sleep lecture P1 - transition into sleep
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Which analgesics work in the central nervous system?
A-Cannabis-based drugs
B-Capsaicin
C-Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g. ibuprofen)
D-Opiates (e. g. morphine)
E -Paracetamol
Answer ADE
A) Cannabis-based drugs – Act on cannabinoid receptors (CB1, CB2) in the CNS to modulate pain perception.
D) Opiates (e.g., morphine) – Act on mu-opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, directly altering pain signaling in the CNS.
E) Paracetamol (acetaminophen) – Though its mechanism isn't fully understood, it is believed to act centrally (possibly inhibiting COX enzymes in the brain and modulating serotonin pathways).
Sleep: an overview
What is sleep ?
• How do we sleep ?
• Circadian rhythms
How do we study sleep? How do we measure sleep
By using a polysomnogram – a test used to study sleep and diagnose sleep disorders , it makes many records of various things(parameters) that relate to sleep simultaneously
what does a polysomnogram measure in relation to sleep?
Polysomnogram = many records of sleep
• EEG (Electro-encephalogram) – brain activity
• EOG (Electro-oculogram) – eye movement
• EMG (Electro-myogram) – muscle activity
• EKG/ECG (Electro-cardiogram) heartrate and rhythm
• Airflow – breathing patterns and airflow
• Oximeter – oxygen levels in the blood
how does a polysomnogram measure different sleep parameters in patients - physically
Go to a sleep clinic and patient will get wired up with all these things that record you while you sleep in a laboratory naturally:
what is a potential caveat that could detract from the value of the polysomnogram?
as patient not sleeping in own bed or familiar surroundings could produce somewhat inaccurate insight into sleep
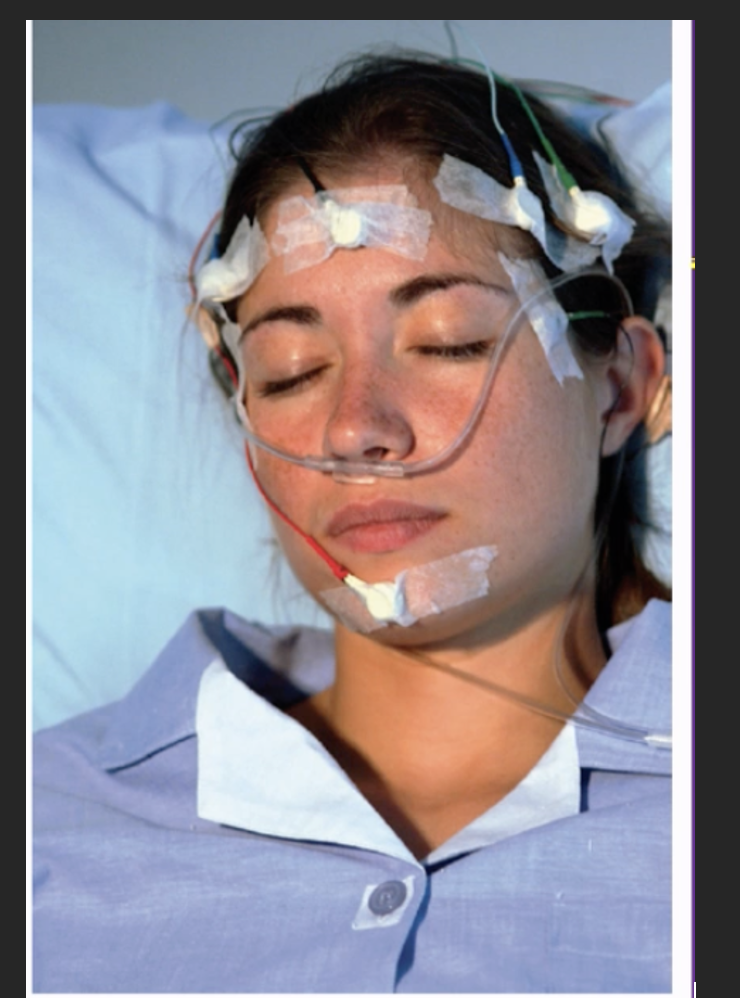
what is this a photo of?
