CELL & MOLEC QUIZ 1 STUDY GUIDE
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Cell Theory
All biological organisms are composed of cells; cells are the unit of life; all life come from preexisting life.
Resolving power of light microscopy
200 nanometers
Resolving power of electron microscopy
.2 nanometers
Prokaryotic cells
lack membrane-bound organelles; retain plasma membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA
Eukaryotic cells
contain nucleus, E.R., Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, chloroplasts, mitochondria; larger and more complex
3 domains of life
Eukarya, Archaea, Bacteria
LUCA
Last Universal Common Ancestor; potential thermophile, in deep sea vents without oxygen
How can bacteria readily adapt to a changing environment despite having a small, stream-lined genome?
Lateral Gene Transfer - prokaryotes exchange genes with neighbors
smaller genomes = more successful
According to Nick Lane, how did the first eukaryotic cell arise?
An archaean cell engulfed a bacterium (LECA); this allowed the endosymbiotic bacteria to lose ~99% of its genome
Nucleus
stores DNA
Mitochondria
generates useable energy; contains inner and outer membrane
Chloroplasts
create energy from sunlight
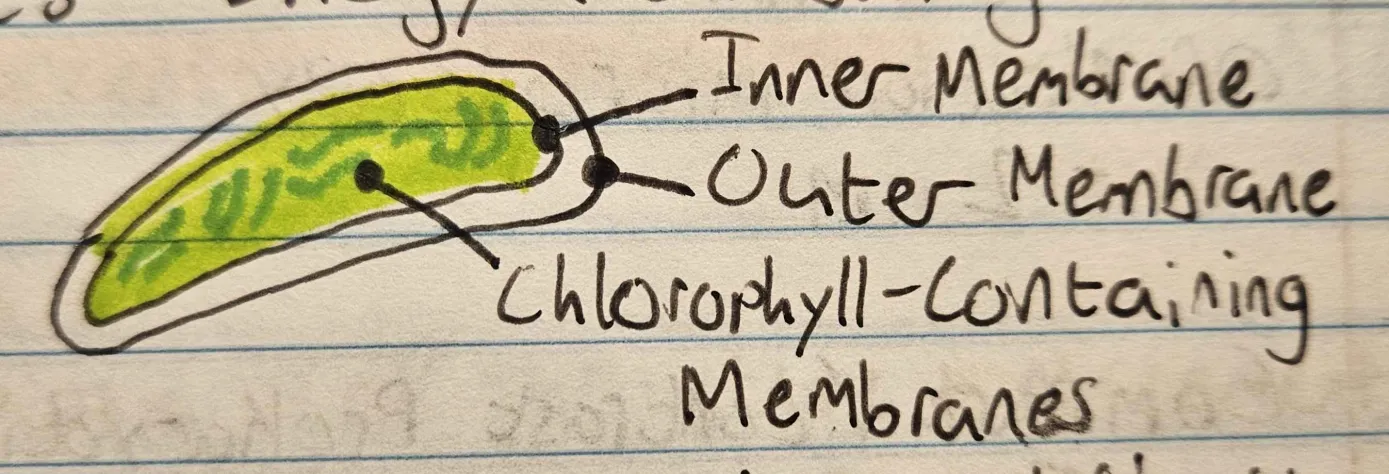
Endoplasmic Reticulum
creation, modification, and transport of proteins
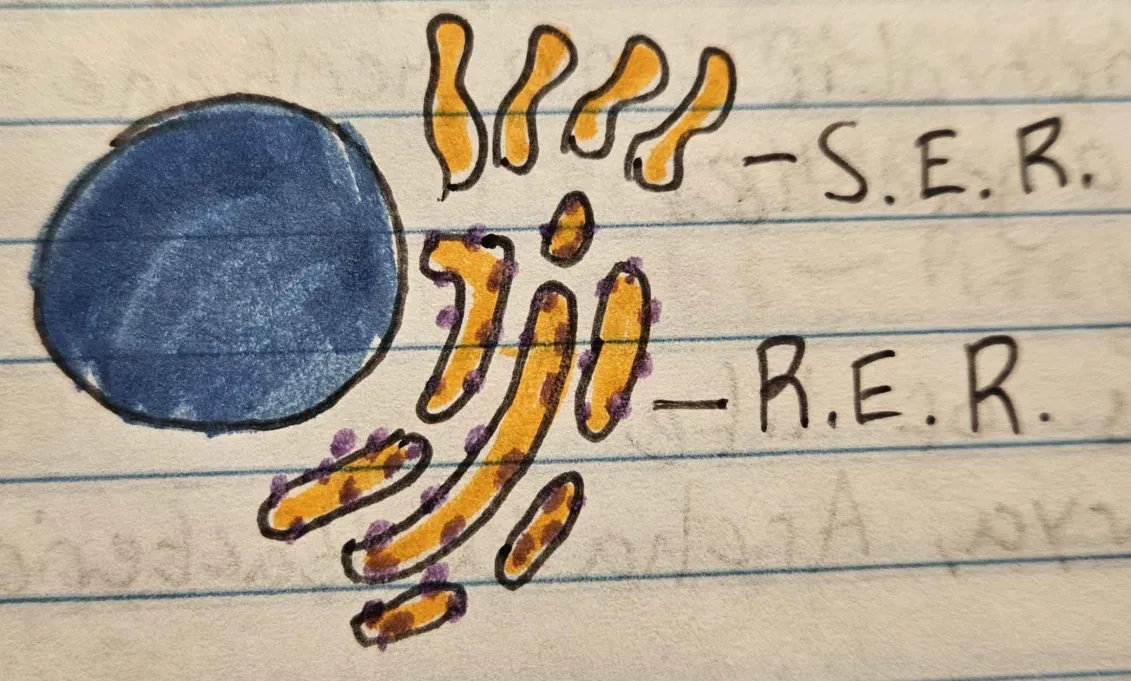
Golgi apparatus
transportation + sorting of proteins
Cytoskeleton
cell structure, mitosis & meiosis
What are the reactant and product molecules produced in cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
What is the endosymbiotic theory?
mitochondria and chloroplasts in eukaryotic cells originated from ancient bacteria that were engulfed by larger cells
How do cells exchange material with the external environment?
Diffusion through the plasma membrane
Microtubules (Cytoskeleton)
support shape, move chromosomes during cell division, enable organelle movement
Actin Filaments (Cytoskeleton)
plasma membrane; mechanical support, enables cell movement
Intermediate Filaments
structural support
What makes model organisms like D. melanogaster, C. elegans, and D. rerio useful for studying cell biology?
Readily accessible and easily modifiable
How do genome size and number of genes in various model species differ?
