ESRD: Dialysis
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
CKD complications
dialysis indications

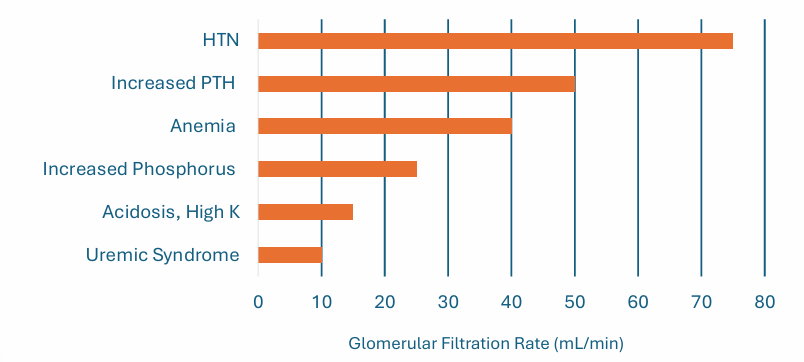
early v late initiation of dialysis

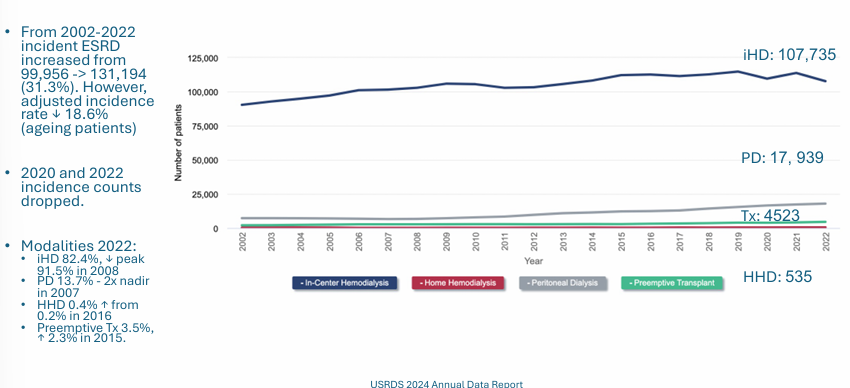
ESRD prevalence
-prevalence of ESRD increased over 30 years (all modalities)
-since 2019 prevalence and incidence counts decreased slightly (COVID-related)
-815,896 patients with ESRD in 2022
ESRD incidence
goals of dialysis
-eliminate nitrogenous waste products
-maintain euvolemia
-control acid base and electrolyte balance
-maintain large proteins and blood in circulation
-additional ESRD treatments: stimulation of erythropoiesis, vitamin D metabolism
