South College AVL Lab Med: CBC,WBC - Lecture 1
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
CBC (complete blood count) with differential (DIFF)
what is the most common lab ordered?
annual physicals, ED and IM workups, trend/follow in the hospital
What are some other important uses of CBC?
CBC (complete blood count)
a set of tests that include all WBC, RBC and platelet measurements.
CBC with differential
look at differential count of WBCs - monocytes, lymphocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, band cells
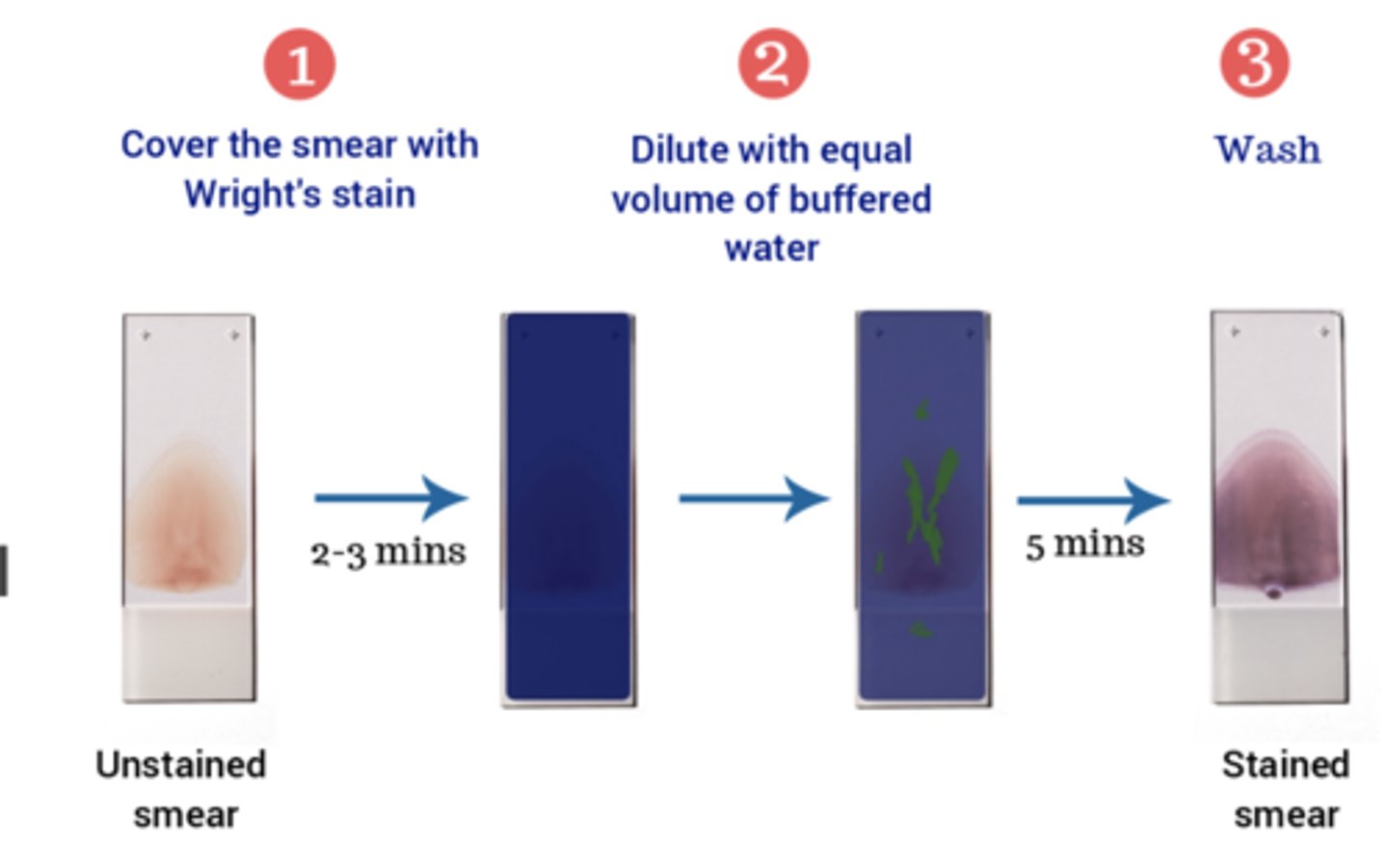
peripheral blood smear: wright stain
RBC, WBC, and platelet morphologies accessed
identifies abnormal cells
No - vary with age, gender, and pregnancy status
Are all CBC ranges the same for everyone?
shorthand lab diagram
what does this picture show?