A subject prepared for a nights sleep in a sleep laboratory – being recorded by a polysomnogram.
What is the main/ defining recording feature used in a polysomnogram?
why?
the measurements taken and changes which occur are recorded by EEG
Because it records and detects the different stages that characterise sleep
What does an EEG measure?
Measures electrical activity in your brain
How does an EEG measure electrical activity in the brain?
by placing electrodes on the surface of the scalp, often via wearing a cap over your head
what does an EEGs electrode have to stimulate through?
Electrode and brain are separated from each other as Hair, skin, tissue between your skin and your skull, your cranium, cerebral flued, lie between the brain
What do EEG signals measure?
• EEG signals are a summation of the activity of many neurons in the cortex closest to the electrode your recording from (as due to the distance between the electrode and the brain, individual neurons can’t be recorded)
EEG electrodes record the summation of all the detected changes in the surrounding neurons membrane potentials
ØSynchronized activity: large deflections (occurs if all neurons change their membrane potential at the same time in the same direction)
ØUnsynchronized activity: averages out – will only see very small changes/ deflections
Analogy: imagine a crowd supporting a team in a football team
Unsynchronised – general buzz but people are saying different things at different times so no distinct noise can be heard from outside the stadium – steady noice with small deflections/ changes
Synchronised – everyone does the same thing at the same time e.g. if a goal is scored everyone cheers and a large chant will be heard – big change and large deviation which can be detected
What do researchers look for in EEGs ?
Patterns of synchrony – checking how big deviations are in the EEG signal
Although unsynchronised patterns of activity are also important e.g. some stages of sleep ae characterised by unsynchronised behaviour

what state of wakefullness/ sleep does this EEG depict?
an aroused (wakeful) state)
brain regions are not synchronised with eachother, observe only small deviations in EEG signal
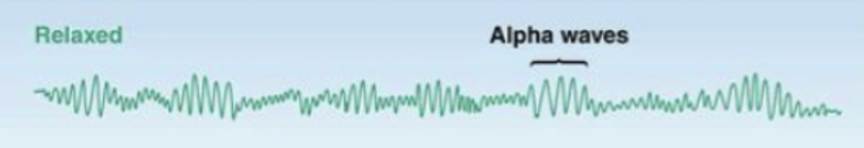
what state of wakefullness/ sleep does this EEG depict?
relaxed but still wakeful state

what state of wakefullness/ sleep does this EEG depict?
asleep - beginning stages/ light sleep
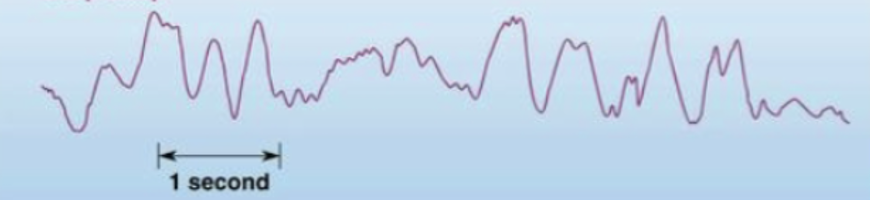
what state of wakefullness/ sleep does this EEG depict?
asleep - deep sleep
large deviations observed as many neurons did the same thing simultaneously – large synchronisations occur and slower rate of change
what uni/ form of measurement are EEG signals measured in?
Expressed as the frequency of waves
What are wave frequencies?
The number of changes (how many times something happens) per second, measured in Hertz
What are hertz (Hz)?
The unit of frequency which measures how many times something happens per second.
1 hertz (hz) = one cycle/ per second

how many hertz (Hz) can be calculated from this image?
5 hz, because you can count five peaks or troughs per second
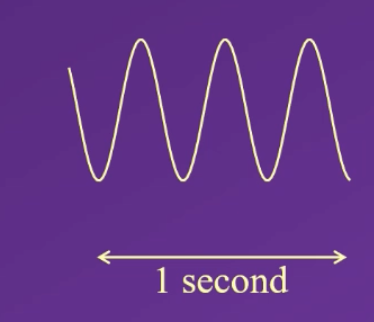
how many hertz (Hz) can be calculated from this image?
