Kidney transplantations
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
YYYYYYYYYYYEH BITCHES
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Kidney functions
removal of waste
regulation of pH
housekeeper for minerals
regulation of body fluids
activation of vitamin D - strong bones production
production of EPO
EPO
Glycoprotein cytokine
Erythropoietin
Causes the body to make red blood cells
Noticing kidney failure thresholds
Transplantation = 45%
bone breaking
red blood cells
pH balance
Dialysis = 15%
Dialysis
procedure to remove waste products and excess fluid from the blood when the kidneys stop working properly
Global burden of kidney failure
Demographic predictions:
2010 - 2.6 million cases
2030 - 5.4 million cases
15-20% of patients die in a month of dialysis
Many ppl live in LICs and LMICs, lack therapy to cure
Global prevalence - chronic kidney disease
64-74 years old = 1/5 men, ¼ women
75+ years = ½ adults
Total patients with kidney replacement therapy - NL
18,000 total
12,000 kidney transplant
6,000 dialysis
Why is a kidney transplant performed?
feel more fit
live longer
gain more freedom
improve chances to work
live normal life + family
Why kidney transplant?
better survival
Better quality of life
More integrated into society
Cheaper
Relative risk of death after transplant
Risk equal: 106 days later
Survival equal: 244 days later
First living related transplant
Marius Renard (1952)
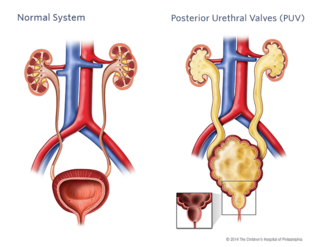
Utheral valves on the kidney
obstructive membranes that develop in the urethra (tube that drains urine from the bladder), close to the bladder
