Planet Earth Geology
1/172
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
Catastrophism Definition
The theory that is opposite of uniformitarianism.
This theory tries to explain that the changes in the earth’s crust was caused by catastrophic events.
Uniformitarianism Definition
The theory that is opposite of catastrophism.
This theory explains that the earth’s crust was changed by normal events that still happen today.
Key quote of Uniformitarianism
“The present is the key to the past“
Age of the Earth
4.6 Billion
Nebular Hypothesis
Theory that the solar and stellar systems were developed from a primeval nebula.
At the same time.
Inner Core
Composed of IRON & NICKEL
Radius: 1,220 km
Temp: 5,700 °C
Solid
Outer Core
Composed of IRON & NICKEL & SULFUR
Thickness: 2,260 km
Temp: 3,700–7,700 °C
Liquid
Mantle
Composed of peridotite
Thickness: 2,900 km
More dense Liquid
Crust composed of?
Composed of Basalt, Granite
Thickness: 7-70 km
Solid
Dynamic Planet
Earth is a dynamic planet due to the inside being hot & radioactive while the outside is cold.
Qualitative
Observations - red, light, heavy
Quantitative
Measuring the color with wavelengths or weighing
Pseudoscience
Collection of ideas that may appear scientific but aren’t
Hypothesis
A proposed explanation for an observation that can be tested.
Deductive Reasoning Example
If all animals that fly are birds, then so are bats
Inductive Reasoning
Establishes evidence to infer truth
Shale
fine grained, thin layering rock (fissle)
Sediment
Pieces of rock that have been weathered & eroded
James Hulton
He came up with uniformitarianism “the present is the key to the past“
Theory of Plate Tectonics
Earth’s brittle Lithosphere is broken into plates that move relative to each other over the plastic asthenosphere
Asthenosphere
The upper layer of the earth's mantle, below the lithosphere, in which there is relatively low resistance to plastic flow and convection is thought to occur.
Lithosphere
The rigid outer part of the earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle
Who thought up continental drift
Alfred Wegener
How was Continental Drift supported?
Showed hypothesis with LOT of evidence
What was the hypothesis for continental drift?
The continents used to fit together as a single supercontinent we named Pangea & have since “drifted” to where they are now.
Why did the theory of continental drift not stand?
The reason why it failed was because there wasn’t enough evidence to support the hypothesis.
Continental Shelf
the true edge of the continent
Paleomagnetism
Magnetism stays with the rock when it cools, so you can see where magnetic north was when that certain rock cooled from magma.
Plate Boundaries
Divergent
Convergent
Transform
Divergent Plate Boundaries
Plates moving away from each other
Convergent Plate Boundaries
Plates moving towards each other
Transform Plate Boundaries
Plates moving next to each other in opposite ways
Rift zones & the Breakup of a continent
upwarping
continental drift
linear sea
mid ocean rift
Element
A group of atoms with a specific number of protons, having specific universal, & unique properties.
Mid Ocean Ridge
Divergent boundary within an ocean plate, where new lithosphere and crust in the created as the 2 plates spread apart
Natural Resources
Items that are found within earth that are valubale and limited
Example of natural resources
Coal, Water, Gold
Fossil Fuels
Energy resources (typically hydrocarbon) derived from ancient chemical energy preserved in the geological record.
Examples of Fossil Fuels
Coal, Oil
Coal
Former swamp-derived (plant) material that is part of the rock record
Petroleum
A fossil fuel from shallow marine rocks.
Made of oil & natural gas
Reservoir
rocks which allow petroleum resources to collect and move
Special characteristics of oceanic crust
high density, more brittle, thinner
special characteristics of continental crust
low density, more ductile, thicker
Where’s the youngest part of the sea floor
near the ridge
Where’s the oldest part of the sea floor
in the trenches
When was the sea floor explored
late 60’s
Geosphere
The solid, rocky parts of the Earth, including the crust, mantle, and core
Atmosphere
gases that are part of the Earth, mainly nitrogen & oxygen
Hydrosphere
The water part of the Earth, solid, liquid, or gasses (literally any water)
Cryosphere
The part of the hydrosphere (water) that is frozen, found mainly at poles
Biosphere
The living things that inhabit the Earth
Magma
Liquid rock within the Earth
Lava
Liquid rock on the surface of the Earth
Definition of crust
Outermost chemical layer of the Earth, defined by its low density & higher concentration of lighter elements
Sea Floor Topography
refers to the physical features & contours of the sea floor, which are influenced by various geological processes
Examples of sea floor topography
Continental shelves, deep ocean plains, mid-ocean ridges, deep ocean trenches
Volcanic arcs are a product of what happening?
The subduction of an oceanic plate under a continental plate
Why does it appear that Hawaii is “moving”?
The Hot spot underneath the pacific plate pushes up magma while the pacific plate moves
Why do Hot Spots occur?