3 Hz , because you can count 3 peaks or troughs per second
list EEG Wave Classifications from fastest to slowest
Fastest waves
• β: 13-30 Hz (per second) = beta waves
• α: 8-13 Hz alpha waves
• θ: 3.5-7.5 Hz theta waves
• δ: < 4Hz (under 4) = delta waves
Slowest waves
why are EEG waves classified differently?
there appears to be a qualitiative shift that occurs between these catagories
Each EEG wave category is functionally different based on frequency, origin and associated brain function (i.e. active / functioning during specific mental and physiological states e.g. delta waves dominant only in deep sleep and unconsciousness),
each category is somewhat synchronised within itself

what sleep stage is this EEG recording?
awake
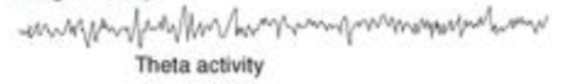
what sleep stage is this EEG recording?
stage 1 sleep
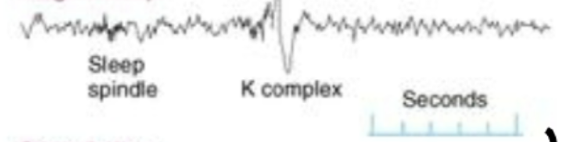
what sleep stage is this EEG recording?
stage 2 sleep

what sleep stage is this EEG recording?
stage 3 - enters and is in slow wave sleep 1/2

what sleep stage is this EEG recording?
stage 4 - slow wave sleep 2/2
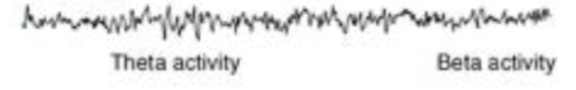
what sleep stage is this EEG recording?
REM sleep
Describe The 3 stages from wakefulness to slow wave sleep to REM sleep through an EEG in recording a typical sleep cycle– describe sleep phenomenologically
1)Wakefulness – distinct stage
While awake, Mostly alpha and beta waves occur, producing mostly unsynchronised frequencies due to frequent quick and small signalling changes– causing desynchrony to be depicted on the EEG.
Due to different neurons processing different things – how our brains normally work when were awake
Describe The 3 stages from wakefulness to slow wave sleep to REM sleep through an EEG in recording a typical sleep cycle– describe sleep phenomenologically
2)stage 1 sleep
slower waves begin to occur i.e lower synchrony and slower changes start to develope causing theta waves to be detected in EEG pattern in addition to the alpha and beta waves, this will last no longer than approximately 10 minutes if individual is undisturbed
individual start falling asleep , their eyes still will occasionally open as they are transitioning to sleep
If someone was to wake you up – individual would believe that they weren’t asleep previously – viewed as the transition stage (don’t have specific function of the own except for preparing our brain to enter a sleep state)
Describe The 3 stages from wakefulness to slow wave sleep to REM sleep through an EEG in recording a typical sleep cycle– describe sleep phenomenologically
3)stage 2 sleep
Characterised by
K complexes - Big deviations which irregularly occur during stage 2 sleep only , and typically last for approx. 10-15 mins
Sleep spindles – short but quite definable features are also visible in EEG, occur from stage 2 onwards
Ask to identify what these look like in MCQs
Describe The 3 stages from wakefulness to slow wave sleep to REM sleep through an EEG in recording a typical sleep cycle– describe sleep phenomenologically