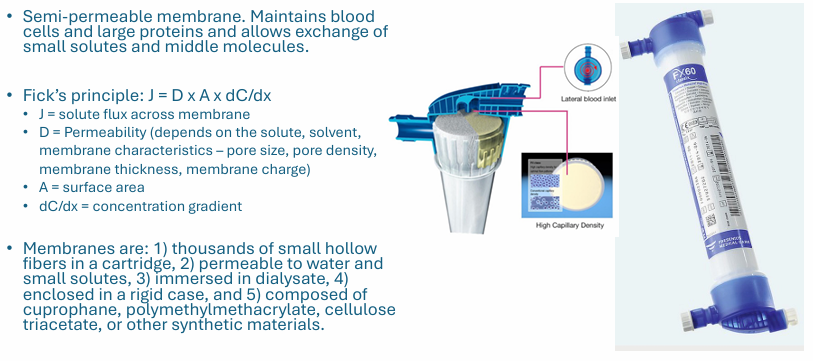
hemodialysis membrane
hemodialysis process
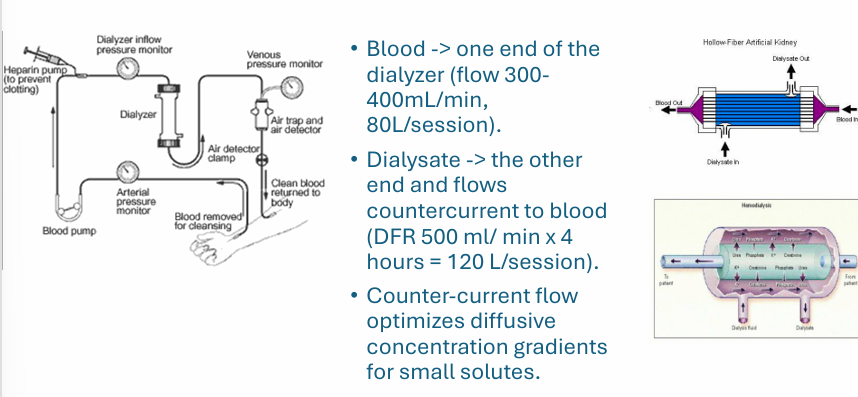
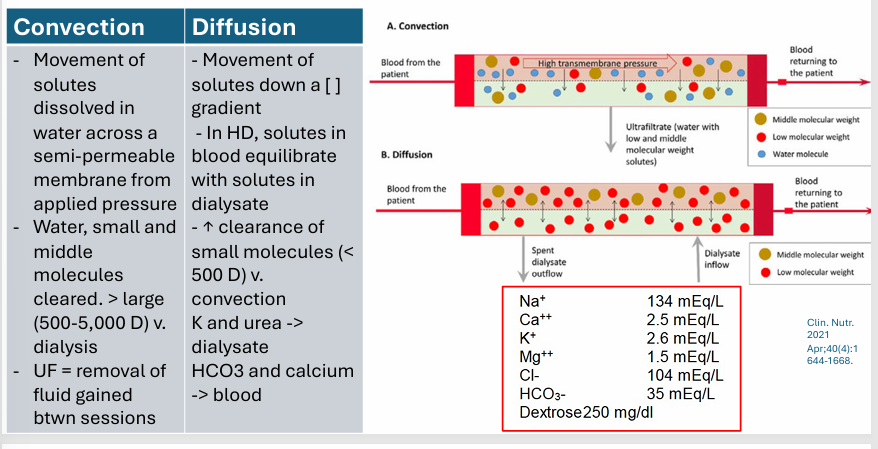
hemodialysis principles
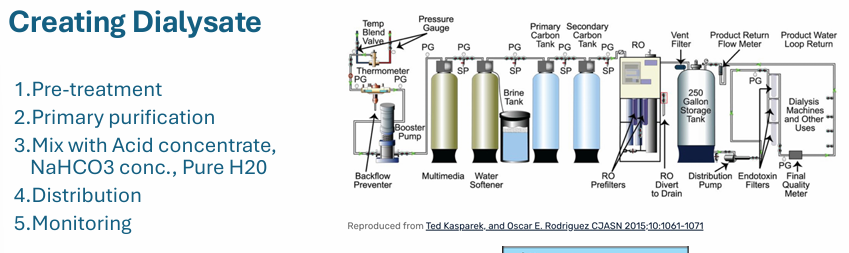
creating dialysate
treatment complications
-allergy to membrane or circuit
-infection from “sterile water”
-hemolysis from contaminants, trauma, temp, osmolarity
-decreased bp from removing blood and plasma
-electrolyte shifts
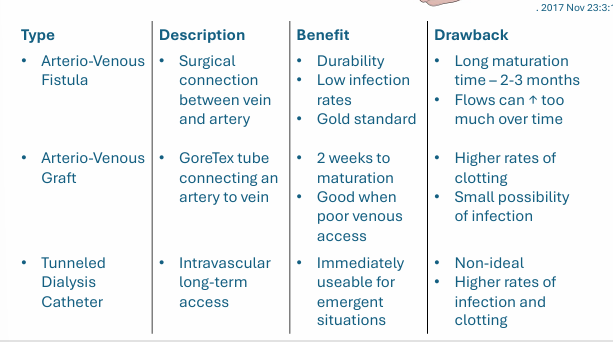
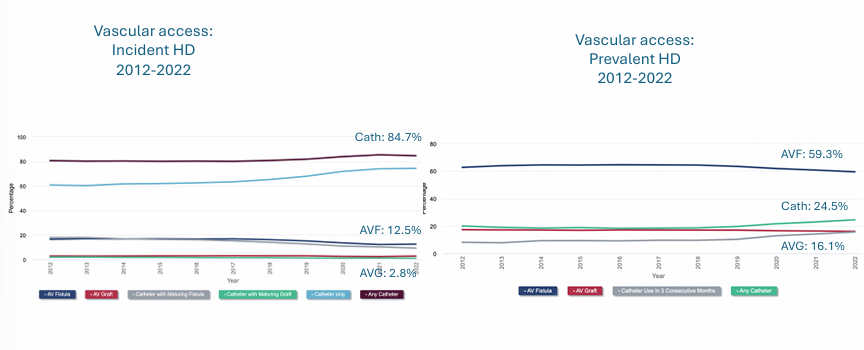
vascular access for hemodialysis- type, description, benefit, drawback