Genome Size: Increases from smaller genomes in D. melanogaster and C. elegans to larger genomes in Danio rerio, Mus musculus, and Homo sapiens
Number of Genes: Varies, with C. elegans having a higher gene count relative to its genome size, while Danio rerio and Mus musculus have more genes overall but also larger genomes
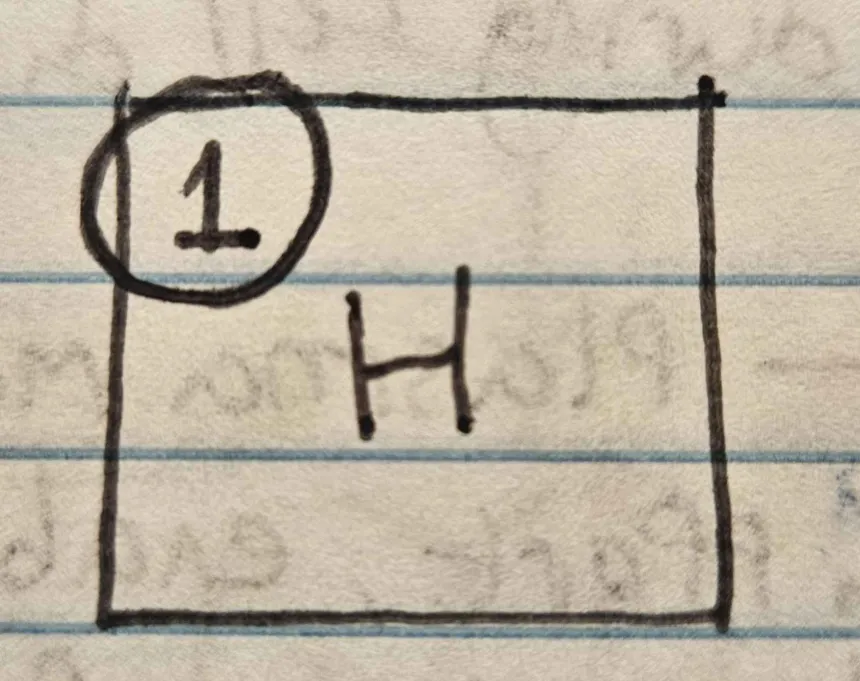
What is the atomic number of an atom?
number of protons found in the nucleus of that atom.
What is the mass number of an atom?
total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.
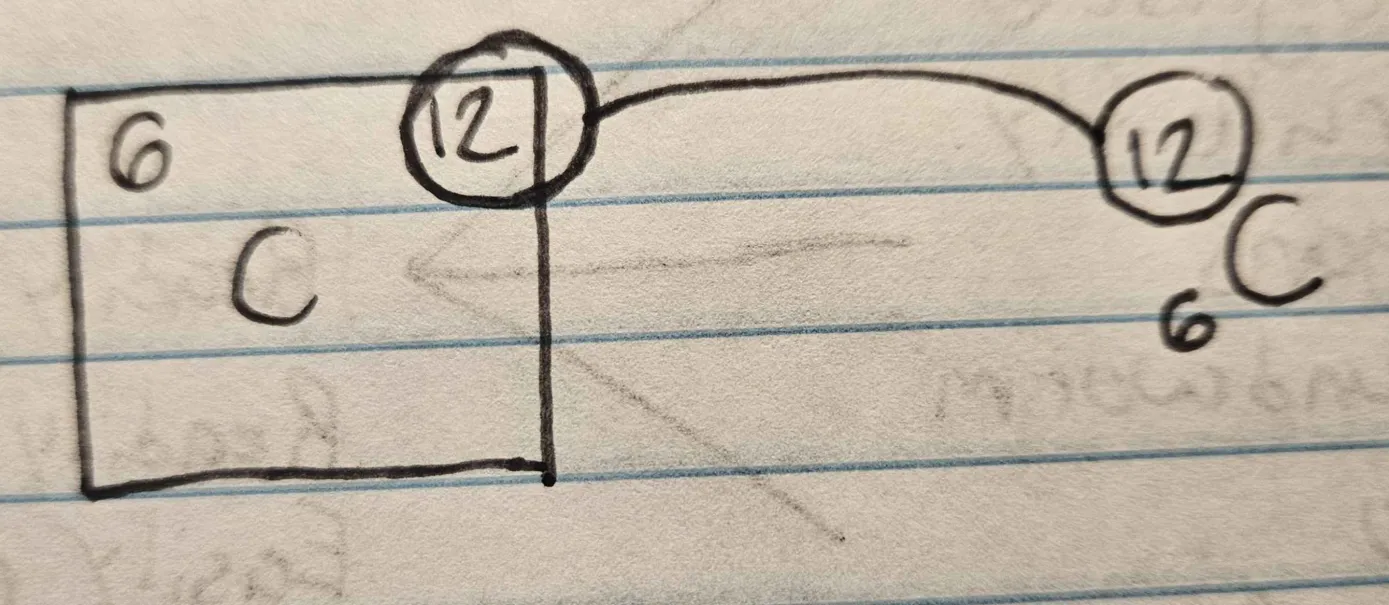
What are isotopes?
different forms of the same chemical element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. (Carbon-14, 6 protons and 8 neutrons)
How much does a mole of NaCl weigh?
