CIE A Level Physics: Atomic Structure and Radioactive Decay Processes (Chapter 11.1)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Alpha-particle Scattering Experiment
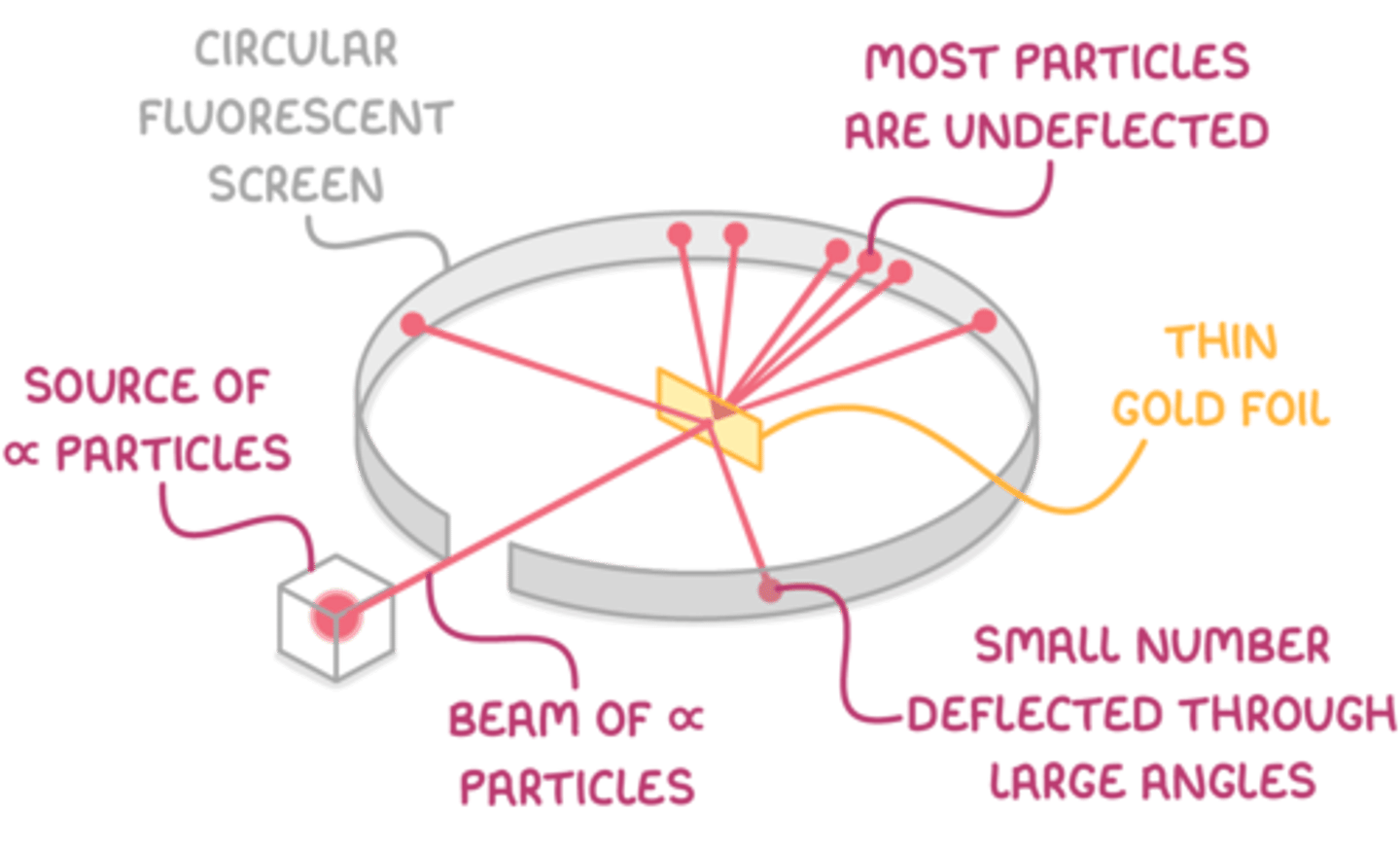
Evidence for the structure of the atom was discovered by Ernest Rutherford in the beginning of the 20th century from the study of α-particle scattering.
α-particles
The nucleus of a helium atom and are positively charged.
