AP Psych
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Consicousness
our awareness of various cognitive processes such as sleeping,dreaming, concentrating, and making decisions;typically use to describe being alert
NREM Sleep (Non-Rem)
non rapid eye movement stages of sleep that alternates with REM stages during the sleep cycles

Dreams
visual and auditory images created by the mind during sleep; often 2 hours a night are spent a night dreaming ( not in a row ); 4-5 vivid dreams during REM; life like dreams occur during NREM sleep
Altered States of Consciousness
mental state that differs noticeably from normal waking consciousness;
Examples:sleep,daydreaming,dreaming,meditation,hypnosis,influence of drugs and alcohol

Insomnia
sleep disorder;difficulty falling asleep or remaining asleep through the night;typically caused by stress and are temporary; treated with prescription medication or relaxation techniques; side effects include anxiety,memory loss,hallucinations, and violent behaviors
Daydreaming
effortless shifts in attention away from the here-and-now into a private world of make-believe; urge comes in waves, surging every 90 min, peaks between 12-2 pm
Sleep Apnea
sleep disorder; characterized by difficulty breathing, snoring, & exhaustion during the day because breathing stops during sleep and individual wakes to just under waking consciousness; individual also complain of depression, sexual dysfunction, difficulty concentrating, and headaches
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
sleep disorder that causes people to act out in their dreams, vocalization, frightening dreams, and other physical movements
Somnambulism
sleepwalking
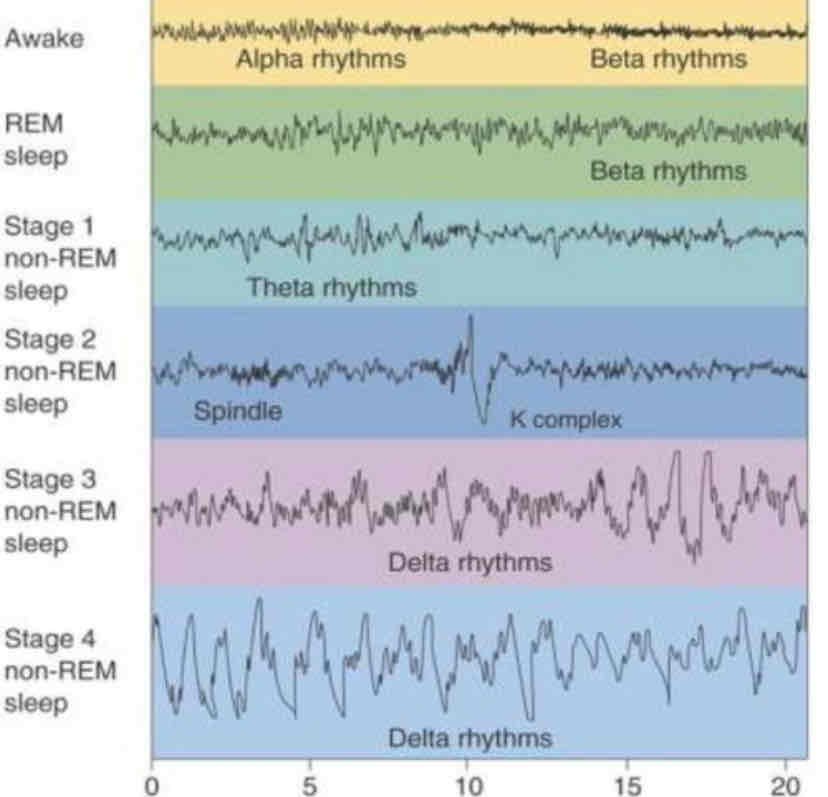
REM paradoxical sleep
physically resembles waking consciousness in measures; characteristics: sleep paralysis, vivid and intense dreams, rapid eye movements; occurs about 4/5 times a night; infants spend more time in REM than any other age

Narcolepsy
hereditary sleep disorder; characteristics: sudden falling asleep into REM, loss of muscle tone following moments of emotion (joke, anger, sex), hallucinations (are often aware)
Meditation
alternative method of concentration,relation,suppresses SNS
Effects-lowers heart/respiratory rate

Tolerance
requirement of higher doses of drugs to produce the original effects or prevent withdrawal symptoms
Hypnosis
altered or trance like state: where a person who is open to suggestions

