Unit 10- Benign Tumors + Renal Disease
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What are characteristics of a Benign Renal Adenoma?
Asymptomatic
Well defined
Hyperechoic to hypoechoic masses
Calcifications in renal cortex
Hypovascular
What are the sonographic findings for an Oncocytoma?
Well defined mass of epithelial cells
Hypoechoic
Homogenous
Spoke wheel pattern of enhancement with central scar
Adenomas and Oncocytomas can resemble malignant tumors, but the sonographer should not rule out ____ as a possibility
RCC
What is an Angiomyolipoma (AML)
Most common benign renal tumor
Contains fat, muscles, and vessels
More common in females
US Appearance of an Angiomyolipoma (AML):
Focal, solid
Hyperechoic
Well defined borders
Posterior acoustic enhancement
Solitary (usually)
Multiple or bilateral-
Tuberous sclerosis
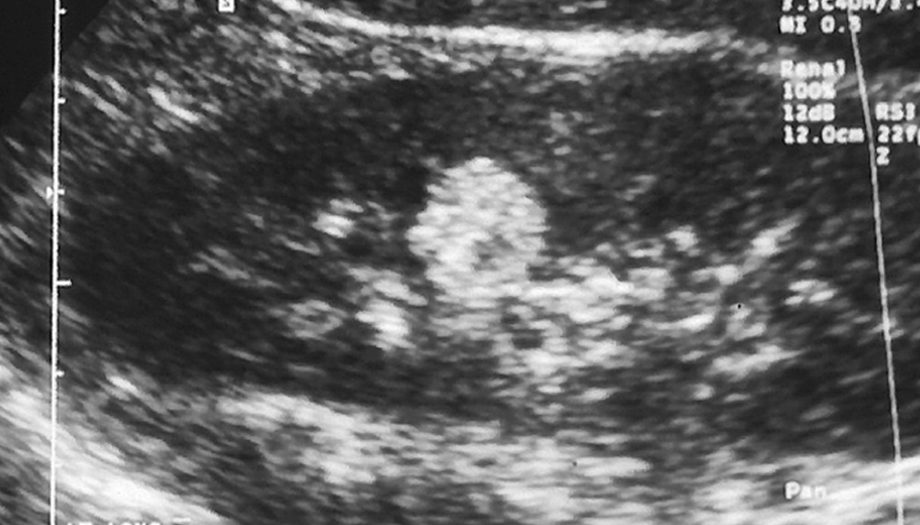
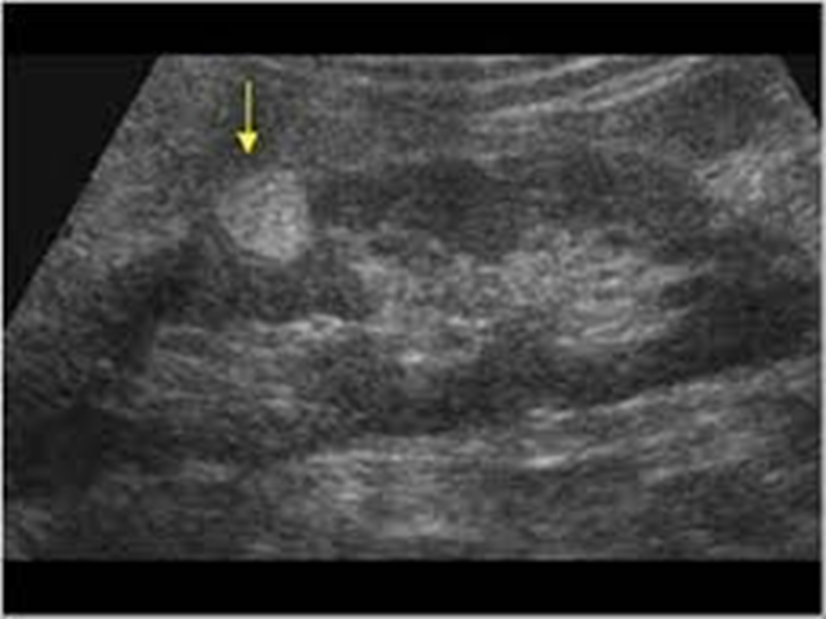
What are these images showing?