vascular access epidemiology
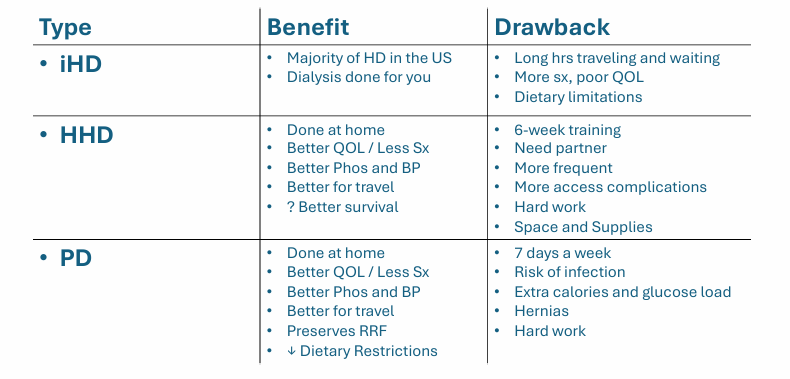
in-center hemodialysis (iHD)
-sessions generally 3x/week at center
-done by dialysis nurse or tech
-high dialysate flows (500-800ml/min) → fast solute removal
-limited weekly dialysis time (average 10.5hrs) → more sx during and after iHD
-travel and wait-times can be burdensome
home hemodialysis (HHD)
-same principles as iHD including access, however a smaller HD machine is brought into the home
-patients trained to do their own dialysis (usually lasts 4-6 weeks)
-to minimize dialysate use, dialysate flows are slower, and blood and dialysate almost completely equilibrate
