Wk 8: Cognitive Behavioral Approaches
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
What is the primary focus of Cognitive Frames of Reference?
They emerged from learning theory and behaviorism, emphasizing observable behavior.
What do behaviorists believe regarding scientific study?
They believe that only observable behavior can be the subject of scientific study.
What are behavioral objectives?
Goals that are observable and measurable, helping to determine if specific interventions are effective.
What is classical conditioning?
A learning process where a neutral stimulus becomes associated with a meaningful stimulus, leading to a learned response.
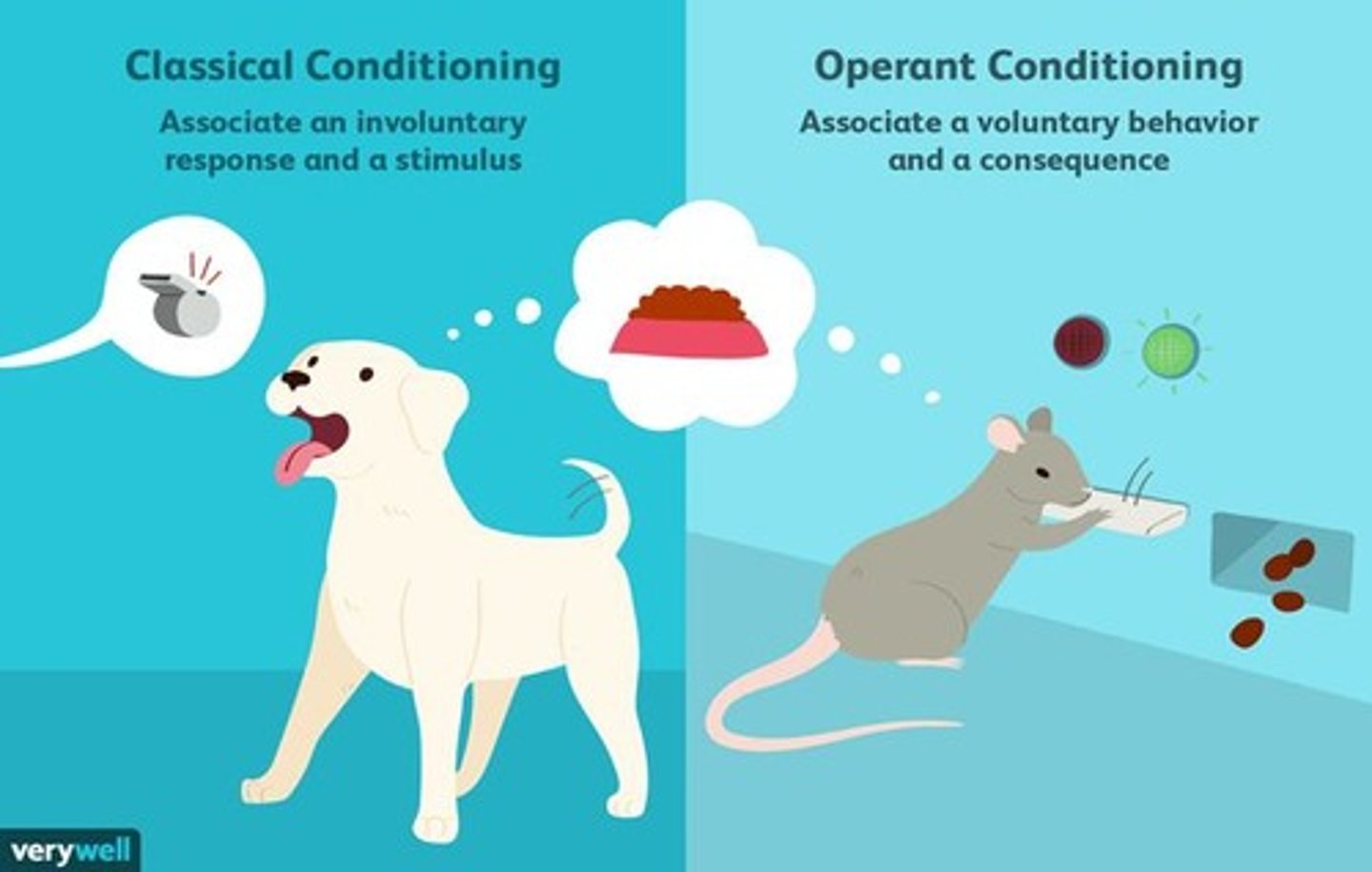
What is operant conditioning?
A method of learning that occurs through rewards and punishments for behavior.
How do habits develop according to operant conditioning?
Behaviors that are reinforced become habitual, requiring less reinforcement over time.
What is shaping in behavioral therapy?
Reinforcing successive approximations of a desired behavior until the complete behavior is learned.
What is chaining in behavioral therapy?
Learning a sequence of actions where each action serves as a stimulus for the next.
What types of reinforcement exist?
External (positive and negative), internal, vicarious, symbolic, and self-produced reinforcers.
What is the role of rehearsal and practice in behavioral therapy?
To reinforce skills across various contexts and enhance real-life application.
What is the purpose of role play in therapy?
To practice new behaviors in a safe environment, develop insight, and decrease anxiety.
What are the four parts of role play?
