apes air pollution
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
incomplete
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
troposphere
where we live
air is most dense
where weather happens + where all pollution is
gets cooler as elevation rises b/c Earth’s surface is the heat source
stratosphere
2nd layer
where the ozone layer is
temp. rises w/ altitude
gases released from volcanic eruptions stay here
outdoor air pollution is considered pollution if…?
it is concentrated enough to cause harm to people and ecosystems
primary pollutants
emitted directly into the air
eg. CO
secondary pollutants
products of chemical reactions in the air
eg. NOx → photochemical smog
carbon monoxide (CO)
source:
incomplete/inefficient combustion
vehicles, furnaces, generators
HH impact:
MAINLY A HH CONCERN
binds to hemoglobin and prevents oxygen transfer → leads to headaches, nausea, dizziness, and eventually death
chronic exposure: heart attacks, lung disease
acute exposure: headache, nausea, drowsiness, death
carbon dioxide (CO2)
source:
burning fossil fuels
deforestation
HH impact:
none
environmental impact:
climate change
ocean acidification
nitrogen oxides (NOx)
source:
high-temp engines
coal plants
lightning/high intensity forest fires
vehicles
HH impact:
respiratory irritant → heart and lung disease
environmental impact:
precursor to acid deposition + smog
sulfur dioxide (SO2)
source:
volcanoes (natural)
burning coal
HH impact:
respiratory irritant
environmental impact:
- precursor to acid deposition
particulate matter (PM)
solid particles + liquid droplets small enough to remain suspended in air → fine + ultrafine particles most damaging
source:
dust storms
construction
volcanoes
forest fires
burning fossil fuels
HH impact:
respiratory irritant
environmental impact:
blocks light for photosynthesis
heavy metals (Pb, Cd, Hg, etc.)
source:
burning coal and industry
HH impact:
cancer
learning disabilities
mutations
environmental impact:
bioaccumulate + biomagnify
volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
gaseous + made up of hydrocarbons
source:
industrial solvents
car exhaust
pine trees
HH impact:
respiratory irritant
environmental impact:
precursor to smog
acid deposition
precipitation below a pH of 5.6 → falls as precipitation/dry deposition (crystals))
SOx + NOx precursors → mix w/ water vapor in air
remains in atmosphere for 2-14 days
consequences of acid deposition
kills plants → displaces aluminum from rock into soil
impacts ability to hold onto nutrients
pH can change aquatic life → bigger problem for smaller bodies of water
resp. disease from dry deposition — HH
damages human-made structures — economic
natural reduction of acid deposition
settling
precipitation
ocean spray wash-out
winds
chemical reactions (neutralization)
factors that increase acid deposition
urban buildings slow winds
hills/mountains
high temperatures inc. reaction rates
VOCs
volcanoes
grasshopper effect → transport by global winds from another city to a new place
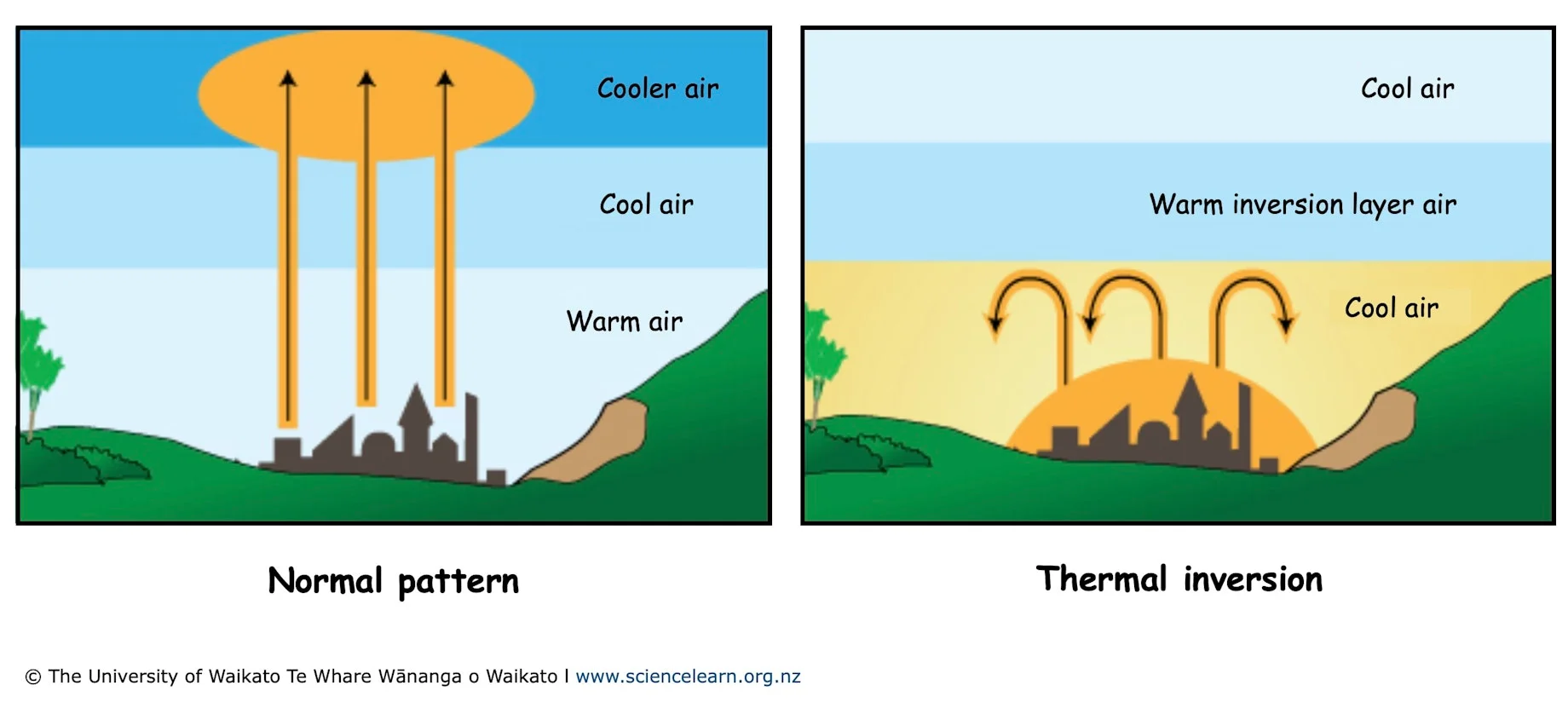
thermal inversion layer
thermal inversion layer
caused by warm fronts especially from ocean systems
causes a buildup of pollution
ozone and smog particularly bad
Clean Air Acts
1970:
set standards for air quality and fines on emissions
funds for pollution control research
allows citizens to sue parties for violating
1990:
strengthens standards for auto emissions, toxic air pollutants, etc.
ambient air quality standards
standards for 6 criteria pollutants: CO, NOx, SO2, O3, Pb, and PM
no legislature around CO2
standards for 188 hazardous chemicals