-slower dialysate flows necessitate more frequent dialysis to get adequate clearance (4-5x/week)
-more frequency HD → decreased symptoms
peritoneal dialysis
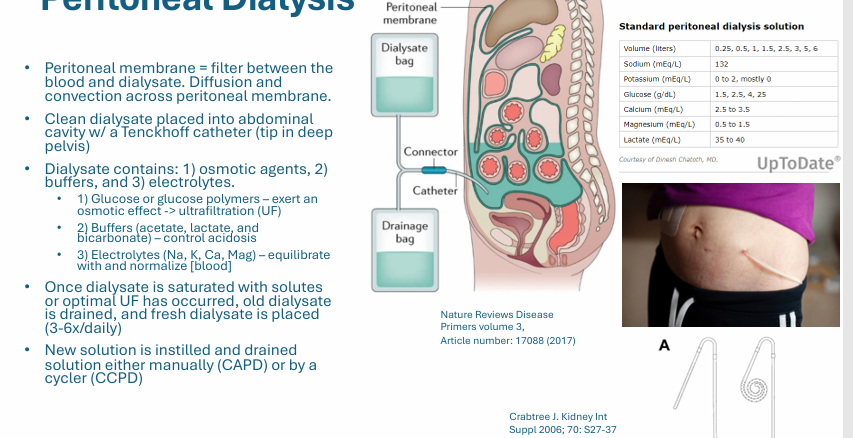
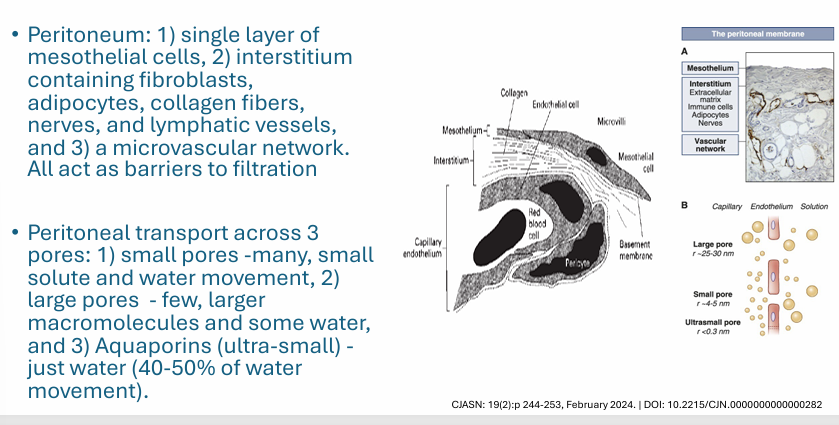
PD membrane
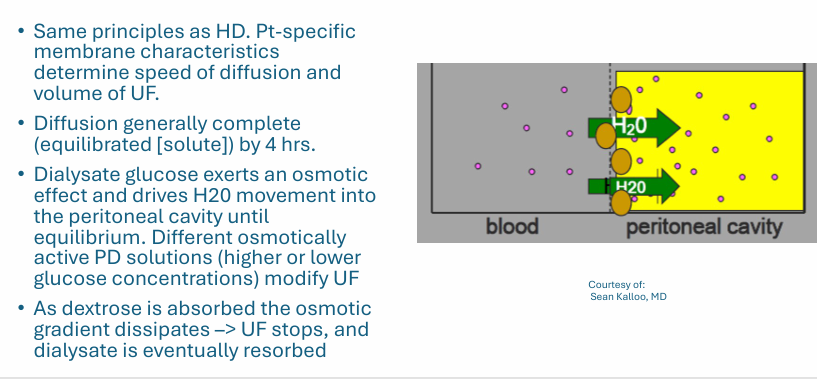
PD diffusion and convection
comparing dialysis modalities- type, benefit, drawback (iHD, HHD, PD)
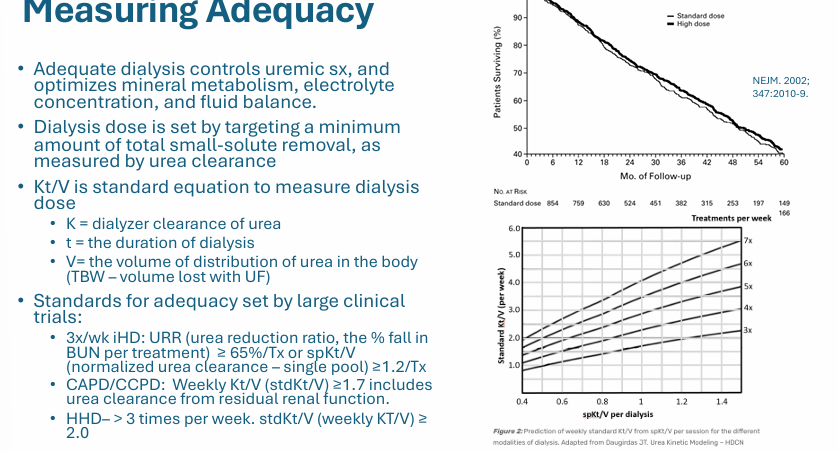
measuring adequacy
conservative kidney management

good candidates for CKM
->/= 1 life-shortening comorbidity
-frailty with significant preexisting functional or cognitive impairment
-reside in long-term care facility