Angiomyolipoma
What are the characteristics of a Lipoma?
Consists of Fat cells
Females >Males
Asymptomatic
Normal Lab values
May cause hematuria
What is the sonographic appearance of a Lipoma?
Well- defined
Echogenic
What are the Differential Diagnosis of a Lipoma?
Fibromas
Adenoma
Angiomyolipoma
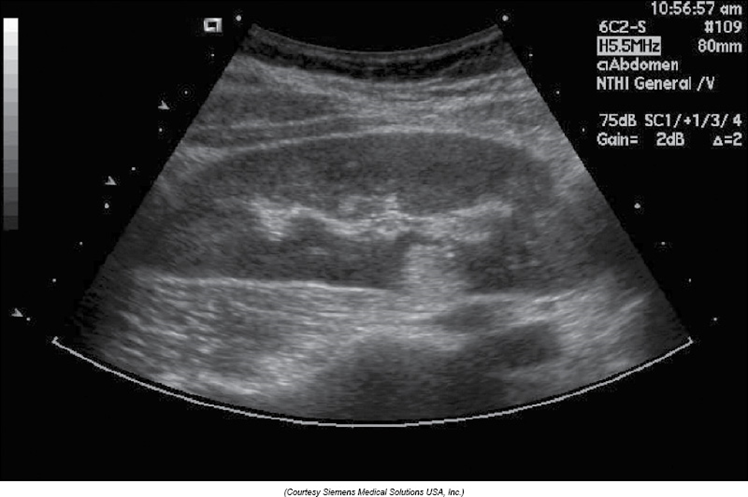
What is this image showing?
Lipoma
What is Group 1 Intrinsic Renal Disease?
Generalized increase in cortical echoes
Results from deposition of collagen & fibrous tissue
What Diseases are included in Group 1 intrinsic renal disease?
Interstitial Nephritis
Acute Tubular Necrosis
Amyloidosis
Diabetic Nephropathy
Lupus
Myeloma
What is Group 2 Intrinsic Renal Disease?
Loss of Anatomic Detail
Cortex & medullary regions
Indistinguishable
What diseases are included in Group 2 Intrinsic Renal Disease?
Chronic pyelonephritis
Renal tubular ectasia
Acute bacterial nephritis
What is seen with end-stage renal disease and renal atrophy?
Increased echogenicity
Decreased in Size
Cortical thickness <5mm
What is seen with Acute renal disorders?
Renal enlargement
Decreased parenchymal echogenicity
Interstitial edema
Renal vein thrombosis
Pyelonephritis
Renal-transplant rejection
What is Acute Glomerulonephritis?
Necrosis &/or proliferation of cellular elements in glomeruli
Results in enlarged & poorly functioning kidneys
Secondarily affected:
Vascular elements
Tubules
Interstitium
US Appearance of Acute Glomerulonephritis?
Increased cortical echoes
Normal to enlarged kidneys
Normal medulla
What are the symptoms of Acute Glomerulonephritis?