4) Stage 3 slow wave sleep – Disntinct stage
delta wave activity begins to occur, delta waves are large and slow – indicating that significant increasing in synchrony in the brain is occurring (i.e, all neurons do the same thing simultaneously), occurs less than half the time in the EEg
state of high synchrony
the stage when we believe our brain recovers from the activity we engaged in during the day – so will not be aware of the environment aound us when we are in this deep sleep state
Describe The 3 stages from wakefulness to slow wave sleep to REM sleep through an EEG in recording a typical sleep cycle– describe sleep phenomenologically
5) stage 4 slow wave sleep
When stage 3 sleep increases to more than half the time observed in the EEG we call it stage 4 sleep
Brain is now in a state where it is no longer processing incoming information
Labelled as slow wave sleep / deep sleep – at this stage it wold be difficult for the external environemtn to wake you up unless it was e.g a loud noise
Describe The 3 stages from wakefulness to slow wave sleep to REM sleep through an EEG in recording a typical sleep cycle– describe sleep phenomenologically
6) REM sleep
REM sleep / paradoxical sleep– distinct stage
REM sleep then occurs
EEG looks similar in REM sleep as it does in wakefulness stage
Theta activity will also occur (similar to stage 1)
rapid eye movement occurs during this stage
typically that skeletal muscles of person are paralysed causing the body to feel very heavy
-when dreams occur
what happens after sleep stage 6 REM sleep
Then Alternate between REM sleep and slow wave sleep occur continuously after REM sleep has been experienced
Chracterised by
90minute cycle between REM sleep and slow wave sleep
As the night progresses the individual will experience a higher proportion of REM sleep and slower proportion of slow wave sleep
This explains why we are more likely to wake up during a dream – due to the increased frequency of REM sleep phases it increases the likelyhoodo f waking up during a dream
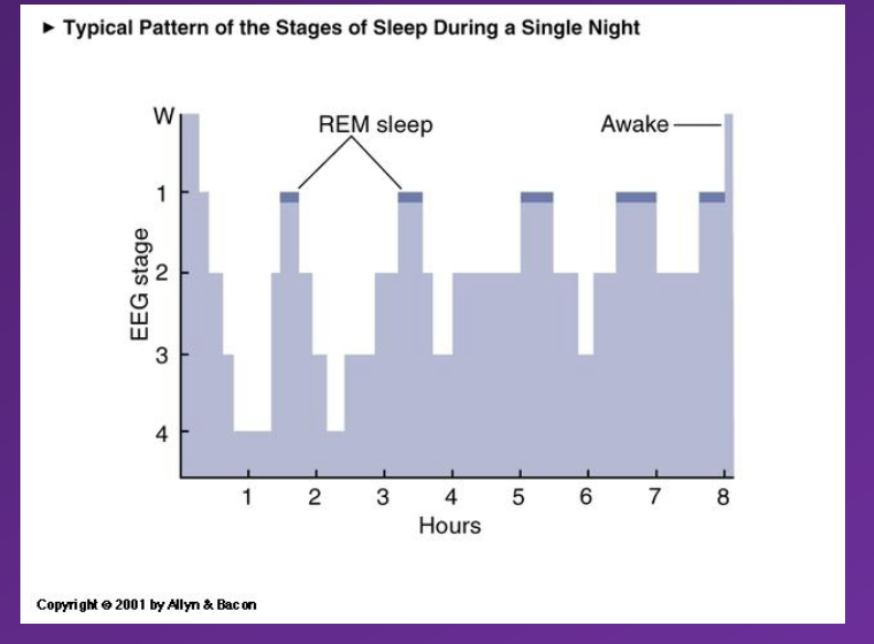
What are stage 3 and stage 4 sleep called together?
Slow wave sleep
Because it has these delta (slow, large) wave features
describe difference between wakefulness slow wave sleep and REM sleep
Slow wave sleep
Slow wave sleep – brain inactive body active
body may be tossing and turning
typically not aware of your surroundings
typically not dreaming- but night terrors may occur
typically not dreaming (although it can occur)
REM / paradoxical sleep = brain active body inactive
• Brain is very active: theta and beta activity occurs
• Rapid Eye Movements (REM) occur while eyes are closed
• Loss of muscle tone: the skeletal muscles are completely relaxed and paralysed – resulting in the body feeling really heavy
• Penile erection/Vaginal secretion – purely physiological response to REM sleep
• Clear, narrative dreams occur– most dreams happen during REM sleep , brain is very active
Why does REM sleep stand for
Rapid eye moment sleep
Why is REM sleep also called paradoxical sleep?