valve can obstruct or block the outflow of urine through the urethra.
What do you need a potential donor to be?
healthy kidneys
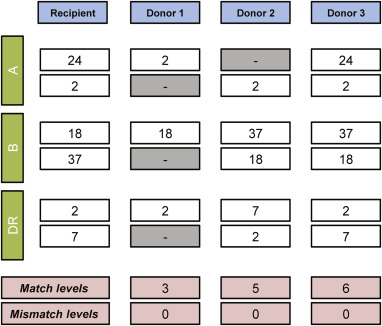
Match!!
HLA matching
on A, B or DR loci
ppl get an alele from each parent
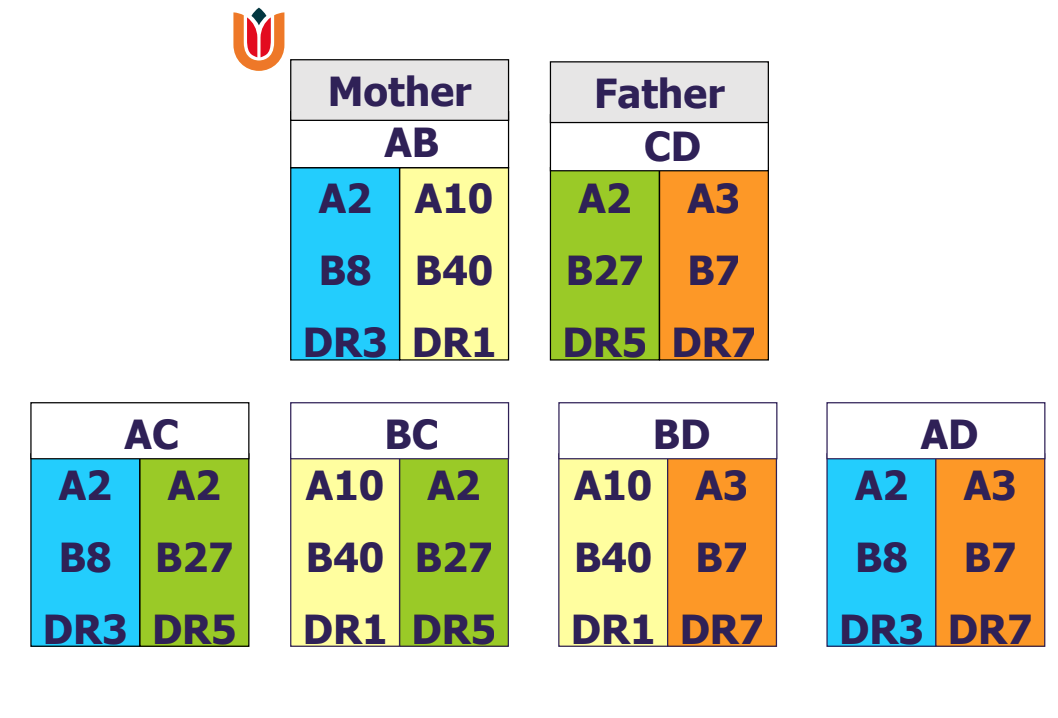
Best/Worst fit - HLA matching
Best fit: mismatch 0-0-0
Worst fit: mismatch 2-2-2
hope to match each allele to the recipient (6 alleles in total: 2 loci, 2 alleles from parents)
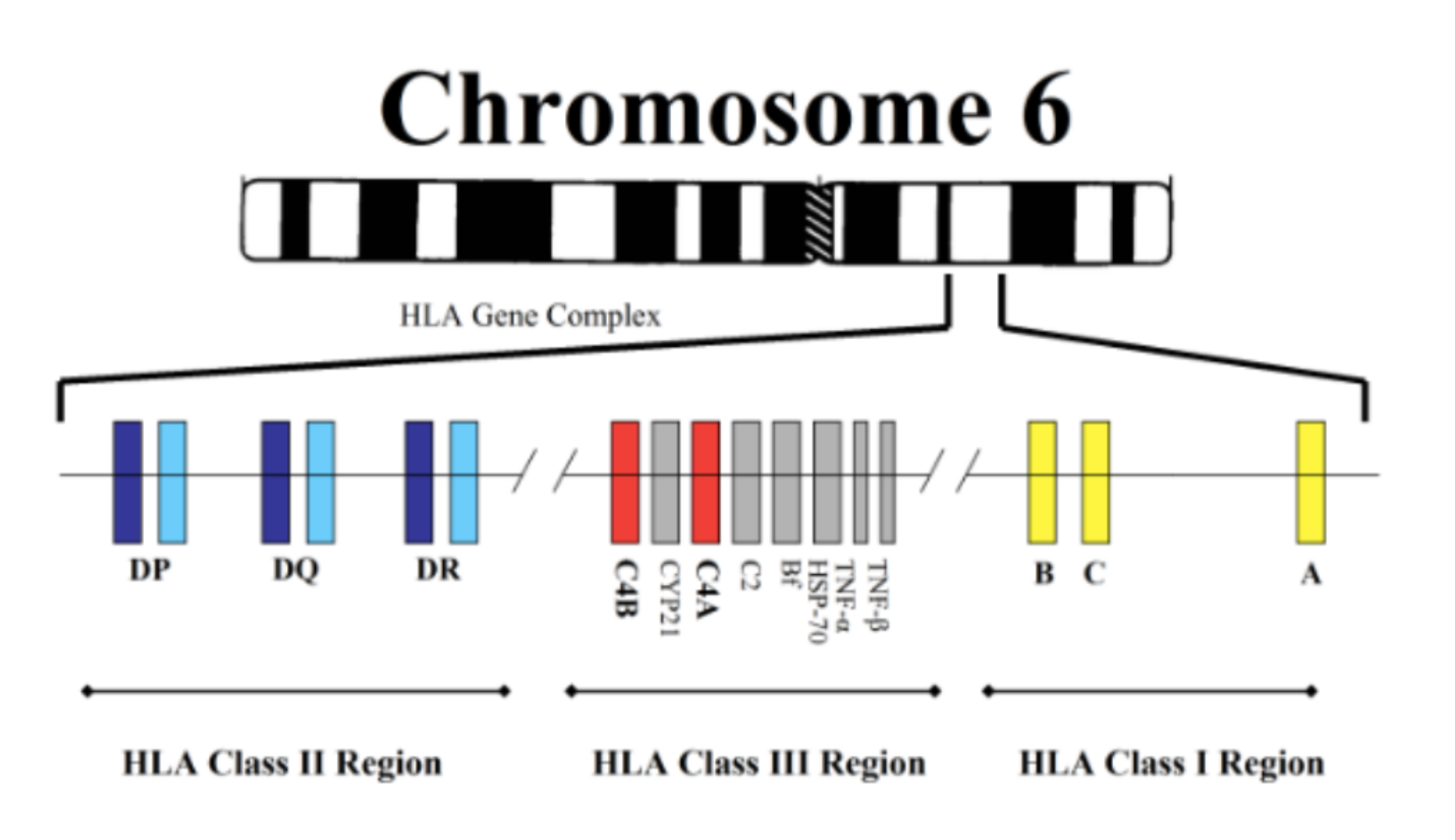
Chromosome responsible for HLA system
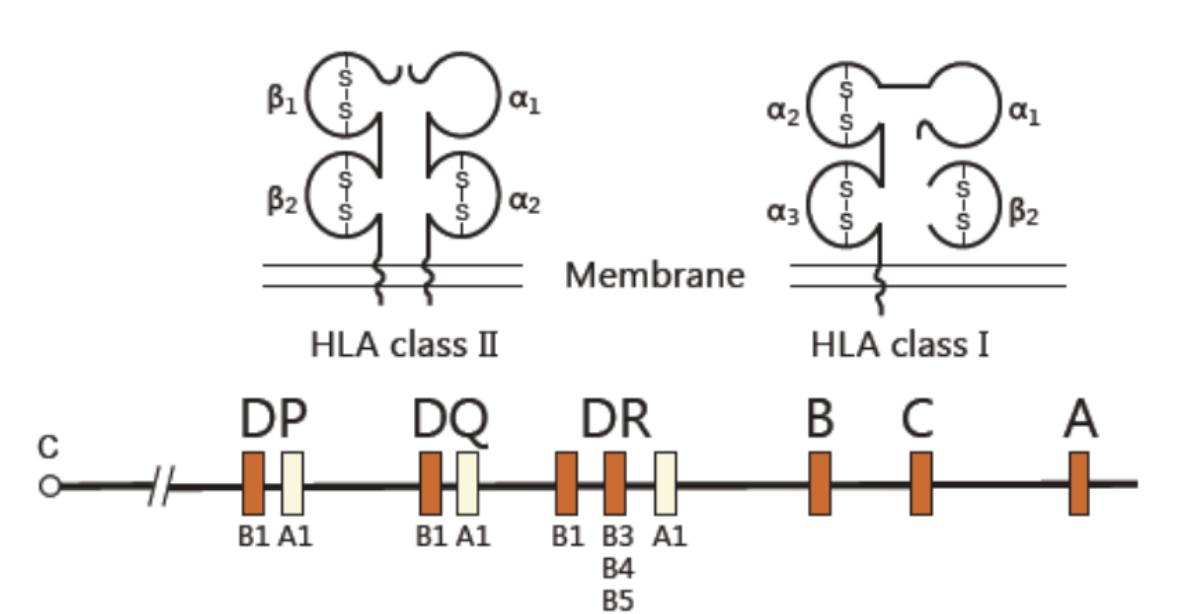
HLA I
A, B, C loci
HLA II
DP, DQ, DR loci
(HLA III)
C4A, C4B
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
highly polymorphic
presents peptides from pathogens or “altered self” to the immune system
