Locomotor appartus
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What is osteology?
it's the osteogenesis, classification of bones and bone structure
What is the Arthrology ?
it's the arthrogenesis, the joint classification and joint elements. But also the joint biomechanics
What is the myology ?
it's the myogenesis, the types and classification of the muscle and how they are organised
What are the muscle accesory structures ?
Can be the fasciae, tendon/ fibrous sheath, the synovial bursa and sheath
What forms the somites ?
the sclerotome (bone and cartilage), the myotome ( the muscle) and the dermatome ( skin and subcutaneous tissue)
What is the function of the locomotor appartus ?
- carry out the body movement
-organ protection
- mineral reserve
-production of blood in the bone marrow
- heat production
what compose the axial region ?
skull, vertebral column, ribs, sternum
what compose the thoracic limb ?
the forelimb
What compose the pelvic limb?
the hindlimb
What is hematopoiesis?
The formation of new blood cell
What is the function of the skeleton ?
support the weight and give protection
give an example of a long, short and flat bone ?
-femur
-carpal
-scapula
give an example of a irregular and sesamoid bone
-vertebrae
-patella
what origin and the end of a tendon ?
muscle to a bone
What the origin and the end of a ligament ?
bone to bone
give the structure of a bone
-osseous/bone tissue
-cartilage
-periosteum
-bone marrow
-vessels and nerves
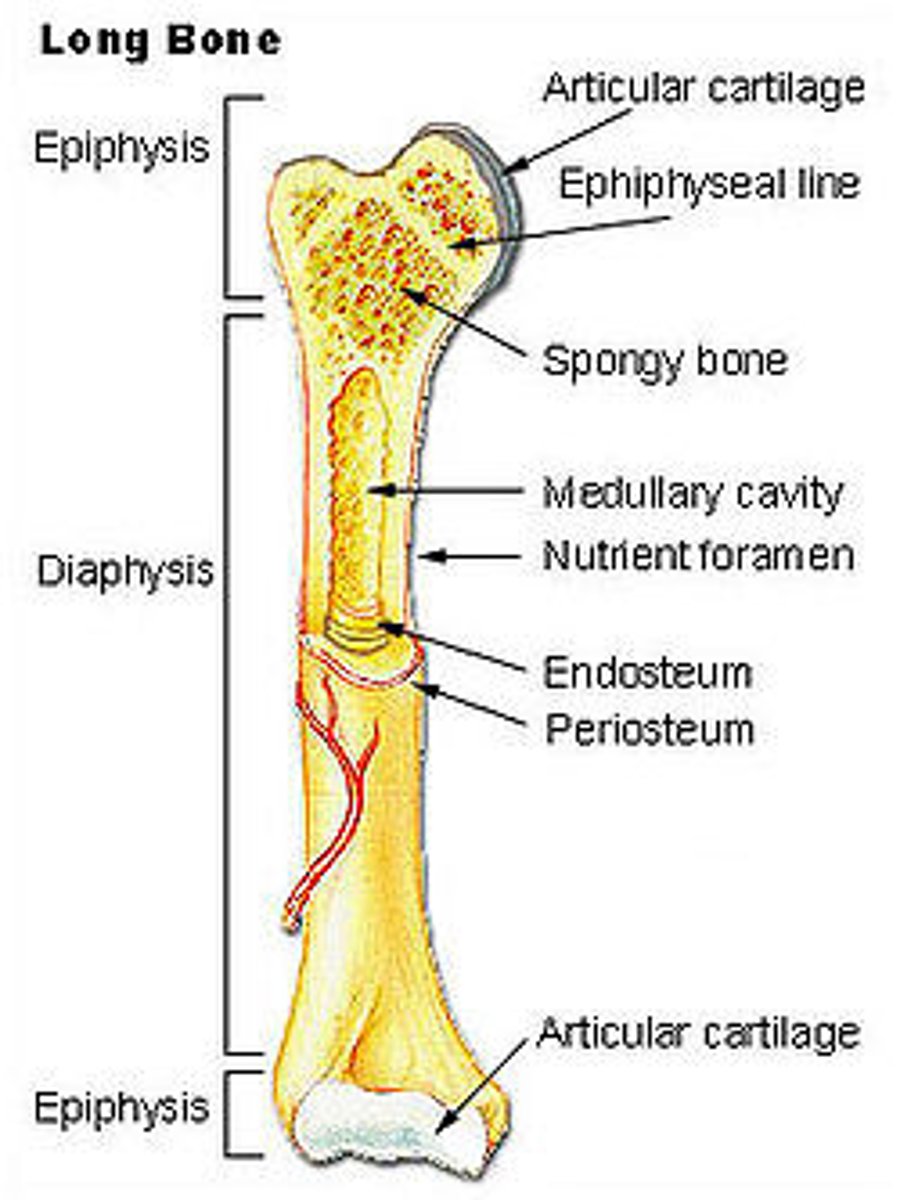
What is the most proximal cartilage of a bone ?
articular cartilage
where can we found the medullary cavity ?
in the middle of the bone, it's surrounded by compact bone
Where is located the growth plate or epiphyseal line ?
It's the area of cartilage near the end of long bones in young animals, it stops growing after 1 year
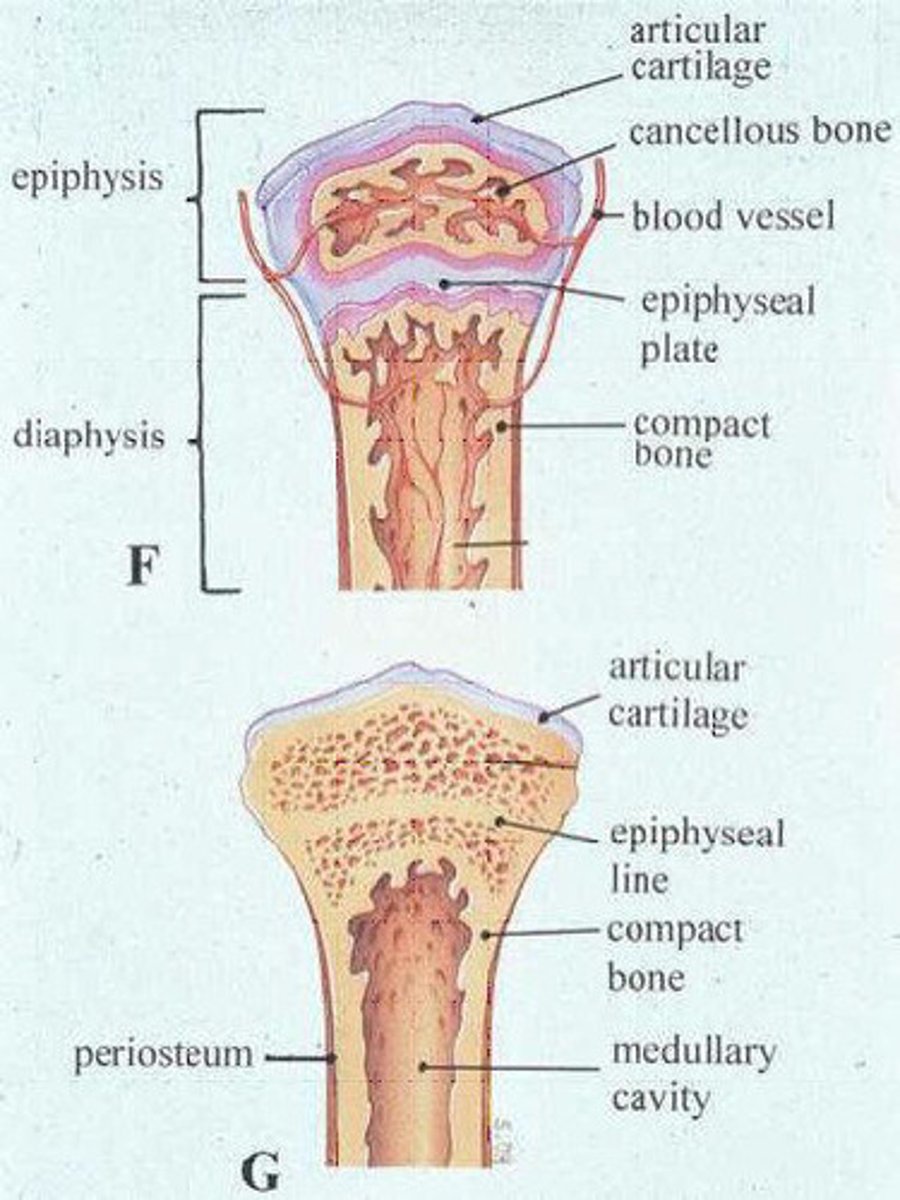
Why we need to be careful while looking at a paw x-ray in young animals?
because we can mistake the growth plate with a broken bone
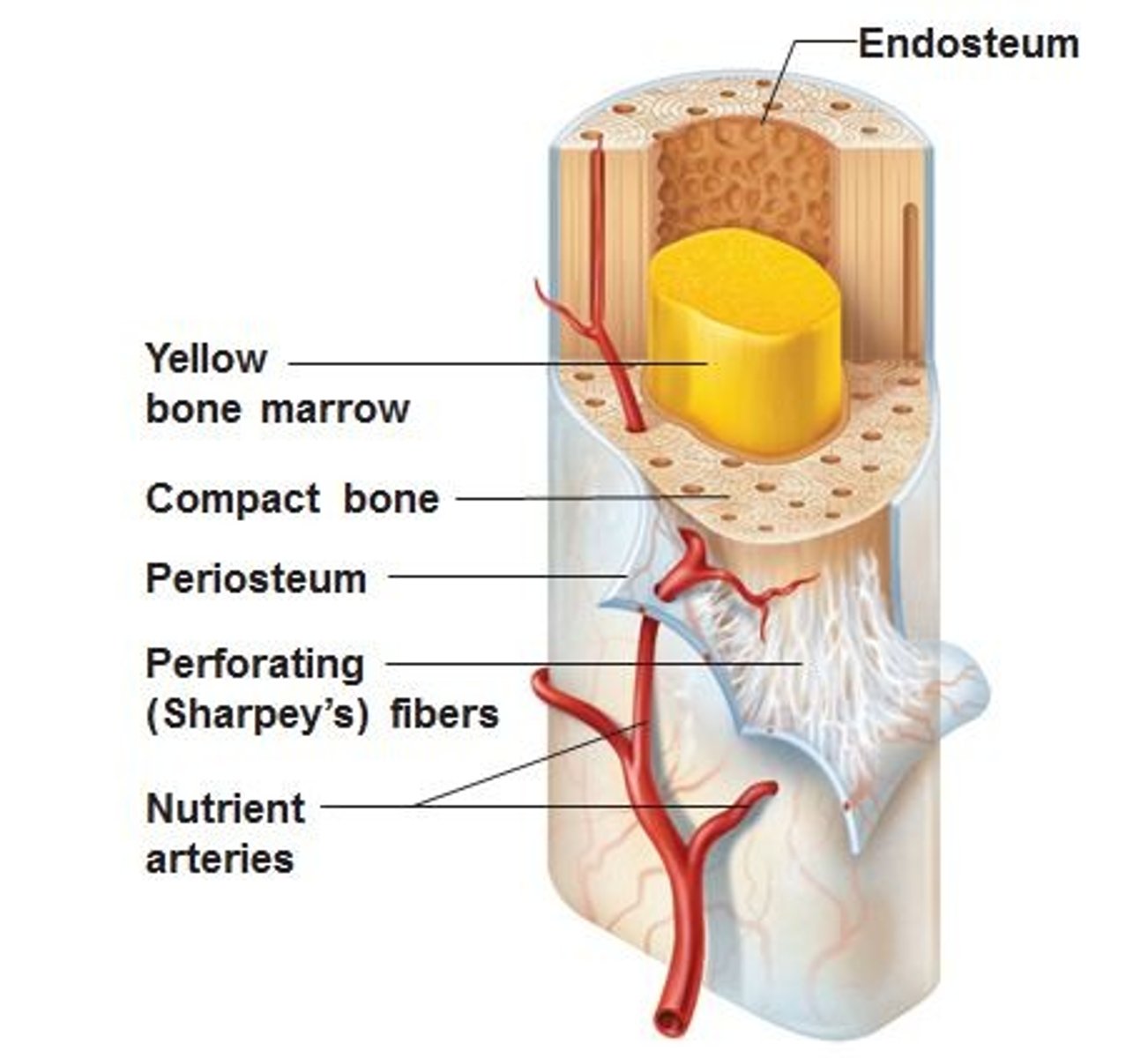
What is the periosteum?