-severe pain or suffering
-cognitive impairment that impairs safe dialysis delivery
-in patients >/= 80, dialysis may not confer a survival advantage
other advantages of CKM
approaching ESRD preparation
-multidisciplinary team- patient navigator, clinical nurse specialist or a NP with expertise in modality education, nutritionist, social worker, nephrologist, palliative care
-discuss pros and cons of each modality- very few absolute contraindications to home dialysis
-education through multimodal means (written, audio, video)
-use decision guides and electronic tools for prognostication
-facility tours and simulation (digital or high fidelity)
dialysis complications

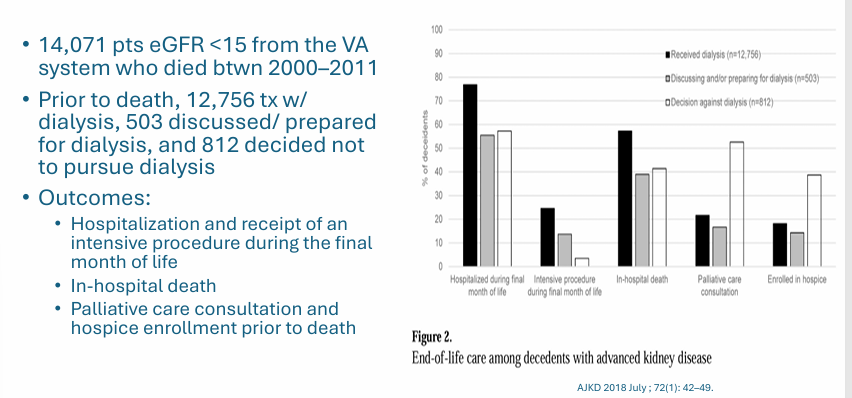
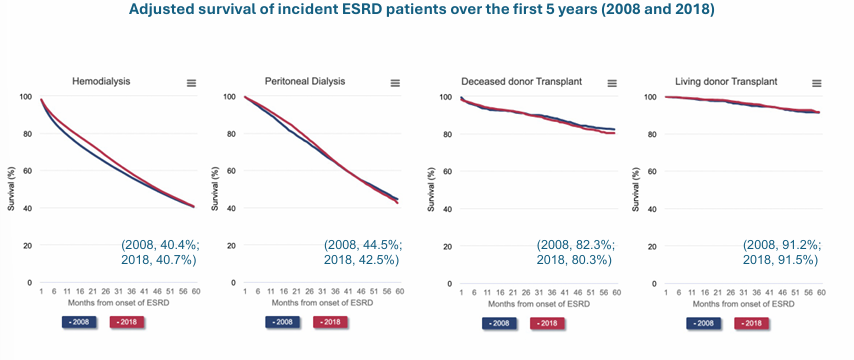
ESRD complications- mortality
causes of death and hospitalization
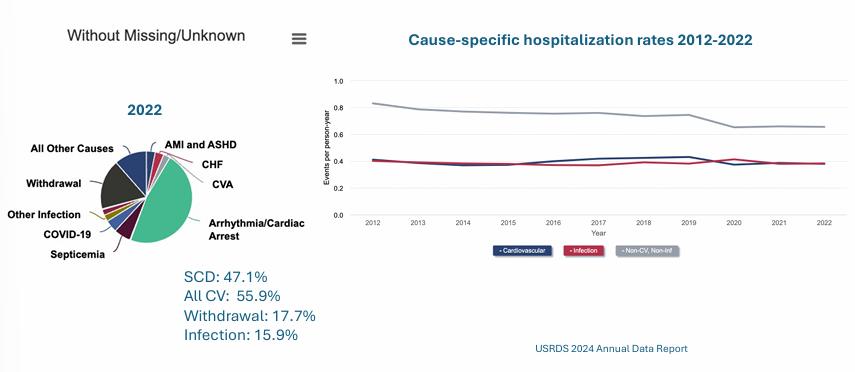
elevated CV risk
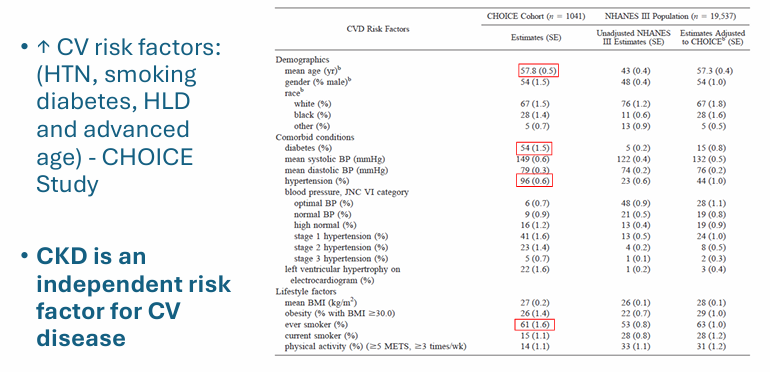
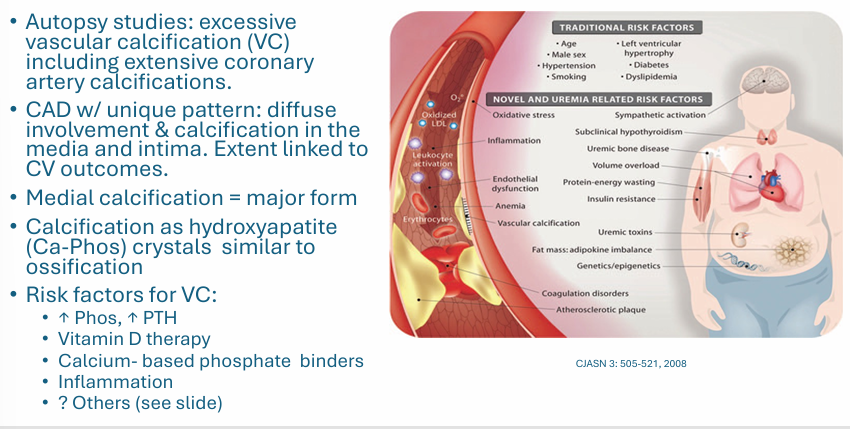
independent CV risk factor
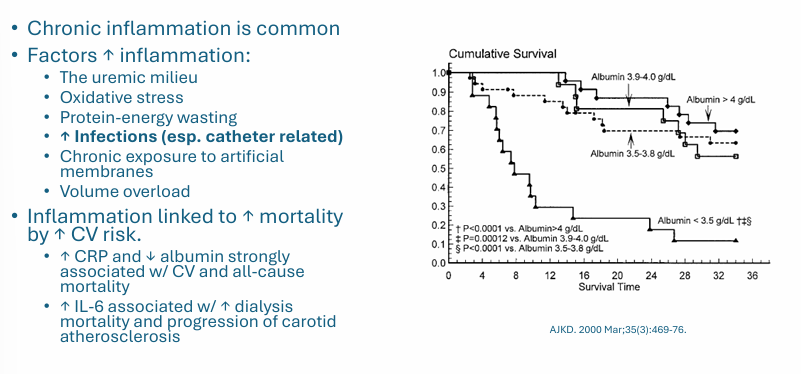
mortality and CV risk- inflammation
morbidity- infection

factors affecting morbidity and mortality

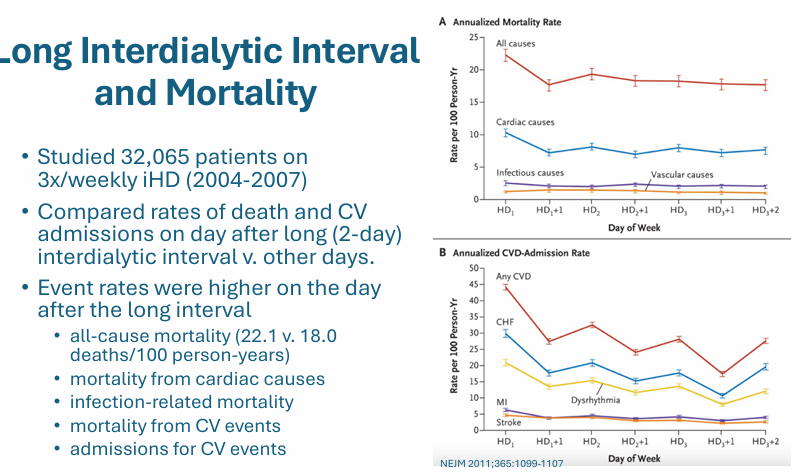
long interdialytic interval and mortality
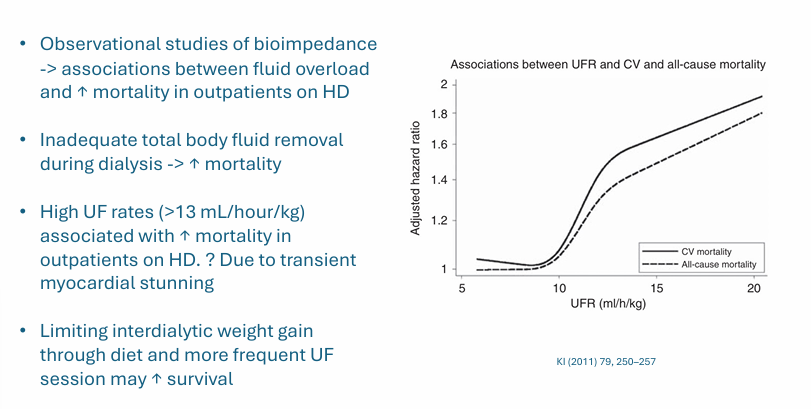
volume overload and mortality