Differences in HLA elicit immune responses (humoral + cellular)
Big barrier in transplantation medicine
Refinement of MHC system over time
DP
B1
A1
DQ
B1
A1
DR
B1
B3, B4, B5
A1
Worst response to transplantation
Immunization: antibodies against foreign tissue (vaccination style)
Maternal immunization
Antibodies pass naturally from mother to baby through the placenta
Reactivity to foreign HLA
????? COMPLETE THIS CARD
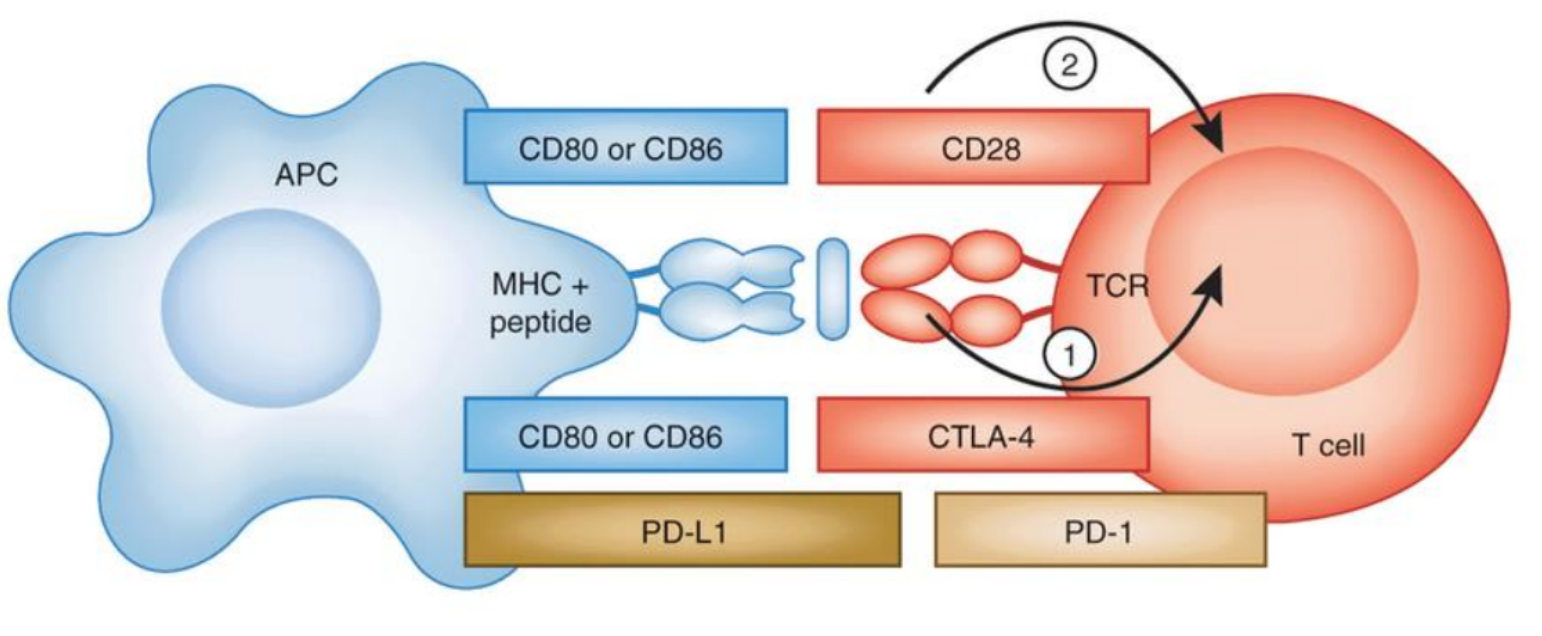
Interraction of APC / T cell regulated by uppers and downers
(APC == T cell)
STIMULANTS
CD80/CD86 == CD28
DEPRESSIVES
CD80/CD86 == CTLA-4
Keeps T cells from killing tumor cells in the body
PD-L1 == PD-1
Best type of donor
Homozygous identical twin
Case: patient immunized against father? what happens?
