Untitled Flashcards Set
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Constructivist view
A perspective on cognitive development where children play an active role and construct an understanding of the world.
Schemas
Cognitive structures that help organize and understand information.
Object permanence
Knowledge that objects continue to exist even when they cannot be seen.
A-not-B task
An experimental task assessing object permanence wherein infants fail to find an object hidden in a different location after repeated hiding.
Violation of expectancy procedure
An experimental method where infants show surprise when observing an event that conflicts with their expectations.
Dynamic systems theorists
Researchers who emphasize that performance on cognitive tasks is influenced by the surrounding context and sensory feedback.
Empiricism
The view that knowledge is gained through sensory experience and interaction with the environment.
Nativism
The view that certain skills or abilities are hard-wired into the brain at birth.
Information processing theory
A perspective that treats the mind as a complex computing system, focusing on how people process, store, and retrieve information.
Core-knowledge theory
The idea that infants come equipped with a set of innate cognitive capabilities that allow for quick understanding of important concepts.
Phoneme
The smallest unit of sound that distinguishes meaning in language.
Cooing
The early stage of speech development when infants produce vowel-like sounds, typically starting at 6-8 weeks.
Babbling
The production of repetitive consonant-vowel combinations by infants, occurring around 6-10 months.
Holophrases
One-word utterances used by infants to express a complete idea.
Telegraphic speech
Two-word combinations used by children to convey meaning, omitting less critical words.
Speech segmentation
The process by which infants learn to identify individual words within continuous speech.
Distributional properties of language
Patterns in language that help infants recognize word boundaries and meanings based on frequency and statistical relationships.
Gaze following
The ability to follow another person’s gaze to infer where they are looking and what they may be thinking.
Theory of mind
The understanding that others have thoughts, beliefs, and desires distinct from one's own.
False-belief task
A test to assess a child's understanding that others can have beliefs about the world that are incorrect.
Altruistic motivation
The desire to help others without any expectation of benefit to oneself.
Social cognition
The process of understanding and interpreting social interactions, intentions, and behaviors.
Vicarious reinforcement
Learning that occurs through observing the consequences of others’ behavior.
Contextual factors
Environmental and situational influences that shape cognitive development and behavior.
Statistical learning
The capacity to deduce patterns and regularities from the environment to facilitate learning.
Served and return interactions
Responsive exchanges between parents and children that support cognitive and emotional development.
Moral development
The process by which children learn to understand concepts of right and wrong, fairness, and justice.
Imitation
The ability to replicate the actions of others, often crucial for the learning of new skills.
Social evaluation
The process by which infants choose between individuals based on their behavior towards others.
Perceptual narrowing
A developmental process wherein infants become less able to discriminate between similar sounds that are not part of their native language.
Head-turn preference procedure
An experimental technique used to study infants' recognition and discrimination of sounds.
Cross-situational word-learning
A hypothesis that posits infants learn word-object mappings by recognizing the same object across different contexts.
Syntactic bootstrapping
Utilizing the arrangement of words in sentences to infer meanings or categories of words.
Empathy
The ability to understand and share the feelings of another person.
Altruism
Selfless concern for the well-being of others.
Social cuing
Using social cues, like gestures and eye gaze, to understand language and behavior.
Conversational babbling
A stage of babbling that mimics the rhythm and patterns of a conversation.
Conditional reasoning
A form of deductive reasoning that involves if-then propositions.
Social referencing
The process by which infants look to caregivers for cues on how to respond to unfamiliar situations.
Moral emotions
Feelings such as guilt or shame that contribute to moral development.
Imitative learning
Learning by observing and replicating the actions of others.
Prosocial behavior
Voluntary actions intended to benefit others.
Gaze as a referential cue
Using the direction of another person's gaze to gather contextual information about objects or events.
Self-concept
A sense of one's identity and personal worth.
Cultural transmission
The process through which culture is passed from one generation to the next.
Visual perspective-taking
The ability to understand that others may see an object differently based on their viewpoint.
Attentional bias
A tendency for individuals to focus on certain types of stimuli over others.
Nonverbal cues
Communications without words, including body language and facial expressions.
Role-play
Acting out or performing the role of a character to learn social interactions.
Imaginary companions
Fictitious friends created by children, often used for imaginative play.
Joint attention
When two individuals use gestures and gaze to share focus on an object.
Social norms
Expected standards of behavior and beliefs within a society.
Emotional intelligence
The ability to identify, understand, and manage one's own emotions and the emotions of others.
Verbal ability
The capacity to use language effectively and understand its complexities.
Self-regulation
The ability to manage emotions, behaviors, and body movement when faced with difficult situations.