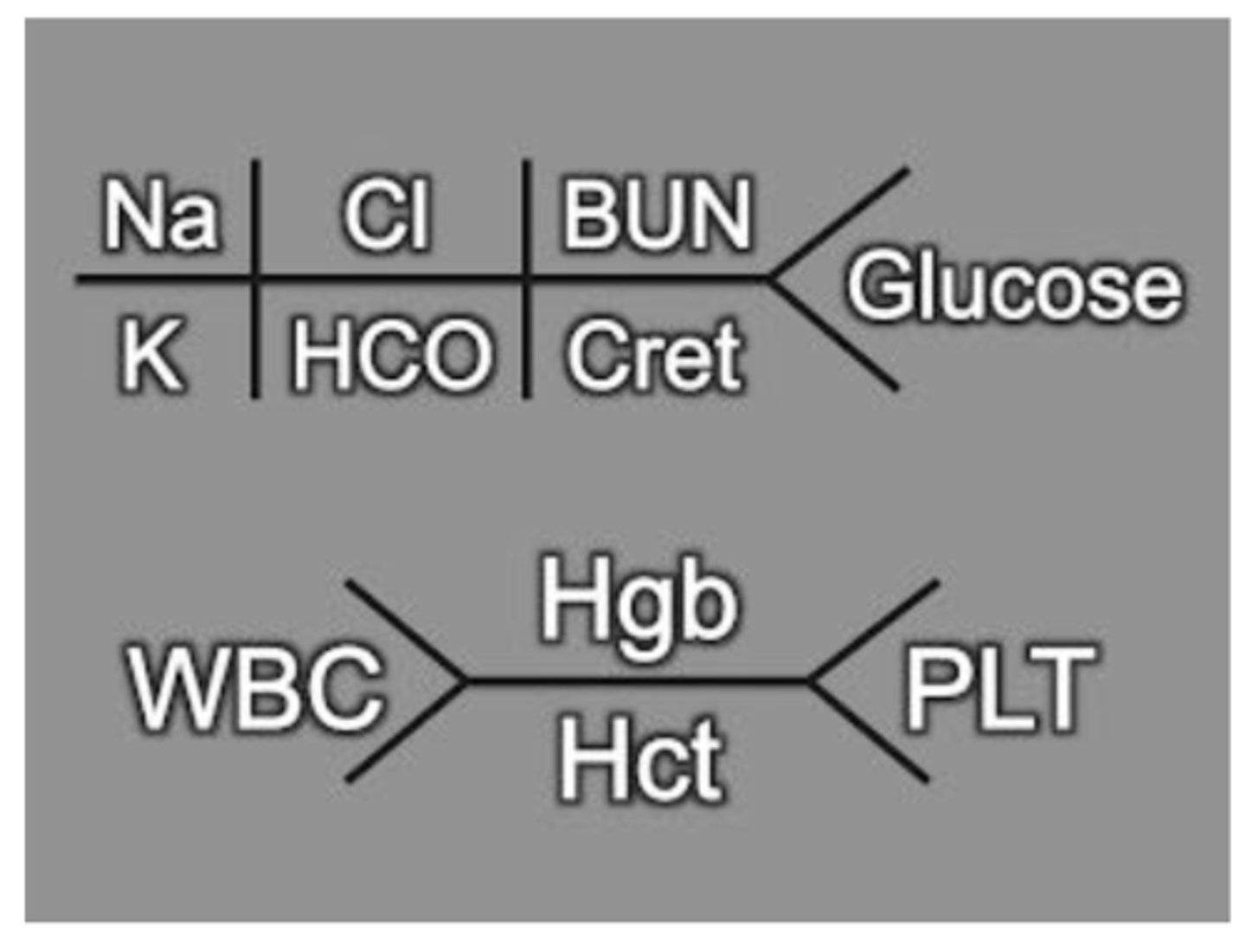
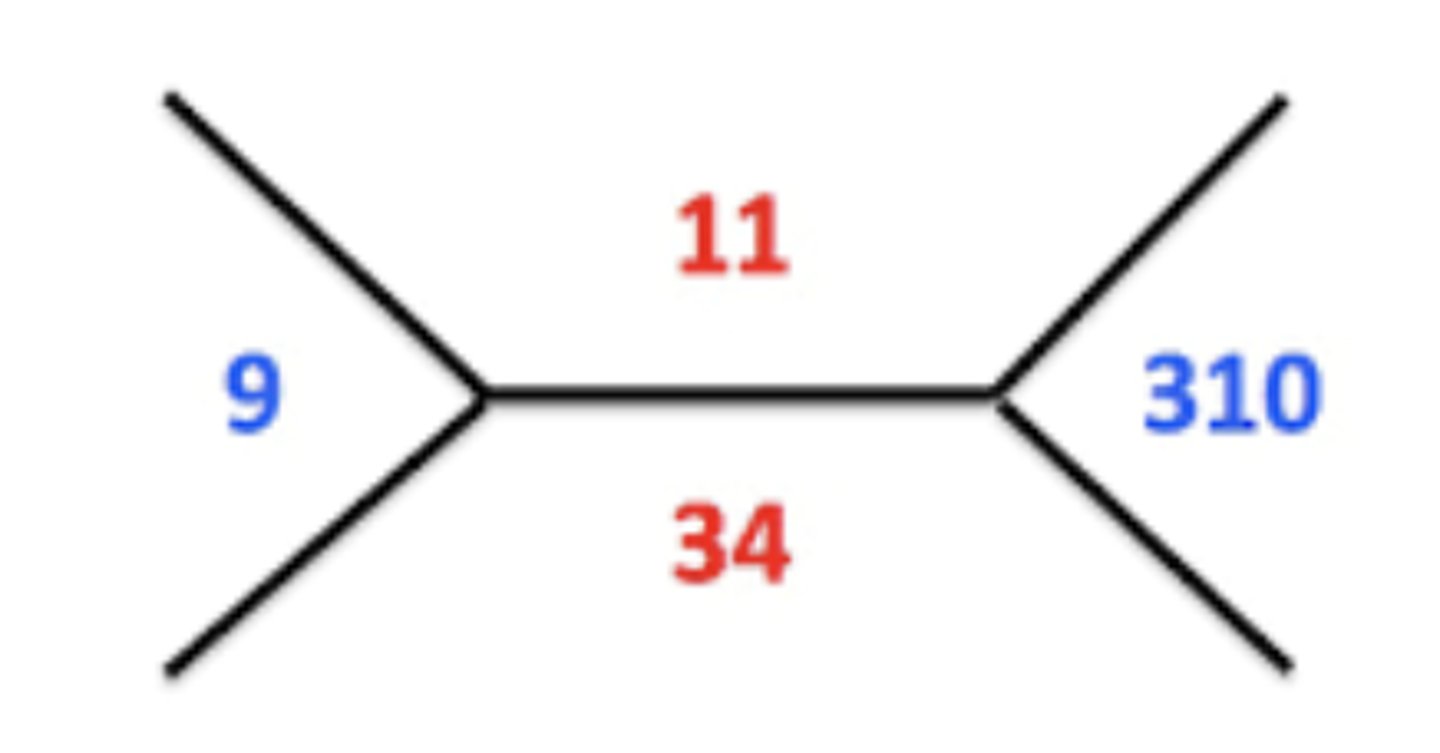
HGB, HCT, WBC, PLT
What does the top value represent? bottom? left? right?