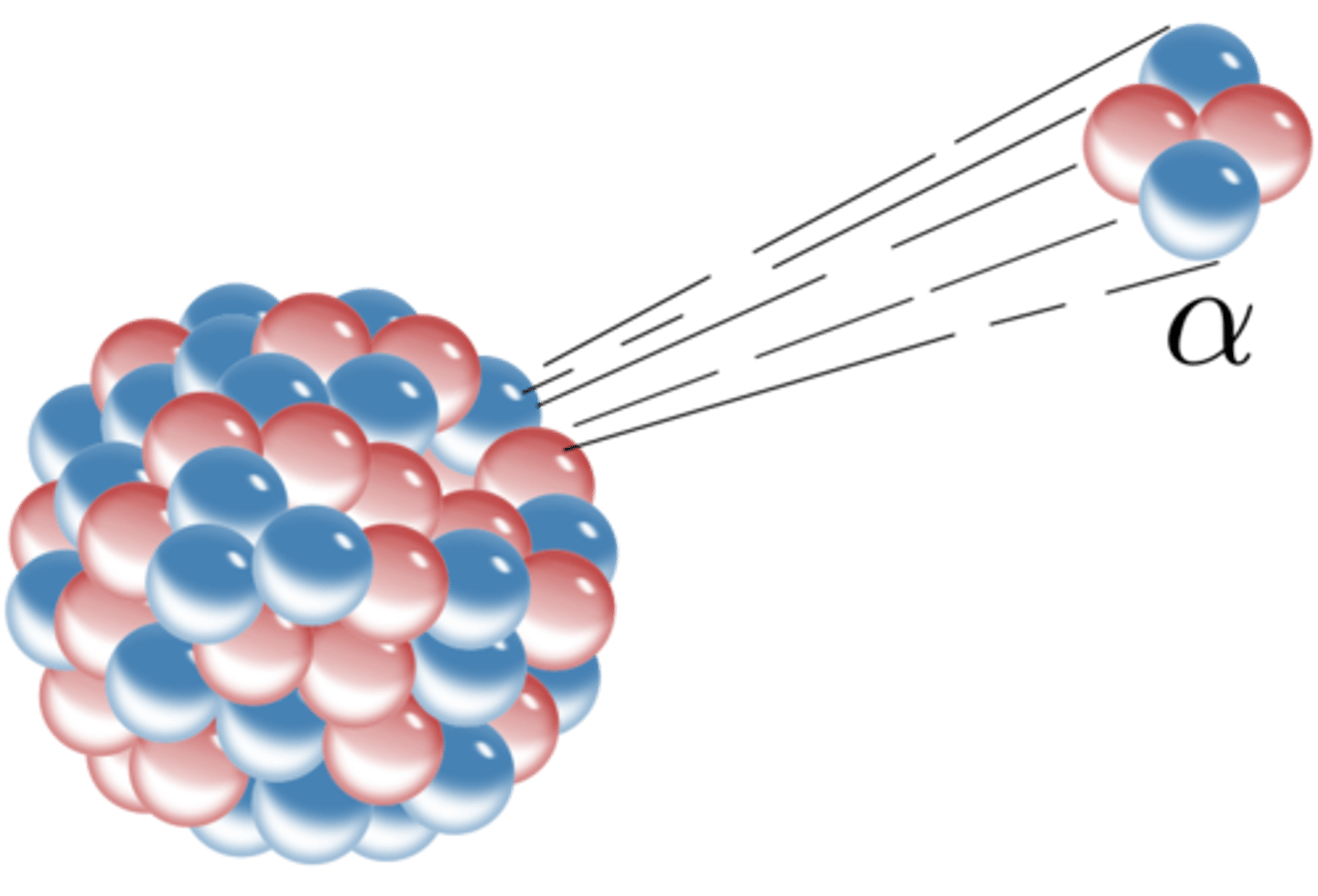
Deflection patterns of α-particles
When α-particles are fired at thin gold foil, most of them go straight through but a small number bounce straight back.
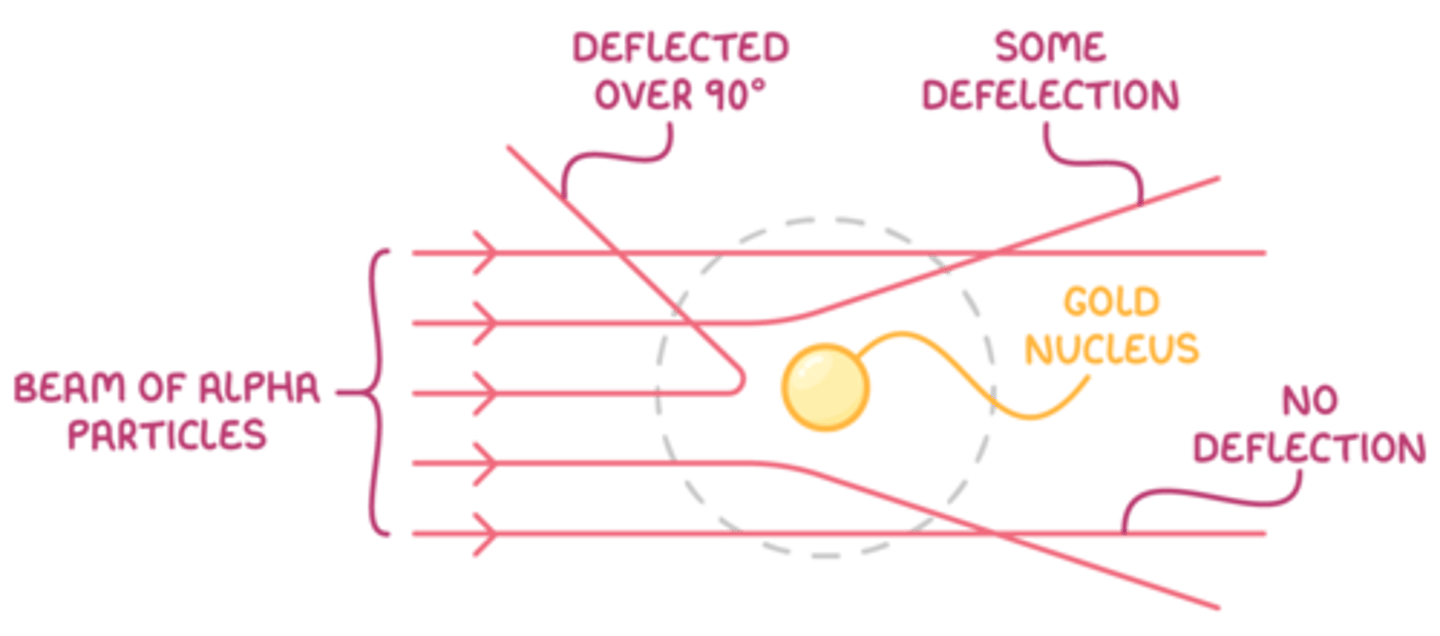
Conclusion from Rutherford's experiment
Atoms consist of small dense positively charged nuclei, surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
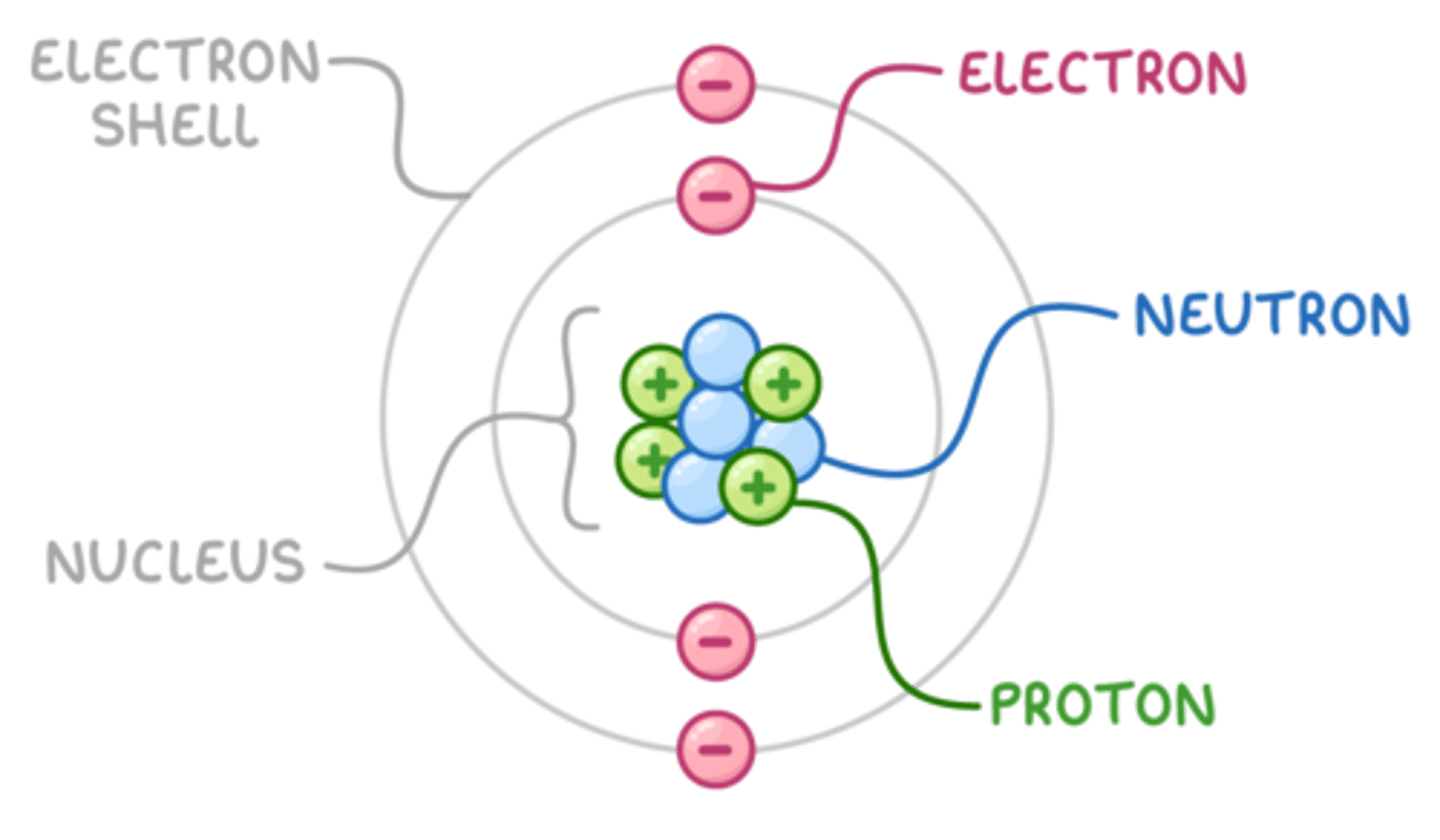
Structure of an atom
A small positive nucleus, surrounded by negative electrons.
Size comparison of atom and nucleus
The atom is around 100,000 times larger than the nucleus.
Stable atom
A stable atom is neutral (it has no charge).
Antimatter
Antimatter particles are identical to their matter counterpart but with the opposite charge.
Atomic mass unit (u)
The unified atomic mass unit (u) is roughly equal to the mass of one proton or neutron: 1 u = 1.66 × 10−27 kg.
Mass of an atom in a.m.u
It is roughly equal to the sum of its protons and neutrons (nucleon number).