Na mass number = 22.99. Cl mass number = 35.453
22.99 + 35.453 = 58.44
How much does .5 of a mole of NaCl weigh?
58.44/2 = 29.22
Covalent Bonds
Electrons are shared
Non-polar: shared equally
Polar: 1 atom is more electronegative than the other
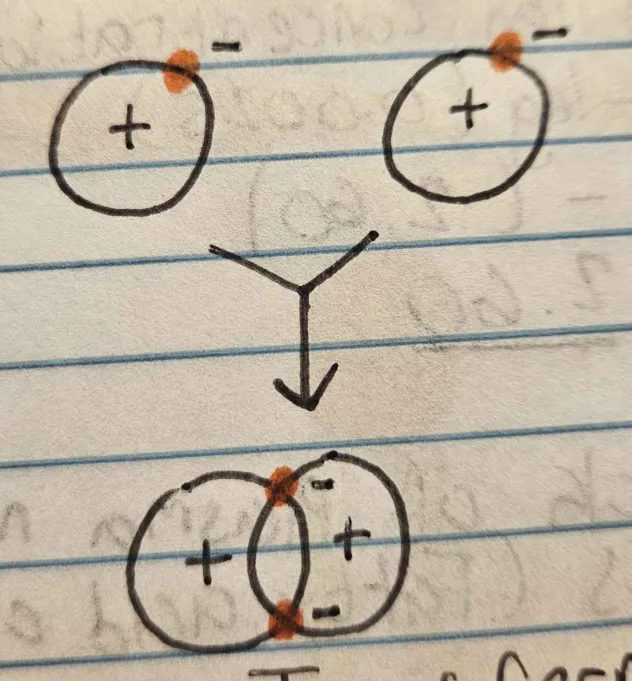
Ionic Bonds
Electrons are transferred, leaving one ion positive and the other negative
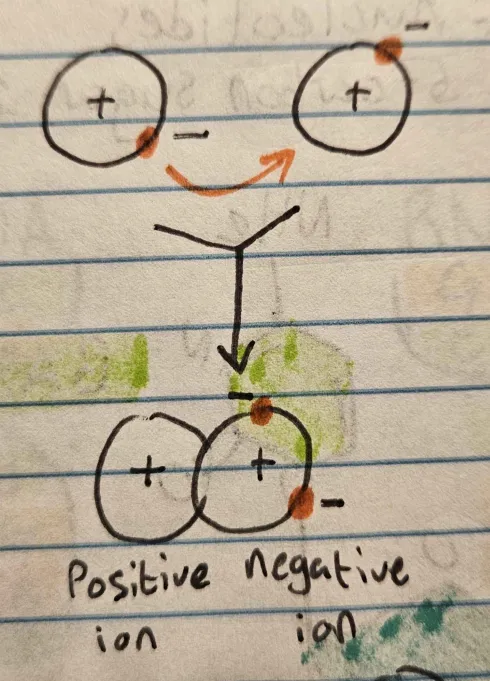

Hydrogen Bonds
hydrogen atom bonds to a strongly electronegative atom ( O — H )
How do electrons influence the activity of atoms?
Determines reactivity, ability to gain or lose electrons, & formation of chemical bonds
Calculating pH of a solution
pH = -log [H3O+]
Find pH of a 0.0025 M HCl solution.
pH = -log (0.0025) = -(-2.60) = 2.60
What is the main building block of plasma membranes?
