as a carbon source
Malonate Reagent:
Bromothymol Bue
Malonate Positive Result:
Dark Blue
Malonate Negative Result:
No color change or slightly yellow
Malonate Test: Determine the chemical reaction that takes place.
competitive inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase.
Malonate Test: What causes the color change?
use of malonate alkalinizes the medium
Malonate Look Like
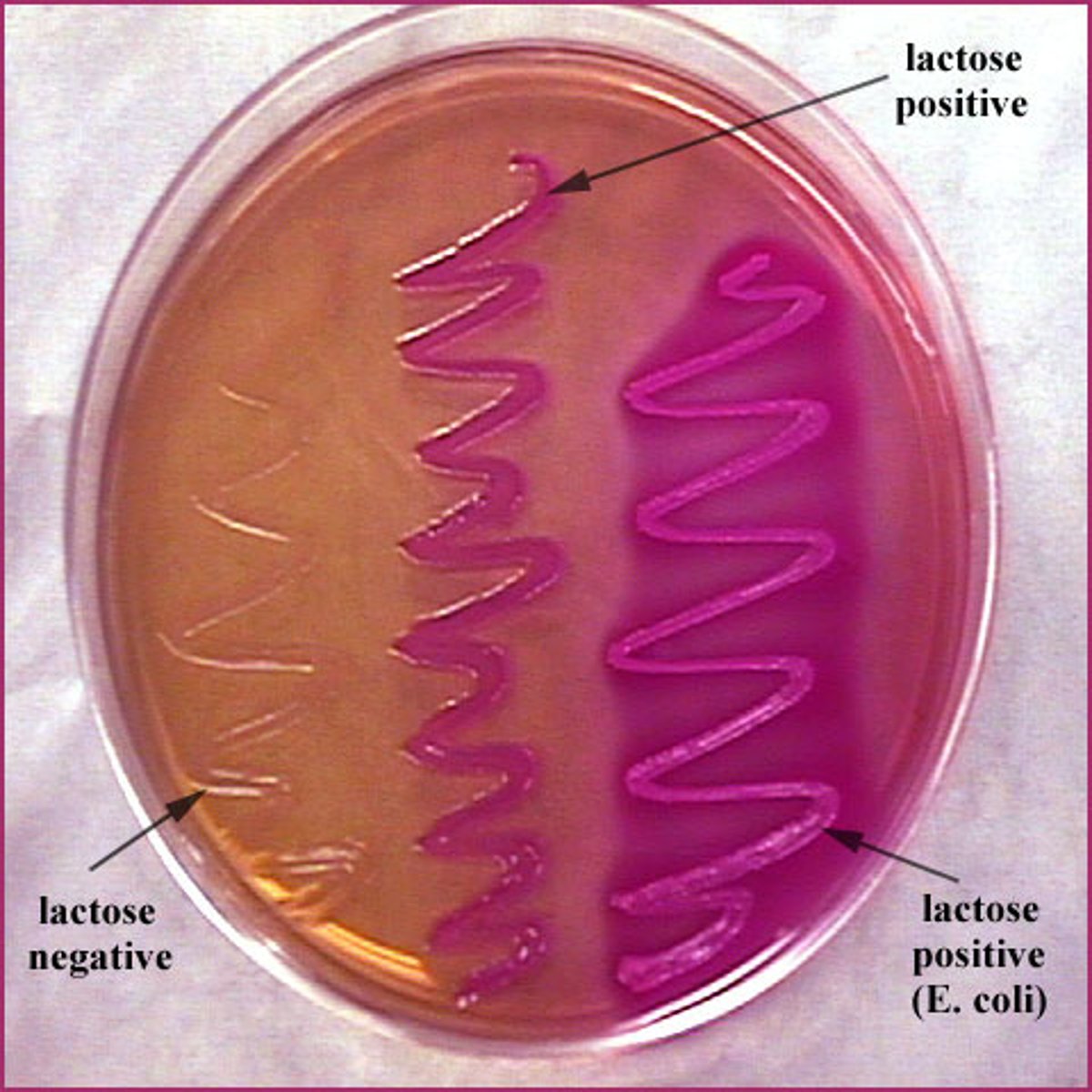
MAC Testing For:
• Growth of Gram Negative
• Bacteria Lactose Fermentation
MAC Growth of Gram Negative Bacteria Reagent:
Cyrstal Violet Bile Salts
MAC Lactose Fermentation Reagent
Neutral Red
Growth of Gram Negative Bacteria Positive Result:
Growth
Growth of Gram Negative Bacteria Negative Result:
No Growth
Lactose Fermentation Positive Result:
Red or Pink
Lactose Fermentation Negative Result:
Colorless (color of agar)
What does the bacteria look like on the media?