Hyper acute rejection: complement binding by preformed antibodies
antigens are completely unmatched
Hyperacute rejection - characetristics
Type II rejection
kidney colour not pink
flabby tissue
no urine production
Hyperacute rejection - cause
Performed HLA (or anti-blood types) antibodies:
preexisting antibodies in the recipient that are directed against donor antigens
Assay def
biochemical test that measures the presence or concentration of a macromolecule or a small molecule in a solution through the use of an antibody (usually) or an antigen (sometimes)
Crossmatch assay - prevent hyperacute rejection
CDC-based assays
Patient serum
> (lympthocytes, T cells usually)
Rabbit complement
> cannot differenciate IgG from IgM)
Red = dead
Green = alive
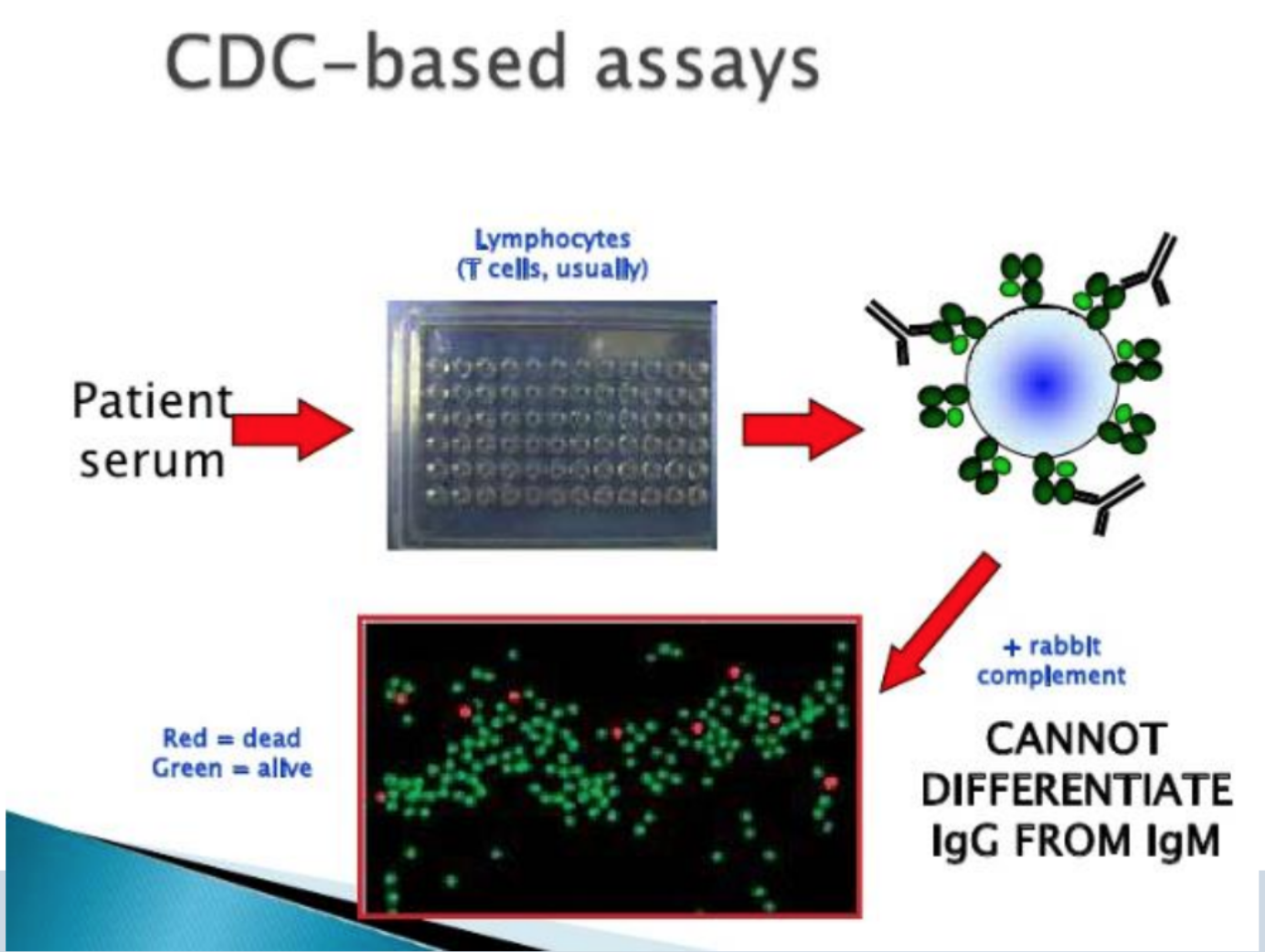
Why use rabbit complement?
it is difficult to obtain normal human serum that lacks intrinsic bactericidal antibodies.
