Physics Final Vocab
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Equilibrium
center of wave motion
Amplitude
maximum displacement from equilibrium. A traveling wave goes from +amplitude to -amplitude
Crest
positive amplitude
Trough
negative amplitude
Wavelength
distance from creast to crest (or trough to trough)
Frequency
measured in Hertz
Medium
the substance/material that the wave energy travels through
Wave motion
the motion of the individual particles of the medium
Transverse wave
wave where the direction of motion of the individual particles of the medium are perpendicular to the direction that the wave travels in.
Longitudinal wave
wave where the direction of motion of the individual particles of the medium are parallel to the direction that the wave travels in
Wave pulse
a single, non periodic excitation of a medium
Law of Reflection
relates the angle of the incoming or incident wave to the angle of outgoing or reflected wave (angles are always measured perpendicular to the surface) FOR MIRRORS
Law of Refraction
If the wave hits the interface between the medium at an angle, the refracted wave angle changes according to Snell’s Law (only occurs when speeds of incident ray are different)
faster medium = bigger angle
Snell’s Law
angle is draw perpendicular to the surface
sin(angle 1)/sin(angle 2) = (v1)/(v2)
Index of Refraction
Speed of wave in vacumn is always 3×10^8 m
n = c(speed of light)/v(material) = c
BIGGER N MEANS SLOWER INDEX OF REFRACTION
Snell’s Law with Index of Refraction
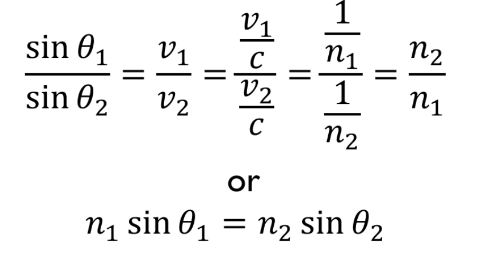
Refraction Concepts
in a new medium, the wave speed changes but frwquency is unchanged
wavelength changes to match the wave equation
index of refraction is always greater than 1
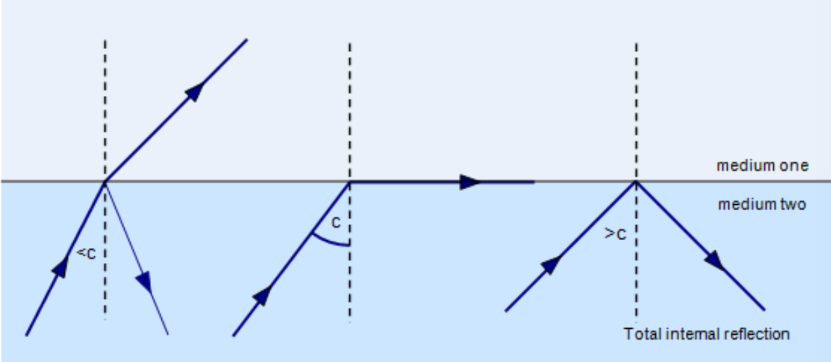
Critical Angle
the angle the incident wave makes
Critical Angle Math
sin(angle) = n2/n1
Total Internal Reflection
After the critical angle is reached, none of the energy is transmitted. Instead, all of the energy is reflected.
Rainbows
The index of refraction is dependent on the frequency or wavelength of the light traveling through it
The different colors of white light get bent differently so the colors get separated.
Light properties
light is an electromagnetic wave (it has particle like porperties)
the speed of light eq is c= 3 × 10^8 ms^-1
wave eq for light is c = f*wavelength
wave reflection
Wave energy tends to reflect whenever the wave hits a change in medium
◦ Sound hitting a wall
◦ Water hitting the edge of a bowl
◦ Light hitting a mirror
wave superposition
two waves add together during the collison
the energy of the two waves continues in their original direction after the collision
interference
when two or more waves collide
Constructive interference
when the collision results in a larger amplitude than individual waves
destructive interference
when the collision results in a smaller amplitude
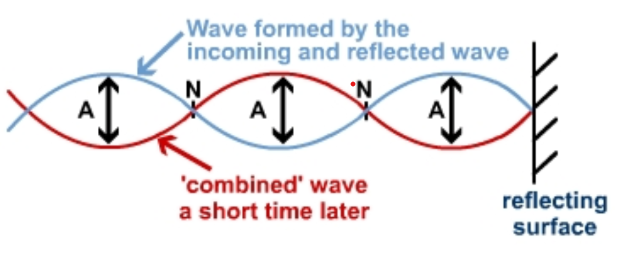
Antinode
point of maximum cconstructive interference; greatest movement
Node
point of maximum destructive interference; no movement
Standing Waves
When a wave collides with its reflection and the conditions are perfect a standing wave is created.
