ess cell TAU
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
function of tau
Tau is a microtubule-
associated protein.
• Its function is to stabilize
microtubules
phosphorylation of tau
When Tau becomes
hyper-phosphorylated it
is unable to bind to
microtubules.
• The microtubules
become unstable and
disorganized.
• This leads to aggregates
of the Tau protein called
tangles.
• This leads to neuronal
death and degeneration
kinases and phosphates
Tau is a microtubule-associated protein (MAP) that plays a crucial role in stabilizing microtubules in neurons. Its function is regulated by phosphorylation, which is dynamically controlled by kinases (which add phosphate groups) and phosphatases (which remove them). Hyperphosphorylation of tau is a key feature of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease (AD), where tau aggregates into neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs).
hyperphosporylation and formation of NFTS
Under normal conditions, tau phosphorylation regulates its binding to microtubules, allowing dynamic assembly and disassembly. However, in pathological conditions, excessive phosphorylation (hyperphosphorylation) disrupts tau’s normal function.
Hyperphosphorylated tau becomes misfolded and aggregates into paired helical filaments (PHFs).
PHFs accumulate to form neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) inside neurons.
NFTs disrupt cellular function and contribute to neuronal death.
Cellular Toxicity and Neurodegeneration
NFTs interfere with neuronal function by:
Blocking proteasomal degradation – Leading to accumulation of damaged proteins.
Triggering mitochondrial dysfunction – Resulting in energy failure.
Activating apoptosis pathways – Leading to cell death.
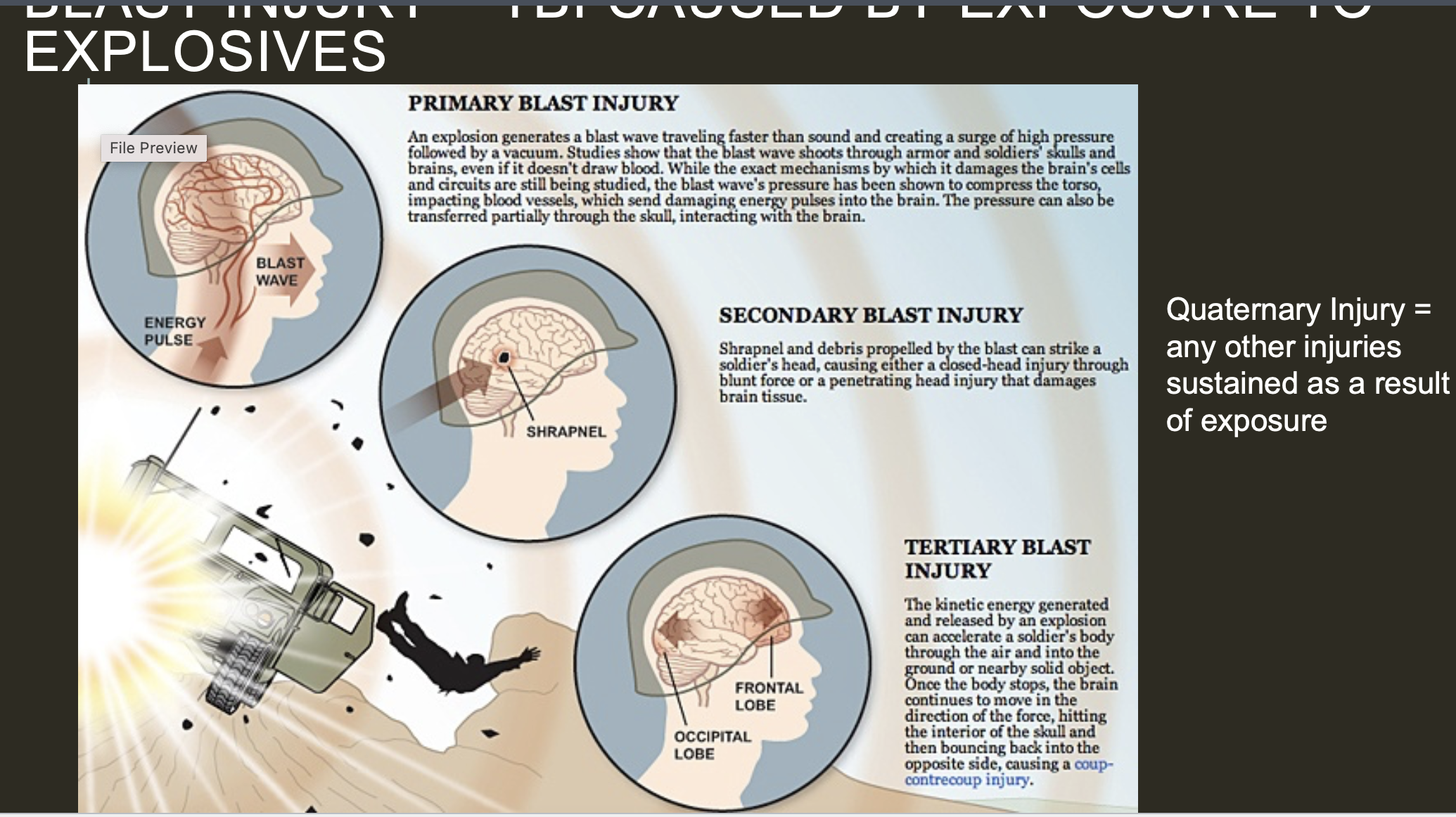
TBI AND FORMATION OF NFTS
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a significant risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease (AD), chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), and other tauopathies. One of the pathological consequences of TBI is the abnormal hyperphosphorylation of tau, leading to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs)—a hallmark of neurodegeneration.
CTE cymptoms and pathology
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy – repetitive brain trauma that subsequently leads to neurological deterioration
Neurodegenerative Disease diagnosed only by neuropathological examination of the brain
Symptoms
Psychiatric and behavioral symptoms
Mood changes
Memory loss/dementia
Cognitive and motor deficits
Parkinsonism
Confusion
Balance deficits
Susceptibility
Soldiers
Athletes
Repetitive concussions/mTBI
Can occur following a single injury (Blast injury)
blast tau
Blast-induced traumatic brain injury (TBI) can cause tau hyperphosphorylation, which may lead to chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). Tau hyperphosphorylation is a hallmark of CTE, a neurodegenerative condition that can cause cognitive and behavioral changes.