One approach to obtain human complement would be to absorb bactericidal antibodies from normal serum.
Different techniques - detect HLA antibodies
Cell-based assays
CDC cross-match
Flow cytometry cross-match
Solid-Phase assays
ELISA
Luminex (microbead with HLA antigen)
Prior sentization def
Someone whose immune system is highly sensitive to non‑self human leukocyte antigens (HLAs). Without the right treatment before surgery, their bodies will reject a new kidney
This feed-forward mechanism increases the response to a stimulus
how to detect prior sensitization?
complement dependant cytotoxicity detects preformed antibodies
Flow cytometry tests antibodies attached to lymphocytes
Solid-phase assays
CDC
Complement dependent cytotoxicity
Solid-phase assays - prior sensitization
antigen-bound microtiter plates
single antigen beads (luminex)
DSA
Donor Sensitive Antibody
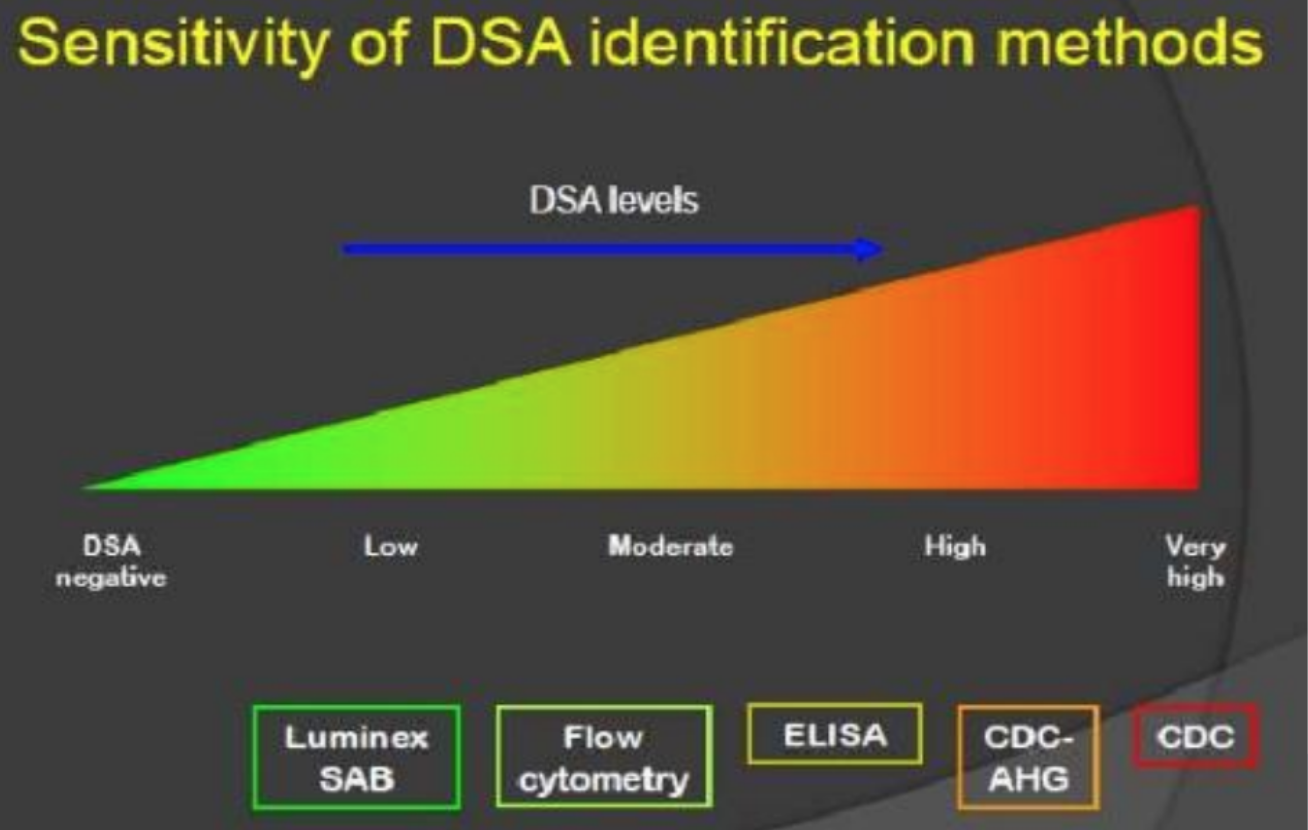
Techniques in detection of HLA antibodies have different sensitivity
LESS SENSITIVE
Luminex < Flow cytometry < ELISA < CDC-AHG < CDC
MOST SENSITIVE
Differences between CELL BASED ASSAYS / solid-phase assays
positive assay = highly clinical relevance (80% rejection of graft)
Often increased by IgG
Dithiothreitol (DTT) to remove IgM
Flowcytometer
Flowcytometer - cell based assays
both complement + non-compliment bindings depend on second antibody
Differences between cell-based assays / SOLID-PHASE ASSAYS
sensitive
both complement and non-complement bind antibodies, no IgGM autoantibodies or nonHLA antibodies
Pathogenic threshold = unknown