Phospholipids
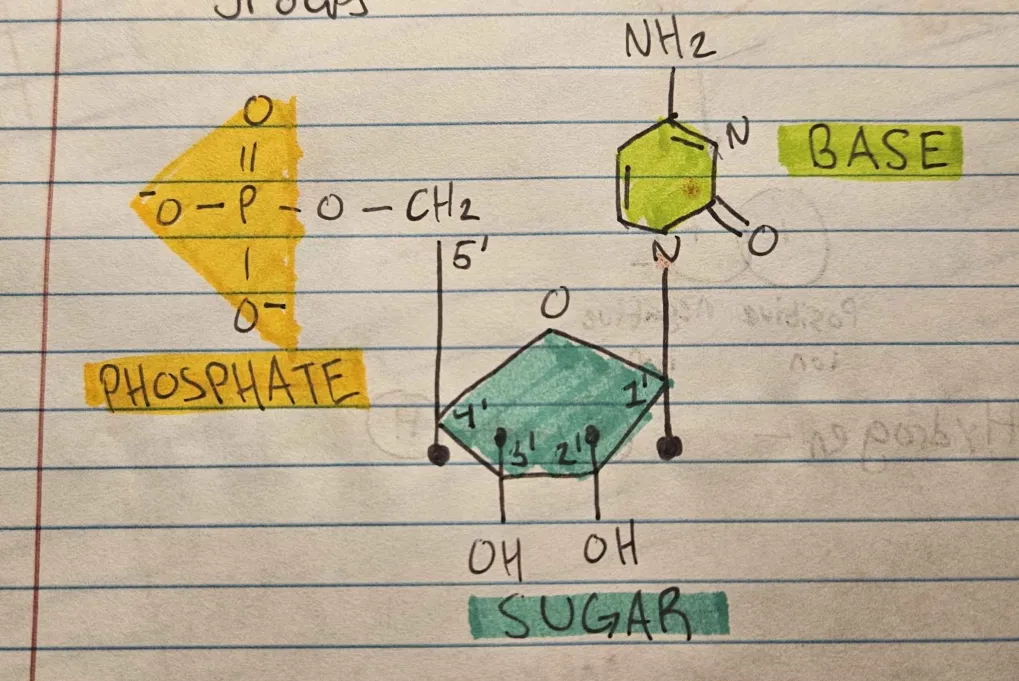
What are the building blocks of nucleotides?
Nitrogen base, 5-carbon sugar, one or more phosphate groups
Saturated Fatty Acids
Single bonded, solid at room temperature (butter)
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Double bonded, not solid (olive oil)
What does amphipathic mean?
Having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts (ex. phospholipid bilayer with hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail)
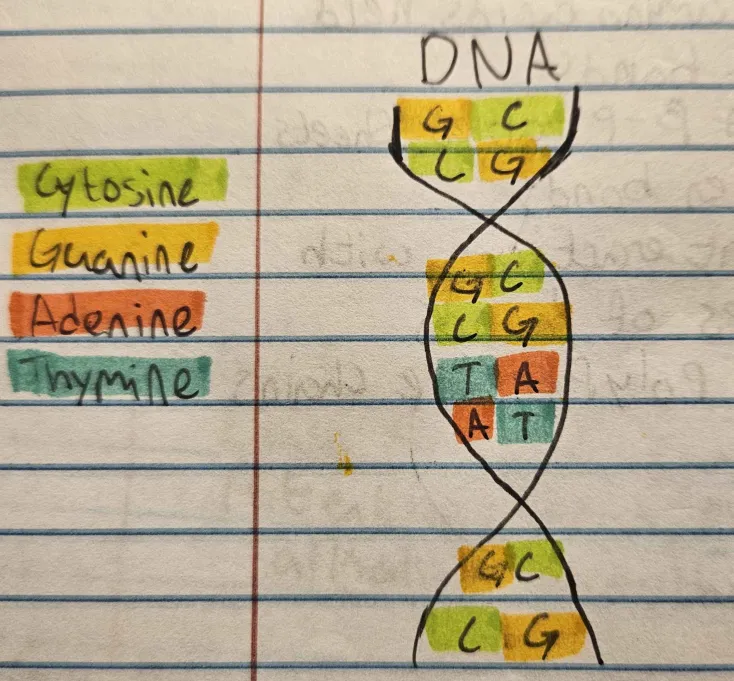
Structure of DNA
Double-helixed, with a deoxyribose sugar and thymine base. Contains Cytosine, Guanine, Adenine, Thymine
Structure of RNA
Single-stranded, with a ribose sugar and uracil base. Contains Cytosine, Guanine, Adenine, Uracil
How do you determine the possible number of DNA or RNA molecules made from a given number of nucleotides?
