Unit 1: Biochemistry
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Isotopes
Same element, different number of neutrons.
Radioisotopes
Unstable isotopes that decay & release radiation.
Valence electrons
Electrons in the outer shell; control bonding.
Ionic bond
Transfer of electrons (NaCl).
Covalent bond
Sharing of electrons (H₂O).
Polar covalent bond
Unequal sharing of electrons (H–O).
Non-polar covalent bond
Equal sharing of electrons (H–H).
Intermolecular bonds
Forces between molecules (e.g., H-bonds).
Intramolecular bonds
Forces inside a molecule (e.g., covalent).
Van der Waals forces
Weak attractions from temporary dipoles.
Hydrogen bond
Weak attraction between H and O/N/F.
Hydrophilic
“Water-loving,” polar, dissolves in water.
Hydrophobic
“Water-fearing,” nonpolar, doesn’t dissolve.
Miscible liquids
Mix completely (water + ethanol).
Immiscible liquids
Don’t mix (oil + water).
Organic compound
Contains C + H (often O, N).
Hydrocarbon
Organic compound with only C + H.
Molecular formula
Actual # of each atom (C₆H₁₂O₆).
Empirical formula
Simplest ratio of atoms (CH₂O).
Monomer
Small building block molecule.
Polymer
Chain of monomers.
Dehydration Synthesis
Joins monomers, removes water.
Hydrolysis
Breaks polymers, adds water.
Monosaccharide
Single sugar unit (glucose).
Disaccharide
2 sugars (maltose, sucrose, lactose).
Polysaccharide
Many sugars (starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin).
Starch
Plant storage polysaccharide.
Glycogen
Animal storage polysaccharide, highly branched.
Cellulose
Plant cell walls, cannot be dugested. Picks up toxins and food for microbiota
Chitin
Insect exoskeletons, fungi cell walls.
Triglyceride
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids.
Saturated fatty acid
No double bonds, straight chain.
Unsaturated fatty acid
Double bond(s), bent chain.
Phospholipid
Glycerol + 2 fatty acids + phosphate group.
Steroid
Lipid with 4 fused carbon rings (cholesterol, hormones).
Waxes
Waterproof coatings in plants/animals, insoluble
Amino acid
Monomer of proteins (NH₂, COOH, H, R).
Polypeptide
Chain of amino acids.
Peptide bond
Link between amino acids.
Denaturation
Loss of protein shape due to heat/pH.
Enzyme
Protein catalyst, lowers activation energy.
Substrate
Molecule enzyme acts on.
Active site
Region where substrate binds.
• DNA
Double-stranded, bases A, T, G, C.
• RNA
Single-stranded, bases A, U, G, C.
• Purines
A, G 5 memebered ring fused to a 6 membered ring (2 rings).
• Pyrimidines
C, T, U 6 membered ring made up of C and N atoms (1 ring).
• Nucleotide
Sugar + phosphate + base.
• Phospholipid bilayer
2 layers, hydrophobic tails inside, hydrophilic heads outside.
• Integral proteins
Span the membrane (transport).
• Peripheral proteins
Surface proteins (signaling, support).
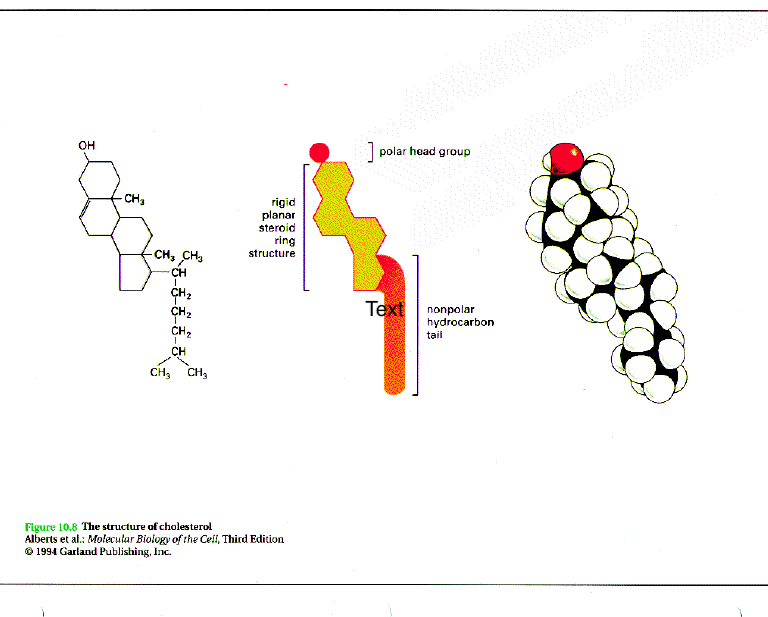
Cholesterol
Reduces membrane fluidity
Hydrophobic with one hydrophilic head
Allows membranes to function in a wide range of temps
Helps in the formation of vesicles.
• Membrane protein functions
Transport, signaling, enzymatic activity, recognition.
• Catalyst
Speeds reaction, not used up.
• Activation energy
Energy required to start a reaction.