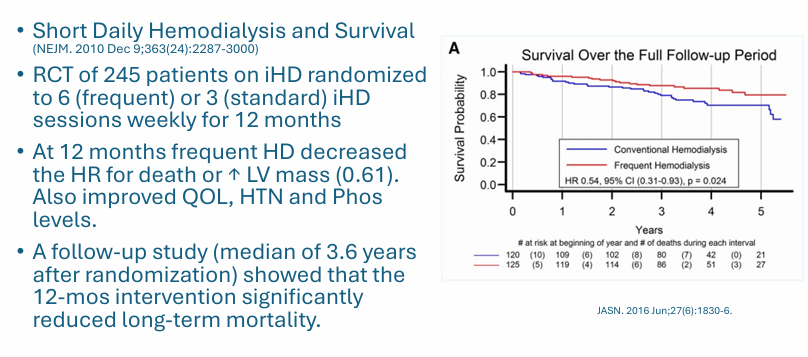
intervention- more frequent dialysis
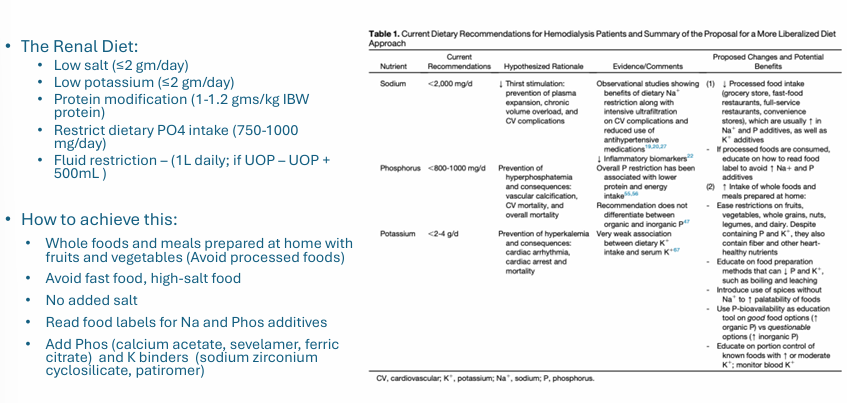
intervention- dietary modification
dialysis complications- poor QOL
-HrQOL for patients on dialysis is significantly worse than the general population and among the worst of any chronic illness
-PCS/MCS are on average 33/46 in US patients on dialysis- both are significantly lower than norms for the general population (~50)
-scores are worse for patients with limited use of arm(s) and/or leg(s), depression, chronic lung disease, CHF, arthritis, cancer, diabetes, angina, hypertension
what leads to poor QOL on dialysis?