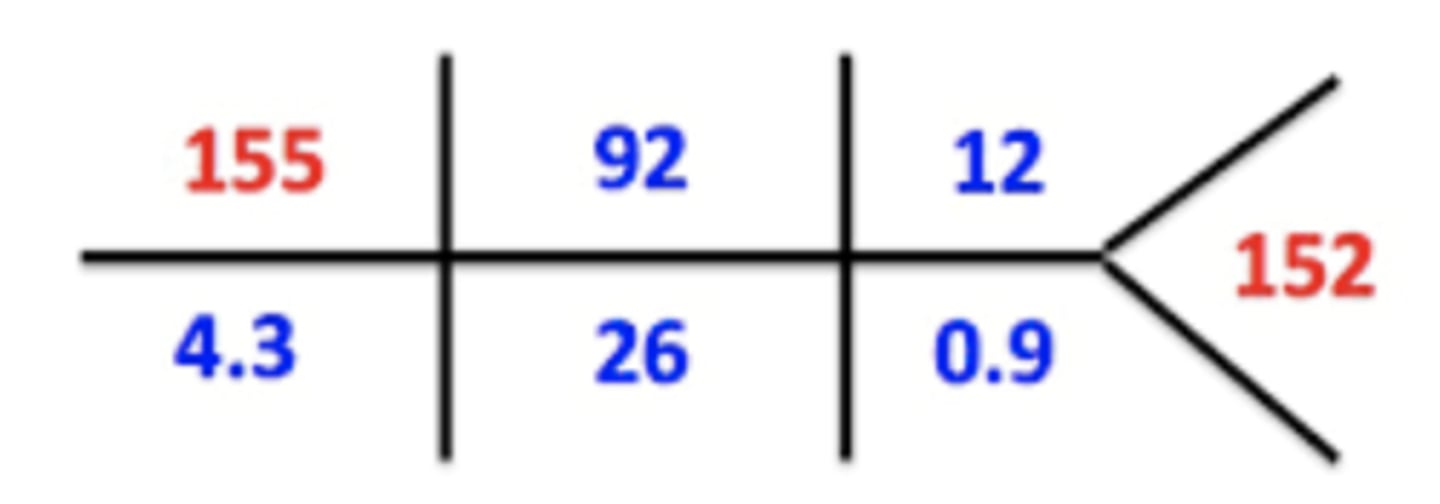
Na, Cl, BUN, GLu
K, HCO3, Cret
Top left? Top middle? top right? farthest right?
bottom left? bottom middle? bottom right?
Neutrophils (55-70% WBCs)
what is the most common WBC? what percentage does it make up in differential?
~20-40%
what percentage does lymphocytes make up in differential?
~2-8%
what percentage does monocytes make up in differential?
~1-4%
what percentage does eosinophils make up in differential?
~0.5-1%
what percentage does basophils make up in differential?
at birth (mean of 25,000/mm^3), puberty
When are WBC at their highest? When do WBC fall to adult levels?
Lymphocytes
What is the predominant WBC from the 2nd week of life until 5-7 years?
neutrophils
What is the predominant WBC after 5-7 years of age?
age, sex, race, pregnancy status, +/- spleen
What do normal ranges of WBC depend on?
evaluating infections, neoplasms, inflammation, and allergies
When is WBC w/ DIFF most helpful?
<2,000/mm^3 OR >40,000/mm^3
what are some critical values of WBC?
Leukocytosis
Abnormally high WBC count
Infections (pneumonia), inflammation, smoking, medications such as steroids and lithium, exercise, stress/trauma, leukemia/cancer (>100,000 per mm^3), thyroid storm, dehydration
what are some causes of leukocytosis?
Neutrophilia
increase in neutrophils (>55-70%)
bacterial infections, cushing syndrome, ketoacidosis, RA, thyroiditis, gout, Myelocytic leukemia, trauma
what are some causes of neutrophilia?