Acute antibody mediated/humoral rejection - what is it
within days/weeks after transplantation
rapid graft dysfunction
main target MHC antigens on the peritubular endothelium and glomerular capillaries
sometimes non-HLA antibodies
Acute antibody mediated/humoral rejection - cause
anamnestic response by previous exposure generating complement-fixing antibodies
anamnestic response
renewed rapid production of an antibody on the second (or subsequent) encounter with the same antigen
Being sensitised increases the risk of:
hyperacute rejection
Memory B cell response => early ABMR
chronic active ABMR
ABMR
Antibody-mediated rejection
=> most common cause of immune-mediated allograft failure after kidney transplantation
=> the earlier the less harm
Living VS post-mortem kidney transplant
Living donor kidneys = better chance of being accepted by the recipient's immune system
kidney lasts longer
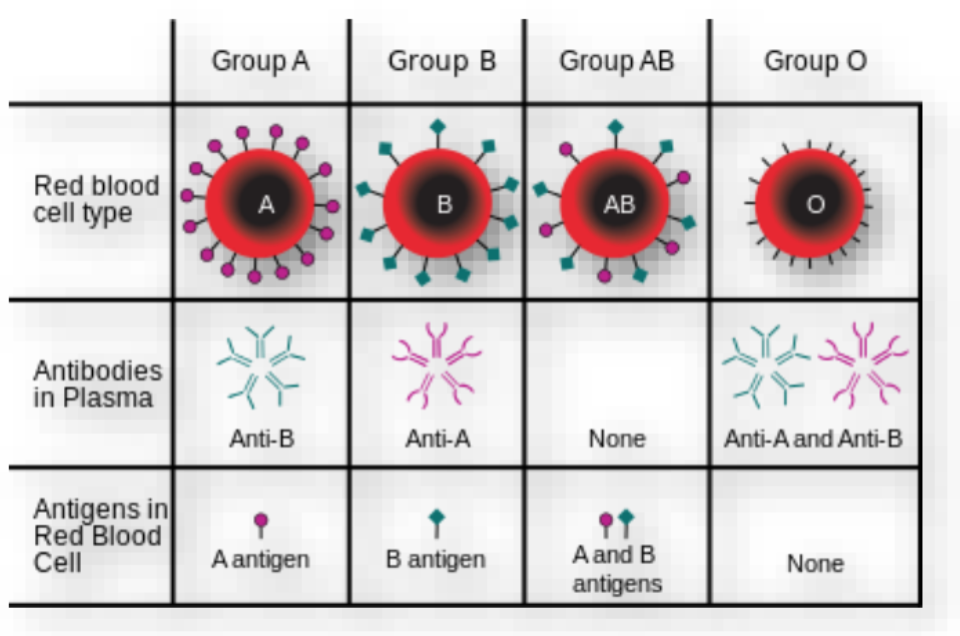
Blood type: ABO system, blood types // antibodies // antigens
Group A
Anti-B
A antigen
Group B
Anti-A
B antigen
Group AB
NO antibody
A and B antigens
Group O
Anti-A and Anti-B
NO antigens
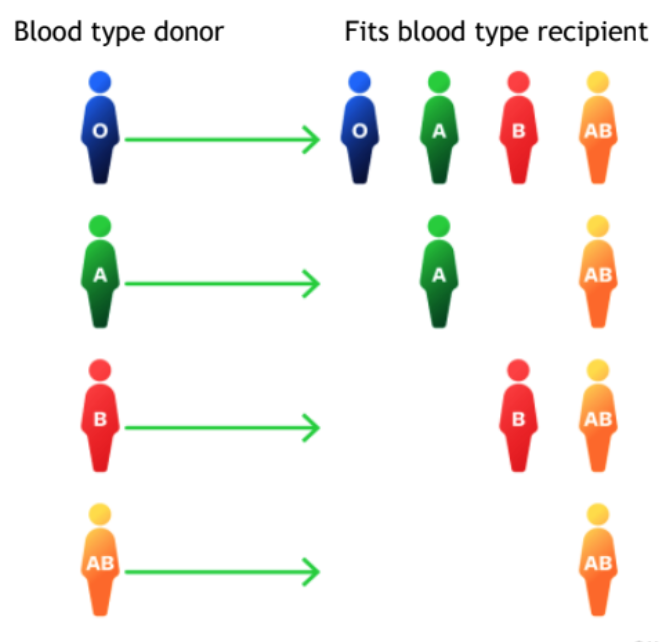
Blood type donors // recipients
O => O AB A B
A => A AB
B => B AB
AB => AB
Blood transfusion - pretreatment
pretreatment (washing) of blood = no effect
Postmortal kidney dorors, where?
Spain
USA
France
Living kidney donors, where ?
Turkey
Netherlands
Timing of transplantation after diagnosis = important
years later, impacts survival
Kidney donation in media before VS now
Before
for compensation
commercial benefit? not good, poorer countries