the tough membrane that covers the outside of the bone
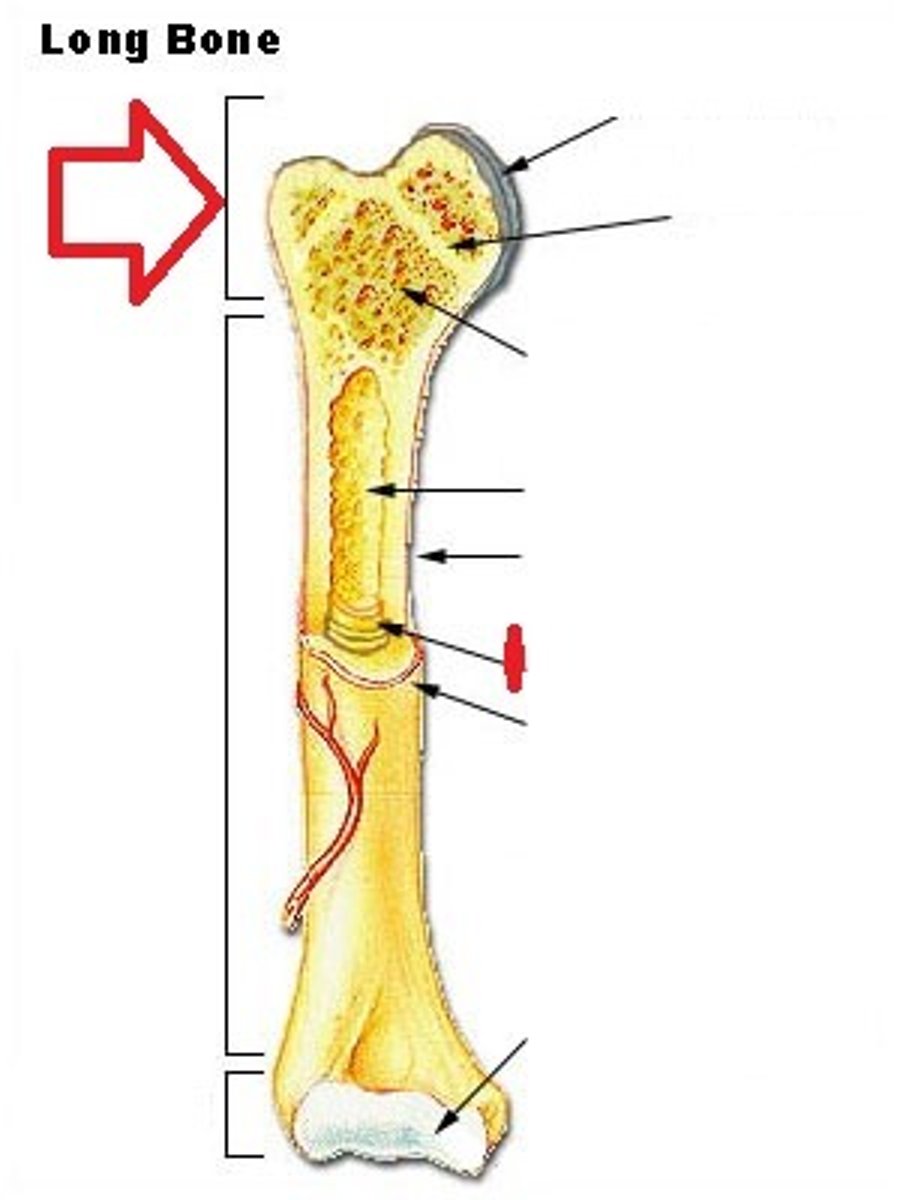
What is the proximal epiphysis
end of the bone closest to the body trunk
What is the diaphysis?
shaft of a long bone
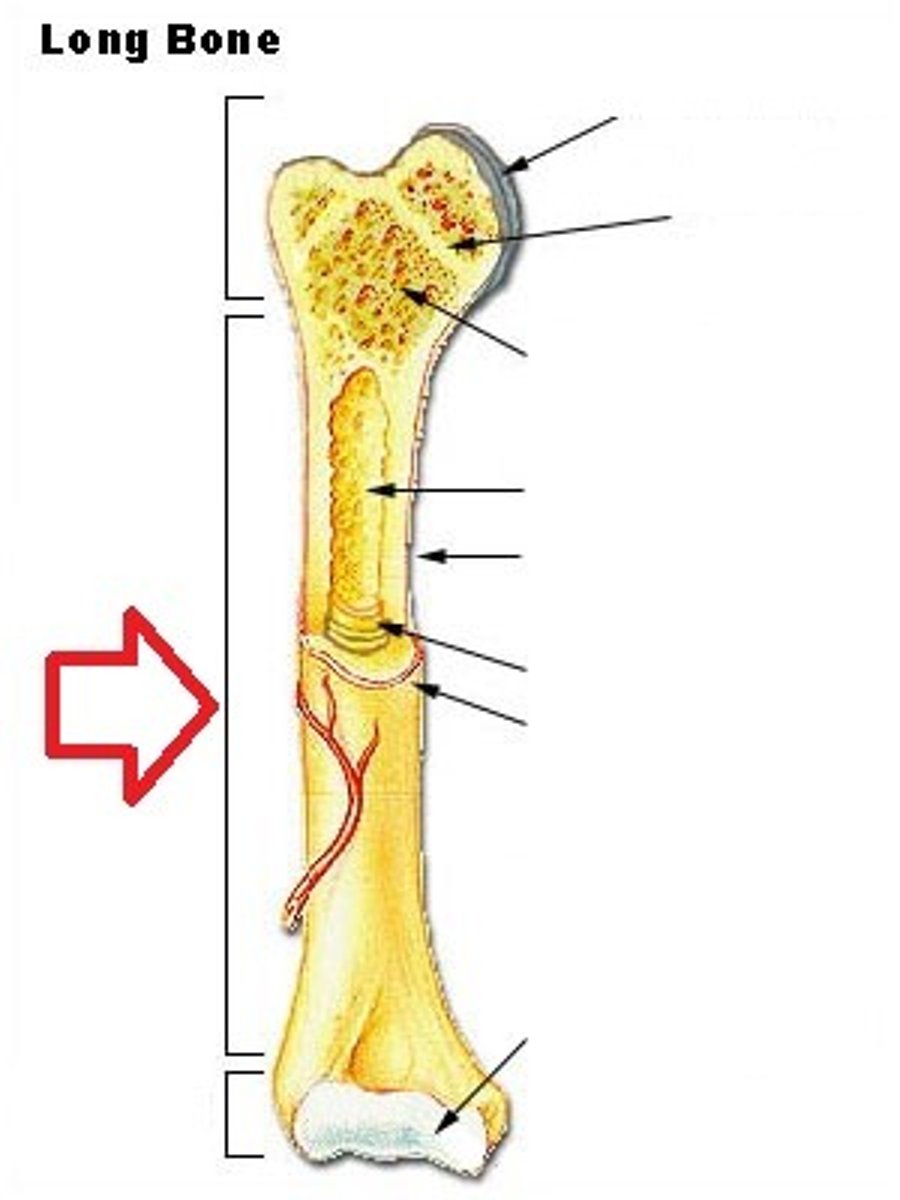
What is the distal epiphysis ?
end farthest from trunk of a bone
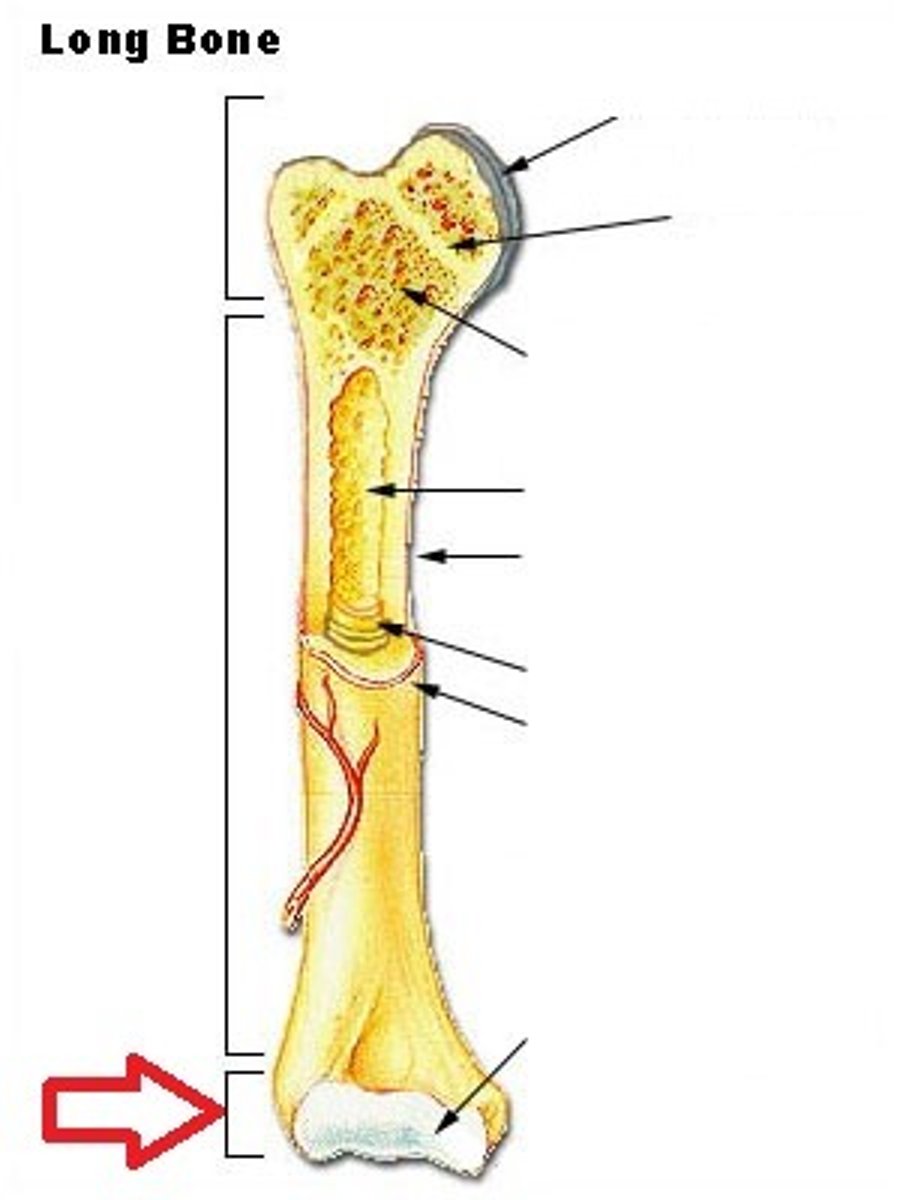
What kind of bone marrow can we find inside a long bone ?