Because from the EEG alone looks like the individuals brain looks awake even though their body is not
what happens if an individual wakes up during slow wave sleep?
feel confused, heavy body, early stages may not believe you were dreaming,
what happens if an individual wakes up during REM sleep
wake up during a dream, vividly remember dream in early phases of re-awakening
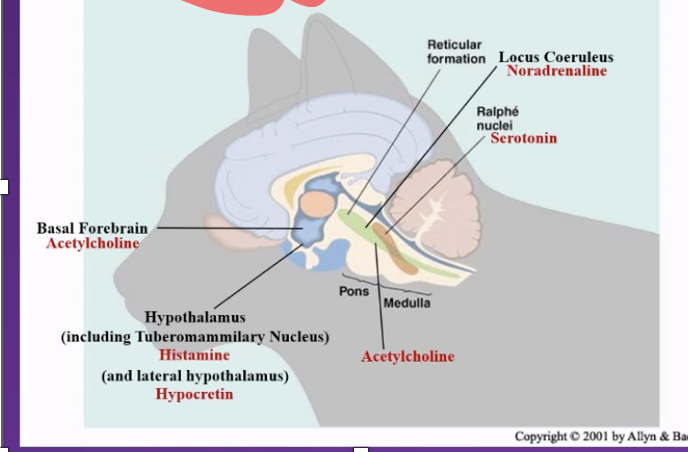
Major Brain Subdivisions involved in keeping the brain aroused/ attentional state are located in the :
• The Brainstem Reticular Formation (BRF) : a group of dozens of nuclei running through medulla, pons and tegmentum (reticular = looks like a net)
• Part of this BRF makes up/ is the Reticular Activating System (RAS) – activating =activating regions involved in i.e getting you alert
Neurotransmitters involved in Arousal (i.e. keeping us awake/ alert and influencing our EEG patterns) within the Reticular Activating System
• Acetylcholinergic
• Noradrenergic
• Serotonergic
• Histaminergic
• Hypocretinergic
Mechanisms of Arousal: Acetylcholine - explain
two groups of acetylcholinergic neurons are involved in sleep/wake states :
– One group is part of the Reticular Activating System and based in the Pons (Metencephalon brain region)
– One group is based in in the Basal Forebrain (Telencephalon)
Both have Has long axons that make synapses In large brain regions. – releasing Acetylcholene over most of the cortical neurons in the brain –
when these groups of neurons are active and releasing acetylcholine they strongly influence the state of lots of the cortex (have very strong neuro modularity influences) which cause the EEG looks wakefulness/ REM stage
Mechanisms of Arousal: Acetylcholine - describe evidence that it is involved in arousal
studies suggest Acetylcholine is responsible for wake like neural activity during REM sleep stage and found:
when people are given acetycholinergic agonists, participants are more likely to enter a REM sleep like state
conversely, giving participants acetylcholinergic antagonists supressed REM sleep, preventing the brain from attain that same highly active, desynchronised level which characterises REM sleep
evidencing that ACh is mechanistically causally involved for at least that aspect of REM sleep, and possibly Explains why ACH is low during slow wave sleep, how
studies founf – neocortex and acetlycholoine levels support this
neocortex activity - neocortex – high acetylcholine conc when in wakeful stage, significant drop during slow wave sleep and high again during REM sleep
neocortex activity is higher during REM sleep than awake
hippocampus: moderate / medium levels during wakefulness, drops significantly during slow wave sleep, highest significantly increase during REM sleep
hippocampus is more activated during REM sleep than during wakefullness
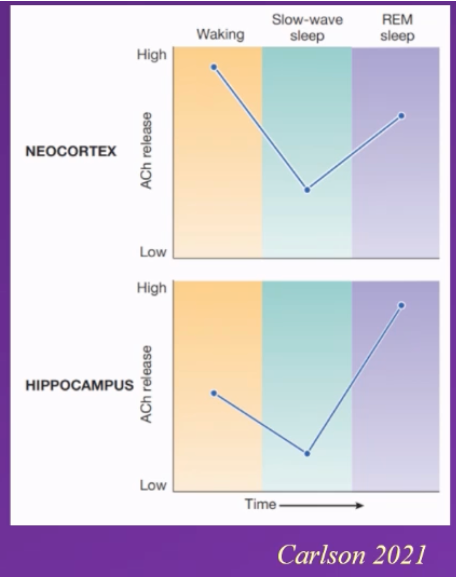
Mechanisms of Arousal: Noradrenaline (Norepinephrin)
produced/ released from Locus Coeruleus (located in RAS in Pons)
Has long axons that make synapses In large brain regions. – releasing Noradrenaline over most of the cortical neurons in the brain –
influence on arousal
• Related to Vigilance, induced by external stimuli: i.e it is active when we engage in vigilance e.g. hear a loud bag and get startled turn around activates the locus coeruleus
Mechanisms of Arousal: noradrenaline - describe evidence that it is involved in arousal
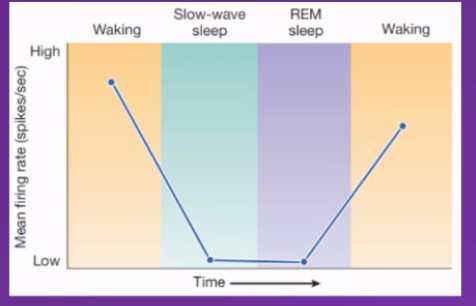
Diagram depicting firing rate of neurons (and noradrenaline release) in the locus coeruleus.