Nucleon number
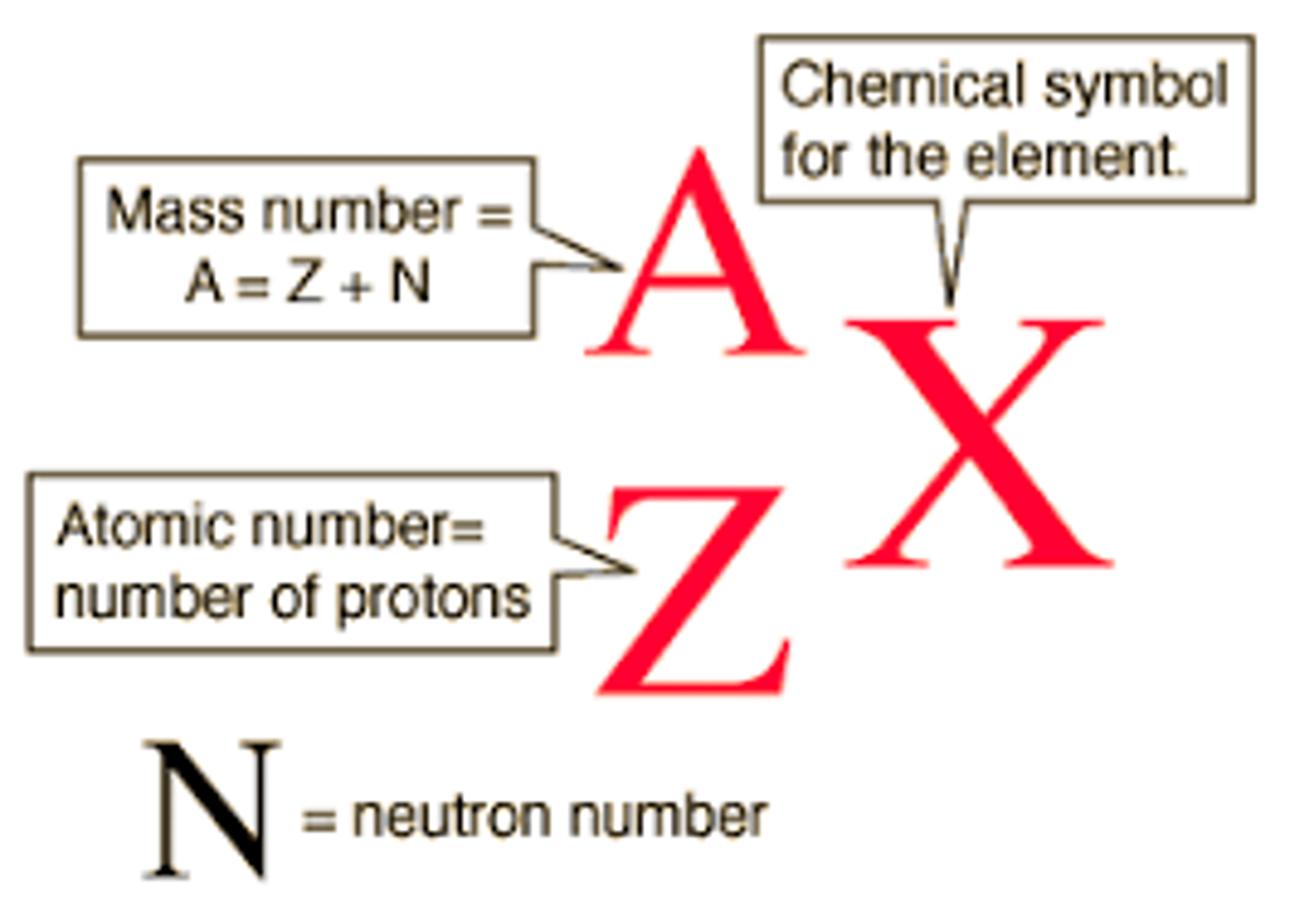
The mass number is the number of particles in the nucleus, which contains protons plus neutrons.
Atomic number
The number of protons in the atom.
Determining proton number
The atomic number
Nuclide notation
The nuclide notation of an element is used to describe the constituents of the nuclei.
Graph of n with θ
The largest value of n will therefore be at small angles, and n drops quickly with increasing angle of deflection θ.
Alpha particle mass
Alpha (α) has a mass of 4 u.
Isotope
Atom with same protons, different neutrons.
Deuterium
Isotope of hydrogen with one neutron.
Tritium
Isotope of hydrogen with two neutrons.
Nucleon Number
Total number of protons and neutrons.
Proton Number
Total number of protons in nucleus.
Radiation
Energy emitted during nuclear decay.
Beta Particle
High energy electron emitted from nucleus.
Gamma Ray
High energy electromagnetic radiation.
Radioactive
Nuclei that emit radiation to stabilize.
Fission
Splitting of a nucleus into smaller nuclei.
Fusion
Combining of nuclei to form a heavier nucleus.
Conservation of Nucleon Number
Total nucleons must equal in nuclear reactions.
Nucleus
Central part of an atom containing protons and neutrons.
Decay
Process of unstable nuclei emitting radiation.
Ionising Radiation
Radiation that can remove electrons from atoms.
Penetration Power
Ability of radiation to pass through materials.
Alpha Decay
Emission of an alpha particle from a nucleus.