• Streak line visible but no colonies - Negative for growth
• Streak line visible positive for growth but not purple - colonies but negative for lactose
• Streak line purple and growth - positive for growth and lactose
MAC: Is this test selective or differential? Why?
• This test is selective because inhibits growth for gram-positive bacteria.
• Differential for lactose fermentation
Testing For
Gram-negative or gram-positive cells based on their peptidoglycan layer and composition of the cell wall.
Reagent/Indicator
• Crystal Violet (Dye)
• Iodine (mordant)
• Ethanol (decolorizer)
• Safranin (Dye)
Gram Postive Results
Purple
Gram Negative Results
Pink
Differential Stain: (ex. 3-7)
Decolorization step is added between two basic stains. Using multiple stains can better differentiate between different microorganisms or structures/cellular components of a single organism.
Distinguishing characteristics of Gram-positive cell wall: (ex. 3-7)
• Peptidoglycan = 90% of cell wall
• Teichoic Acid inserted within the peptidoglycan layer
• A greater degree of cross-linking
• No outer membrane
Distinguishing characteristics of Gram-negative cell wall: (ex. 3-7)
• Thin layer of peptidoglycan (10%)
• Outer membrane layer = lipid bilayer
• Innermost layer = phospholipid bilayer
• Outermost layer = lipopolysaccharides (lipids and sugars)
How and why the stains interact with a gram-positive cell. (ex. 3-7)