yellow bone marrow
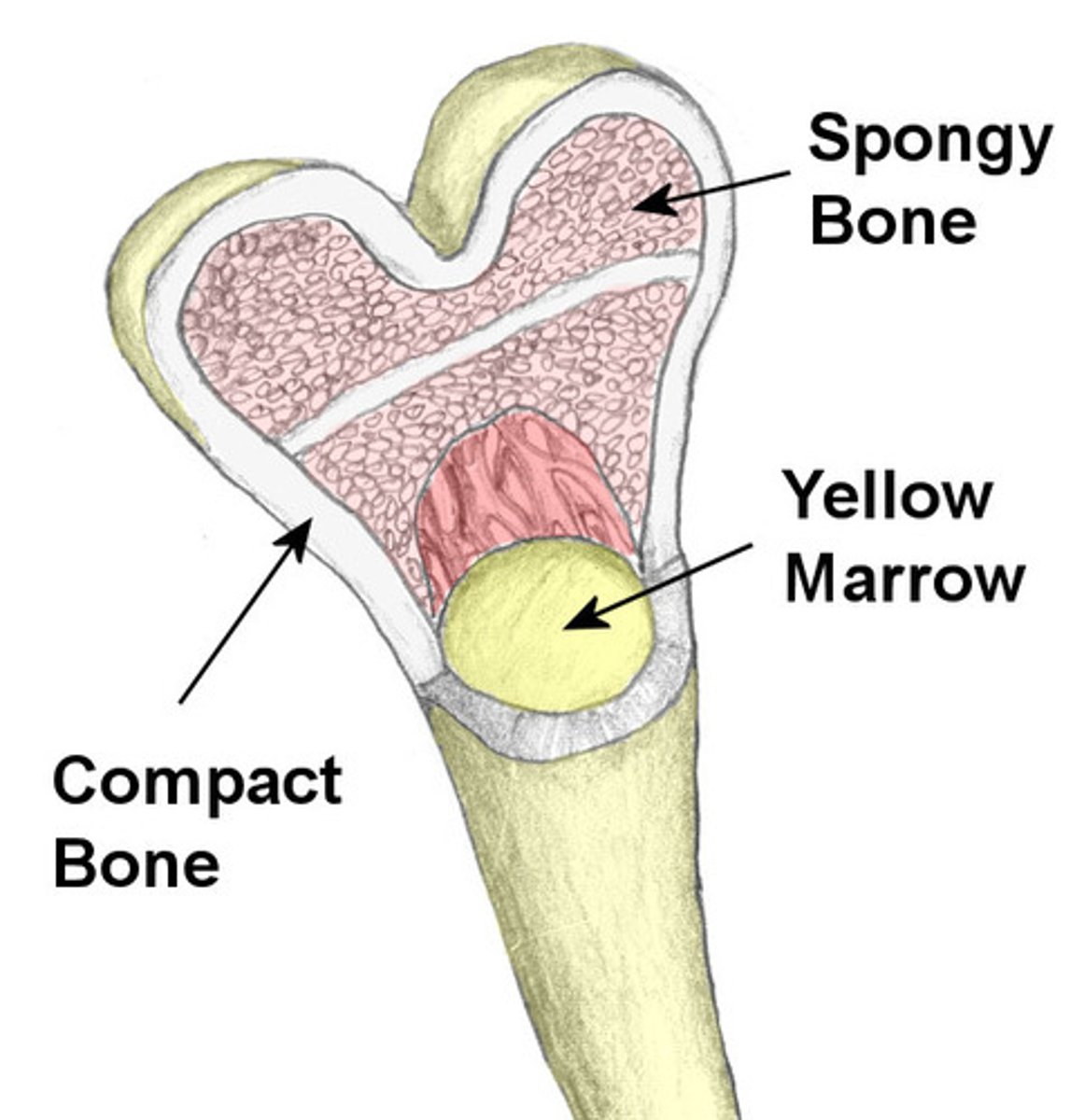
What are the two types of bone tissue ?
compact and spongy
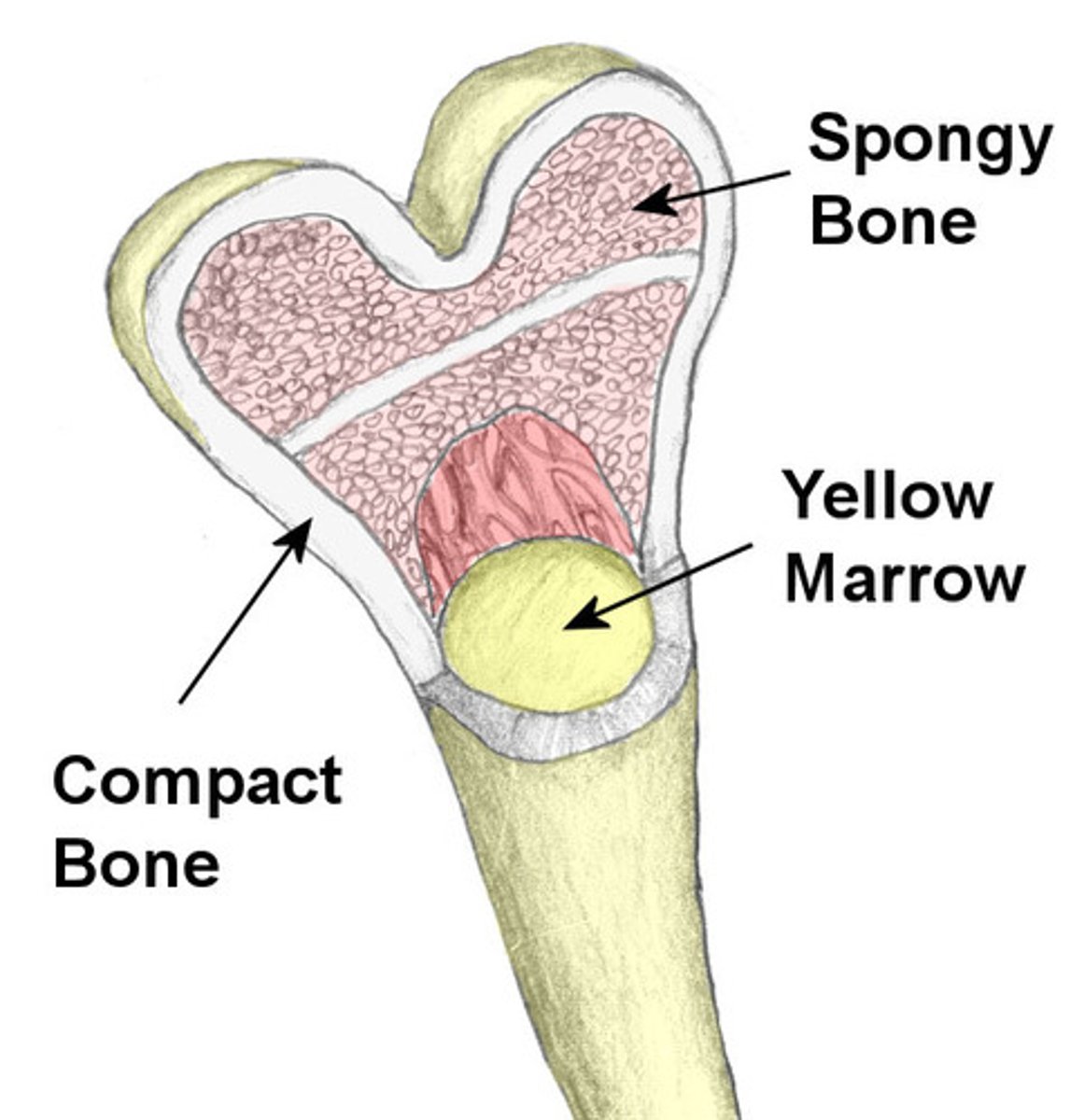
What is the primary bone development direct ?
When the bone is formed without using a cartilagenous tissue
Give an example of a direct primary development bone
skull
What is the primary bone development indirect ?
transform a cartilagenous model into bone
Give an example of a indirect primary development bone
long bone
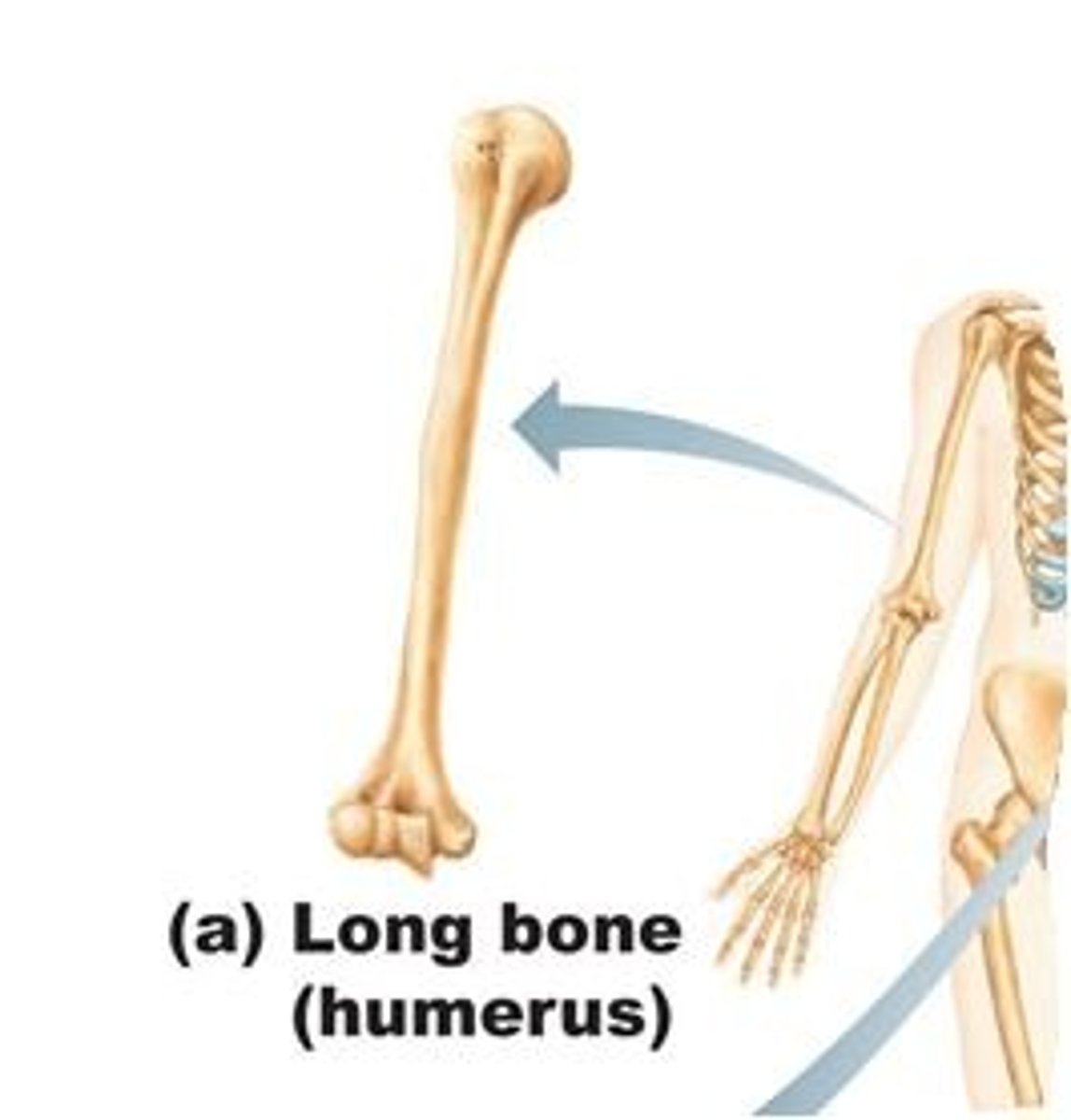
What is the secondary ossification ?
It's when the "immature" primary bone is replaced by osteoclast action into "mature" bone tissue
Give an example of mature bone
the lamellar bone, improves the mechanic function
What is bone remodeling?
it's the dev of osteoclasts and osteocytes, the goal is to store minerals and reorganize the bone architecture
What are the two types of cartiage tissue?
- articular cartilage
-epiphyseal cartilage
Articular cartilage ?
in the joint, surround the articular surface of the bone
epiphyseal cartilage
The cartilaginous region between the epiphysis and diaphysis of a growing bone
Periosteum function
protects and supports
endosteum function
bone growth, repair, and remodeling
What are the 3 types of bone marrow ?
- red (young animal hematopoiesis)
- yellow (fat storage)
- grey
Where can we found red bone marrow ?
in the sternum ribs skull base vertebrae and flat bones
What are the vessels in the afferent system ?
