Microbiology Lab Quiz 6
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are some reasons we have to monitor microbial growth in the lab?
Evaluating the effectiveness of antimicrobial treatments
Sanitation
This determines the infection severity of a microbe
Evaluating the effectiveness of antimicrobial treatments
pasteurization
food preservation methods
disinfectants/antiseptics
antibiotics
Sanitation
drinking water quality
wastewater quality
What are some ways to count microorganisms in the lab?
Microscopically used a hemocytometer (direct method)
Plate count assays (direct method)
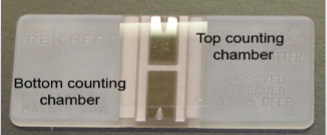
Hemocytometer
uses a microscope and chamber like grid to count microbes in the lab setting
Problems:
cant distinguish live/dead microbes
dirt in samples can be mistake for microbes…miscounted


What is this and what does it do?
Autoclave: a container used for sterilization + heating purposes

What is this and what does it do?
Autoclave tape: a special tape that is placed on items placed in an autoclave to determine if it reached the proper temperature for heating and/or sterilization

What is this and what does it do?
Autoclave ampoules: special sealed glass container to hold substances (like Geobacillus stearothermophilus) which changes colors when heated to the right temperature which indicates proper temp for heating and/or sterilization
Plate count assays
paired w/ serial dilution tactics to quantify the # of living (viable) bacterial cells in a culture medium
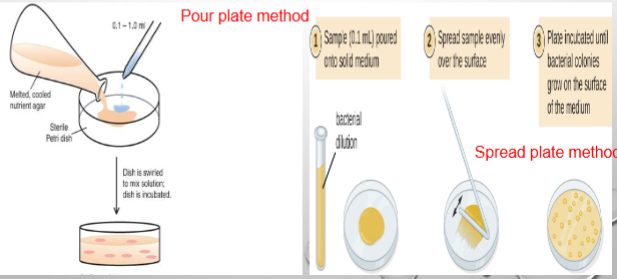
Two methods: Pour plate (lab) & Spread plate
*tend to underestimate the # of viable bacteria in samples…b/c of the # of colonies

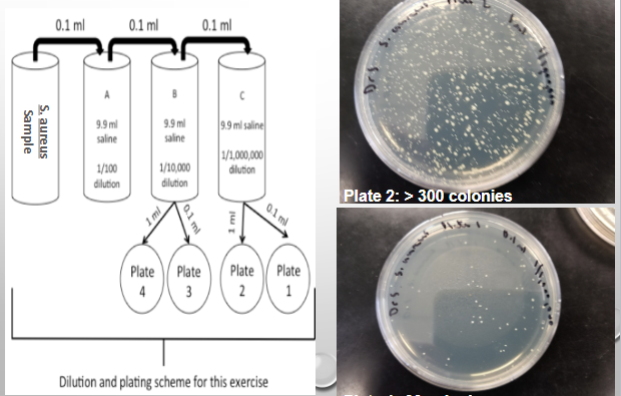
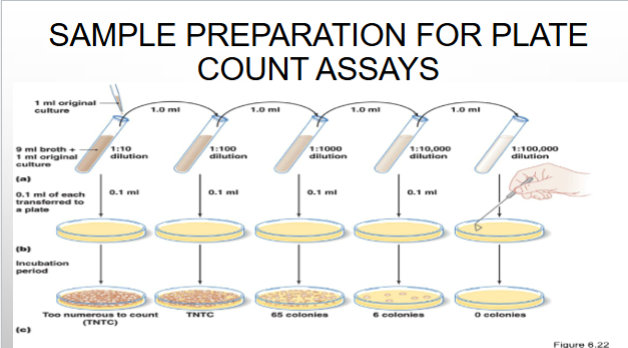
Sample prep for plate count assays
For example: Fecal slurry, raw sewage sample is obtained and a volume of that sample (1 ml) is poured or spread onto an agar plate (subsample/aliquot)
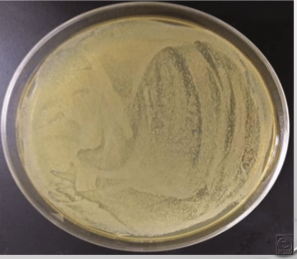
Colony Forming Units (CFUs)
a colony of bacteria that forms on agar plates during plate count assays
Serial diluting
the process of preparing subsamples (small vl of each dilution; aliquots) of different concentrations of microbes on a agar plate to estimate the # of CFU/ml or CFU/g in a given sample
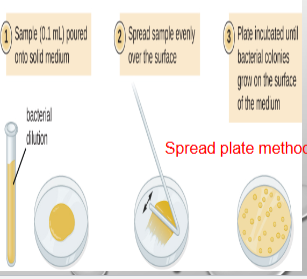
Spread plate method
aliquots of diluted samples are first placed on the surface of the agar medium and the aliquots are then spread across the surface of the afar using a sterilized glass rod
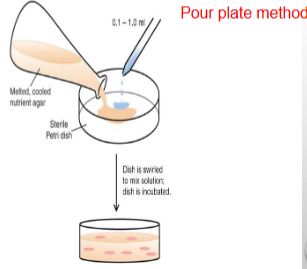
Pour plate method
aliquots of diluted samples are first placed in an empty, sterile petri dish then the agar (melted) is added to the petri dish and mixed w/ the sample of microbe
*colonies formed are smaller than those formed in spread plates b/c slower growth rates from reduced O2 conc. (facultative anaerobes)
What makes a plate “countable” during the plate count assay?
plates are considered countable if they contain between 30-300 colonies
Aliquot size
an estimate of the cell density in the original sample (CFU/ml) that is obtained by counting the # of colonies on a plate then dividing by the volume of sample that was plated.
CFU/ml = (# of colonies / vl (ml)) x dilution factor
Dilution
vol. of sample/ vol. of sample + vol. of dilution
when samples are diluted multiple times, the calculations are multiplied
Dilution factor
the dilution is just flipped
ex. 1/10 dilution > 10 dilution factor
Micropipette parts
Volume adjustment knob: turned either clockwise or counterclockwise in order to obtain the correct vol. of liquid
Volume indicator window: tells you how much liquid that your are collecting with the micropipette
Plunger: obtains the correct vol. of sample to collect + dispense
Tip ejector: ejects the micropipette tip to discard (must be changed between each sample)
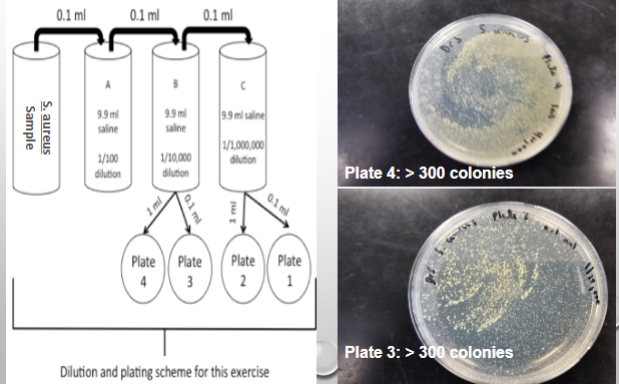
Overview of Lab:
1 tube of a bacterial broth culture
1 micropipette
7 sterile micropipette tips
4 sterile petri plates
3 tubes with 9.9 ml of sterile 0.85% NaCl solution
1 bottle of liquified agar (store in 53*C to melt)
1 small biohazard cup for micropipette tip disposal