-depression
-burdens of self-care: dietary restrictions, medications, comorbid conditions, HD treatment
-symptoms: itching, cramping, fatigue, sexual dysfunction, sleep disorders
depression in ESRD
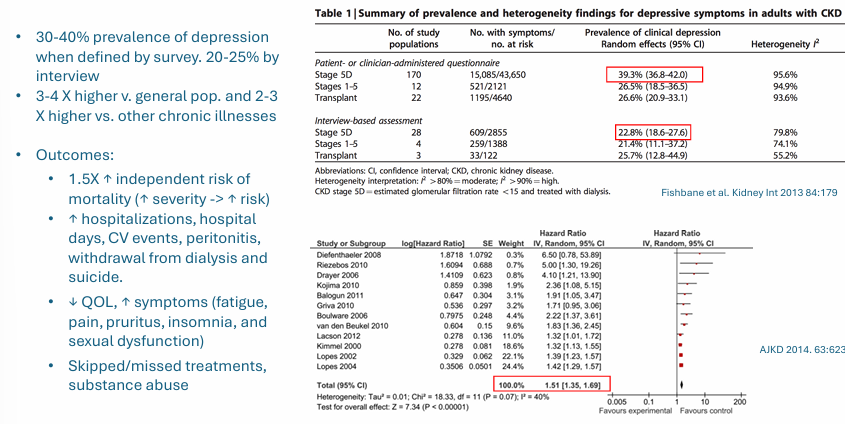
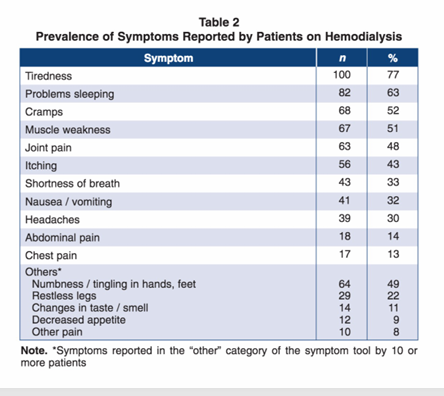
symptoms in hemodialysis
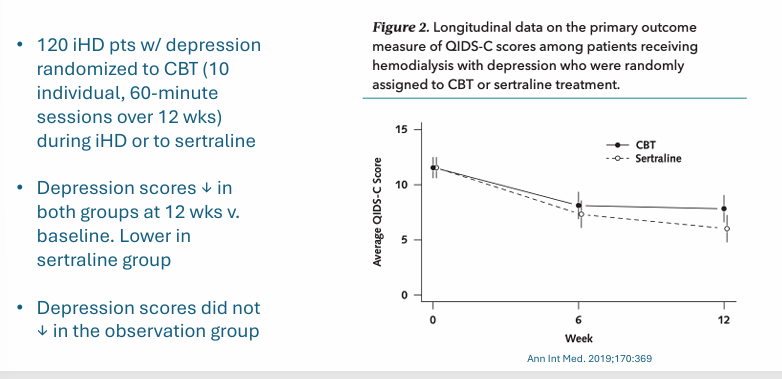
improving QOL- depression
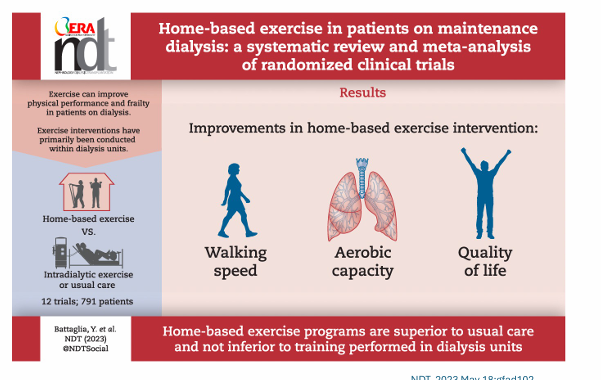
exercise and QOL
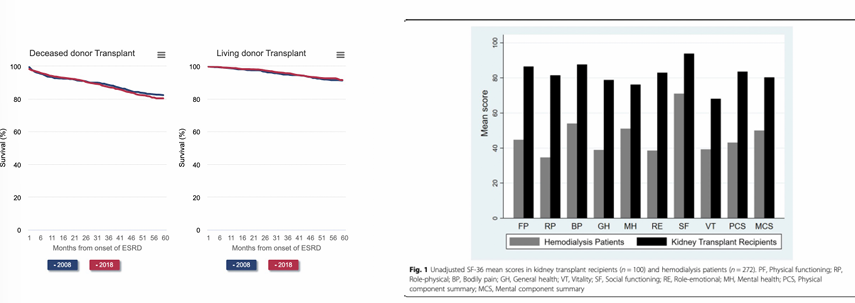
benefits of transplant