Now
Donor can choose a recipient
Conditions for kidney donation
Organ donation act (1998): competent, >18, clearly informed consent, benefit someone else
voluntary, not paid, always revokable
socially feasible
good chance of success of donation + transplantation
Who are the donors that volunteer?
Related
family
Unrelated
Collegues + friends = targeted donation (emotional bond)
Altruist not targeted = samaritan, charitable donor
Altruist targeted = supply/demand
CONCLUSION - vaguely
HLA matching super important
Immunosuppressants must be taken sadly
Donor shortage possibly caused by: Xenotransplantation, Donation after euthanasia
Cross-match test (for ex: CDC)
test the compatibility of (a donor's and a recipient's blood or tissue).
anamnestic
enhanced reaction of the body's immune system to an antigen which is related to one previously encountered
3 different types of transpalnt rejections
Hyperacute rejection occurs a few minutes after the transplant when the antigens are completely unmatched.
Acute rejection may occur any time from the first week after the transplant to 3 months afterward.
Chronic rejection can take place over many years.
Hyperacute rejection
the recipient is presensitized to alloantigens on the surface of the graft endothelium.
Acute rejection
when your body's immune system treats the new organ like a foreign object and attacks it.
treat this by reducing your immune system's response with medication.
chronic rejection
can take a year or more
progressive form of graft injury that usually results in graft failure