• Crystal violet and the iodine turn stain purple
• Decolorization keeps stain purple
• Adding safranin keeps stain purple
• Teichoic Acid helps Trap crystal violet - iodine complex more effectively (helps keep the purple color)
• Less susceptible to decolorization so the stain doesn't turn clear
How and why the stains interact with a gram negative cell. (ex. 3-7)
• Crystal violet and the iodine turn stain purple
• Decolorization turns stain clear
• Safranin turns stain pink
• Decolorization extracts the lipid
• D/C makes it more porous, making wall incapable to retain crystal violet - iodine complex (turns clear)
• Because stain is clear safranin turns stain Pink
Gram Staining: Physically repeating this procedure. (ex. 3-7)
• Heat fixed smears (after stain has dried)
• Cover smear with crystal violet (1 minute)
• Rinse with distilled water
• Cover smear with iodine (1 minute)
• Rinse with distilled water
• Rinse smear with decolorization (ethanol) until clear
• When clear, rinse with distilled water
• Cover smear with safranin (1 minute)
• Rinse with distilled water
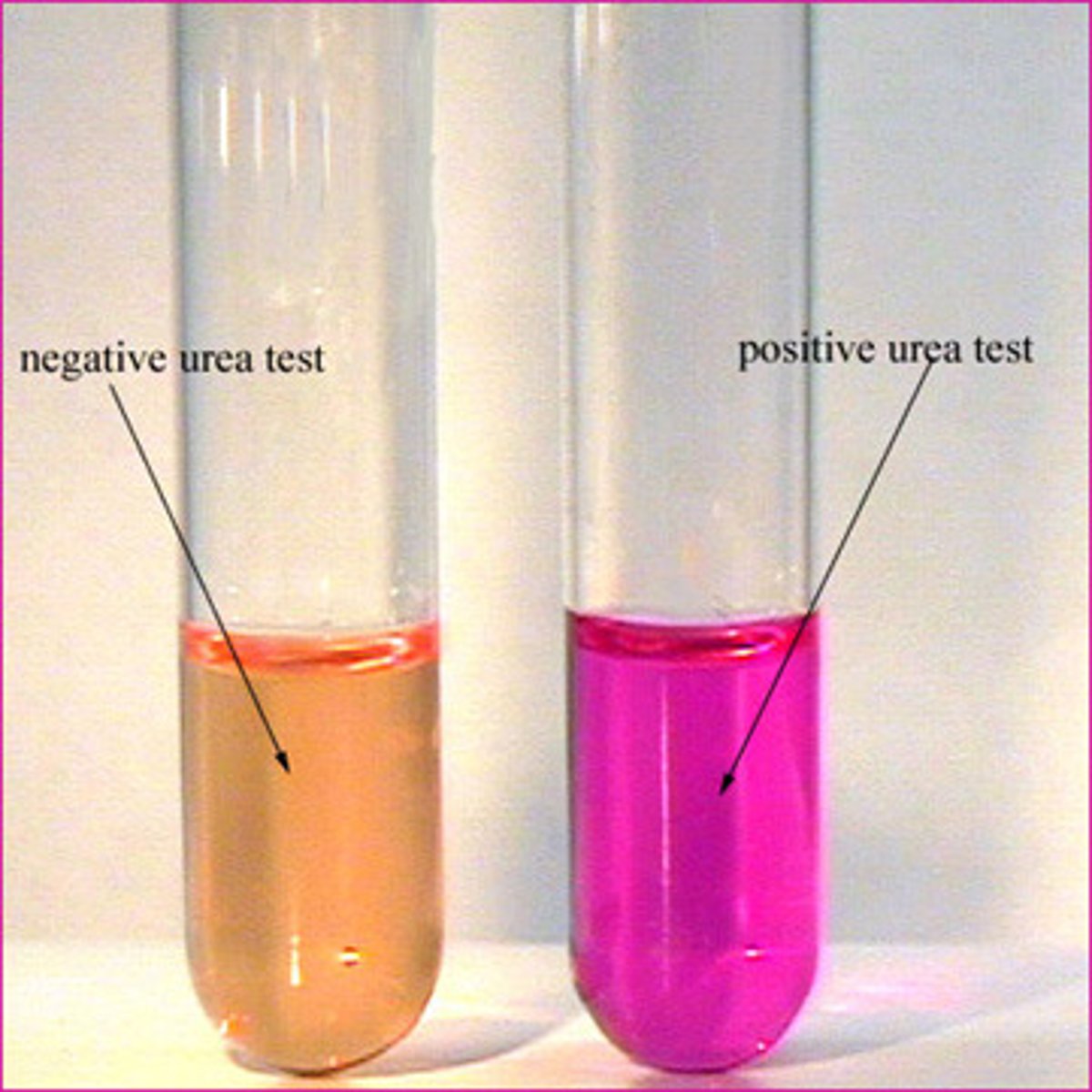
Urea Testing For:
Ability to hydrolyze urea
Urea Reagent:
Phenol Red
Urea Positive Result:
Bright Pink
Urea Negative Result:
Orange/Yellow
Determine the chemical reaction that takes place.
catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia. The reaction occurs as follows: (NH2)2CO + H2O → CO2 + 2NH.