- nutrients arteries
-epiphysis and metaphysis
-periosteal arteries
What are the vessels in the efferent system ?
the veins
origin and end of veins ?
body to lungs
origin and end of arteries
lungs to body
nerves can be what ?
- vasomotors nerves fibers
-sensitive nerves fibers
fibrous joints ?
consists of inflexible layers of dense connective tissue, holds the bones tightly together, no movment
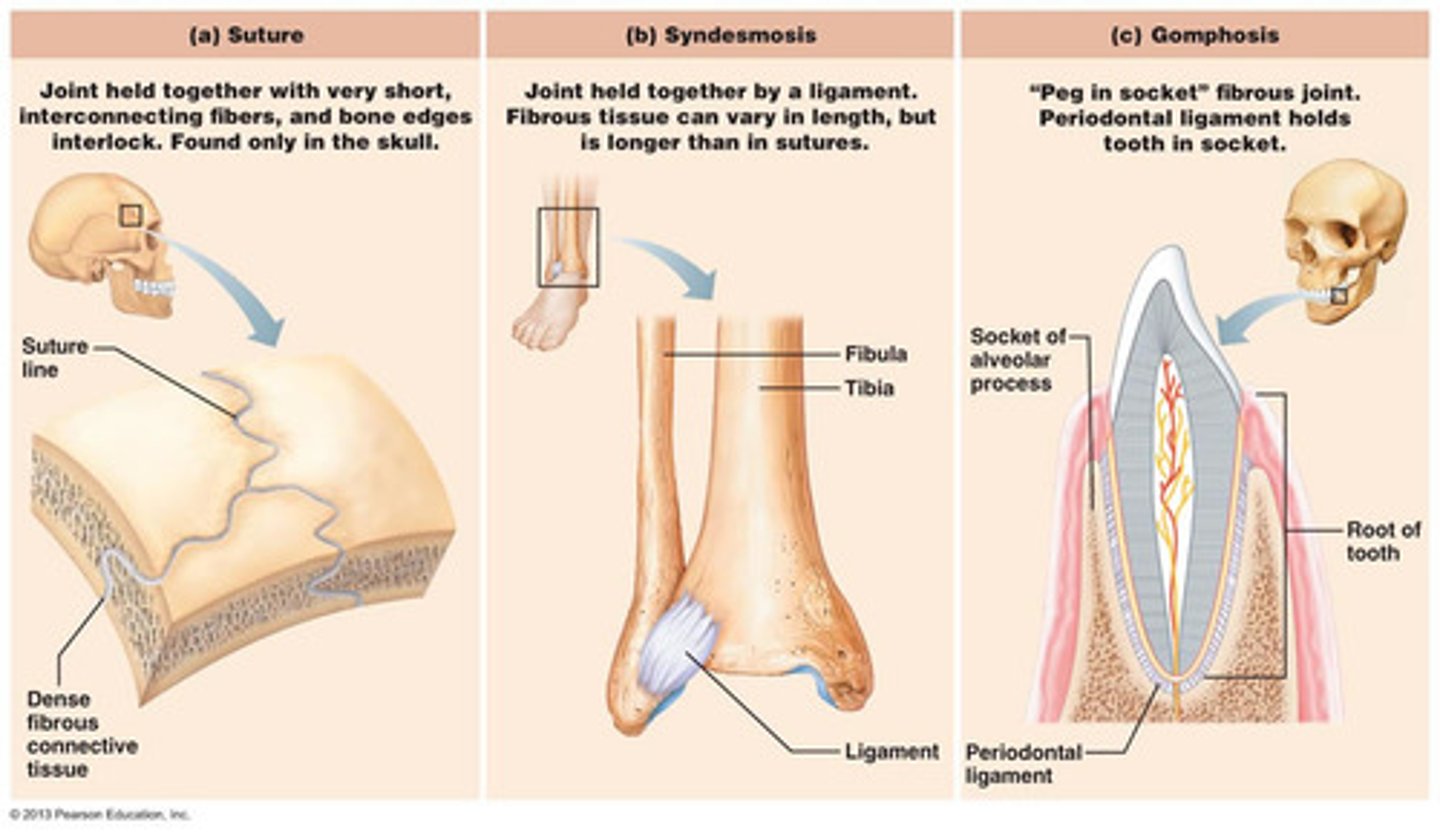
Where can we find fibrous joint ?
Between tibia and fibula, between the teeth and alviolar bone and in the sutures of the skull
What are the 3 differents types of fibrous joint ?
syndesmosis, gomphosis and sutures
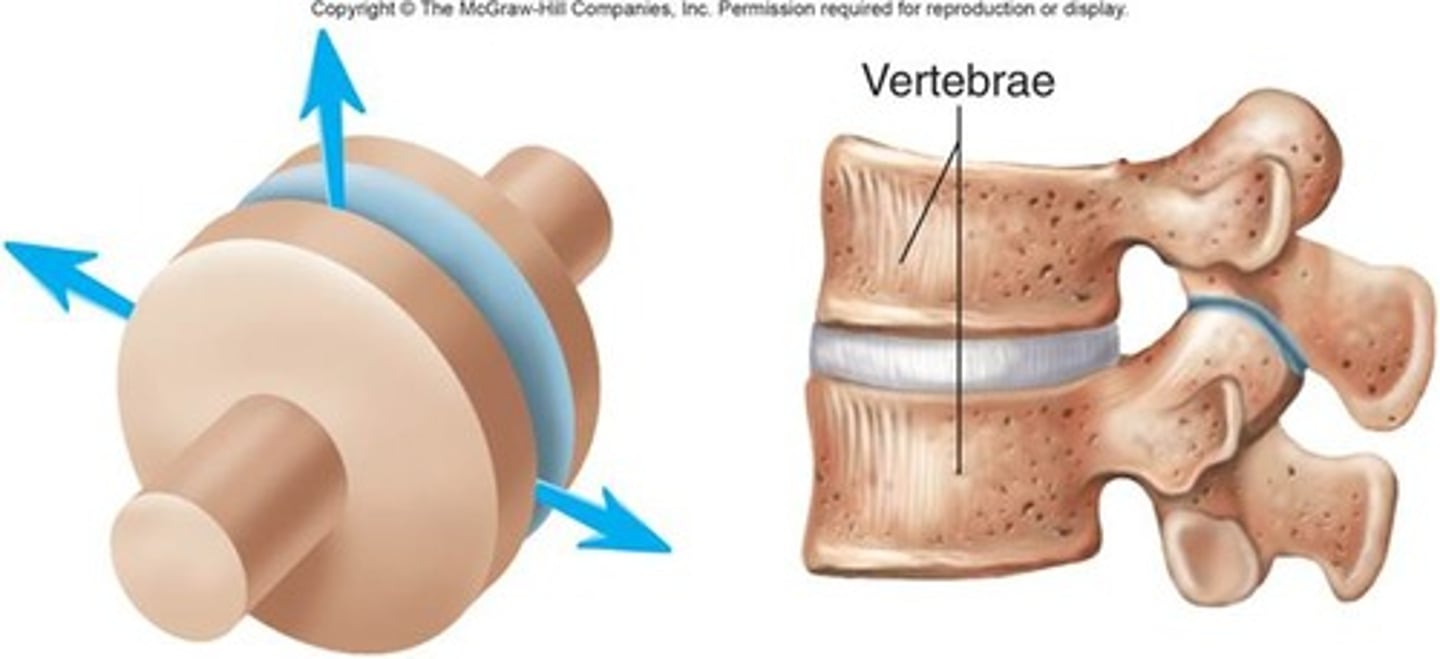
cartilaginous joints
allow only slight movement and consist of bones connected entirely by cartilage
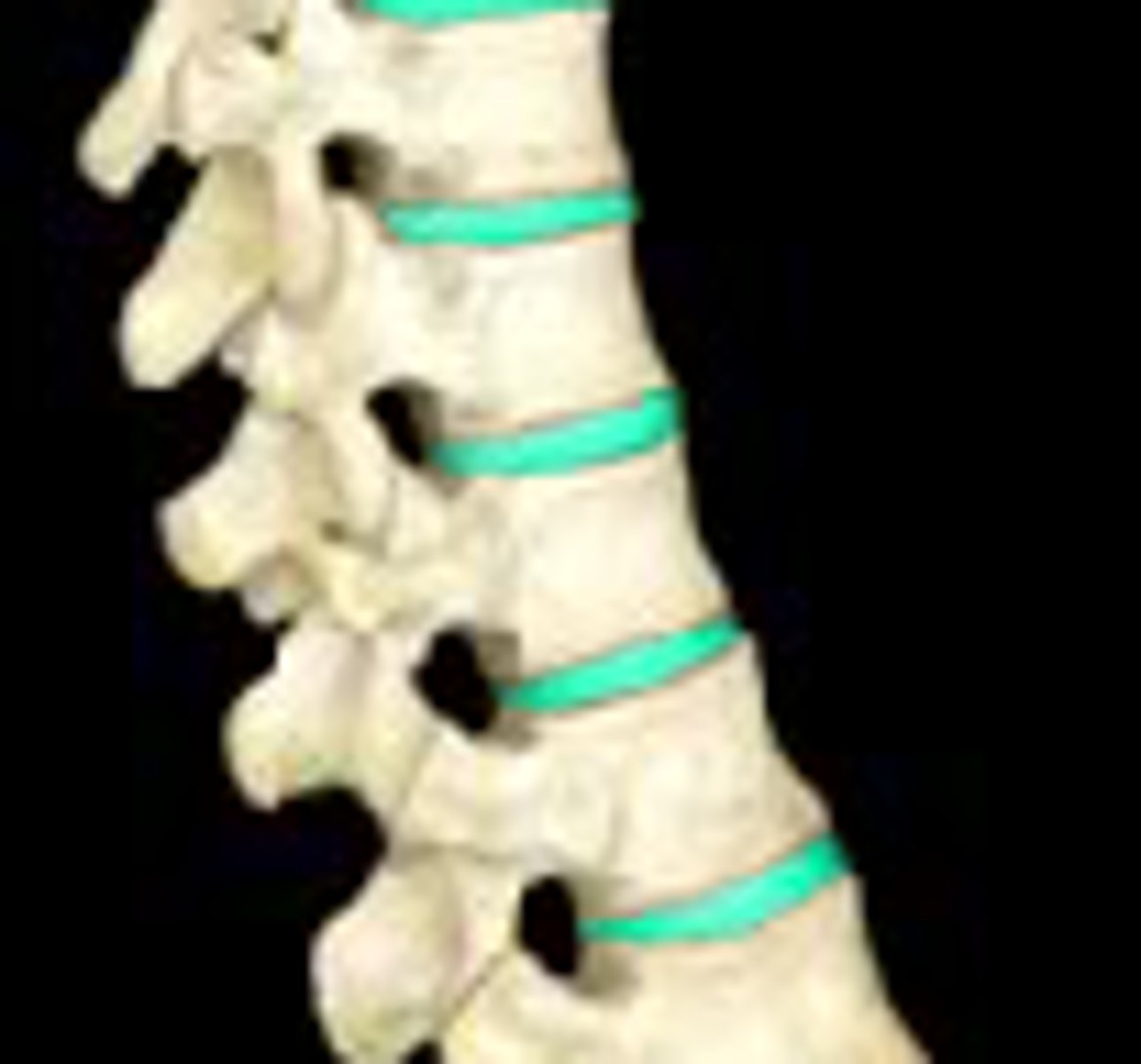
What are the two types of cartilaginous joints ?