Speed is controlled by the medium (v)
Length is controlled by the setup (L)
Frequency is controlled by the setup (f)
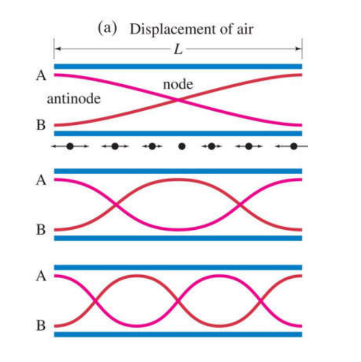
Harmonic
longest is the first harmonic or fundemental frequency
wavelength formula - harmonic
wavelength = 2L/number harmonic
frequency formula - harmonics
fn = number harmonic * frequency
sound
The wave is longitudinal.
The air molecules move back and forth, being compressed and stretched (compression/rarefaction).
sound is a wave
we use a number around 340 m/s
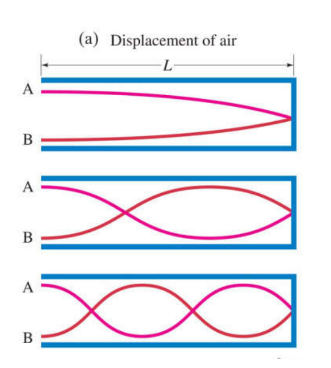
open-open air tube
open ends must be antinodes - the air has the most freedom to move
L = n(wavelength/2)
wavelength = 2L/n
Frequency at n harmonic = number harmonic x initial frequency
closed-open air tube
closed ends must be nodes - the air cannot move
L = n x (wavelength/4)
wavelength = 4L/number harmonic (but n can only be odd)
Frequency at n harmonic = number harmonic x intial frequency
doppler effect
the change in the frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the source of the wave.
closer = higher freq; farther = lower freq
Vision
light is an electromagnetic wave
generally travels in packet called photons and these packets travel in a straight line
photons hit retina
rods and cones convert light energy to neural signals
photons can either be absorbed or reflected
object distance d0
the distance of the object to the mirror or lens
image distance di
the distance of the image to the mirror or lens
upright images
vertially oriented the same way as the object
inverted images
vertically oriented upside-down compared to the object
virtual images
appears on the other side of the mirror or lens from the observers viewpoint
real image
appears on the same side of the mirror or lens
magnified image
appears larger than the object
reduced or demagnified
appears smaller than the object
coverging
an optical device that focuses light rays (e.g. concave mirror or convex lens)
diverging
an optical device that spreads light rays out. The focal point is on the “wrong” side (e.g. convex mirror or concave lens)
plane mirror image
virtual image
appears upright, same size as object
d0 = di
spherical concave mirrors
designed to focus incoming light from far away on a single point called focal point
f is used to represent distance from mirror to focal point
center of curvature
spherical mirrors have a center of curvature
c is used to represent distance from mirror to center of curvature
c is equal to center of circle and distance to mirror/lens is radius of the circle
FOCAL POINT IS HALF THE RADIUS
c= 2f or f = c/2
spherical convex mirror
has a focal point is the point where the light rays appear to originate from
negative distance from the mirror
ray diagram
only draw 2 rays
image places where the reflected rays intersect
extend lines to achieve nessecary intersections
convex mirror
center of curvature and focal point are on opposite sides of mirror
flat (plane) mirror
has a radius of curvature of infinity
Lens Ray Diagram Rules
First Ray: Parallel to the first focal point and through it
Second ray: through the second focal point then parallel
Third ray: through the center of the lens itself
concave lens
follows the same ray diagram rules
focal points are reversed
f (distance from mirror to focal point) is negative
atoms
made up of protons nuetrons and electrons
a material where the elctrons can move freely about (metals, wires, water)
has a lot of ions
a material where the electrons are not free to move
rubber glass air
a special type of material that acts as both a conductor and insulator depending on the situation
can act like a switch letting electrons pass (conductor)
can block electrons from passing (insulator)
key to the information revolution
strong nuclear force, electromagnetic force, weak nuclear force, gravatational force
describes force between two charged object
“The force between two charged objects is proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the objects.”
use newtons
inversly proportional the the square of distance
measured from centers
proportional to the product of the two charges
very strong
attractive or repulsive
use newtons
inversely proportional to square of distance
measured from centers
proportional to product of the two masses
very weak
attractive only
unit for charge
rubbing
contact (conduction)
induction
polarization
one object will become positive and one object will become negative
ONLY ELECTRONS MOVE NEVER PROTONS
charges shifted slightly to one side
overall nuetral
positive on one side and negative on the other
electric potential
two stored energy assosciates with two charges held in position'
same as voltage
formula is V = K * Q/r
equipotential lines
always drawn perpendicular to the electrical field
electrical field always goes in direction of decreasing voltage
uniform electrical field
formula: change in voltage = Ed
equipotential lines are parallel to plates
electric potential at multiple charges
the electric potential at a given points is the sum of the electric potential from each charge (keep sign from charge)
work on a charge
equipotnetial lines assist in calculating work on a charge and therefore kenetic energies
w= -q(change in V) = change in KE
if a charge moves from VOltage A to Voltagee B then the field does work on the charge
thin lens formula
1/f = 1/do + 1/di
convex mirror and cocave lens
negative focal point
magnification
M = hi/ho = -di/do
all real images are inverted
real distances are positive
virtual distances are negative
|M| > 1 magnified
|M| < 1 means reduced