Urea

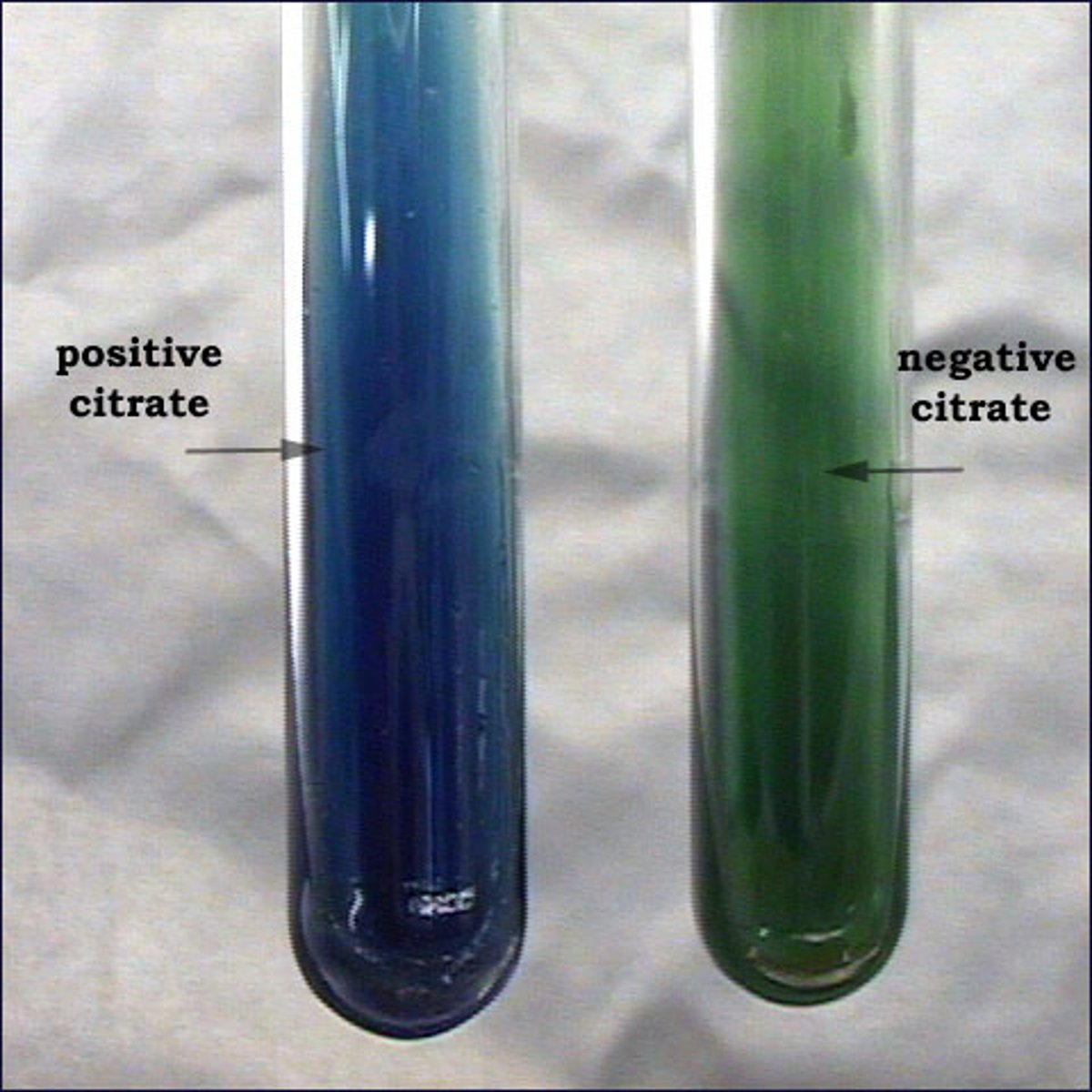
Citrate Testing For:
Utilization of citrate as a carbon source
Citrate Reagent:
Bromothymol Blue
Citrate Positive Result:
Blue or no color change with growth
Citrate Negative Result:
No color change with no growth
Citrate Test: Determine the chemical reaction that takes place.
Citrate Fermentation
Citrate Test: What causes the color change?
bromomethyl blue is used which is green when acidic and blue when basic. conversion of green to blue is positive because pH goes up. If no color change or no growth, citrate is being utilized and it is positive.