- synhondroses (hyaline cartilage)
-symphysis ( firbocartilage)
synovial joints
created where two bones articulate to permit a variety of motions, filled with synovial fluid
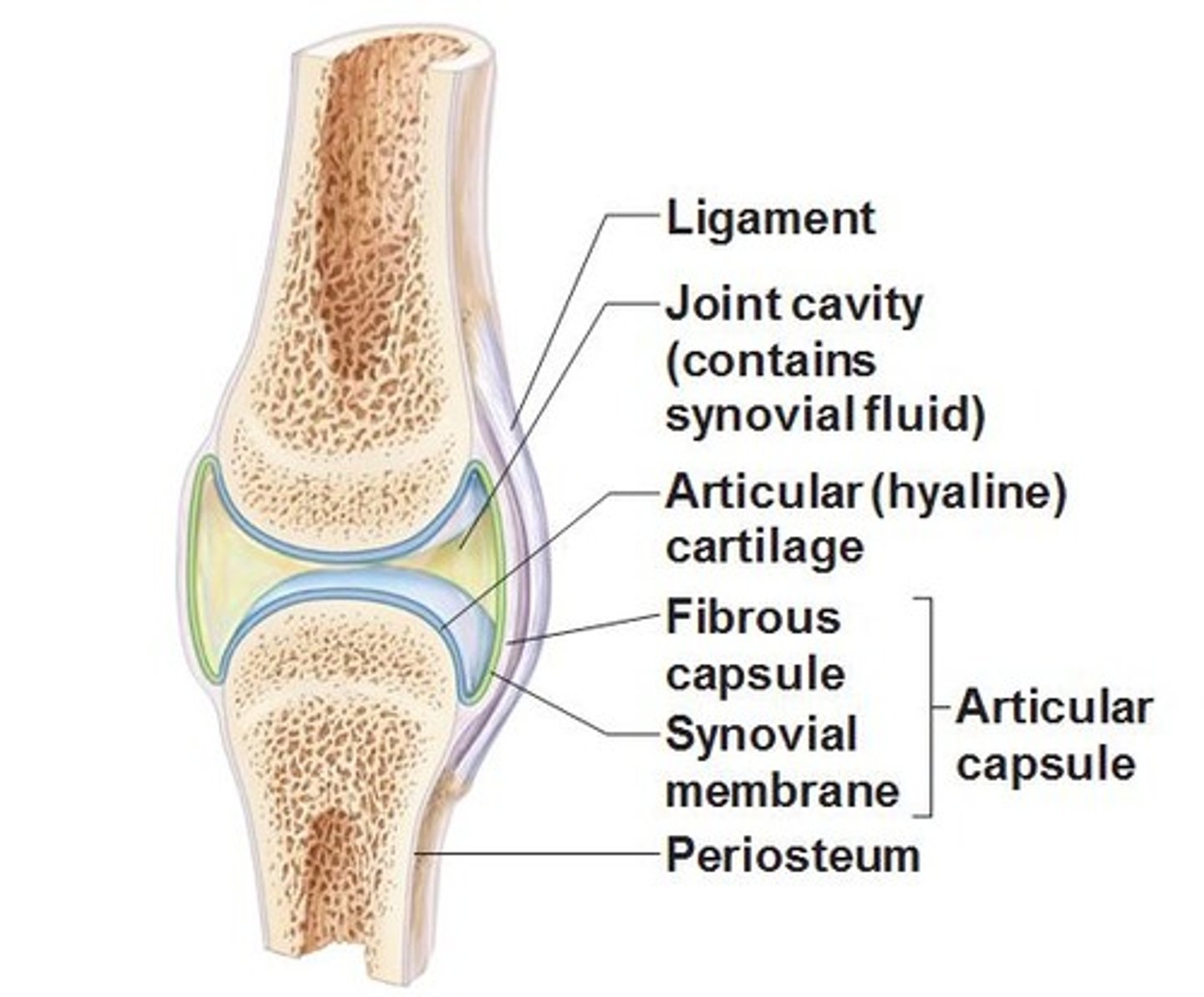
caracteristics of synovial joint ?
-articular cartilage
-joint cavity
-joint capsule
-ligaments
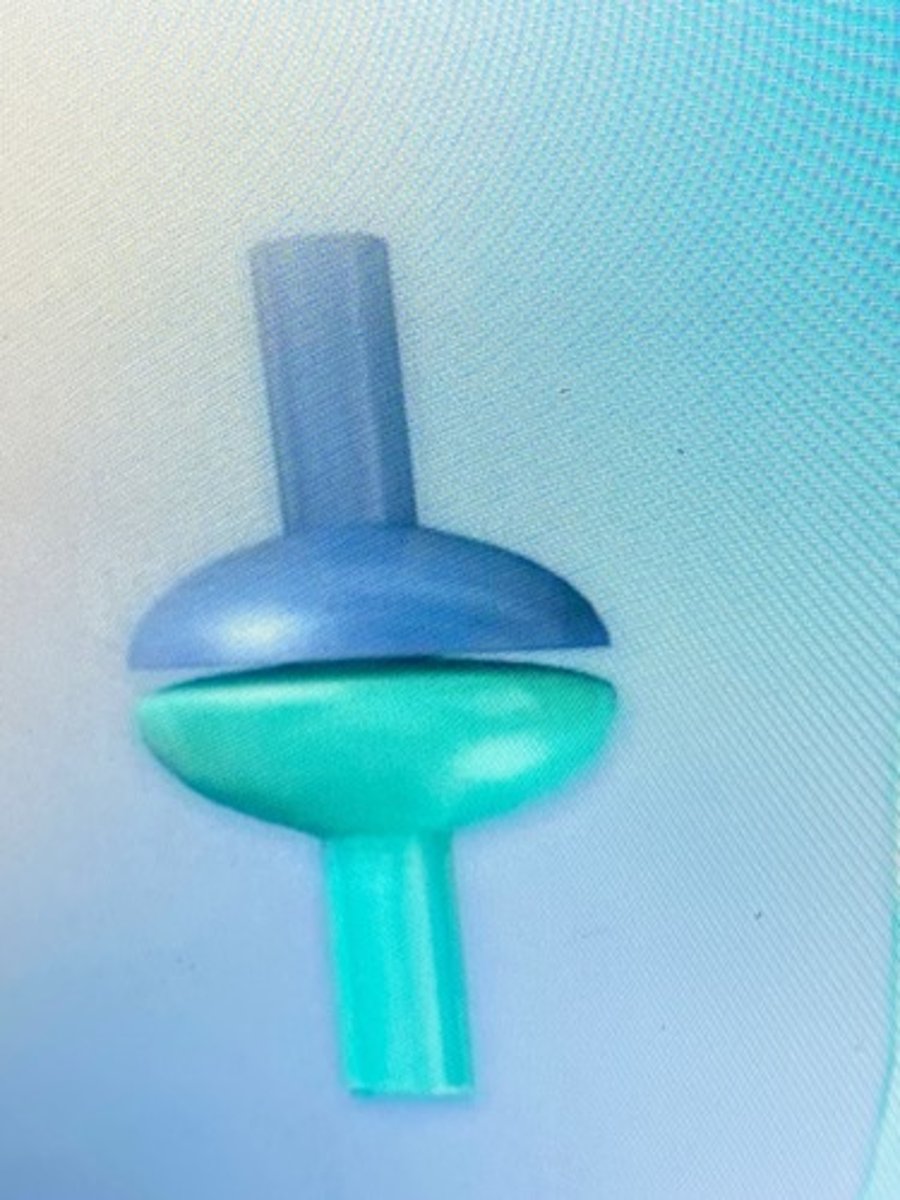
plane joint
intervertebral joint
where is located the condylar joints elipsoidal ?
in the knee

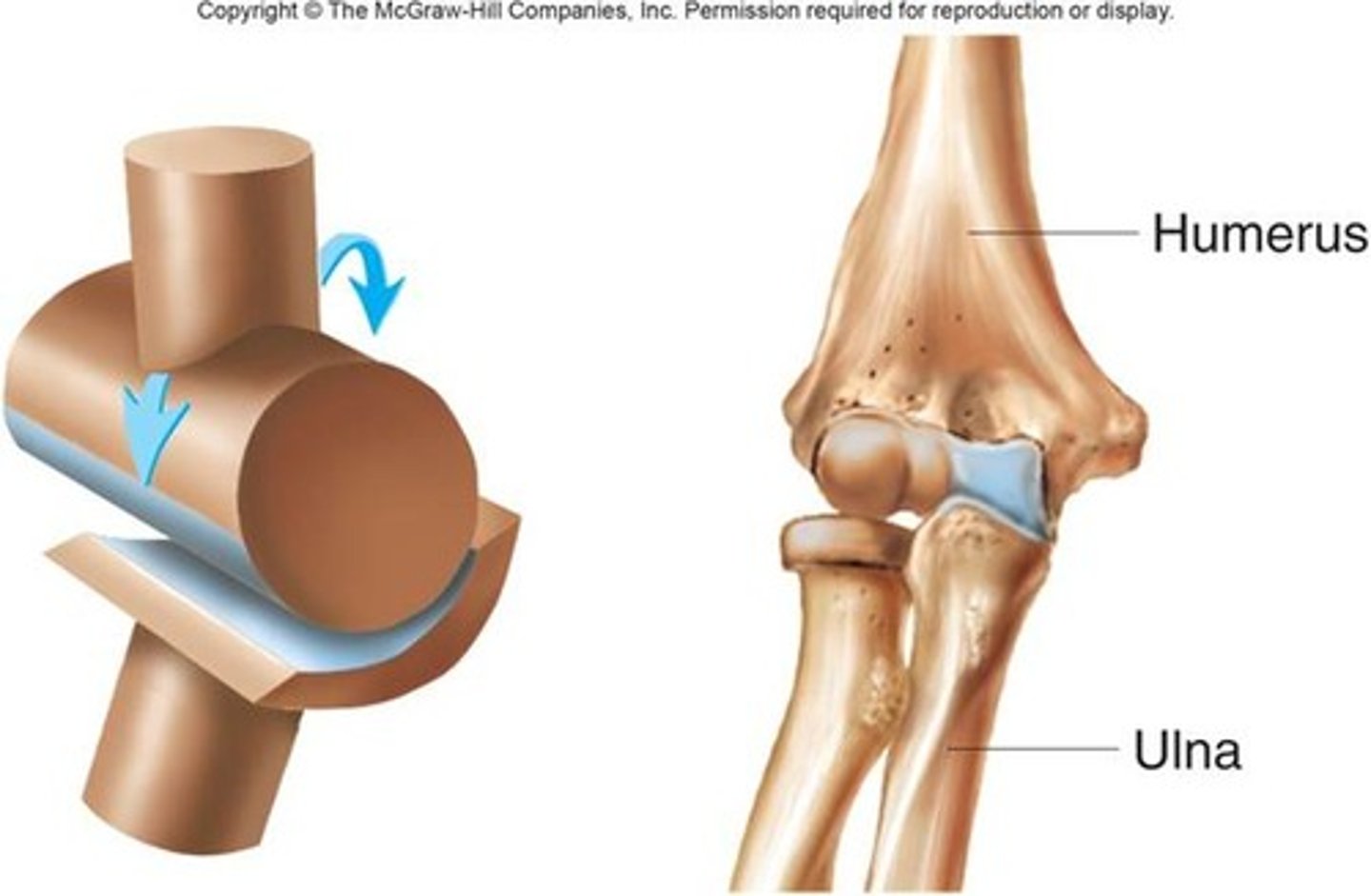
Where is located the hinge joint ?
