Brain Anatomy Parts 2 & 3 (Week 1, Mod 8)
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What is the meninges of the skull and spinal cord?
A three layered membranous sheet that covers the brain and spinal cord
Arrangement of meninges is different between skull and vertebral column
Same layers but different attachments to surrounding structures
What are the 3 layers of the meninges, from inside to outside? What are the names of the 3 spaces BETWEEN the layers?
Meninges layers: PAD
Pia mater (innermost, comes into contact with the CNS)
Arachnoid mater
Dura mater (outermost)
Spaces BETWEEN layers:
Epidural space (between bone (skull) and dura)
Subdural space (between dura and arachnoid)
Subarachnoid space (between arachnoid and pia) - CONTAINS CEREBRAL FLUID
Describe the spinal cord’s meningeal arrangement… what is the dura’s interaction with the periosteum of the spine like?
In spinal column dura is a free tube
Dura merges with periosteum at foramen
Separation from periosteum is at foramen magnum
Though continues along floor of C1/C2
What is the meningeal arrangement in the skull? How is it different from the arrangement of the meninges in the spine?
In the skull:
Dura contributes to the inner periosteum, fusing the meninges directly to the skull bone (aka calvarium)
Epidural space doesn’t really exist here anatomically like it does in the spine
If it IS present, usually indicates something is wrong (dura should not be separating from the calvarium)
The dura ALSO contributes to the division between the two hemispheres of the brain; dips into the longitudinal fissure and the transverse fissure (divides cerebrum from cerebellum) of the brain
What is the cisternae magna of the meninges?
Is the largest of the subarachnoid cisterns, which is a fluid-filled space at the back of the brain containing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Is essentially an enlargement of the subarachnoid space
located below the cerebellum and above the medulla oblongata, crucial for CSF circulation, acting as a reservoir that connects to the spinal canal and fourth ventricle.
What 2 layers can the dura of the BRAIN be split into?
The two layers:
Outer layer remains fused to bone
Inner layer FOLDS BETWEEN THE MAJOR DIVISIONS OF THE BRAIN
Falx cerebri -
Is the dura fold that fills the longitudinal fissure
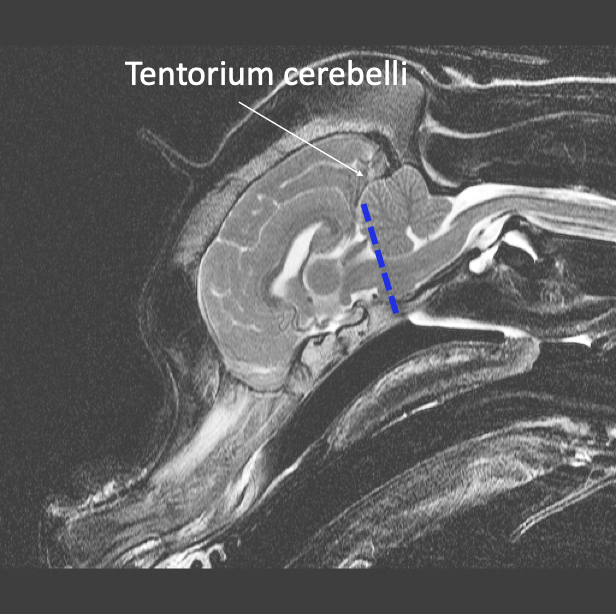
Tentorium cerebelli -
Dura that fills the transverse fissure
What is another adaptation of the brain’s dura?
The Diaphragma sellae
Dura that SURROUNDS STALK OF PITUITARY
Offers protection
What exactly is the “fossa” of the brain supposed to describe? What are the two kinds of “fossa” of the brain?
Fossa describes a VOLUME of the brain, not necessarily an anatomical structure
Is used for the division of the brain on a clinical, anatomical, and imaging basis
Is a straightforward way to describe the location of structures in tomographic images of the skull/brain
Is divided into the rostral fossa and the caudal fossa
Describe the rostral fossa… what is it composed of?
Caudal border
The rostral aspect of the cerebellum and a line connecting the touching point of the cerebellum with the brainstem to the rostral border of the pons
Forebrain
Cortex
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Mid brain (part of)
Cranial nerves
I and II (optic chiasm)
Ventricles
Lateral ventricles
Third ventricle
Describe the caudal fossa… what is it composed of?
Caudal border
line between most caudal point of the foramen magnum
Contents
Cerebellum
Mid-brain (part of)
Medulla oblongata
Majority of cranial nerves
III-XII
III course rostrally
Fourth ventricle (choroid plexus)
What does abnormal rostral and caudal fossa look like? What can happen as a result of this?
Chiari-like malformation
Usually brachycephalic dogs
Large brain and small skull
Alters CSF flow between brain and spinal cord
Can cause very severe symptoms