Citrate

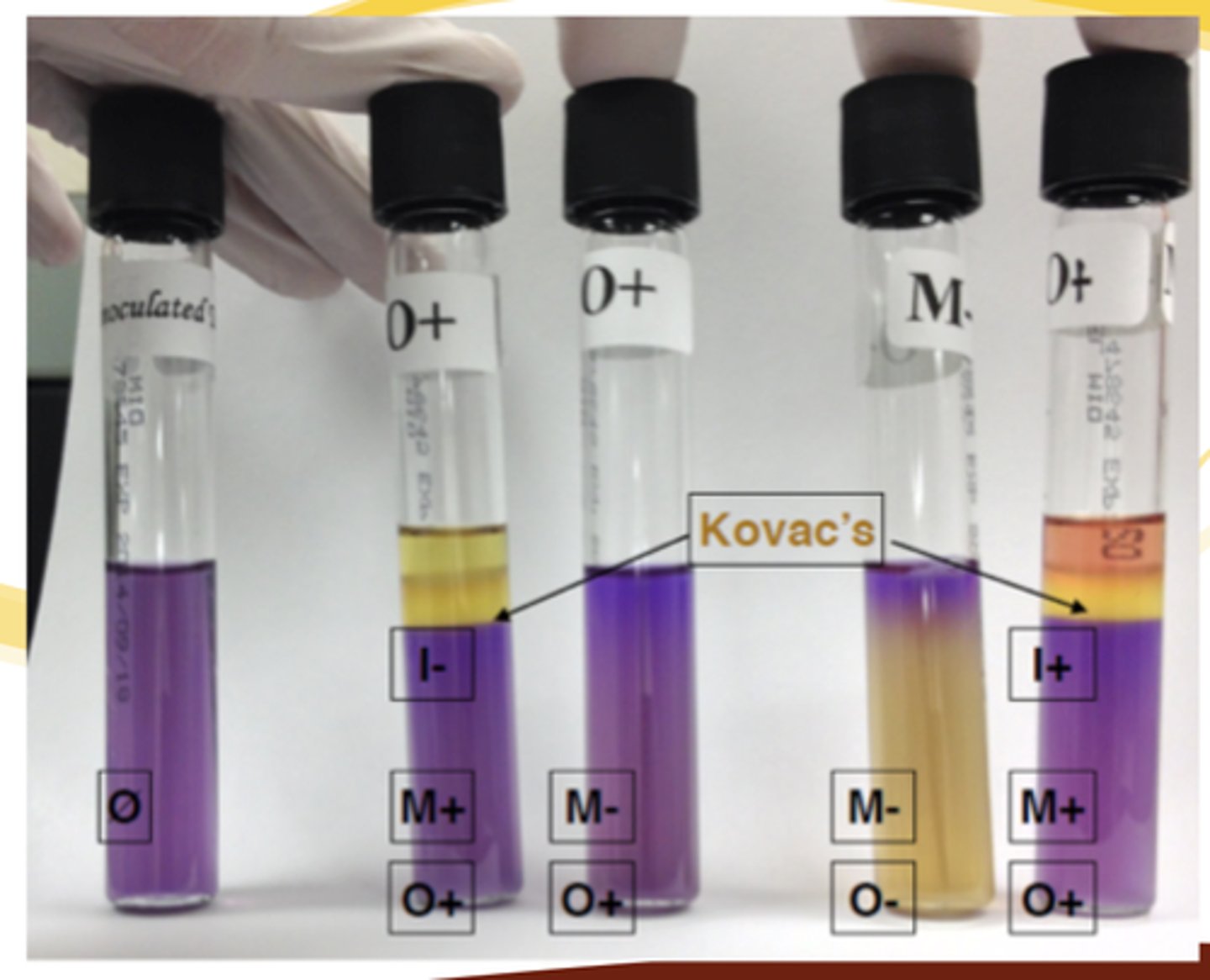
MIO Testing For:
• Motility
• Indole Production
• Ornithine Decarboxylation
MIO: Motility Reagent
Semi-Solid Agar
MIO: Indole Production Reagent
Kovac's Reagent
MIO: Ornithine Decarboxylation Reagent
Bromocresol Purple
MIO Motility Positive Result:
Medium Appears Cloudy
MIO Motility Negative Result:
Original stab line is visible
MIO Indole Production Positive Result:
Red Layer on top of border
MIO Indole Production Negative Result:
No Color Change
MIO Ornithine Decarboxylation Positive Result:
Purple
MIO Ornithine Decarboxylation Negative Result:
Yellow
MIO Test: Why is this a semisolid medium?
To allow culture to move around easier if motile
MIO Test: In what order should the tests be read?
• After incubation, read motility and ornithine decarboxylation first.
• After reading motility and ornithine results, add 5 drops of Kovac's reagent to test for indole production.
MIO Test: What causes the color change?
If the organism can decarboxylate ornithine then there is an increase in ph - turns purple
MIO Test: Understand the biochemical reactions that are taking place.
First the organism must ferment glucose. This will create acid turning the media yellow. If present, Ornithine and the acid will initiate decarboxylation yielding putrescine, which increases pH and turning bromocresol purple back to purple.