Change in chemistry in the mantle
Mantle Plum
Column of magma from deep within the mantle
Hot spot definition
mantle plume magma breaks through the surface
Mineral def
Naturally occurring, inorganic, solid, narrowly defined chemical property, ordered internal atom structure
How minerals form
Cooling of magma/lava, in solution, organisms construct carbonate shell, metamorphisms
mineral physical properties
crystal form, color, luster, quality & intensity of light reflected from surface, streak
Streak of a mineral
color of powdered mineral
hardness of a mineral
resistance to abrasion
mineral shape properties
cleavage, fracture
Silica Tetrahedron
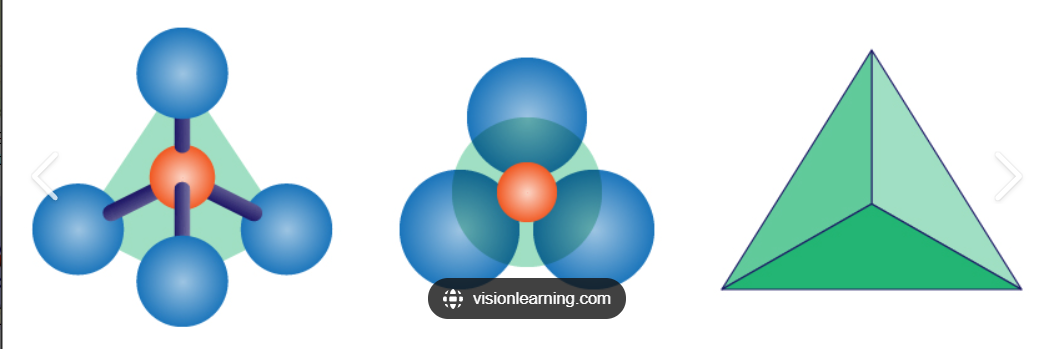
Magnetic reversals
refers to the phenomenon where Earth’s magnetic field changes direction, resulting in the magnetic north and south poles to switch directions
Lithification
process where loose sediments become solid rocks through compaction and cementation
common rock forming minerals
Quartz, K-Feldspar, Plagioclase, Micas, Calcite
What’s the most significant mineral?
Silicate
Thermal convection
cells driven by the heat from Earth’s interior
Convection current
magma in the mantle
Slab-pull
Subducting colder slab pulls rest of plate down into the asthenosphere.
The pull of the oceanic lithosphere helps the plate separate.
Ridge-pull
Gravity pushes plate from higher ocean rides to trenches.
What’s the building blocks of rocks?
MINERAL!
Steno’s Law
Minerals can be different colors, big or small, but the angle between equivalent faces are the same
think the box minerals (cleavage)
Luster of a mineral
Quality & intensity of light reflected from the surface of the mineral.
Which Paleoclimate evidence was used by Alfred Wegener to support continental drift?
Rocks formed by glaciers in South America & South Africa
This layer of the Earth is Liquid Iron & Nickel
Outer core
What are rocks?
Rocks are aggregates of minerals
How are igneous rocks classified?
Igneous rocks are classified on the basis of composition and texture
Intrusive or Plutonic
formed when magma cools within the earth
Extrusive or volcanic igneous
form when magma cools on the surface of the earth
Felsic
Light colored igneous rock, containing light colored minerals
Quartz, Feldspars, Muscovite, Plagioclase
Intermediate
In between mafic and felsic and its lowk like half and half black and white but there’s no quartz
Mafic
made up of almost all dark minerals such as amphibole, pyroxene, biotite and olivine
Coarse grained texture (Phaneritic)
Refers to an igneous rock with crystals visible to the naked eye
Pegmatitic texture (very coarse grained)
Refers to an igneous rock that is composed of minerals larger than 1cm
Fine grained texture (Aphanitic)
Refers to an igneous rock that is composed of minerals that are too small to be seen by the naked eye
Porphyritic Texture
Refers to an igneous rock that has 2 noticeably different crystal sizes.
The large crystals are called “Phenocrysts” and the smaller crystals are said to make up the matrix or groundmass
Complicated cooling history, at first slow so big crystals grow then quick make small crystals
Glassy Texture
Refers to an igneous rock that is cooled extremely fast and as a result, becomes glassy
Vesicular Texture
Applies to an igneous rock that was cooled quickly while gas was escaping
Vesicles
holes in the rock from gas bubbles in the lava
Frothy texture
Characterized by many very small voids and resembles the head on a beer
Pyroclastic Texture
Found in igneous rocks that were produced during violent volcanic eruptions such as the eruption of Mt. St. Helens on May 18, 1980
Texture is characterized by a large number of angular grains that have been deposited together
Granite
Phaneritic, Coarse, Felsic
Diorite
Phaneritic, Coarse, Intermediate