Fetlock joint and metacarpal joint.
cochlear joint
hock joint of the horse
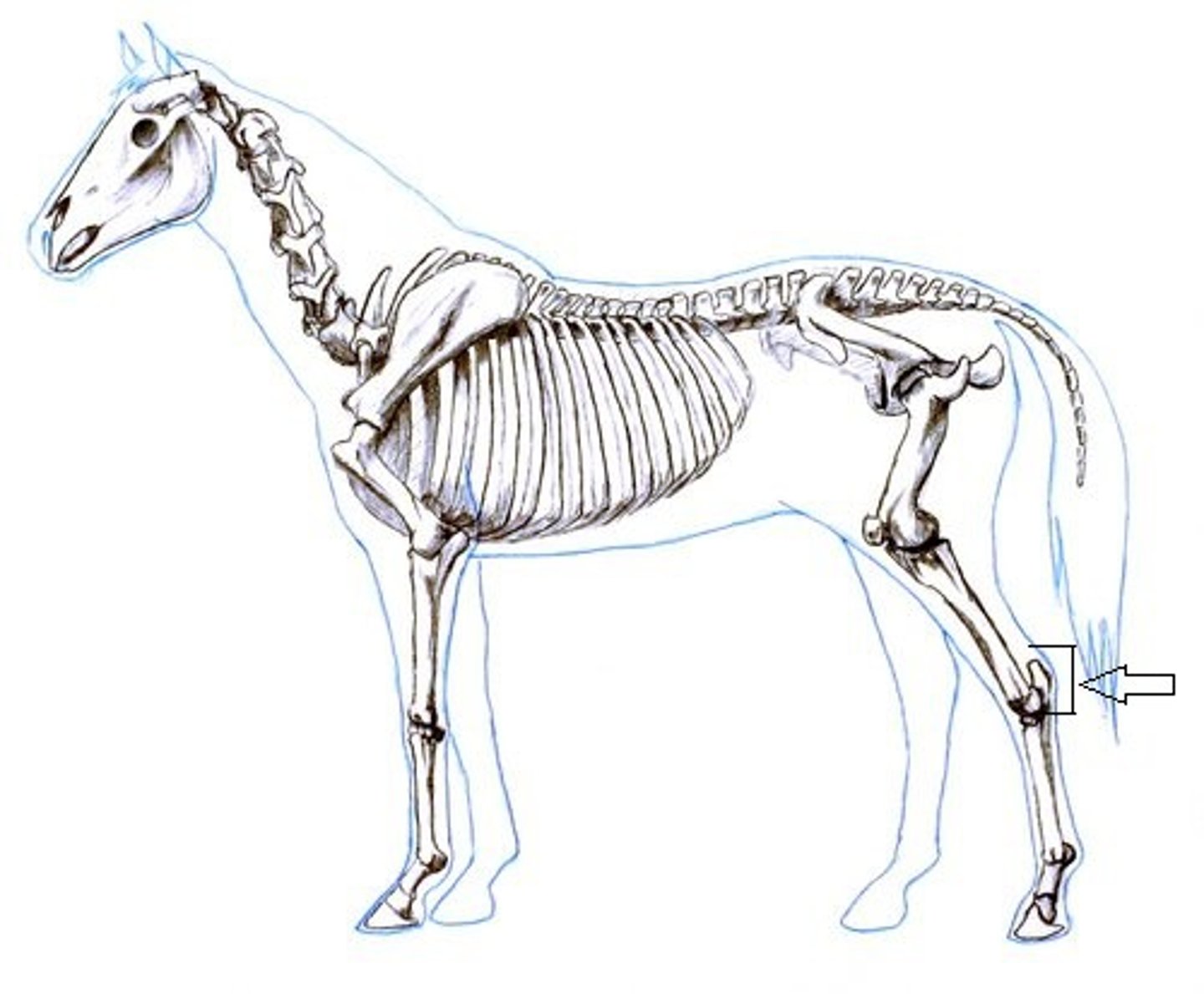
sledge joint
femoropatellar joint
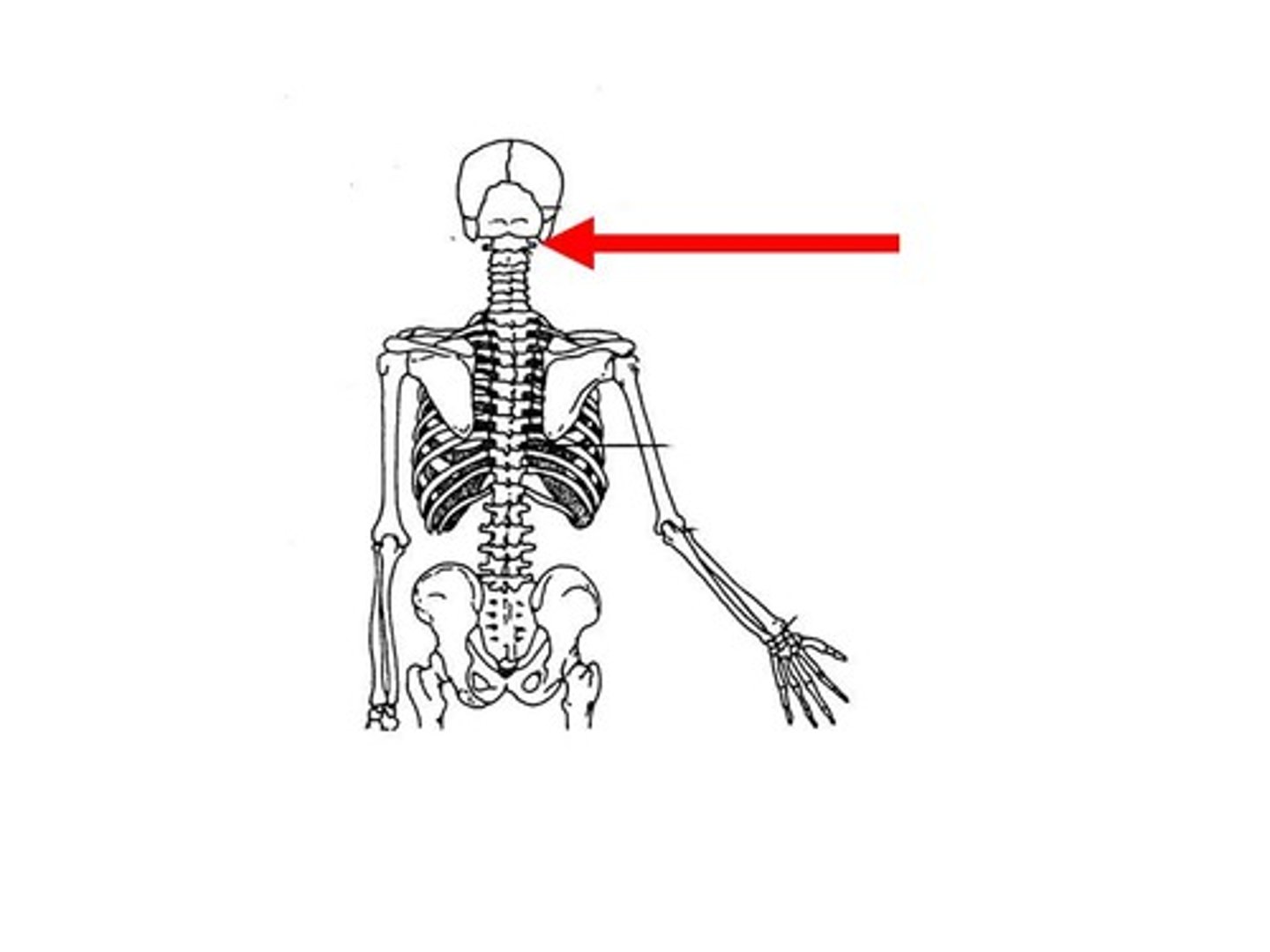
pivot joint
the joint axis is parallel to the long axis of the bones (atlantoaxial joint)
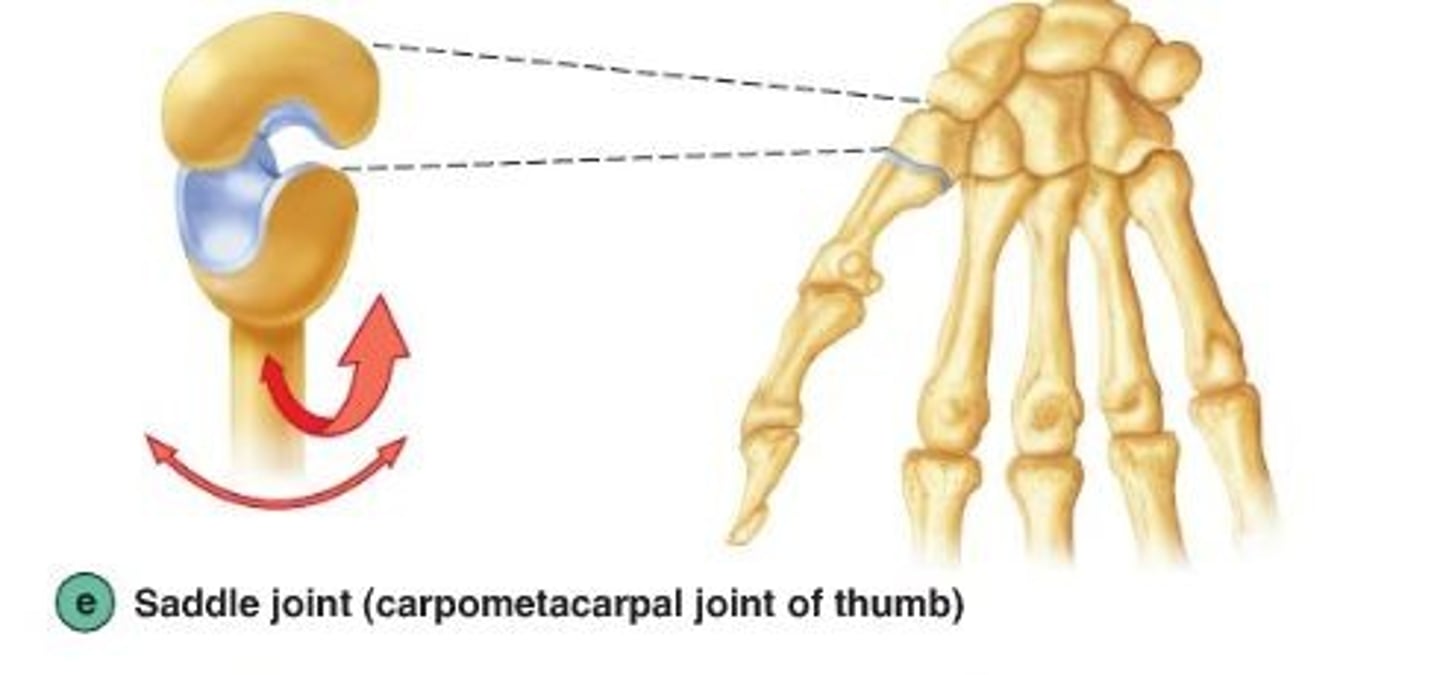
saddle joint
interphalangeal joints.