MIO

Catalase Testing For:
Catalase Production
Catalase Reagent:
Hydrogen Peroxide
Catalase Positive Result:
Bubbles
Catalase Negative Result:
No Bubbles
Catalase Test: How is the catalase test performed?
1. Place culture on slide
2. Add 1 drop of hydrogen peroxide
3. Look for bubbles
Catalase Look Like
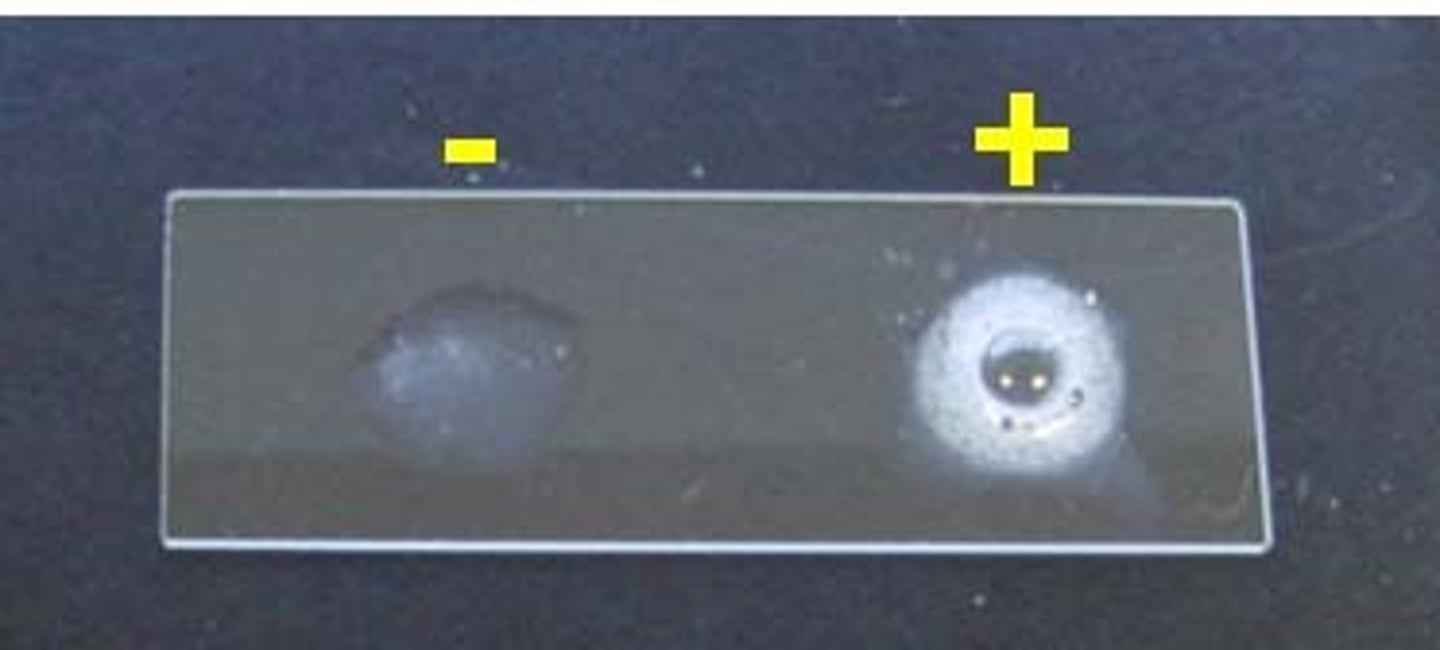
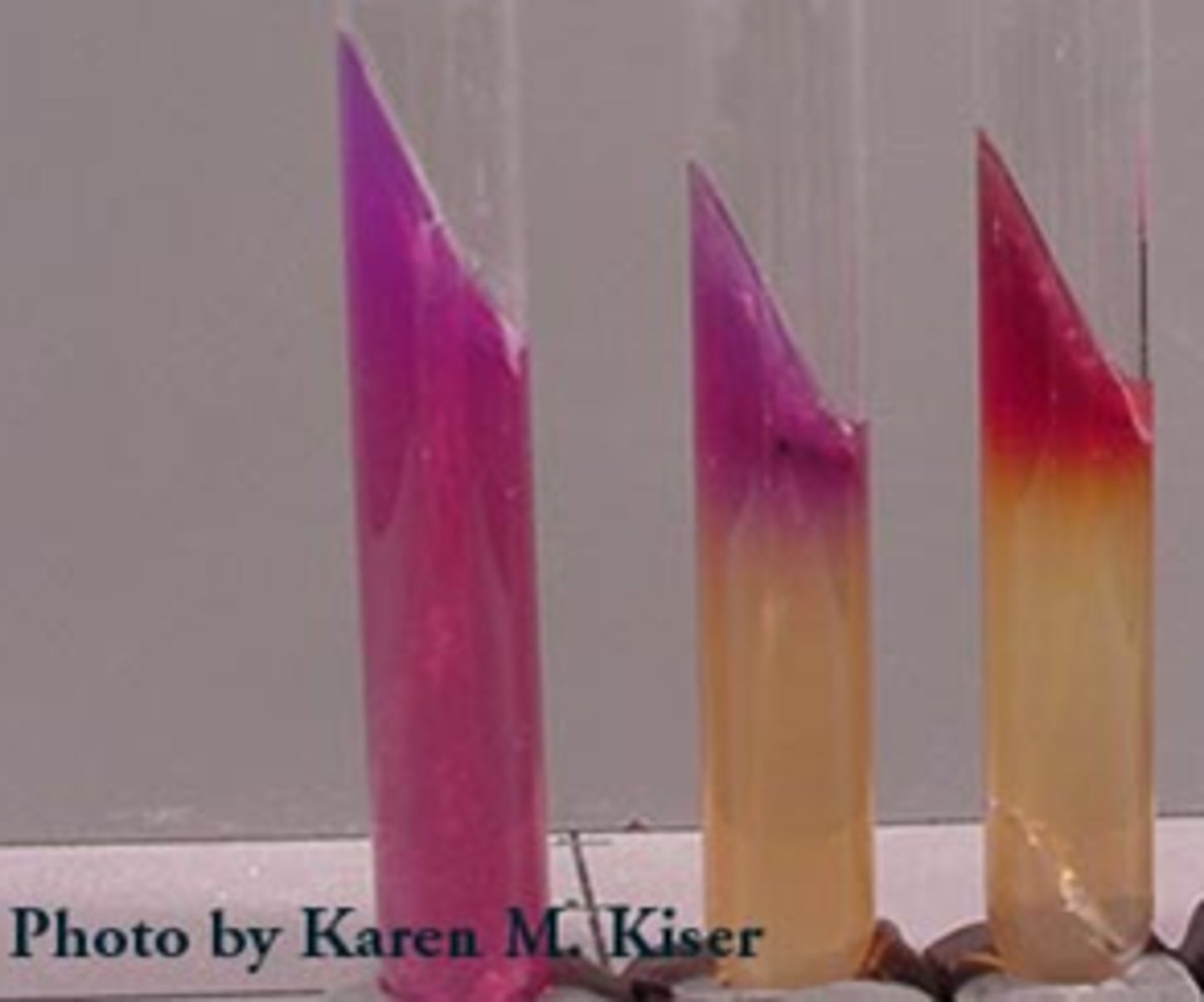
Lysine Iron Agar Testing For
• Lysine Deaminase
• Lysine Decarboxylate
Lysine Reagent used for Deaminase
Ferric Ammonium Citrate
Lysine Reagent used for Decarboxylate
Bromcresol Purple
Lysine Positive Result for Deaminase
Red Slant/Yellow Butt
Lysine Negative Result for Deaminase
Purple Slant/Yellow Butt
Lysine Positive Result for Decarboxylate
Purple Slant/Purple Butt
Lysine Negative Result for Decarboxylate
Purple Slant/Yellow Butt
Lysine Test: How is the burgundy slant helpful diagnostically?
This result is interpreted to mean that deamination is happening
Lysine Test: What causes a burgundy slant and what three genera is this indicative of?
The beginning of decarboxylation process
Proteus, Morganella, Providencia
Lysine Test look like

Blood Agar Testing For:
Hemolysis of RBC's
Blood Agar Reagent:
5% sheep blood in blood agar