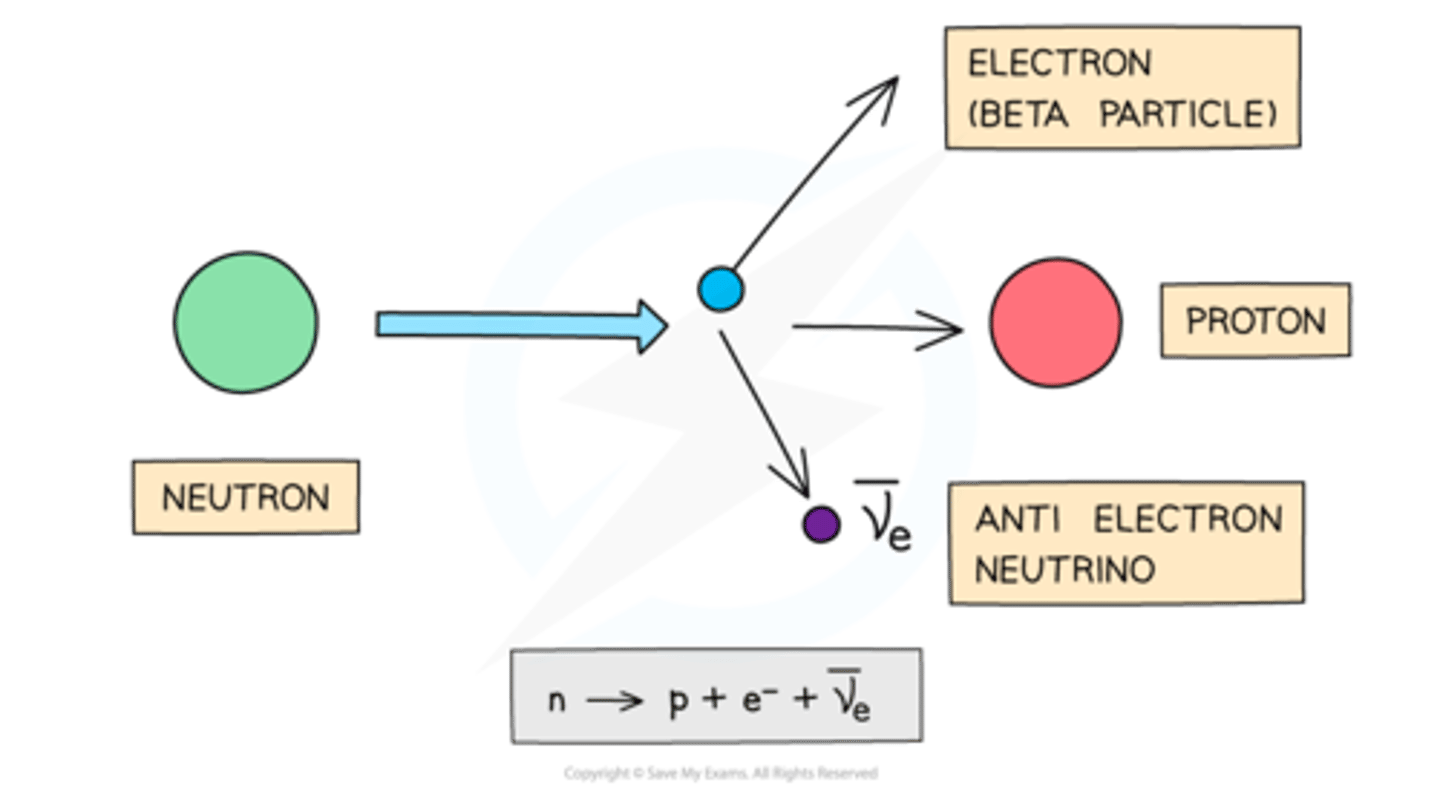
Beta-minus Decay
Neutron converts to proton, emitting electron.
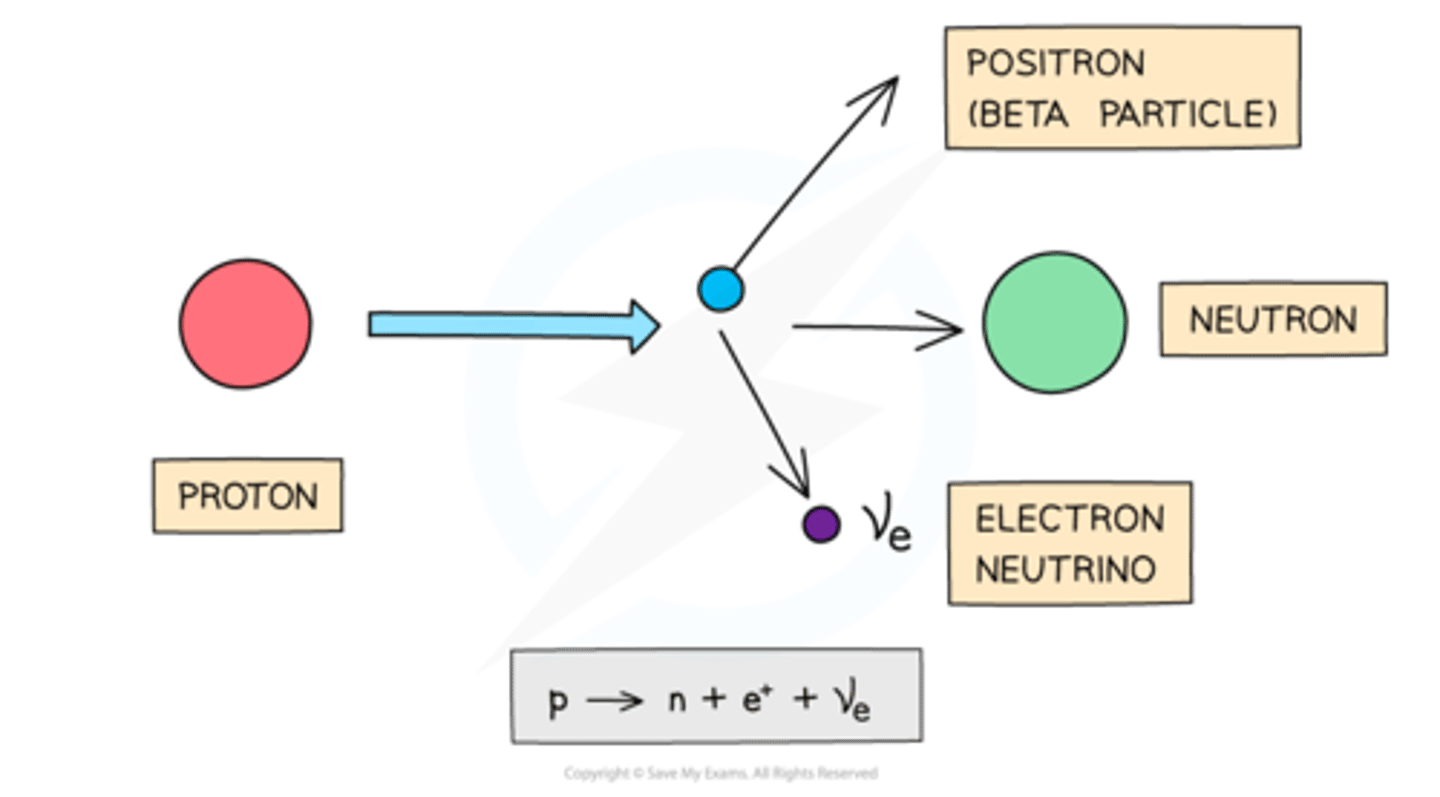
Beta-plus Decay
Proton converts to neutron, emitting positron.