The number of possible DNA or RNA molecules is 4n, where n is the number of nucleotides.
How do you determine the possible number of polypeptide chains made from a given number of amino acids?
The number of possible polypeptide chains is 20n, where n is the number of amino acids.
How are proteins synthesized?
Dehydration reaction & loss of a water molecule
Primary Protein Structure
sequence of amino acids held together by peptide bonds
Secondary Protein Structure
a-helixes and B-pleated sheets maintained by hydrogen bonds
Tertiary Protein Structures
3-D shape, interactions with R-groups and all types of bonds
Quaternary Protein Structure
multiple polypeptide chains
How to denature proteins
Expose to high heat
Alter pH of a solution
Expose to alcohol
Reducing & oxidizing agents
Concentrated brine solution
How do misfolded proteins lead to neurodegenerative diseases?
Aggregate and damage cells & whole tissues. Usually due to an abnormally expanded range of sequence copies
Huntington’s: CAG
Normal: 9 - 37
Abnormal: 37 - 121
Chaperone Proteins
Guide folding of newly synthesized peptide chains to save energy & prevent misfolding (requires ATP hydrolysis)
Form isolation chambers to prevent single chains from aggregating
a-helixes
N-H is Hydrogen-bonded to C=O of a neighboring peptide bond in some chain
B-helixes
Several segments held together by Hydrogen bonding between adjacent strands
Coiled Coils
Formed when 2-3 helixes wrap around one another. Twist facing inward due to non-polarity
Amyloid Fibers
Stacking of sheets allows some misfolded proteins to aggregate
Associated with Alzheimer’s & prion diseases
Used by infection bacteria for biofilms that enable colonization of host tissues
Ligand
Any substance that binds to a proteins; must fit perfectly; binds proteins to the substrate
Antibodies
Formed from 2 identical light polypeptide chains and 2 identical heavy polypeptide chains
How are infections handled?
Antibodies attack antigens on the viruses, raising body temperature & denaturing proteins
Catalyzing Chemical Reactions
Enzymes make & break covalent bonds at will w/o being consumed
Lower activation energy required to start reactions
Bind 2 substrate molecules to encourage reactions
Feedback Inhibition
Enzyme that acts early in a reaction pathway is inhibited by a late product
Allosteric Enzymes
Have 2+ binding sites that influence each other based on if they are on or off ATP/phosphate groups, acetyl groups, ubiquitin, GTP binding proteins
Unidirectional Movement
ATP Hydrolysis allows motor proteins to produce directed movements
Coupling conformational change with ATP Hydrolysis makes movement unidirectional
Hydrolase
General term for enzymes that catalyze a hydrolytic cleavage reaction
Nuclease
Breaks down nucleic acids by hydrolyzing bonds between nucleotides
Protease
Breaks down proteins by hydrolyzing peptide bonds between amino acids
Ligase
Joins 2 molecules together; DNA ligase joins two DNA strands together end to end
Isomerase
Catalyzes the rearrangement of bonds within a single molecule
Polymerase
Catalyzes polymerization of bonds within a single molecule
Kinase
Catalyzes the addition of phosphate groups to molecules. Attach phosphate groups to proteins
Phosphatase
Catalyzes the hydrolytic removal of a phosphate group from a molecule
Oxido-reductase
Catalyze reactions in which one molecule is oxidized and another is reduced
ATPase
Hydrolyzes ATP