Nephrotic Syndrome
HTN
Anemia
Peripheral Edema
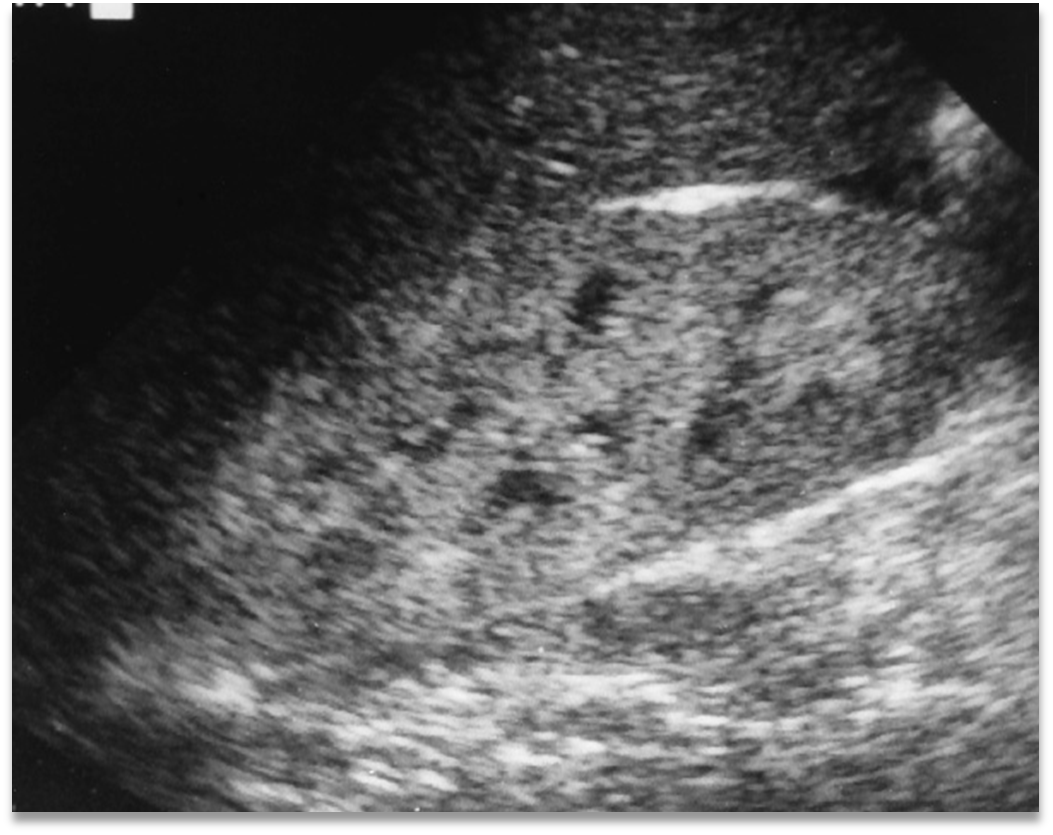
What is this image showing?
Acute Glomerulonephritis
What is Acute Interstitial Nephritis?
Associated with infectious/inflammation processes:
Scarlet fever
Diphtheria
Allergic reaction
What are the symptoms of Acute Interstitial Nephritis?
Azotemia
Rash
Fever
US appearance of Acute Interstitial Nephritis?
Enlarged + mottled kidneys
Increased cortical echogenicity
What is Lupus Nephritis?
Connective Tissue Disorder – results from an abnormal immune system
Females > Males
20 – 40 years of age
50% involve kidneys
What are the renal manifestations of lupus nephritis?
Hematuria
Proteinuria
HTN
Renal Vein Thrombosis
Renal insufficiency
US appearance of Lupus Nephritis:
Increased cortical echogenicity
Renal Atrophy
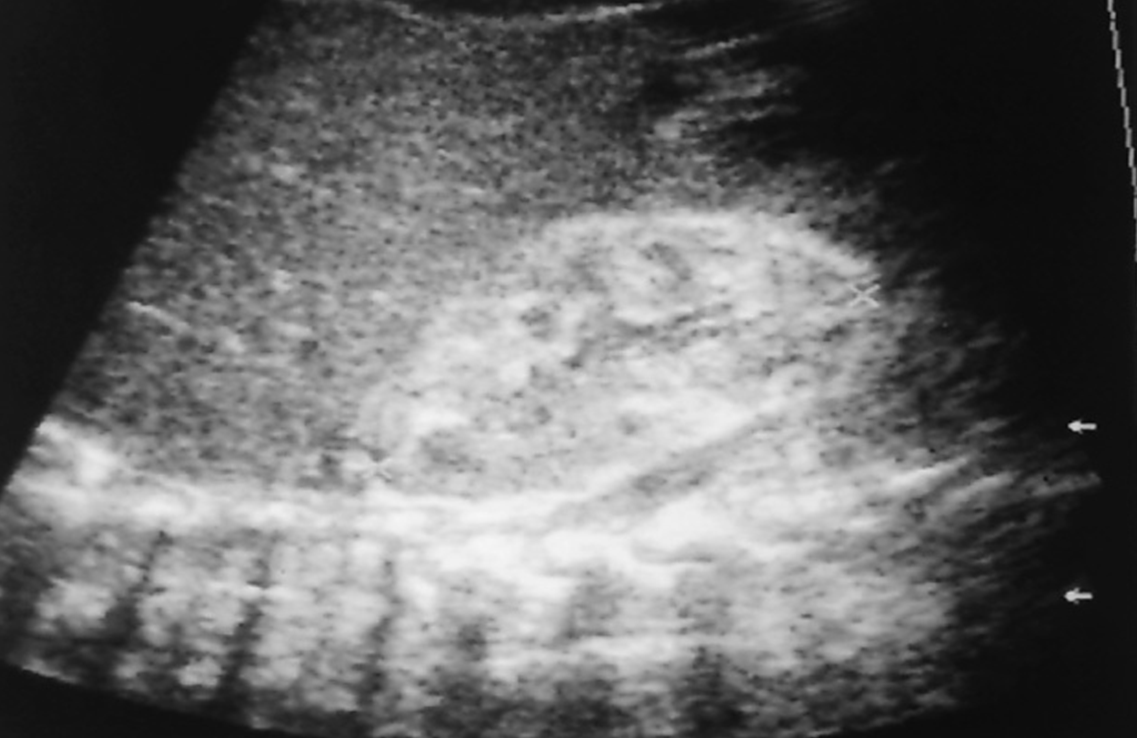
What is this image showing?
Lupus Nephritis
What are the Renal Dysfunction indicators of AIDS