Theory of mind training
Interventions aimed at improving a child's understanding of others' mental states.
Peer relationships
Connections and interactions between individuals of similar age or maturity.
Prosocial development
The growth of behaviors that benefit others.
Cognitive flexibility
The ability to adapt one's thinking to new and unexpected conditions.
Understanding of intentions
Comprehending the reasons behind others' actions.
Social learning theory
A theory suggesting that people learn from one another through observation, imitation, and modeling.
Attachment theory
The theory that a strong emotional and physical bond to one primary caregiver is critical to personal development.
Emotional responsiveness
The ability to react appropriately to emotional stimuli.
Shared attention
The experience of focusing on the same object or event as another person.
Cognitive schemas
Frameworks that help organize and interpret information.
Behavioral adaptation
Changes in behavior in response to new experiences.
Social perception
The processes by which people form impressions of and make inferences about other individuals.
Contextual learning
A style of learning that occurs within the environment in which it will be applied.
Interactive learning
Learning that takes place through engaging with others.
Independent play
Play that children engage in alone, not involving interaction with others.
Play-based learning
A teaching method that uses play to promote learning.
Empathetic understanding
The skill of seeing things from another's viewpoint and feeling compassion.
Collaborative learning
Learning that occurs through collaboration with peers.
Language development
The process by which children come to understand and communicate language.
Adaptive behavior
Skills and behaviors that enable a person to meet the demands of everyday life.
Social anxiety
The fear or apprehension of social situations.
Competence motivation
The drive to engage in activities that will increase one's abilities.
Inductive reasoning
Generalizing from specific instances to form a general conclusion.
Cognitive development
The progression of thinking abilities throughout childhood and into adulthood.
Affective development
The development of feelings and emotions.
Linguistic ability
The capacity to use languages.
Cultural factors
Elements that influence an individual's behaviors and beliefs based on their cultural background.
Moral reasoning
The process of determining right from wrong.
Transitional probabilities
The likelihood that one sound will follow another in a sequence, helping infants segment words.
Social comparison
Evaluating oneself against others to gauge personal worth.
Cross-cultural comparison
Analyzing the differences and similarities between cultures.
Biological factors
Genetic or physiological influences on behavior and development.
Emotional development
The emergence and maturation of an individual's emotional capacity.
Resilience
The ability to recover from or adjust easily to misfortune or change.
Play therapy
A therapeutic approach that uses play techniques to help children express their feelings.
Cultural context
The setting in which a cultural practice takes place and how it influences behavior.
Neuroscientific perspectives
Insights derived from studying the brain concerning behavior and cognitive processes.
Expressive language
The ability to express thoughts and feelings verbally.
Receptive language
The ability to understand language and spoken information.
Peer influence
The effect that peers have on an individual's attitudes or behaviors.
Emotional literacy
The ability to recognize, understand, and express emotions.
Experiential learning
Learning through action rather than theoretical knowledge.
Language exposure
The amount and variety of language a child hears; crucial for language development.
Cross-modal perception
The integration of information from different sensory modalities.
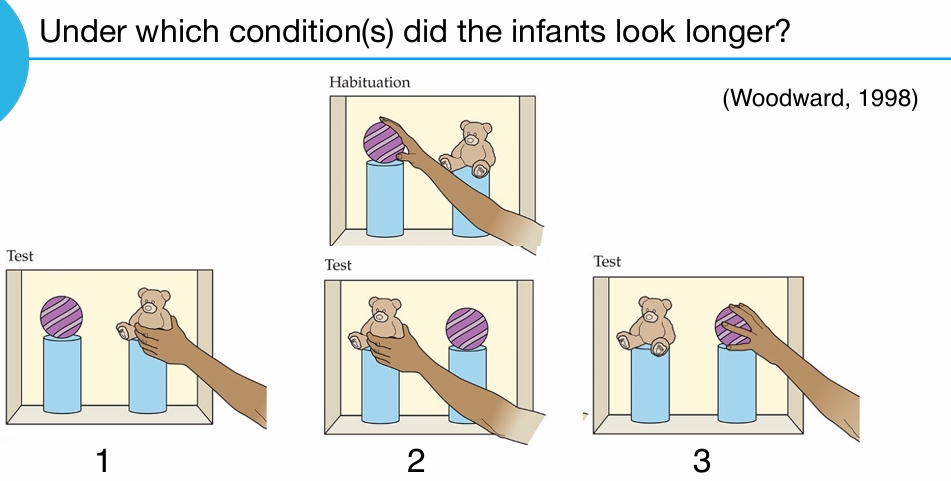
Under which condition(s) did the infants look longer?
1 and 2