APHUG Module 1 Vocabulary
1/39
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
geography
where things are, why they're there and how they got there
human geography
studies how human activity affects or is influenced by Earth's surface
globalization
the process by which businesses and other organizations develop international influence or start operation on an international scale
sustainability
the group of practices that meet the needs of the present without compromising future generations ability to meet their needs
gender
a general term for the ways in which a society defines the differences between males and females
global citizen
a person who is aware of and understands the wider world and his/her place in it
culture
shared practices, techniques, attitudes and behaviors that a society transmits from one generation to the next
infrastructure
basic physical and organizational structures and facilities needed for the operation of a society
geographic literacy
general understanding of the geographic forces at work in the world
irrigation
process of harvesting water
spatial relationships
connections between two places
spatial representation
how those connections are demonstrated (ie. maps, charts, graphs)
map
2-D flat representation of a geographical area
cartographer
a person who makes maps
data aggregation
the process of collecting and organizing large amounts of information
spatial perspective
the placement or arrangement of objects on Earth's surface; also includes the space
time-distance decay
first law of geography; the idea that things nearby are more related than distant things, and interaction between two places decrease as they get further apart
map symbols
graphic elements that help organize the information in a map
legend
a key to the meaning of the symbols and colors on a map
compass rose
shows the four cardinal directions and map orientation
absolute direction
directions on a compass (NESW)
map scale
distance on a map in relation to the distance in actual space
scale
the territorial extent of an idea/object