Anti-electron Neutrino
Particle emitted during beta-minus decay.
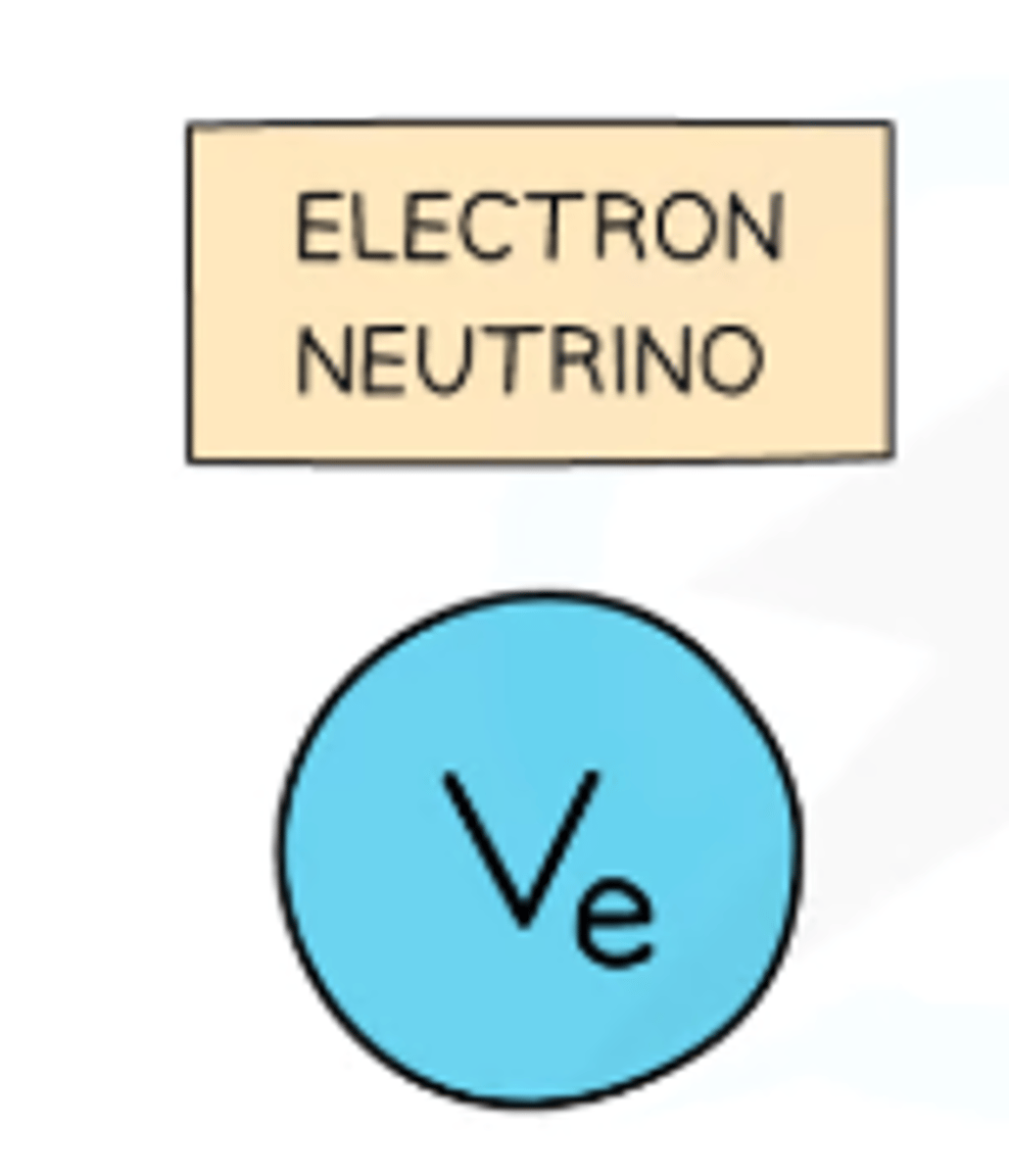
Electron Neutrino
Particle emitted during beta-plus decay.
Aluminium Foil
Material that can stop beta particles.
Range of Alpha Particles
A few centimeters in air.
Range of Beta Particles
20 cm to 3 m in air.
Ionisation
The process by which radiation knocks out electrons from atoms, causing chemical changes and potential damage to living cells.
Beta minus particle (β )
An electron emitted during beta minus decay, with a mass of 0.0005 u and a charge of -1.
Beta plus particle (β )
A positron emitted during beta plus decay, with a mass of 0.0005 u and a charge of +1.
Gamma radiation (γ)
An electromagnetic wave with no mass and no charge, traveling at the speed of light.
Charge of the electron (e)
1.60 × 10^-19 C.