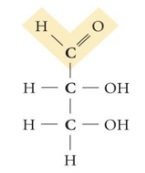
Glyceraldehyde
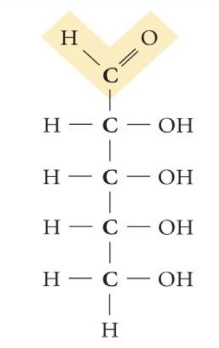
Ribose
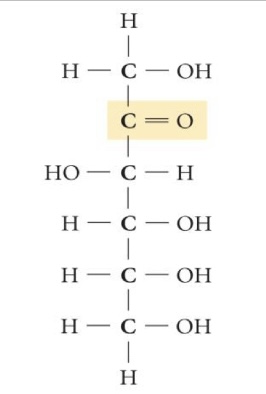
Fructose
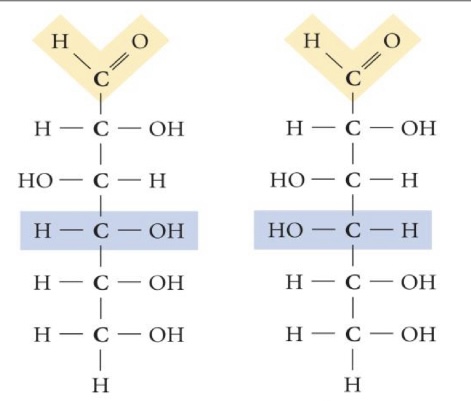
Glucose + Galactose
Phosphodiester Linkage
formed between the phosphate of one nucleodtide and the sugar of the next
Alfa-a helix
helical coil stabilized by h-bonding between every 4th peptide bond. found in filaments proteins
Beta-b pleated sheet
a sheet of antiparellel chains (lysosomes, spidersilk)
Primary Structure
Amino acids joined to form a polypeptide chain, has a unique sequence
Secondary Structure
Regular repeating COILING oof a proteins polypeptide backbone, h-bonding
Tertiary Structure
Irregular contortion of pretin due to bonding between r-groups, important in determining the specificity of enzymes.
Quaternary Structure
Structure thet results from the interaction amond several polypeptides in a single protein (hemoglobin)
Oligosaccharides
Contain small numbers of monosaccrides (3-10)
Structural Isomers
Differ in covalent arrangement of their atoms
Geometric Isomers
Differ in spatial arrangment, subtle difference (swap)
Enantiomers Isomers
Mirror imgaes of eachother. One form can only be biologically active at a time
Metabolism
The sum of all the thousands of different chemical reactions that occur constantly within cells. Anabolic Reaction + Catabolic Reactions
Endergonic Reactions
require energy in order to proceed, products with MORE energy than the reactants ex. photosynthesis
Exergonic Reactions
Release energy, products with LESS energy than the reactants
Exothermic Reaction
More energy is released from the new bonds being made
Negatve
Products < Reactants
Endothermic Reactions
More energy is required to break the bonds in the reactant molc
Heat will show as reactant
Products > Reactants
Work
Transfer of energy from one body or place to another
Potential Energy
Chemical energy stored in molecular structure
Gravitational P.E
Chemical P.E
Kinetic Energy
The energy possessed by moving objects
Mechanical Energy
Electrical Energy
Thermal Energy
Electro-magnetic Energy
Entropy
A measure of the randomness or disorder in energy or in a collection of objects.
Coupled Reactions
Endergonic reactions that used free energy released by the exergonic reactions.
Non Spontaneous rxns use energy released from spontaneous rxns.
The Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed it can only be converted from one to another.
Law Bioenergetics
Entropy constantly increases with any changes that occurs
Lock and Key Throey
The active site is designed to precisly fit the substrate
The Induced Fit Theory
The enzyme is flexible and only the proper substarte os capable of inducing the proper alignment of the active site.
Cofactor
non-proteins essential for enzyme activity (Ex: ions like K, Mn, Fe)
Coenzymes
non-protein organic molecules bound to enzymes near the active site. Ex: NAD, Niacin, NADP
Competitive Inhibitors
A molecule that blocked the substrate from interecting with the enzyme, dramtically slows down reaction rate. Ex: Cyanide
Non-Competitive Inhibitors
Molecules that bind to a different site on the enzyme, changing the shape of the active site.
Allosteric Regulation
Molecules that naturally regulate enzyme activity, either active or inactive.
Feedback Inhibition
Metabolic control, if too much product accumulates, it will inhibit the action of the first enzyme.
Integral Proteins
Embedded in the bilayer, provide pathways for the selective transfer of certain substances. Have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
Peripheral Proteins
Attached to the outside/inside of membrane, associated with cell shape and mobility.
Passive Transport
No energy is required for the movement of molecules along a concentration gradient (high to low).
Active Transport
Cellus use energy to transport material against a concentration gradient (low to high).
Simple Diffusion
O2 and CO2 move from an are of high concentration to low
Osmosis
Refers to the diffusion of water through a membrane of lower solute concentration to higher solute.
Isotonic Solutions
The water and the solute concentration inside the cell equals the concentration outside the cell, balanced movement of water
Hypotonic Solution
More water outside the cell than that inside the cell, water molecules move inside the cell causing it to burst (lysis)
Hypertonic Solution
More water inside the cell than outside, water moved out the cell cause it to shrivel up (plasmolysis)
Hemolysis
Blood serum is diluted, RBC’s will swell and burst.