Lymphocytosis
increase in lymphocytes (>20-40%)
childhood viral illnesses - mumps/rubella, infectious hepatitis, mono, lymphocytic leukemia, multiple myeloma, radiation
what are some causes of lymphocytosis?
Monocytosis
increase in monocytes (>2-8%)
chronic inflammatory disorders, UC, malaria, TB, mono
what are some causes of monocytosis?
Eosinophilia
increase in eosinophils (>1-4%)
allergic conditions, asthma, eczema, parasite infections, autoimmune diseases
what are some causes of eosinophilia?
Basophilia
increase in basophils (>0.5-1%)
allergic conditions, myeloproliferative diseases (ex: myelofibrosis), PV, leukemias
what are some causes of basophilia?
Leukopenia
deficiency of white blood cells
after bacterial/viral infections, medications (chemo, RA), autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus), vitamin deficiency (B12, iron), bone marrow failure, leukemia/cancer, hypersplenism
what are some causes of leukopenia?
Neutropenia
deficiency of neutrophils
(<55-70%)
aplastic anemia, overwhelming bacterial infections (esp. elderly), viral infections, radiation therapy, chemo, Addison disease
what are some causes of neutropenia?
lymphocytopenia
deficiency of lymphocytes (<20-40%)
leukemia, sepsis, SLE and other immune diseases, late stage HIV, adrenocorticosteroids, radiation therapy
what are some causes of lymphocytopenia?
Monocytopenia
deficiency of monocytes (<2-8%)
aplastic anemia, hairy cell leukemia, prednisone
what are some causes of monocytopenia?
eosinopenia
deficiency of eosinophils
(<1-4%)
increased adrenosteroid production
what are some causes of eosinopenia?
Basopenia
deficiency of basophils
(<0.5-1%)
acute allergic reaction, hyperthyroidism, stress
what are some causes of basopenia?
Neutrophils (PMNs)
which WBC has the function of phagocytosis?
produced in 7-14 days, circulate for ~6 hours
what is the life cycle of neutrophils?
Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC)
helpful in determining the patients risk for infection
WBC x (%neutrophils + %bands or immature neutrophils)
how do we calculate ANC?
1000
An ANC value of what would indicate severe immunocompromised/high risk for infection?
band cells