Speed of light (c)
3 × 10^8 m/s.
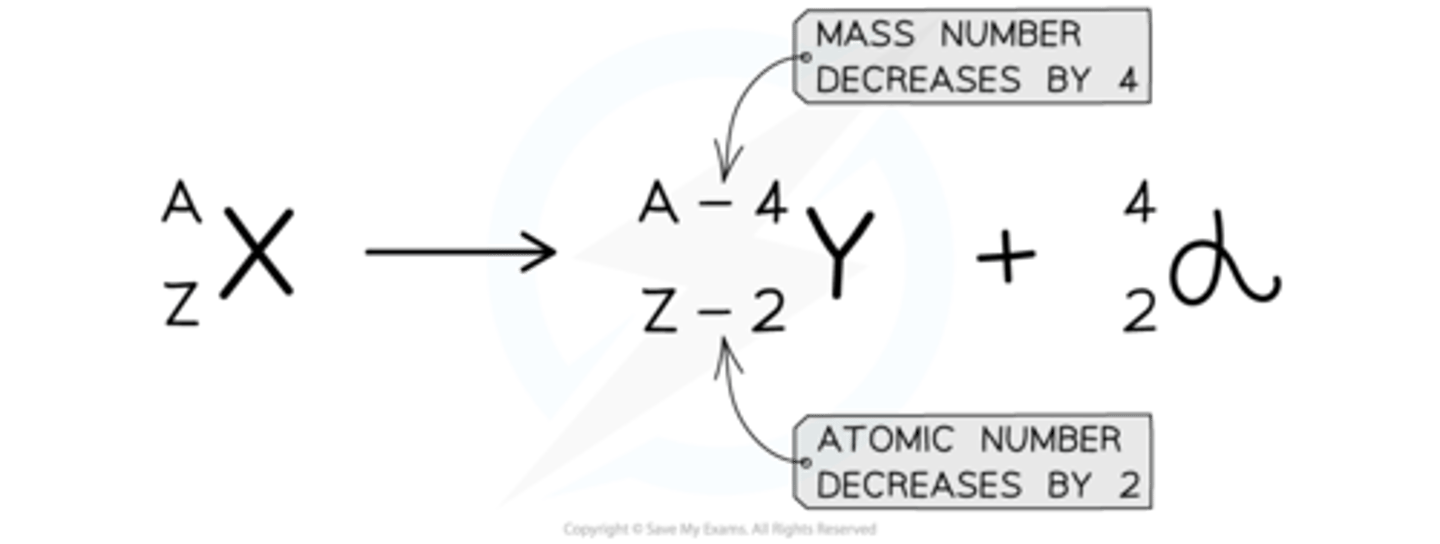
Alpha decay
A decay process common in large, unstable nuclei where an alpha particle is emitted, reducing the nucleon number by 4 and the proton number by 2.
Decay equation for beta-minus decay
AX → AY + 0β + 0⎯⎯ve.
Decay equation for beta-plus decay
AX → AY + 0β + 0ve.
Decay equation for alpha decay
AX → AZ−4 + 4α.
Daughter nucleus
The new nucleus formed after a radioactive decay process.
Neutrino
A subatomic particle with no charge and negligible mass, emitted during certain types of decay.
Anti-neutrino
The antiparticle of a neutrino, produced during beta minus decay.