Uremia
Azotemia
Acute tubular necrosis
Nephrocalcinosis
Interstitial nephritis
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
US appearance of AIDS affecting the kidney:
Kidneys normal size to enlarged
Echogenic parenchyma
Increased cortical echogenicity
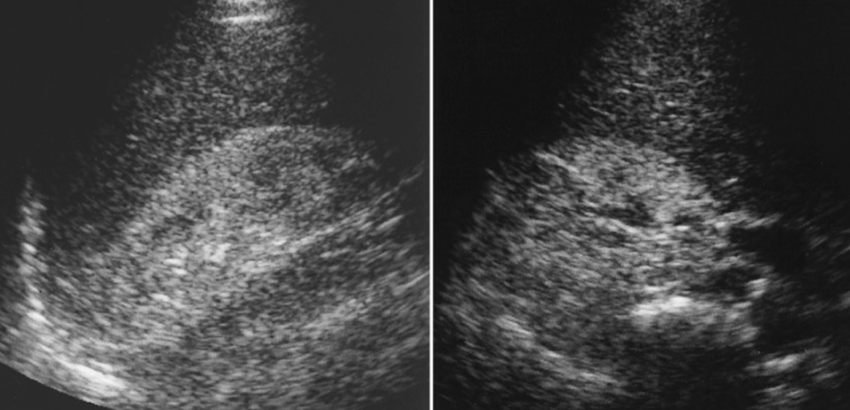
What is this image showing?
AIDS in the Kidney
Renal Involvement is common in _____ ____ _________
Sickle Cell Nephropathy
Renal involvement with Sickle Cell Nephropathy includes:
Glomerulonephritis
Renal vein thrombosis
Papillary necrosis
Hematuria
US appearance of Acute Sickle Cell Nephropathy:
Acute (0-4 days) renal vein thrombosis
Enlarged kidneys
Decreased echogenicity
US appearance of Subacute Sickle Cell Nephropathy:
Subacute (4-14 days) thrombosis
Enlarged kidneys
Increased cortical echogenicity
With Sickle Cell Nephropathy, diagnosis is specific if _______ is seen:
Thrombosis
What is Hypertensive Nephropathy?