Typically – activity in the locus coeruleus is
High when awake
Continuously declines until the individual enters slow wave sleep
Continues to decline during slow wave sleep (not reaching 0 though)
During rem sleep firing rate is reduced to 0, and locus coeruleus becomes inactive during REM sleep
When individual wakes up activity significantly increases, spikes as locus coeruleus activates again
Conclusion
As no activity in locus coeruleus during REM sleep, no noradrenaline released during this time, indicating that no noradrenaline can be present for REM sleep to occur and that it is involved in arousal
And might contribute to the switch between slow wave and REM sleep, as its only when low enough threshold is attained can we transition from slow wave to REM sleep
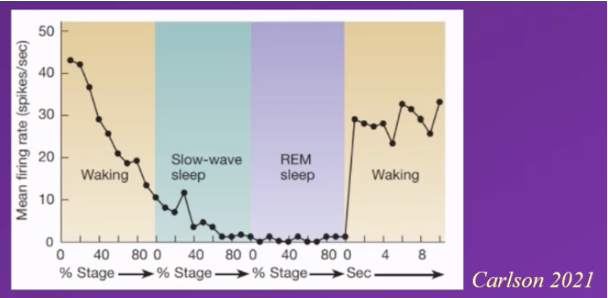
where does noradrenaline come from?
Noradrenaline produced From Locus Coeruleus (located in RAS in Pons) – Locus Coeruleus – translates to the blue place because it looks blue –
Mechanisms of Arousal: Serotonin - explai n
Serotonin comes From Raphe Nuclei (which axons release serotonin into the brain) (is part of the RAS in Pons and Medulla)
Influences locomotion and cortical arousal, but not sensitive to external stimuli
correlation evidence
Is highly active when awake and continually decrease in activity as the individual transitions from wakeful to slow wave sleep
during
Slow wave sleep: Continues to decrease in activity – mean firing rate of neurons releasing serotonin reduces.
REM sleep: Slowly after entering REM sleep stage the lowest activity rate occurs
First second after individual enters REM sleep stage activity significantly spikes and increases
Conclusion
Can infer there's an incompatibility between serotonin levels being high and REM sleep happening.
Serotonin levels need to be low during slow wave sleep and very low during REM sleep for these stages to occur
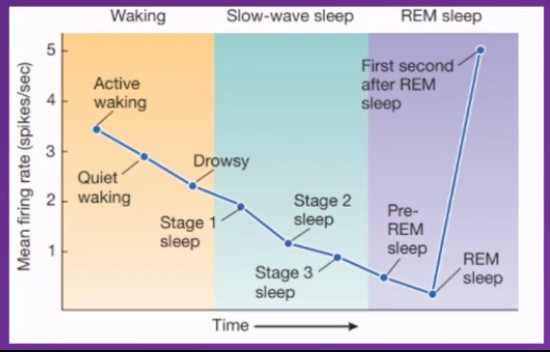
Where is Serotonin produced
Serotonin comes From Raphe Nuclei (which axons release serotonin into the brain) (is part of the RAS in Pons and Medulla)
Influences locomotion and cortical arousal, but not sensitive to external stimuli
How does serotonin differ from noradrenaline/ what does noradrenaline do differently than noradrenaline
Both contribute to keeping us awake (if they are high we will be awake/ not sleep, and need to be low for us to fall asleep) and influence out alertness and vigilance but under different conditions/ circumstances – what they share in common
Where do they differ?