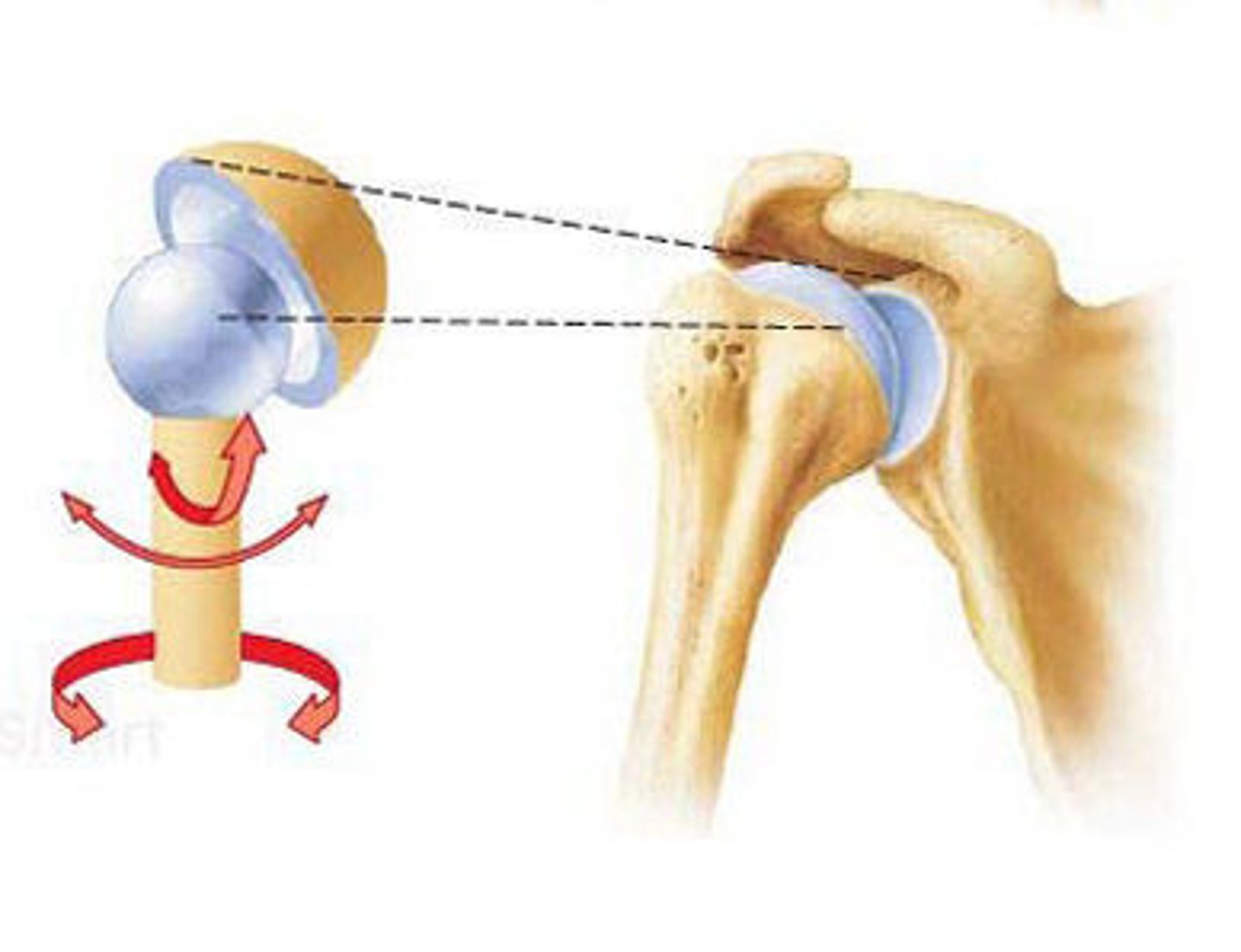
ball and socket joint
shoulder and hip
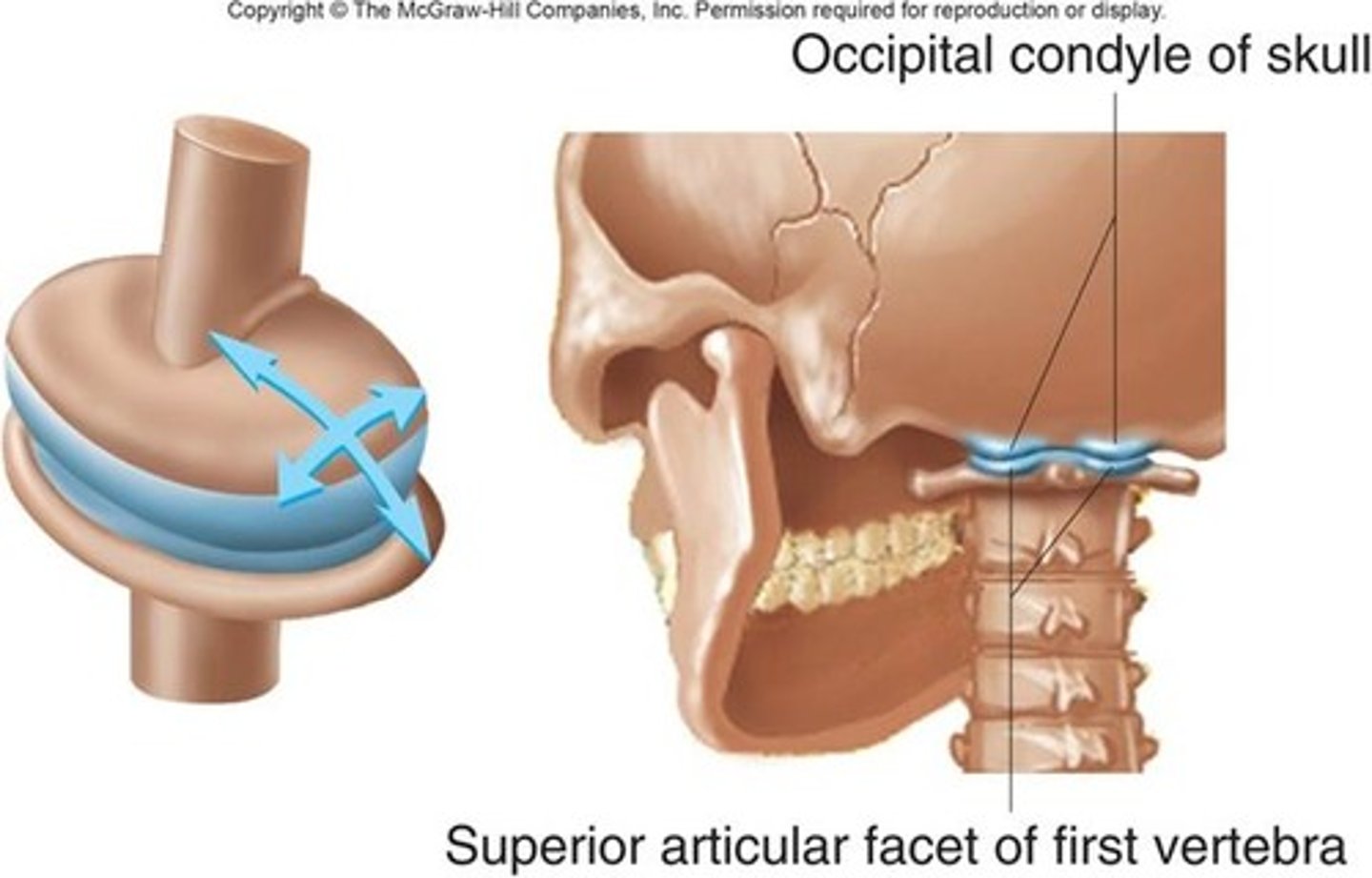
ellipsoidal joint
beetwen the occipital joint and the first cervial vertebra.
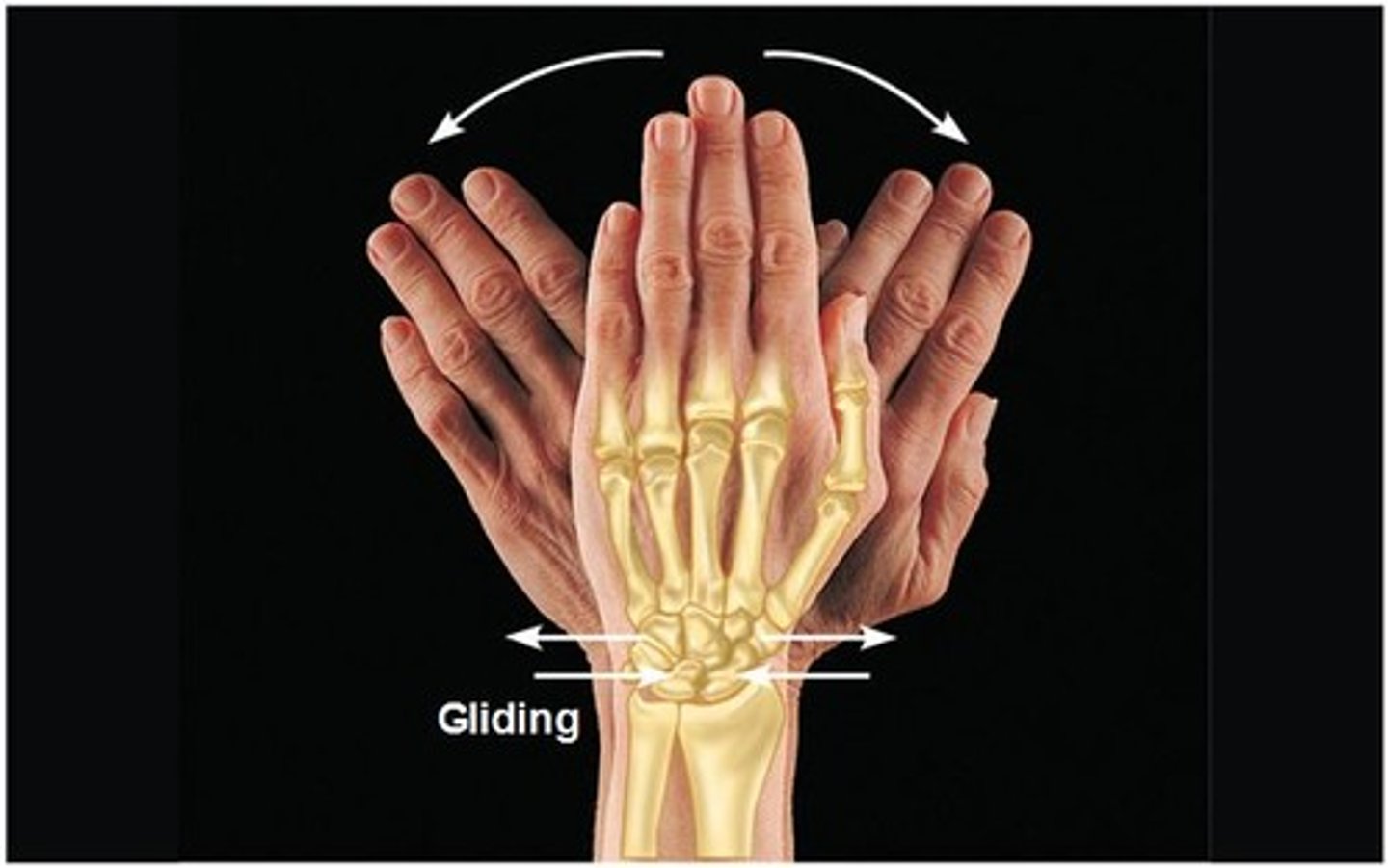
gliding movment
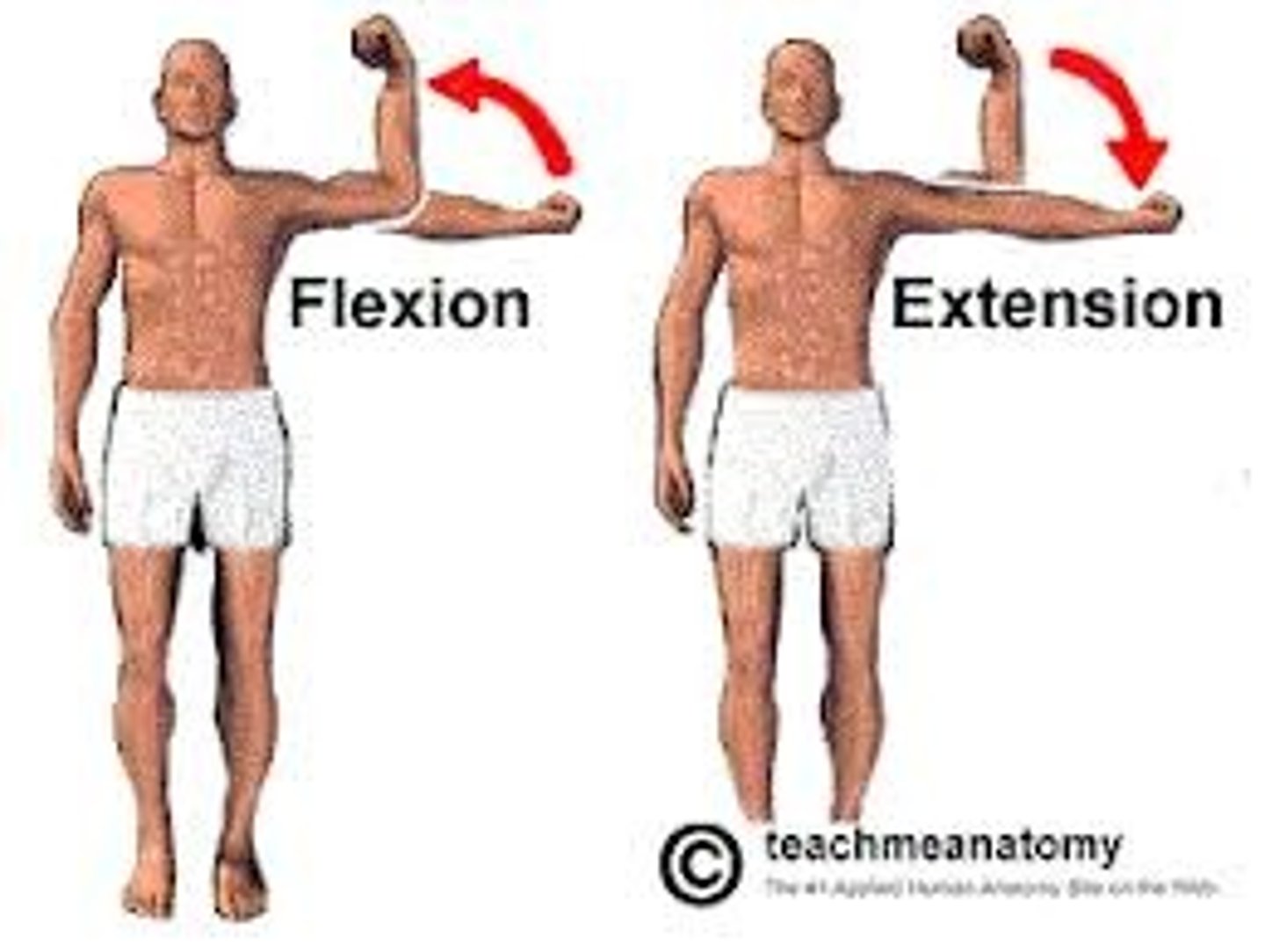
angular modification movement : flexion extension
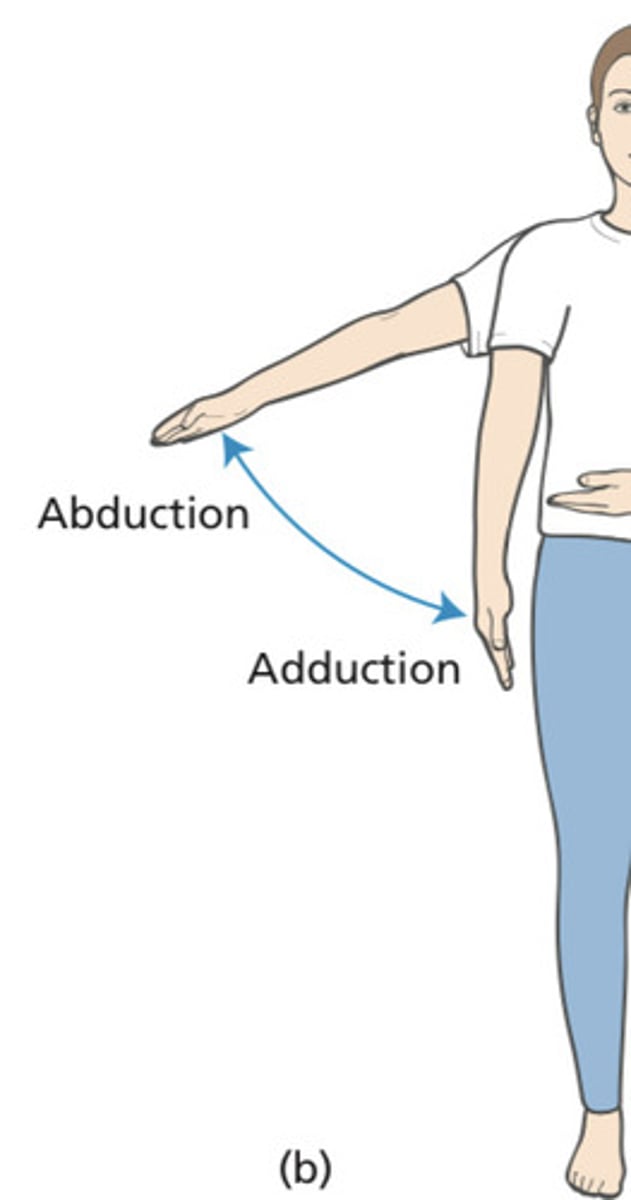
angular axial distance modification : abduction aduction
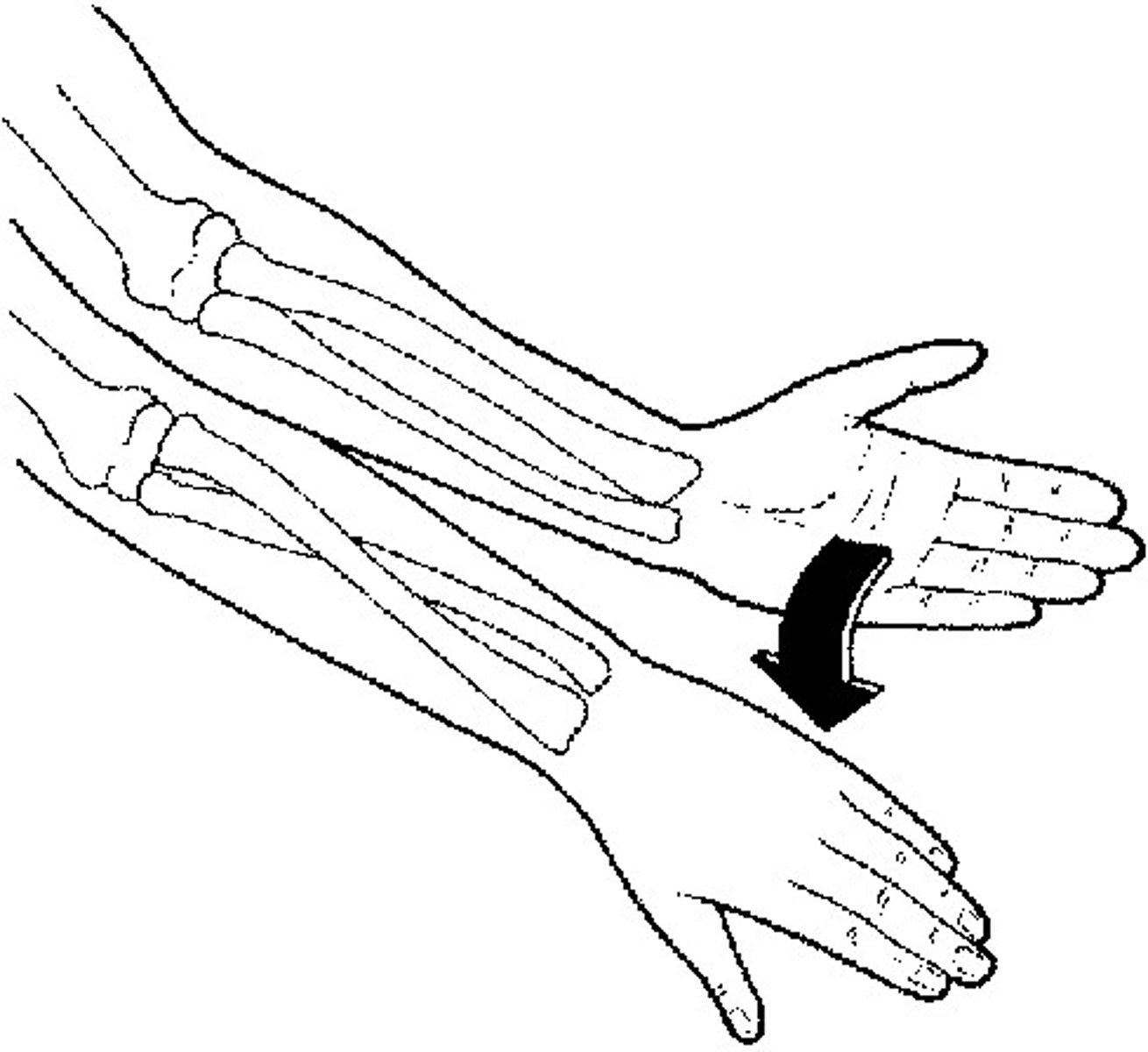
Supination
movement that turns the palm up
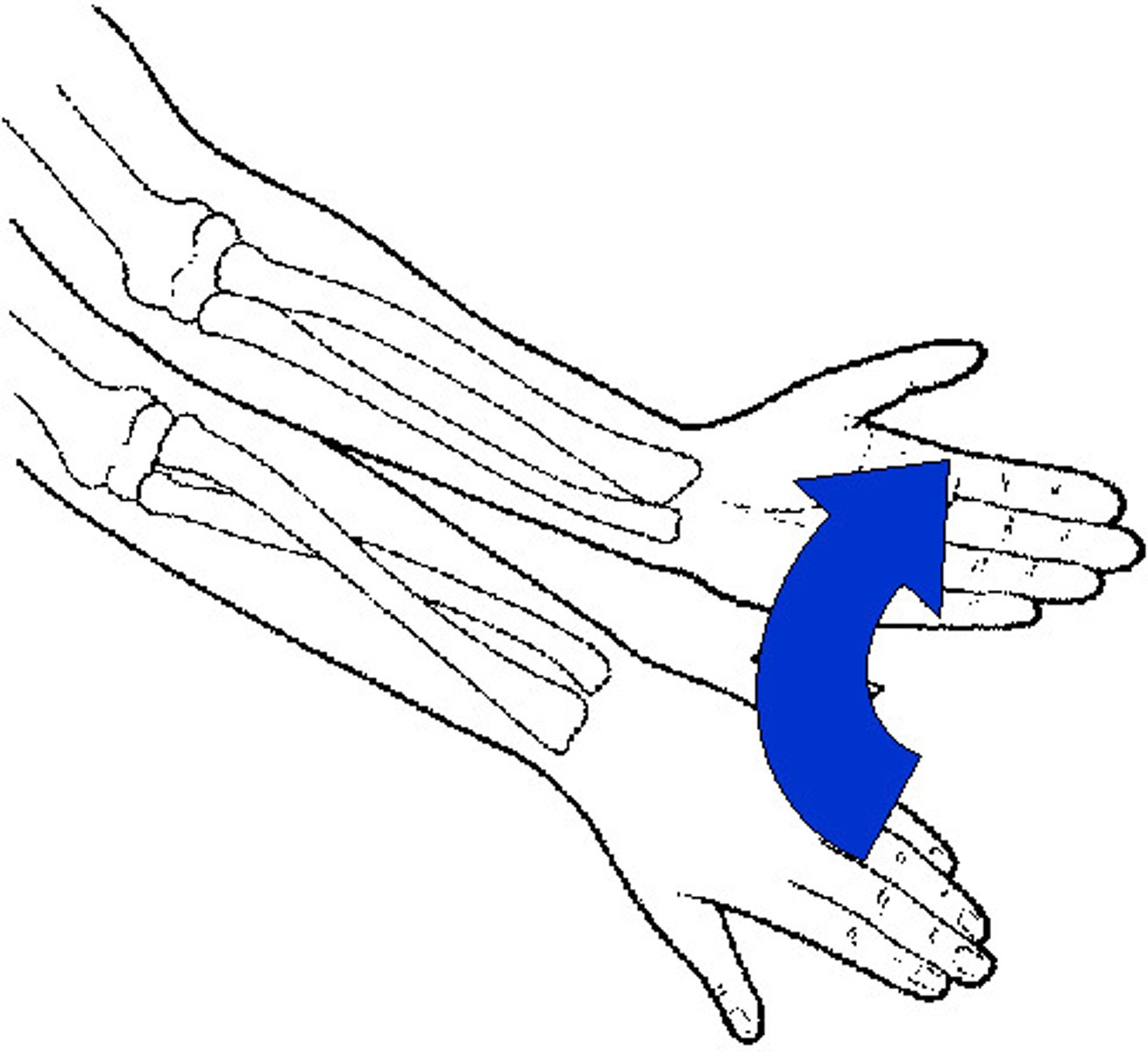
Pronation
turning the palm downward
anteversion
turning forward
retroversion
turning backward
Circumduction
circular movement of a limb at the far end
what is the muscle hilium ?
he provide vascularization to the muscle and the nerves
what is a fasciae ?
Can be superficial or deep, surrounds the muscle
What is a fibrous sheaths?
they support the fascia, tendon, and keep enerything joined to a bone
What is a synovial bursas ?
it's a sac filled with synovial fluid, it's for protection
What is a synovial tendon sheaths?
it's a special sinovial bursa