immature neutrophils, unsegmented nuclei
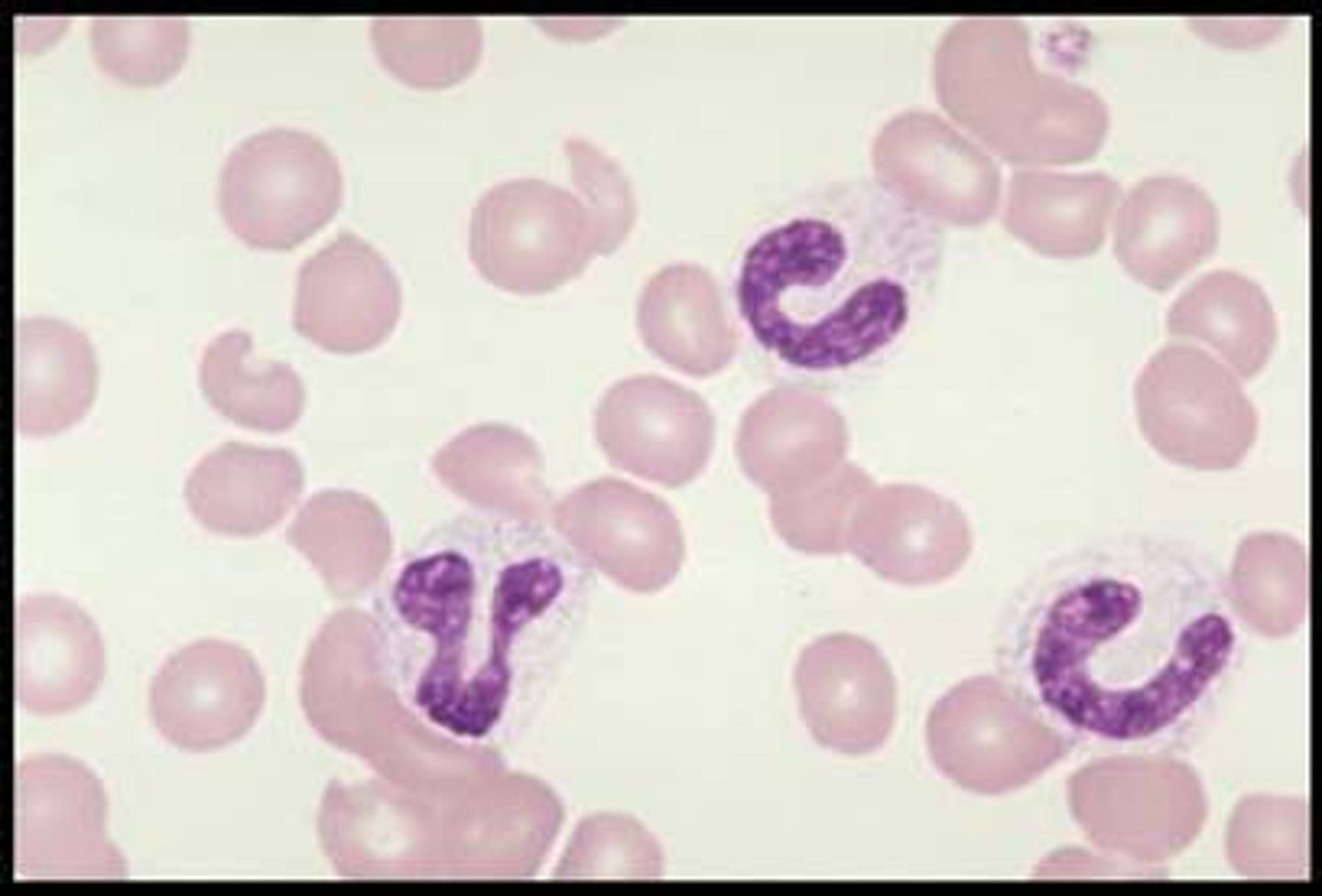
~0-3%
what is the normal value of band cells?
left shift
neutrophil production is stimulated, early immature forms of neutrophils enter circulation
(Band/stab cells)
increased number of band cells = ?
ongoing acute bacterial infection
toxemia, hemorrhage, myeloproliferative disorders
what would a left shift indicate?
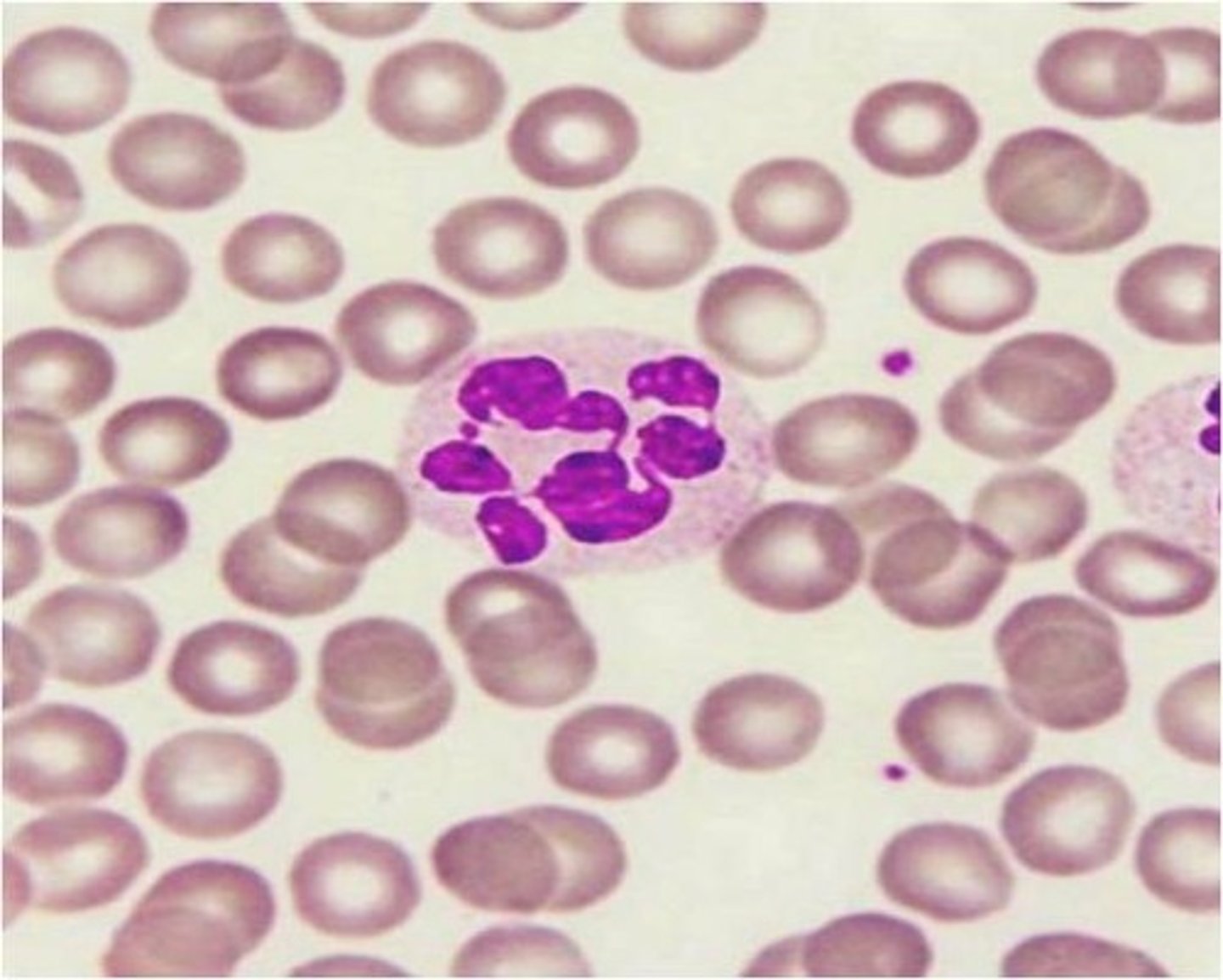
right shift
increased numbers of hypersegmented neutrophils (bone marrow issue), 5+ nuclear lobes, reduced number of bands or stab cells (folic acid or B12 deficiency)
increased number of neutrophils = ?
Megaloblastic anemia (fat RBCs), liver disease, chronic infections/inflammation, glucocorticoid use/Cushing's syndrome, radiation, chemo
what would a right shift indicate?
megaloblastic anemia
red blood cells are larger than normal
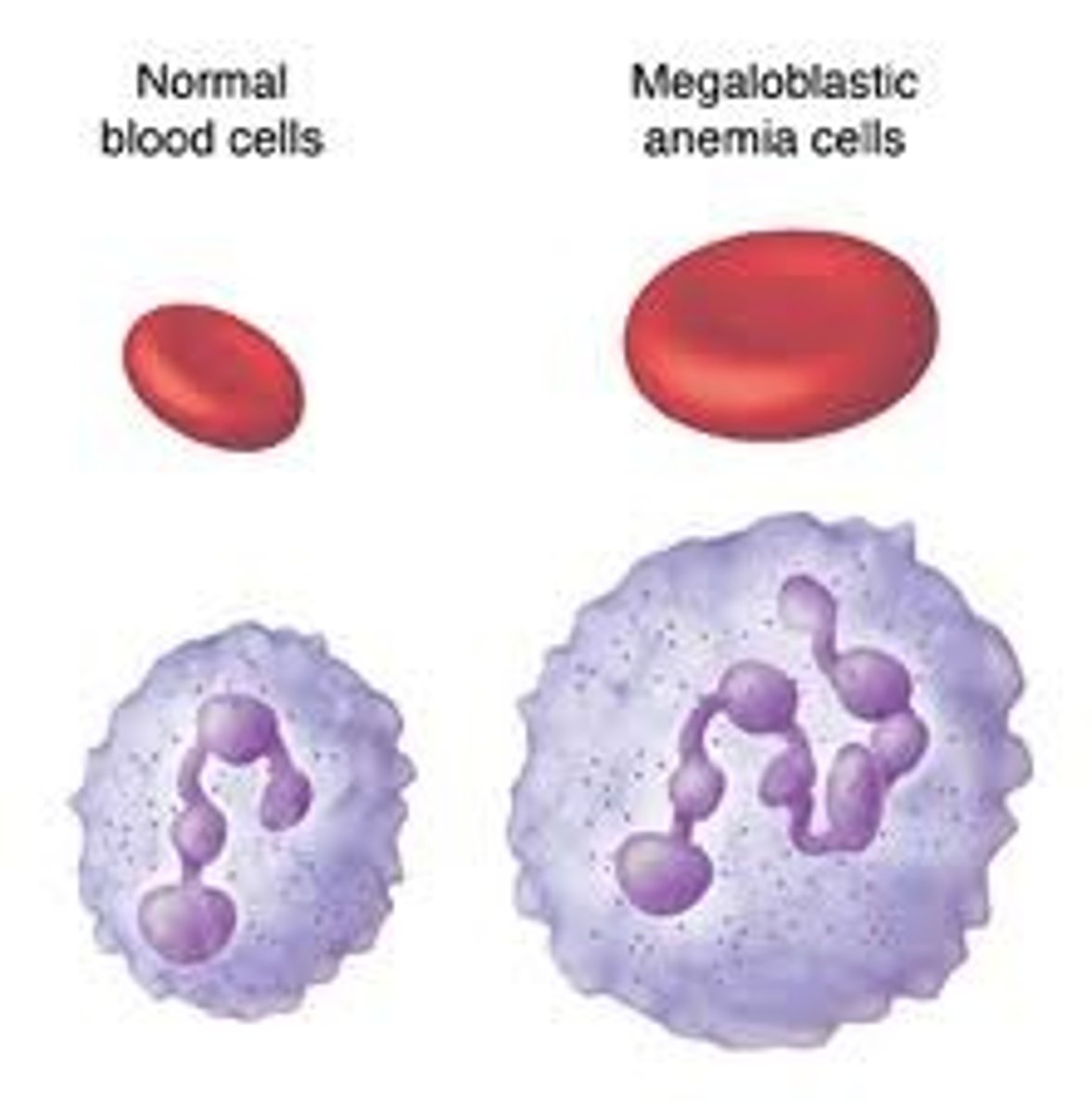
Hypersegmented neutrophils
in megaloblastic anemia, these cells have six or more lobes, and tapering chromatin strands
hemoglobin (HGB), hematocrit (HCT), RBCs, mean corpuscular volume (MVC), RBC distribution width (RDW), WBCs, platelets
What are the components of a CBC test that we care about?
neutrophil, lymphocyte, monocyte, eosinophil, basophil
What are the components of the differential test that we care about?
carry oxygen to remove CO2 from cells
how to explain RBCs to patients?
fight infections
how to explain WBCs to patients?
clot the blood, stop bleeding
how to explain platelets to patients?
iron that carries oxygen in the blood
how to explain hemoglobin to patients?
a measure of the amount of space that RBCs take up in the blood
how to explain hematocrit to patients?
average volume/size of RBCs
how to explain mean corpuscular volume (MCV) to patients?
anemia, dehydration, bleeding
what can abnormal RBC numbers mean?
infection, blood cancer, immune system issue
what can abnormal WBC numbers mean?
bleeding, clotting disorder
what can abnormal platelets mean?
blood disorders
what can abnormal hemoglobin levels mean?
blood, bone marrow disorders
what can abnormal hematocrit levels mean?
anemia, thalassemia
what can abnormal mean corpuscular volume (MCV) levels mean?