While noradrenaline seems to be involved in vigilance that is driven by external stimuli triggered by external stimuli
Serotonin tends to be involved in vigilance and alertness that's internally driven e..g consciously choosing to pay close attention to something driven by personal motivation, crashing noise will not cause raphae nuclei to fire and subsequently release increased serotonin, it will only cause locus coeruleus neurons to fire.
Where is serotonin used in clinical settings artificially?
It is the same serotonin, the same source of serotonin that we believe to be involved in depression and in antidepressant drug treatment
Mechanisms of Arousal: Histamine neurotransmitter
◦ Where are histamine releasing neurons located?
a group of neurons in the In the Tuberomammilary Nucleus (in the Hypothalamus)
◦ High during waking, low during sleep – i.e involved in keeping us awake
Anti-histamines put you to sleep
How do antihistamines influence wakefulness?
If antihistamine crosses the blood brain barrier (some do, some don't) then it will not just have an effect on the allergy allergic reaction but will also influence our wakefulness, and cause drowsiness
Mechanisms of Arousal: Hypocretin (also called Orexin) neurotransmitter
Why does it have two names?
Because different people discovered the same neurotransmitter and named it independently of each other (i.e unaware it had already been named)
Extra – anecdotal info. I think
Why would you take anti-histamines?
Two functions unrelated to each other
Allergies – because histamine is involved in allergic reactions: it is a signalling molecule all through your body and involved in the inflammatory response and allergic reactions
Wakefulness – it is a neurotransmitter in the brain involved in keeping us awake
Can be prescribes as a sleep inducing agent
Mechanisms of Arousal: hypocretin neurotransmitter
Where are hypocretin producing neurons located?
Located and produced in the lateral hypothalamus
Function relating to wakefulness – contributes to keeping us alert and awake via its
◦ excitatory (hypocretinergic) connections to (i.e increases activity in) the:
◦ Locus coeruleus
◦ Raphé nuclei
◦ Tuberomammillary nucleus
◦ Dorsal Pons
◦ Basal Forebrain
◦ Cerebral cortex
◦ … which contribute to keeping us awake
• is Active during active waking and exploration, So keeps us alert
Hypcretin must be high when awake and really low during slow wave sleep and REM sleep , gradualy increase during REM sleepunitl threshold activity has been surpassed and wakefullness can be attained
Seems to be master controller
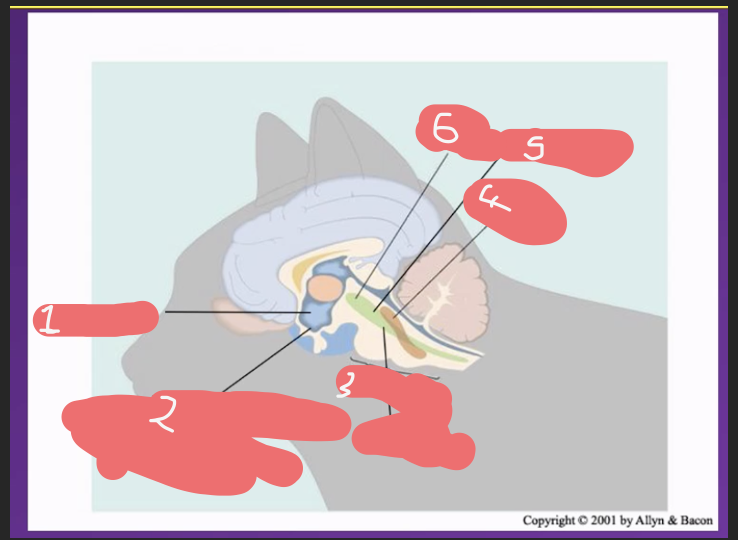
list brain areas involved in arousal in a cat brain