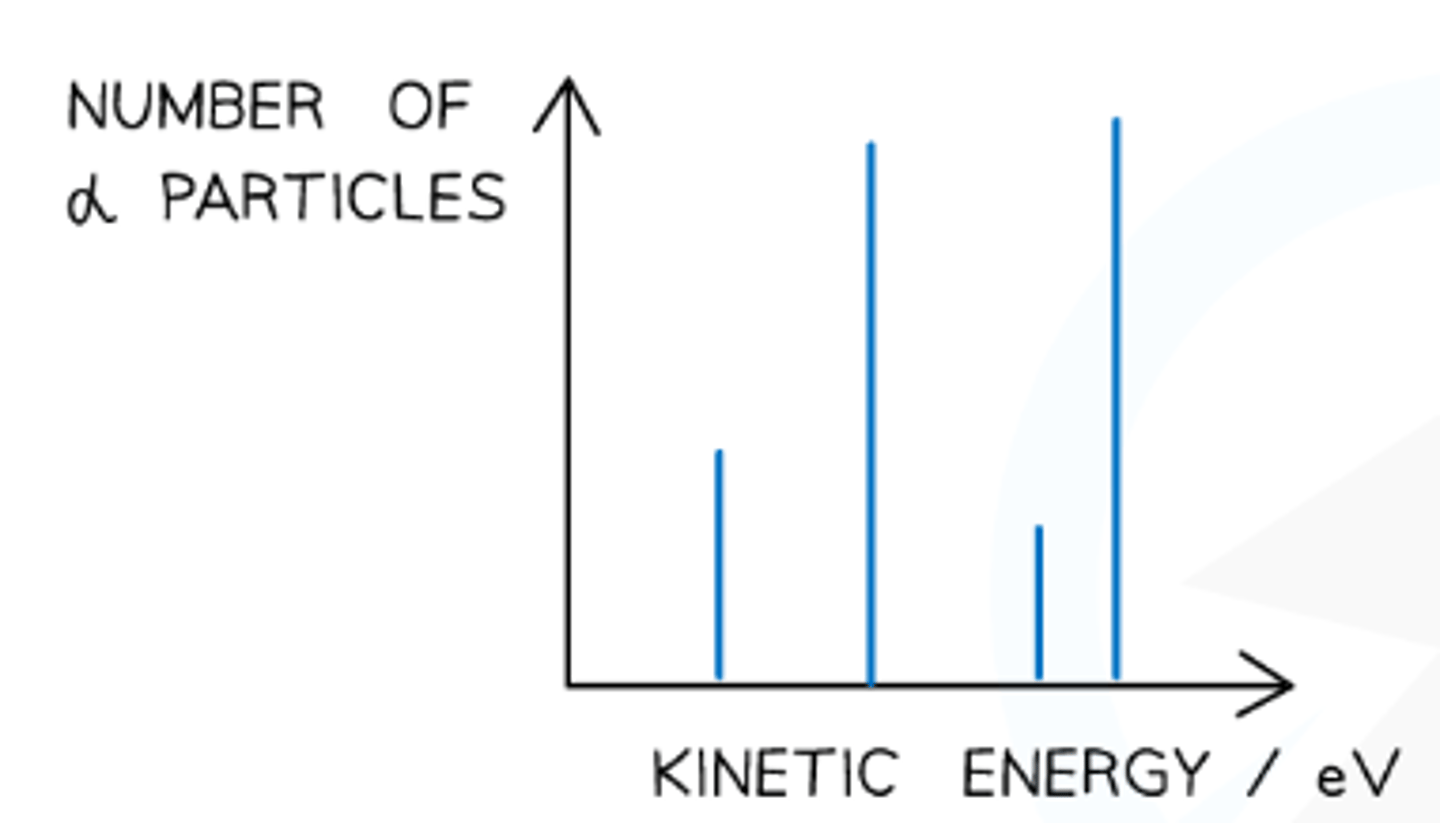
Energy of alpha particles
Alpha particles have discrete energy levels, resulting in spikes when plotted against kinetic energy.
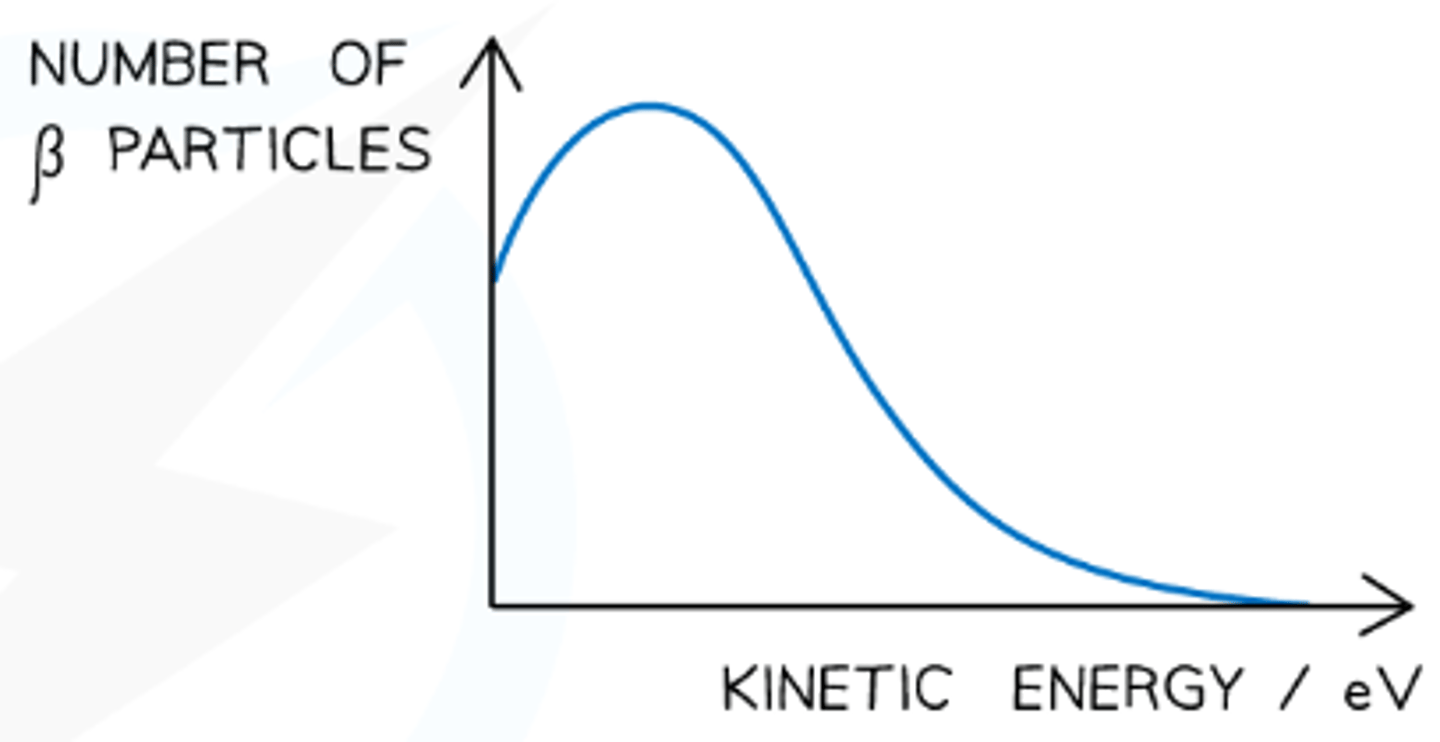
Energy of beta particles
Beta particles have a continuous range of energies, demonstrated by a curve when plotted against kinetic energy.
Conservation of momentum and energy
A principle that applies in both alpha and beta emission.
Proton number
The number of protons in a nucleus, which determines the element.
Determining nucleon number
Subtract the proton number from the nucleon number