baghouse filter
fabric filter → removes PM
scrubbers
send exhaust in → spray mist → toxins dissolve in water
removes PM, SO2, + NOx
causes water pollution
electrostatic precipitator
removes ALL PM (incl. ultrafine particles)
vapor recovery nozzle
VOCs pumped out of gas tank → recover gasoline
catalytic convertor
reduces amt of NOx, CO, and gas fumes (VOCs) emitted from cars
ozone
stratospheric = good
tropospheric = bad
formed by oxygen and high energy light → UV light breaks apart O2 and stray O molecule joins O2 → O3
not a stable molecule → O3 naturally decays into O2 and O
stratospheric ozone
good
absorbs harmful UV radiation — UV-B+C
hole in the ozone layer
chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
major cause of the hole in the ozone layer
primarily used as a refrigerant
very persistent molecule → one molecule has a BIG impact
strong greenhouse gas
prevent formation of new ozone and facilitate breakdown
Montreal Protocol
agreement between 24 countries to phase out the use of CFCs → huge success
passed in 1987
will take a long time for the environment to recover from CFCs b/c they remain in the atmosphere for a very long time
tropospheric ozone
very bad
secondary pollutant → formed from NOx, VOCs, and UV light
concentration varies w/ season + time of day due to UV concentration and temperature
consequences: formation of smog, resp. irritant, damage to plant leaves
monitored by CAA
photochemical smog
secondary pollutant
mix of pollutants: O3, NOx, PM, & VOCs
O3 = major component
indoor air pollution
different sources in developing/developed countries
more harmful than outside → level s generally higher in homes (5x) and cars (18x)
common indoor pollutants
pesticides + lead → common in old paint
dust mites + droppings
molds + mildews
formaldehyde + other VOCs
asbestos
radon
asbestos
from insulation/other building materials
very strong carcinogen
no longer used but still present in old buildings
radon
comes from radioactive decay that seeps + settles into basements
strong carcinogen
natural pollutant
sick building syndrome
when there is a build up of indoor VOCs, chemical contamination, biological contamination, + other materials that cause residents/those inside to feel sick
symptoms: headache, nausea
solution: air out building
common in new office buildings
main source of indoor pollution in developing countries
burning biomass/coal in an open fire indoors
PM, CO, NOx
health effects of indoor pollution
asthma aggravation
emphysema
lung cancer
heart disease
dose-response studies
different experimental groups with different doeses
usually animal studies
goal: to find LD-50 + ED-50
acute + chronic studies
LD/ED-50
LD-50: lethal dose that kills 50% of individuals
ED-50: effective dose that causes 50% of individuals to display harmful but nonlethal effects
threshold
dose where any impact was had
safe dose
animals: LD-50/10
humans: LD-50/1,000 (super cautious for people)
acute study
lasts 1-4 days; studies short-term effects
chronic study
long-term; often from young age to reproductive age
retrospective studies
looks at human/animal populations over time (exposed/non-exposed)
looks at past events
est. exposure to a chemical in environment + evaluates health problems
eg. Bhopal, India → maj. pesticide leak
prospective studies
monitors people going forward if they are already exposed/might be in the future
used for tobacco/alcohol studies, vapes, lead exposure on IQ
bioaccumulation
process of a toxin being absorbed + accumulating in an individual/s body
typically fat-soluble
biomagnification
producer gets