Uncontrolled HTN
Progressive renal damage
Azotemia
US appearance for Hypertensive Nephropathy:
Small kidneys with smooth borders
Scarring
Lobar infarction
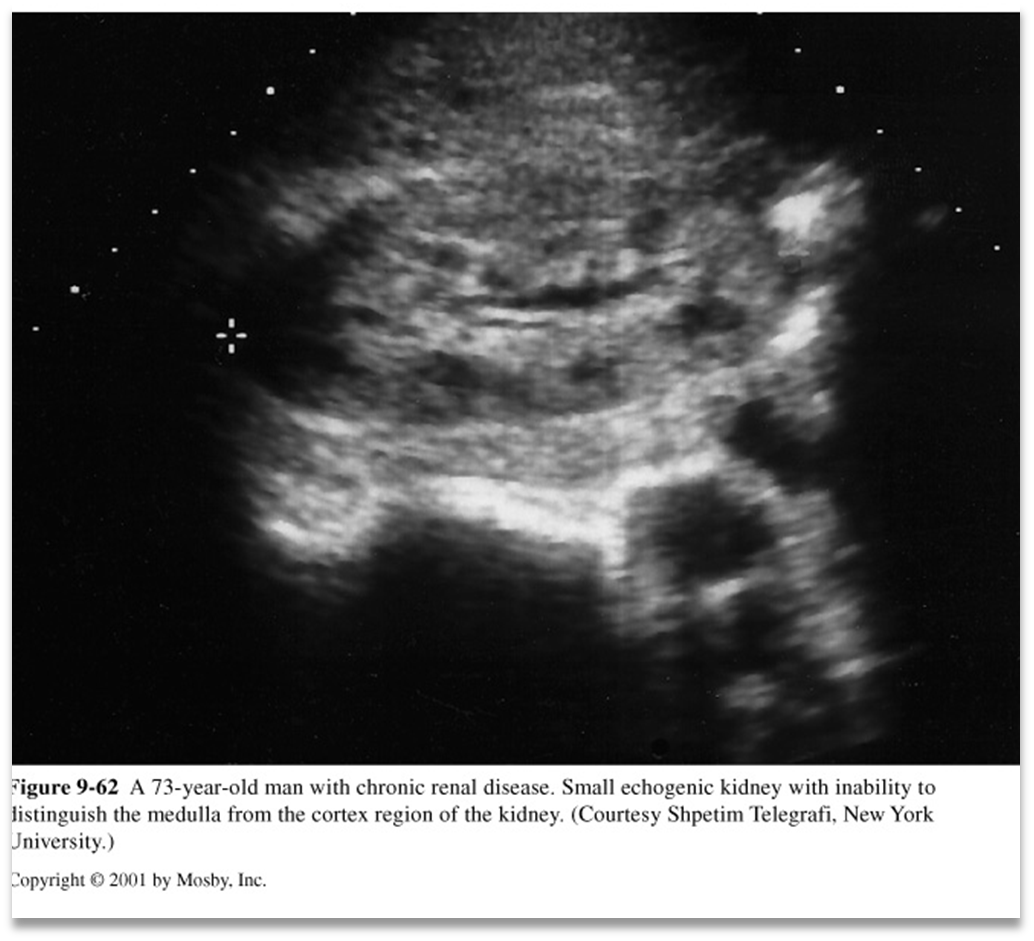
What is this image showing?
Hypertensive Nephropathy
What is Papillary Necrosis (Condition)
•Papilla swells & communication with calyceal system occurs
•Papilla may calcify
•Papilla may slough into collecting system
What are the causative factors of papillary necrosis?
**Diabetes*
Analgesic abuse
UTI
RV Thrombosis
Prolonged hypotension
Urinary tract obstruction
Dehydration
Sickle cell anemia
Tuberculosis
Renal transplant
What are the symptoms of Papillary Necrosis?