absolute distance
the distance that can be measured with a standard unit of length
relative distance
a measurement of the level of social, cultural or economic similarity between places despite their absolute distance from each other
relative direction
direction described as position (left, right, forward, behind)
elevation
distance above sea level
isoline
a line that connects or links to different places that store a common or equal value
topographic map
a graphic representation of the 3-D configuration of Earth's surface
reference maps
an informational map that shows geographic locations on Earth's surface
thematic maps
a type of map that emphasizes the spatial patterns of geographic statistics or attributes and sometimes the relationship between them
choropleth maps
a thematic map that shows data aggregated for a specific geographic area, often using different colors to represent different values
proportional or graduated circle maps
a map that uses symbols (dots or circles) of different sizes to represent numerical values
dot density or dot distribution maps
a map that uses dots to represent objects or counts
map projection
the Earth's surface on a 2-D surface
Mercator Projection
a map projection useful for navigation because the lines connecting points on the map represent the true compass direction
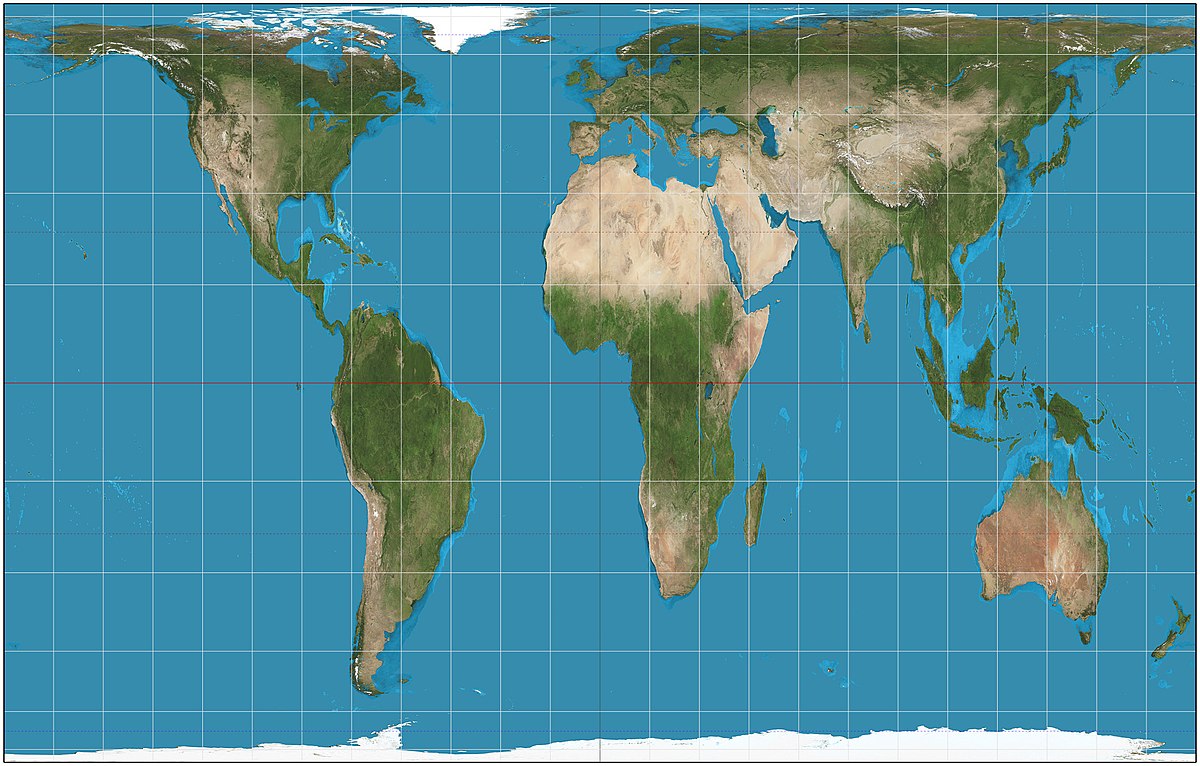
Peters Projection
a map projection that shows all land masses with their true areas but distorts their shape
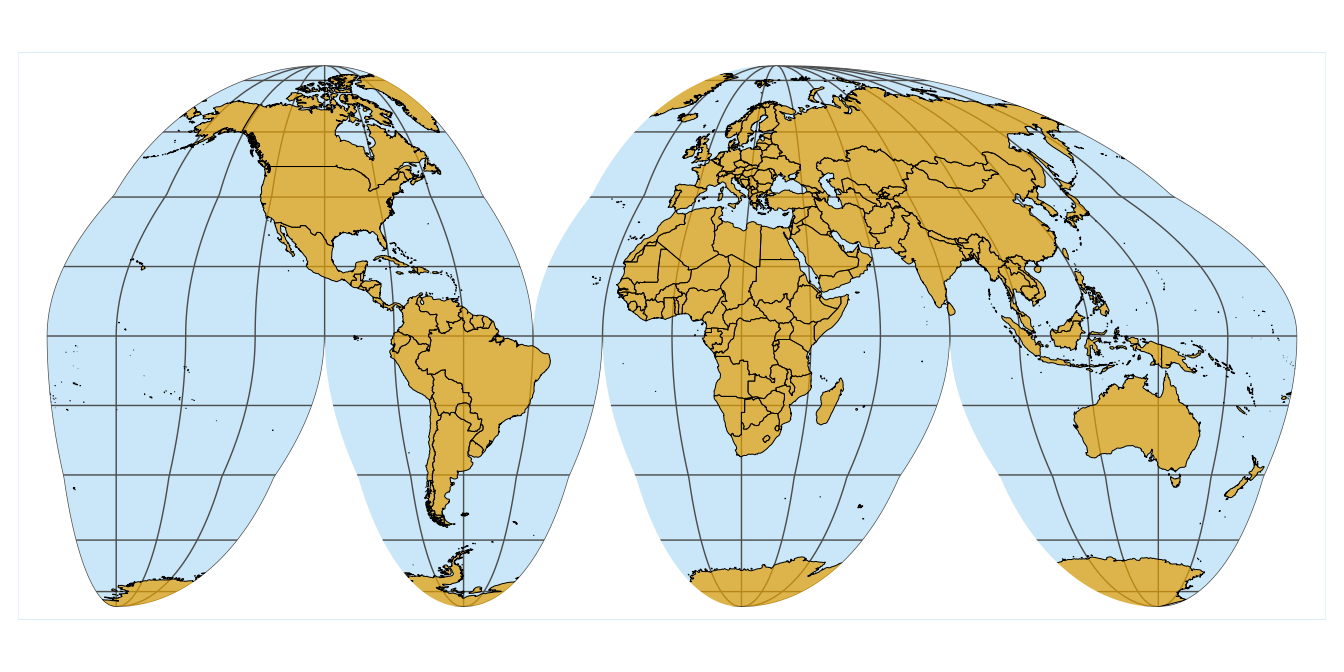
Goode Homolosine Projection
a map projection that avoids shape distortion and the restrictions of a rectangle map by creating “interrupts” in maps “continually"; map projection shown equally
Polar Projection
a map projection that looks down at Earth from the perspective of one of the poles
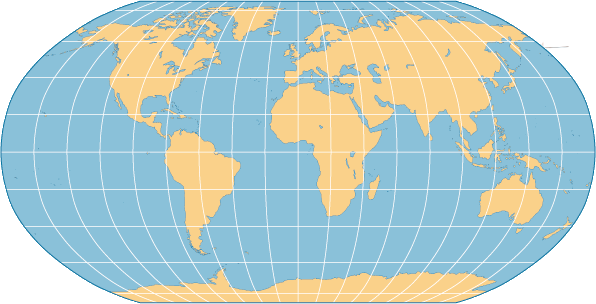
Robinson Projection
a map projection that attempts to create the most visually appealing representation of Earth by keeping all types of distortion relatively low over most of the map (typical map)