Define the problem, assume roles, enact the scenario, and discuss the outcomes.
What is systematic desensitization?
A technique used to reduce phobias by gradually exposing the individual to the fear while in a relaxed state.
What is biofeedback?
A technique that involves monitoring bodily functions to help manage stress and anxiety.
What is the first step in systematic desensitization?
To evoke a state of relaxation before gradually introducing fear-inducing stimuli.
What is the significance of client involvement in setting goals?
Goals should be set collaboratively by the client and occupational therapist to ensure they are meaningful and relevant.
How can environmental factors influence behavior according to behavioral concepts?
Environmental reinforcement can lead to either maladaptive or constructive learning patterns.
What is the importance of discussing practice results in therapy?
It allows the therapist to provide reinforcement and adjust strategies based on client experiences.
What are some examples of external reinforcers?
Positive rewards such as treats or privileges, and negative reinforcers like the removal of unpleasant stimuli.
What role does personal satisfaction play in reinforcement?
Feelings of self-worth and competence can reinforce behaviors, leading to their repetition.
What is the definition of function in the context of cognitive behavioral approaches?
Function refers to adaptive behavior and learning.
What does dysfunction signify in cognitive behavioral approaches?
Dysfunction indicates maladaptive learning.
What is a key focus of cognitive behavioral approaches?
The focus is on observable behavior.
What are some behavioral principles included in cognitive behavioral approaches?
Conditioning, habit formation, shaping, chaining, rehearsal, practice, and measurable goals.
What does cognitive rehabilitation focus on?
It is fully functional when information is processed correctly and generalized to other contexts.
What common problems may indicate dysfunction in cognitive behavioral approaches?
Decreased organization, priority setting, and shifting perspective.
What is the basic strategy for change in cognitive behavioral approaches?
Reinforcement, which can be external or internal.
What is self-reinforcement in the context of motivation?
Self-reinforcement is the highest form of motivation a client can achieve.
What is the purpose of starting with simple tasks in cognitive behavioral approaches?
To facilitate the development of competence before moving to more complex tasks.
What are the goals of group interventions in cognitive rehabilitation?
Goals are always specific, observable, and measurable.
What is the recommended size for homogenous groups in cognitive rehabilitation?
No bigger than 8 members.
What are some deficit areas addressed in cognitive rehabilitation groups?
Orientation, attention, neglect, visual processing, executive functioning, motor planning, and awareness.
What is the focus of psychoeducational groups?
Skill training, such as assertiveness, social skills, and stress management.
What does Dialectical Behavior Therapy emphasize?
Self-regulation and addressing dysregulation of emotions, interpersonal relationships, and cognition.
What are core mindfulness techniques designed to achieve?
To focus on one thing at a time, pay attention to all information, and refrain from quick judgments.
What is one technique used in core mindfulness?
Writing about a conflict to slow down responses and promote rational thinking.
What role does the occupational therapist play in psychoeducational groups?
The OT acts as an educator.
What is the significance of therapeutic relationships in group interventions?
They are crucial for effective communication and support during the change process.
What is a common outcome of clients who resist change in group settings?
The group focuses on identifying and naming emotions rather than discussing past behaviors.
What cognitive skill does the cognitive behavioral approach aim to enhance?
The ability to think logically and form accurate perceptions of self and environment.
What is the goal of teaching social-emotional learning (SEL) to children?
To develop skills in self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making.
What are the goals of interpersonal effectiveness in group intervention?
Goals include getting and keeping good relationships, and maintaining self-respect in relationships.
What are some strategies for improving interpersonal effectiveness?
Strategies include recognizing factors that interfere with relationships, challenging negative factors, expressing feelings and opinions, negotiating, and making specific requests.
What is the focus of emotion regulation in group interventions?
Focus includes describing and naming emotions, challenging beliefs about emotions, working on self-interventions when emotions overwhelm, and building positive emotions and experiences.
What techniques are taught for distress tolerance in group intervention?
Techniques include distraction, self-soothing methods (like prayer and deep breathing), and discussing the pros and cons of distress tolerance.
What is the role of the leader in group intervention?
The leader is directive and active, assisting with cues, asking questions, redirecting, and monitoring group interactions.
What should the goals of a group intervention be like?
Goals should be behaviorally defined, specific, observable, measurable, and focus on functional performance.
How should culture and individual values be considered in group interventions?
It's important to consider client preferences and social expectations to enhance motivation and effort.
What are some activity examples used in group interventions?
Examples include imagery and visualization, relaxation with guided imagery, drawing images, journaling, behavior rehearsal, and self-reward.
What is the structure of group leadership during the beginning of a session?
The problem should be defined, goals set, and expectations communicated without the need for a warm-up.
What is the purpose of sharing in group interventions?
Sharing allows group members to read aloud or share items made, with feedback primarily coming from the therapist.
How should processing occur in group interventions?
Most interaction should be between the leader and individuals, focusing on learning rather than group dynamics unless they interfere.
What is the goal of generalizing in group interventions?
Group members should verbalize learned principles and strategies, which may require assistance from the clinician.
What is the application phase in group interventions?
Discussing how to carry over learned strategies to the community and applying them to everyday life.
What types of homework might be assigned in group interventions?
Homework can include time frames for completion and sharing insights or experiences related to the group goals.