Hematuria
Flank pain
Dysuria
Fever
HTN
Acute renal failure
US appearance of Papillary Necrosis:
Fluid spaces at cortical-medullary junction corresponding to pyramid distribution
Round or triangular shaped
Mimics calculi
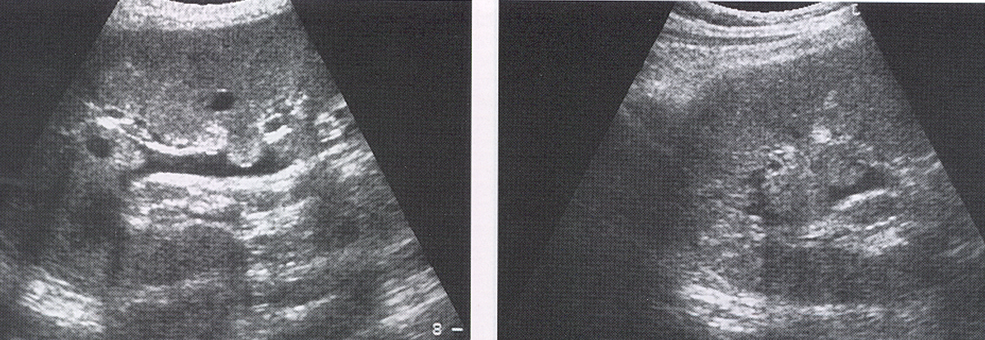
What is this image showing?
Papillary Necrosis
What is renal atrophy?
Intrarenal anatomy is preserved with uniform loss of renal tissue
US appearance of Renal Atrophy?
Smaller Kidneys
Highly enlarged renal sinus
Thin cortical rim
< 5mm is abnormal
Renal ______ ________ occurs secondary to renal atrophy
Sinus Lipomatosis
Renal Sinus Lipomatosis US appearance:
Enlarged kidneys
Highly echogenic & enlarged renal sinus
Thin cortical rim
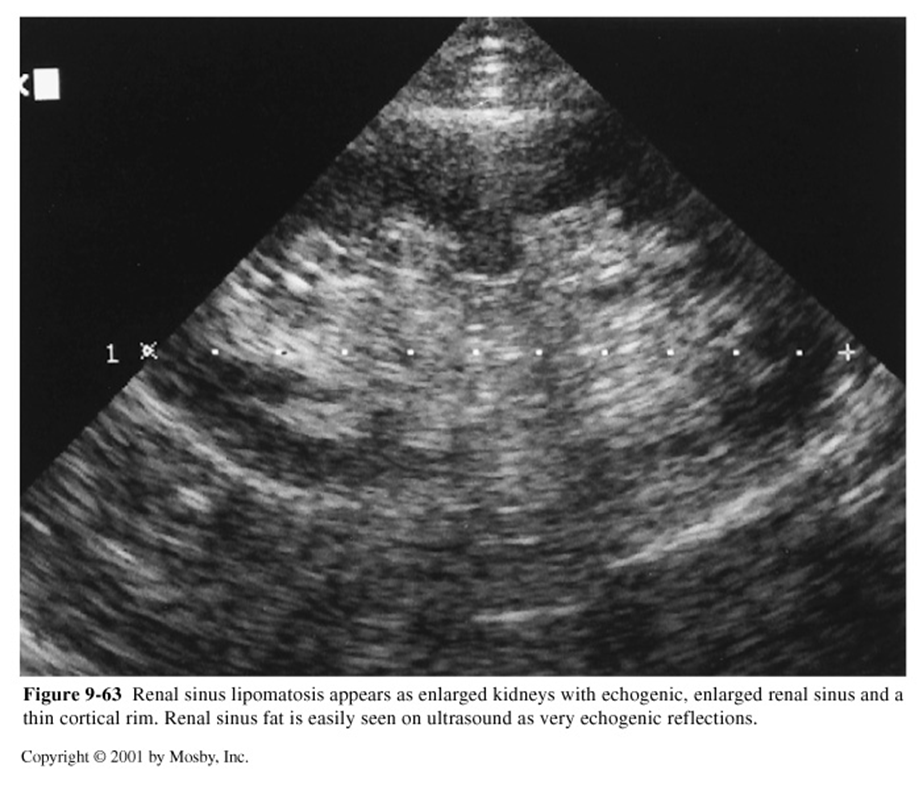
What is this image showing
Renal Atrophy Sinus Lipomatosis