Withdrawal symptoms
unpleasant physical or psychological effects following discontinued use of a drug, can include shakes, blood pressure/heart rate changes
Psychoactive drugs
chemical substances that change or alter people’s moods, perceptions, mental functioning, or behavior
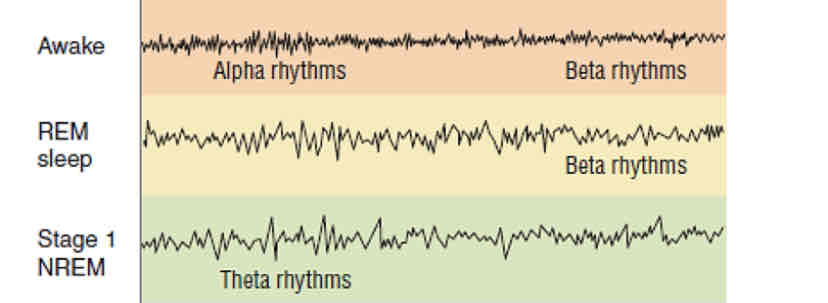
NREM Stage 1
first stage of non rapid eye movement sleep characterized by drifting in and out of sleep, lasting only a few minutes
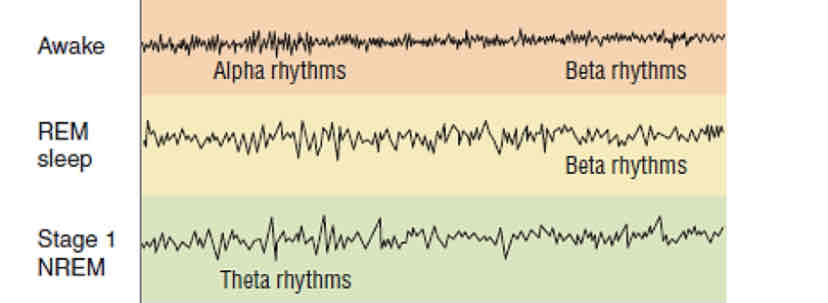
NREM Stage 2
second stage of non rapid eye movement characterized by LIGHT sleep, lasting 20 minutes
Hypnic Jerks
brain waves slows down, muscles relax, and individuals may experience sudden muscle contractions ( happens during NREM Stage 1)
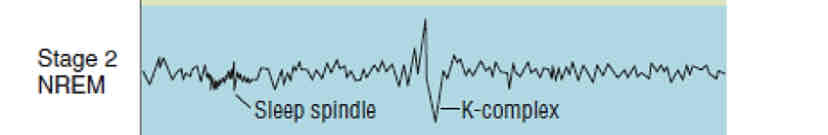
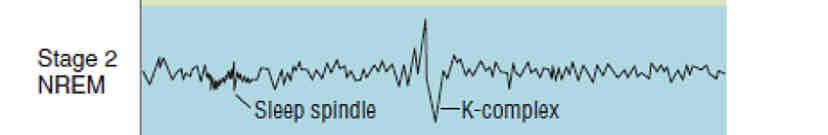
Sleep Spindles and K-Complexes
when brain waves slow down in Stage 2 of NREM, short burst of activity come out
sudden,sharp waveforms appear
Circadian Rhythm
the natural, internal process that regulates the sleep-wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. it influences patters if ALTERNESS,HORMONE RELEASE, BODY TEMP., and other PHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESSES.
Jet Lag
a temporary disruption of the body’s circadian rythym due to rapid rebake across multiple time zones.
result in fatigue, sleep disturbances, and difficulty concentrating as the body adjusts
Shift Work
employement schedules that require working outside of typical daytime hours, often disrupting the body’s natural circadian rhythm
Restoration of Resources
the process during sleep where the body and brain replenish energy,repair tissues, and remove waste products,promoting physical and mental well-being
REM ( Rapid Eye Movement) Sleep
a stage of sleep characterized by rapid eye movements, vivid dreams, and muscle paralysis
it is also associated with increased brain activity, including dreaming, and plays a role in memory consolidation and emotional processing
REM Rebound
phenomenon where the body increases the time spent in REM sleep after the period of REM deprivation
occurs as a compensatory response to the lack of REM sleep, often resulting in more intense and frequent REM sleep episodes
How does Light influence the Pineal Gland?
causes the pineal gland to increase or decrease production of the hormone melatonin
Activation Synthesis
theory proposing dreams are the result of random neutral activity in the brain stem during REM sleep, which is interpreted and formed by the cerebral cortex into a story
Consolidation Theory
a theory suggesting dreams play a role in they memory consolidation and processing of memories. during sleep, the brain organizes and intergrates information acquired throughout the day, contributing to memory storage and learning
psychoactive drugs
drugs that alter perception and mood (changes consciousness)
psychological dependence
psychological need for a drug for example to relieve negative emotions
Addiction
compulsive drug craving
Tolerance
diminishing effect with regular use
Withdrawal
discomfort and distress that follow discontinued use
Neurotransmitters
chemicals that use neurons use to communicate with other each other
with using drugs, they can change the way our transmitters work
Agonist
BIND to receptor sites and MIMIC neurotransmitters
Antagonists
BIND to receptor sites and BLOCK neurotransmitters from binding
Stimulants
drugs that increase neural activity and arousal, leading to higher alertness, attention, and energy levels
CAFFEINE, METHAMPHETAMINES, COCAINE,MDMA, NICOTINE
Depressants
drugs that slow down neural activity and bodily functions.
they induce relaxation,sedation, and can lower inhibition
ALCOHOL,ANTIDEPRESSANTS, ANTIHISTAMINES
Hallucinogens
drugs that alter perception,mood, and cognitive processes, often causing hallucinations
MARIJUANA, LSD, SALVIA,KETAMINE
Opioids
Psychoactive drugs that act an opioid receptors in the brain and body, producing pain relief, euphoria, and sedation
Light striking the retina causes the __________(a tiny neural center in the hypothalamus) to alter the production of biologically active substances, such as melatonin production by the pineal gland
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus