11. Autonomic Nervous System
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
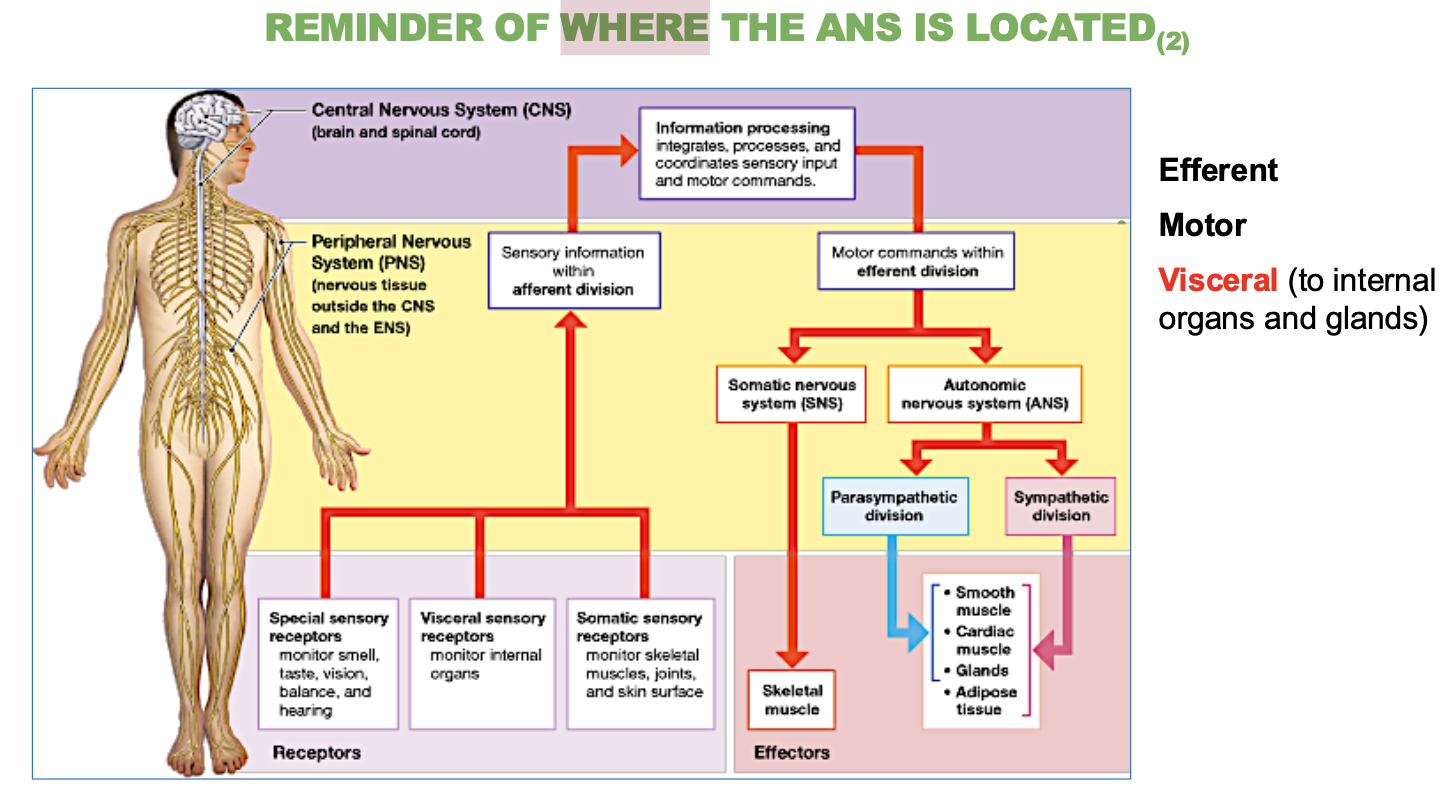
Where is the autonomic nervous system (ANS) located?
In the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
It controls involuntary bodily functions, such as heart rate and digestion.
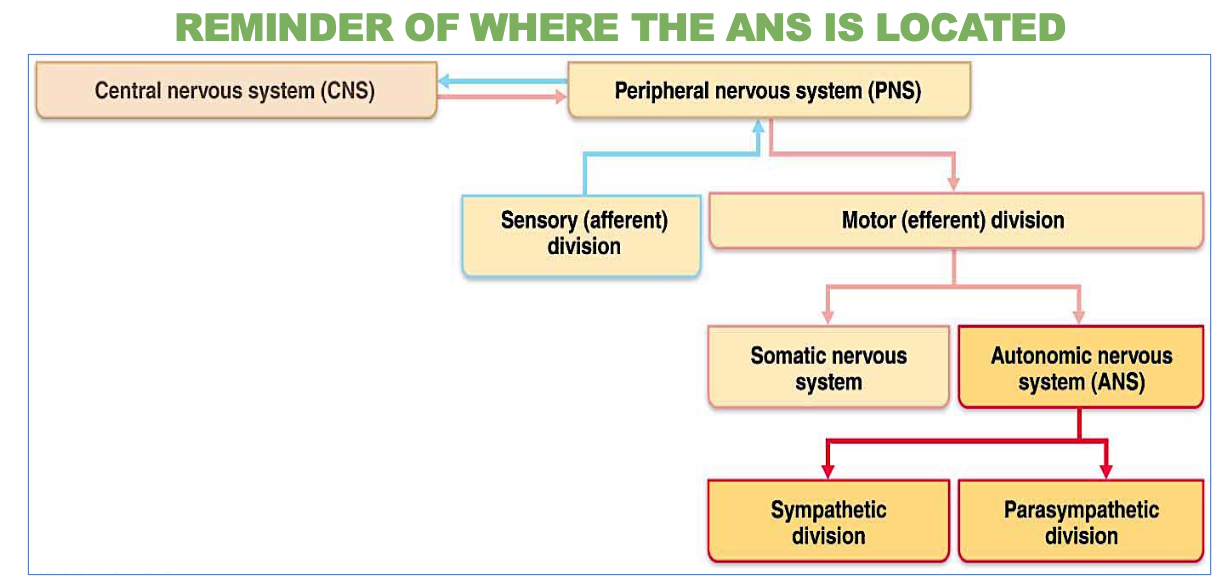
Is the ANS afferent or efferent?
Efferent – it carries signals away from the brain and spinal cor
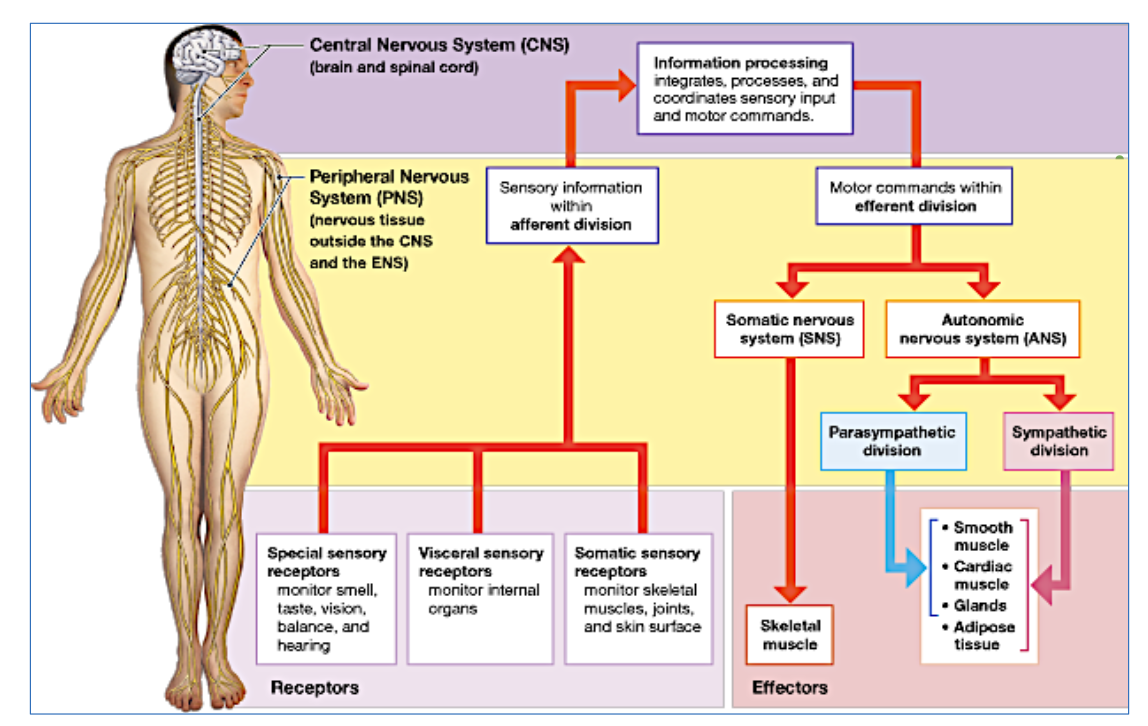
Is the ANS sensory or motor?
Motor – it controls movement in internal organs and glands.
Whats another name for the Motor Visceral?
Autonomic nervous system
What are the 3 characteristics of the ANS?
Involuntary (self-governed
Regulates heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, temperature, gland secretion.
Visceral motor division that controls cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and gland secretion functions.
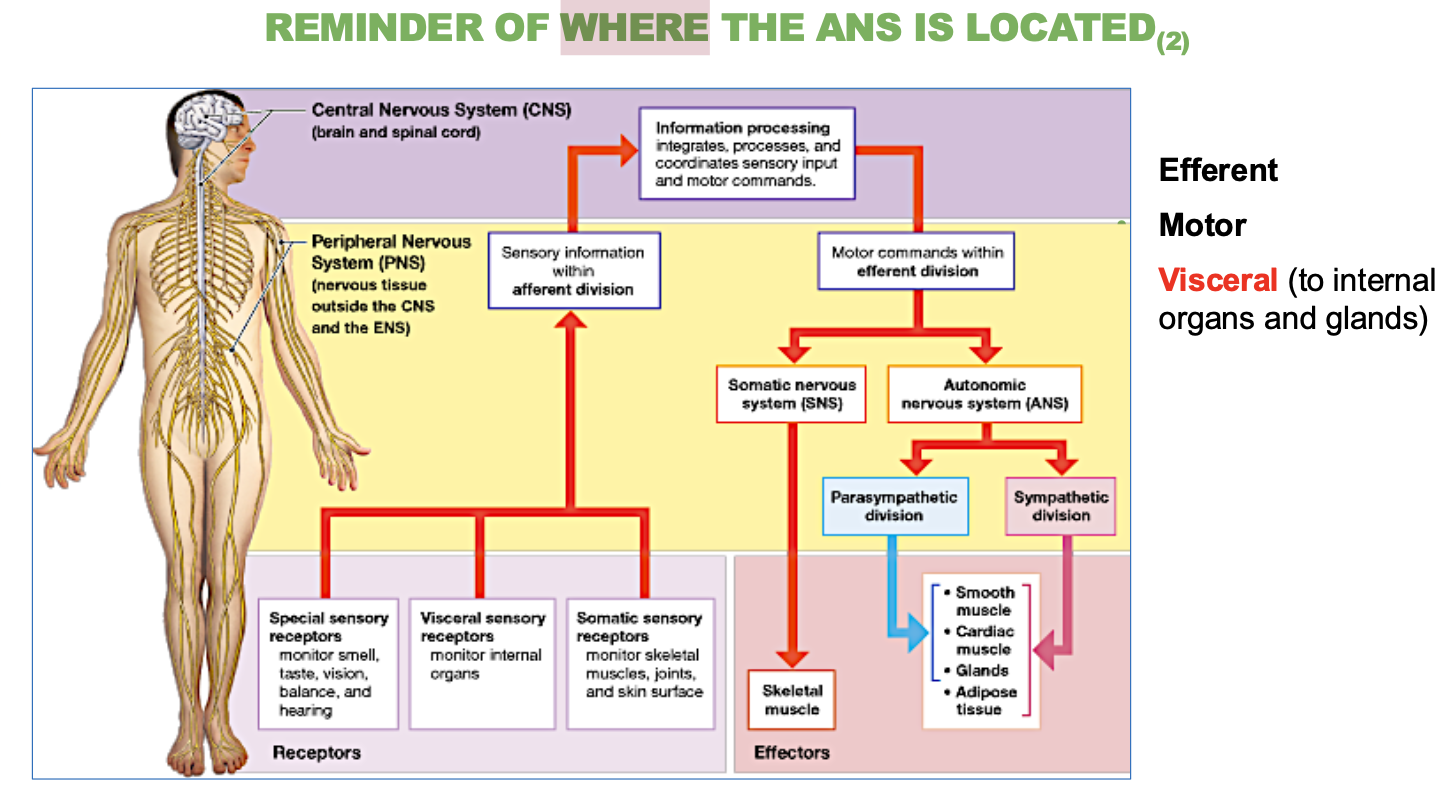
Is the autonomic nervous system (ANS) voluntary or involuntary?
Involuntary (self-governed).
What does the ANS regulate? (5 answers)
Heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, temperature, gland secretion.
3 divisions that the Visceral motor (or ANS) controls?
cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and gland secretion.
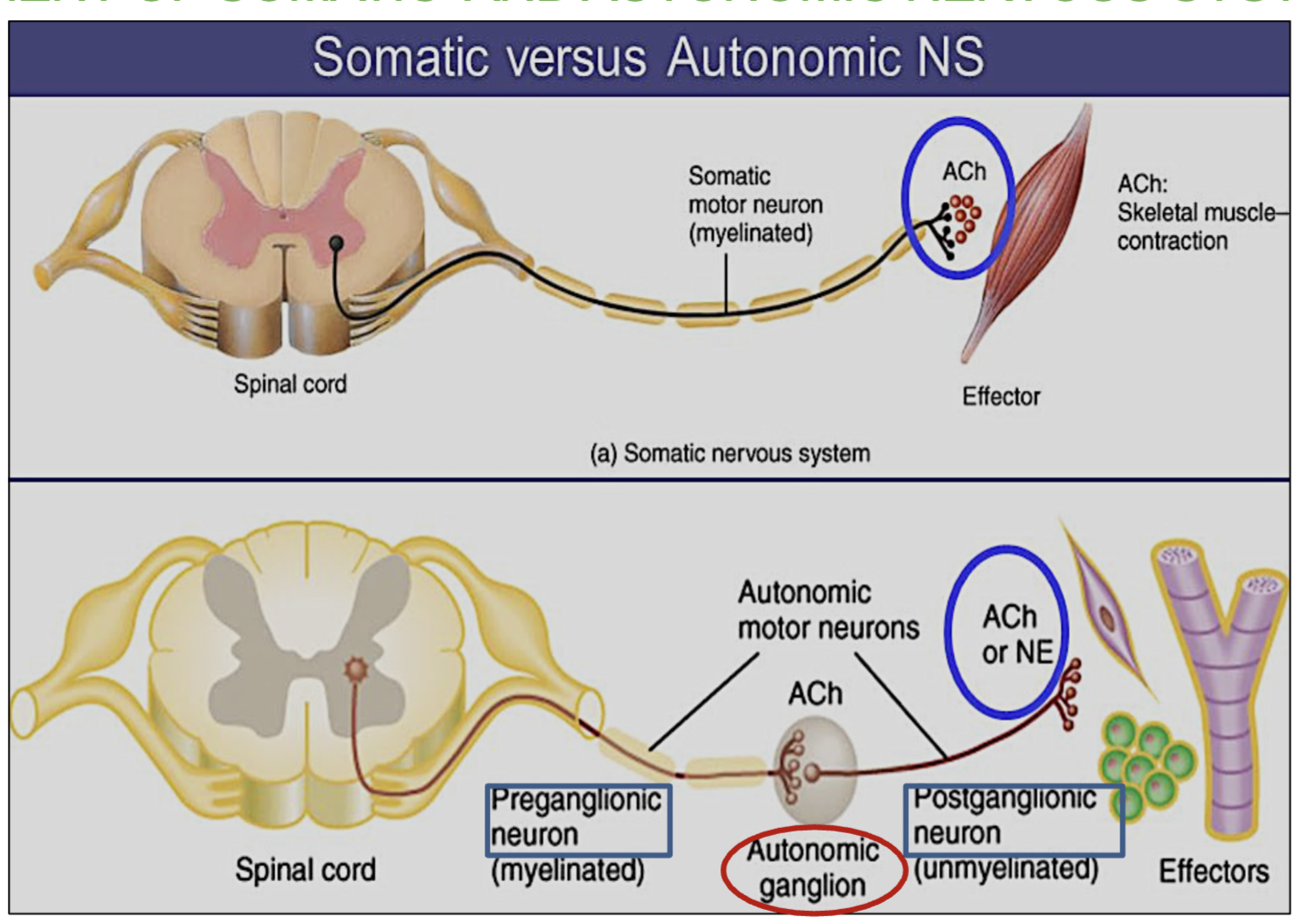
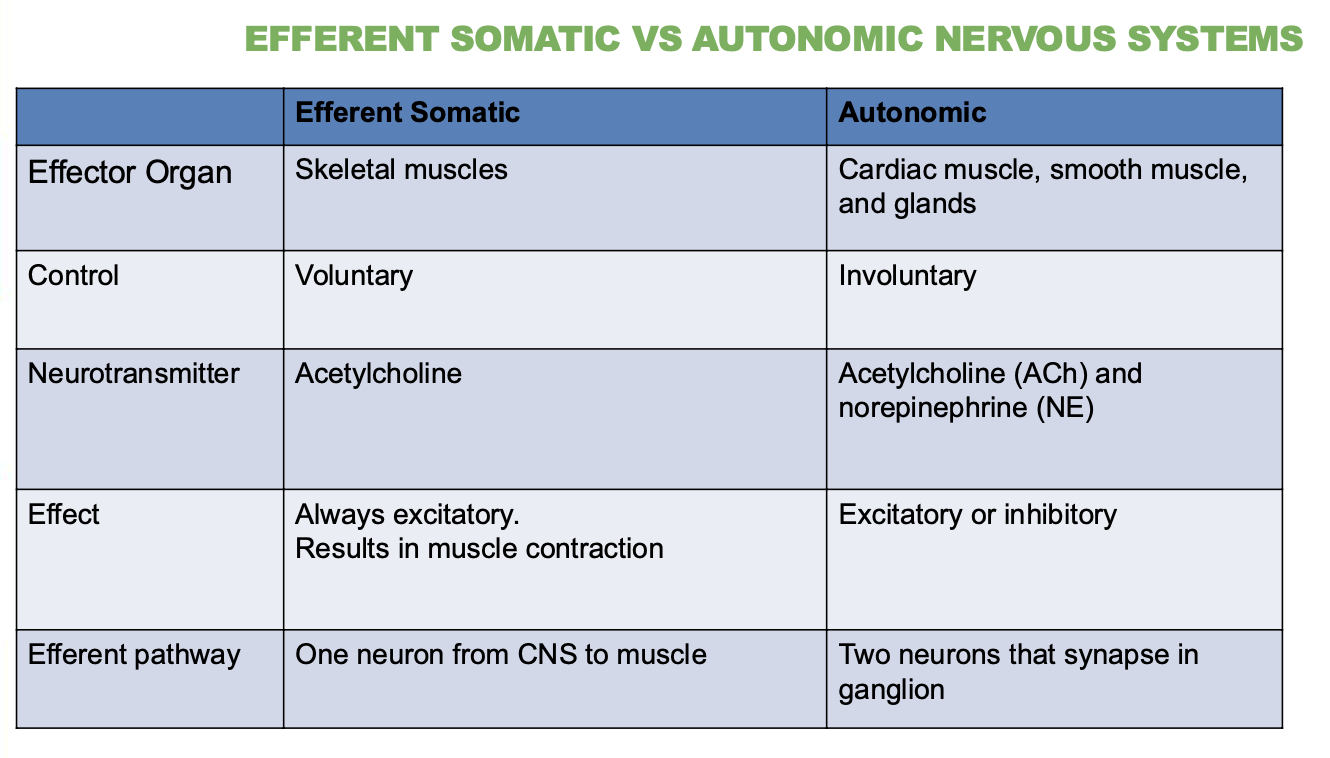
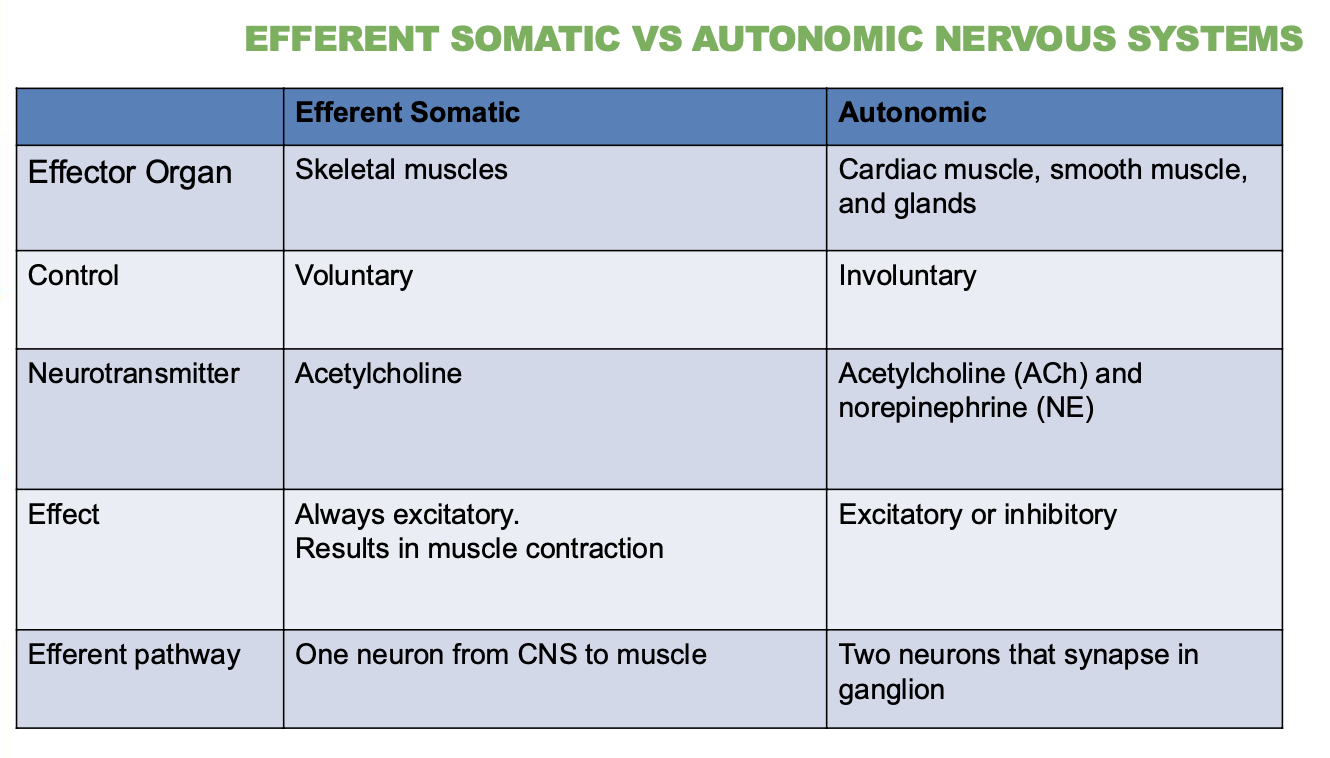
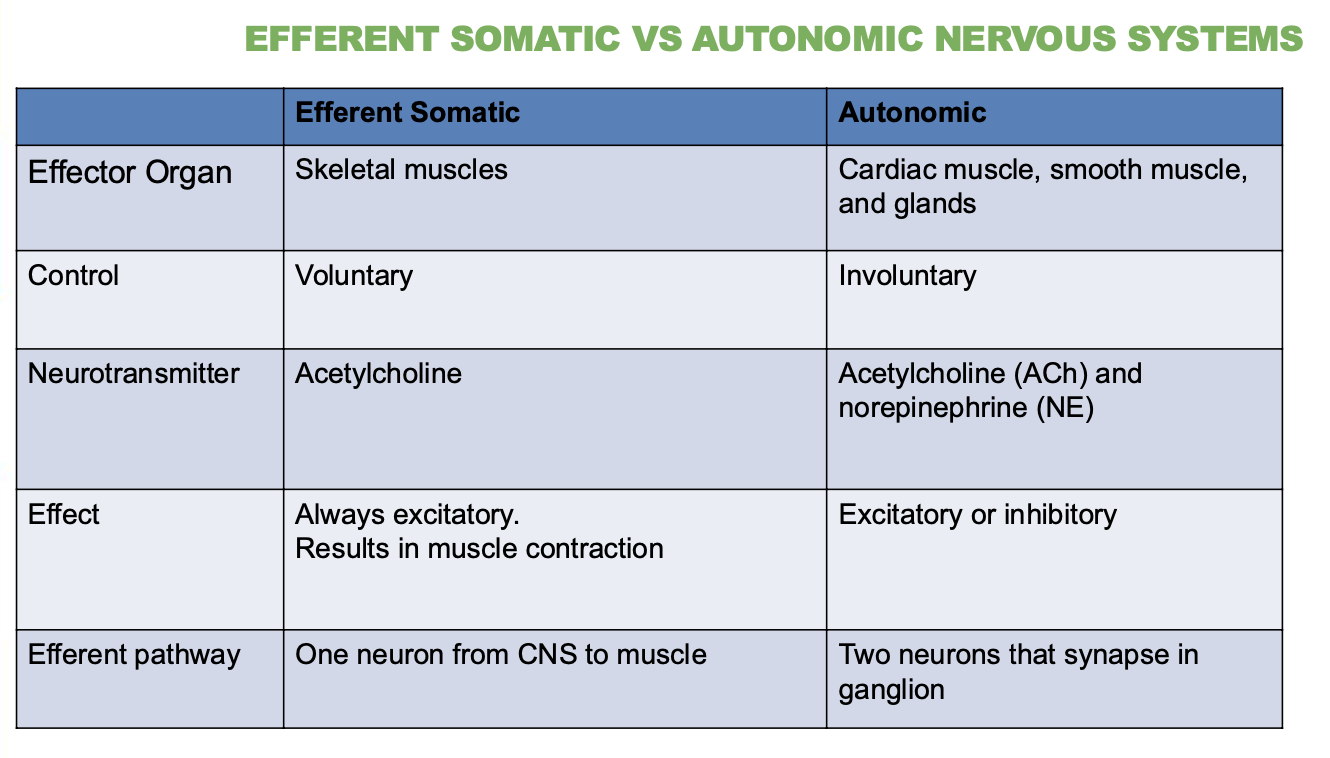
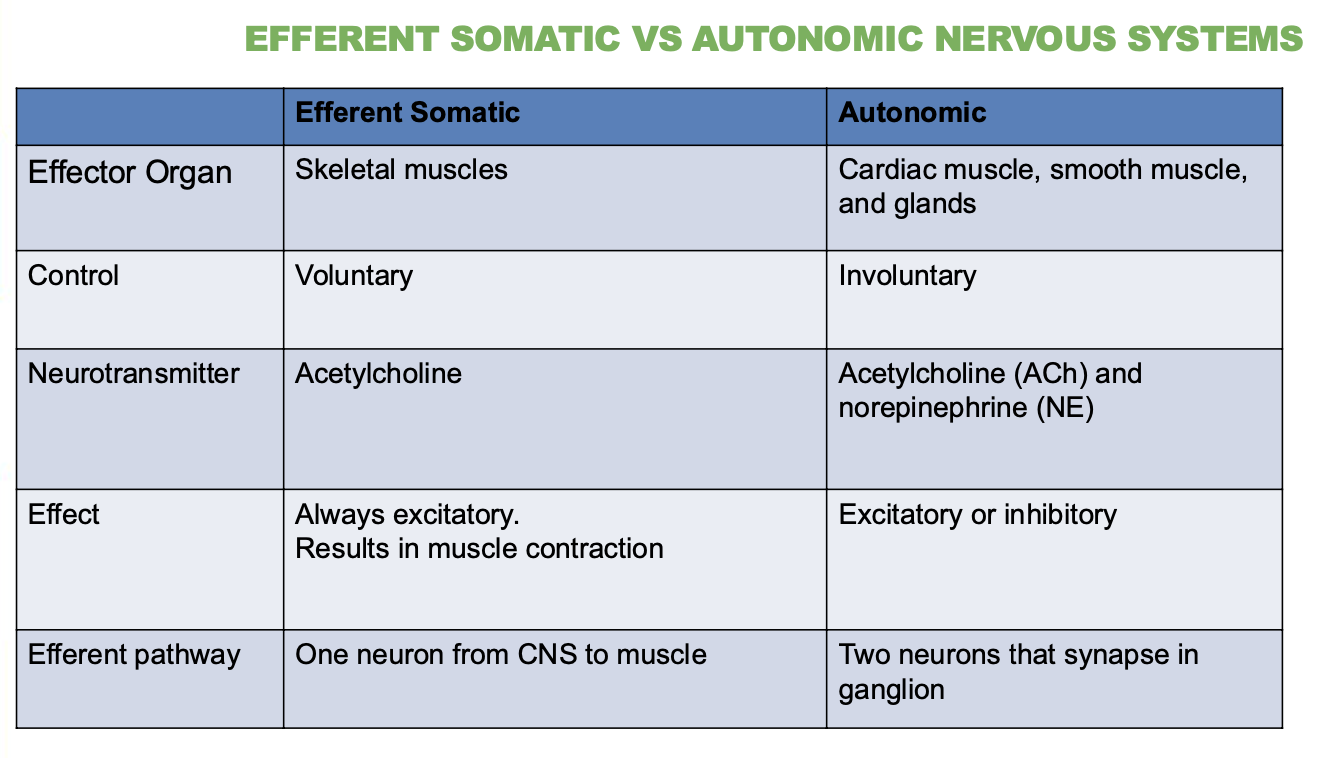
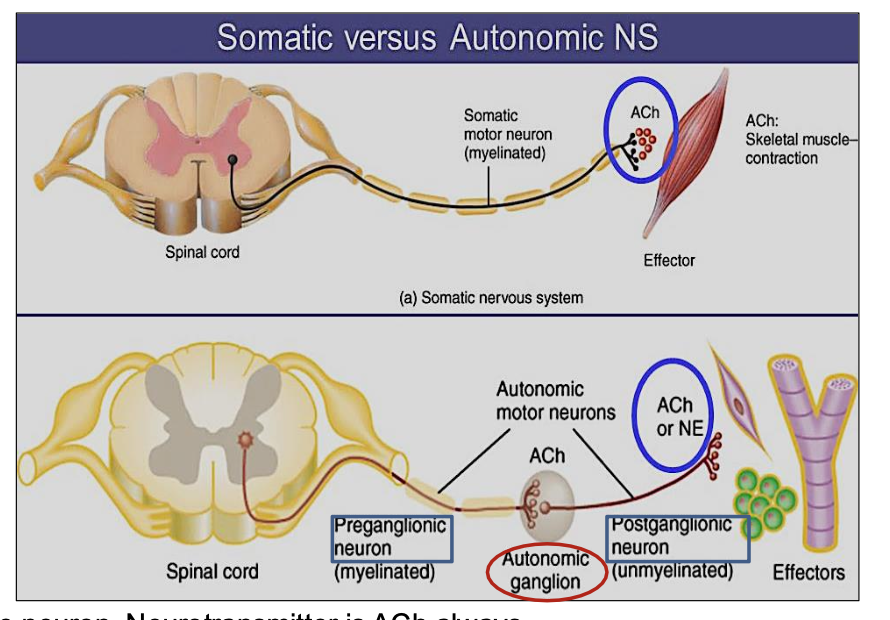
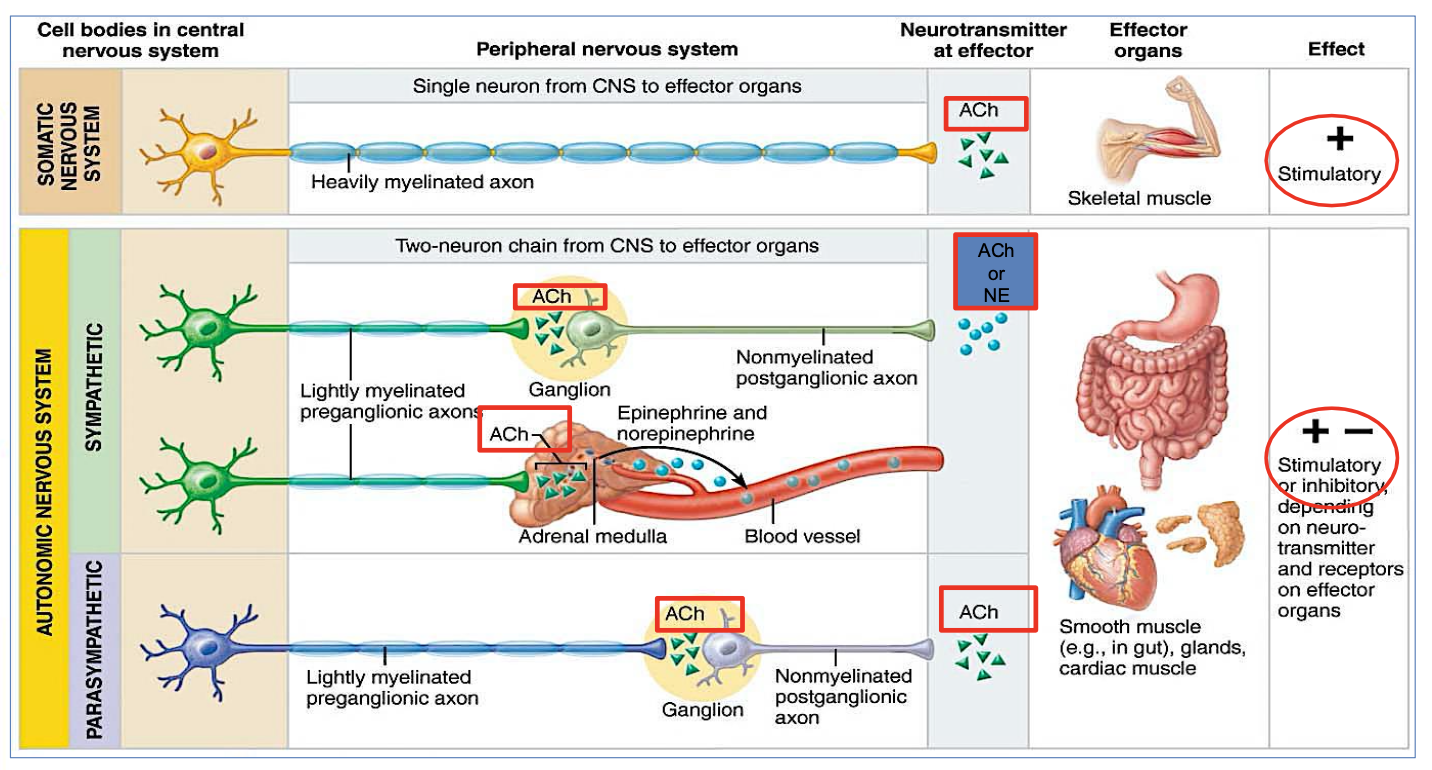
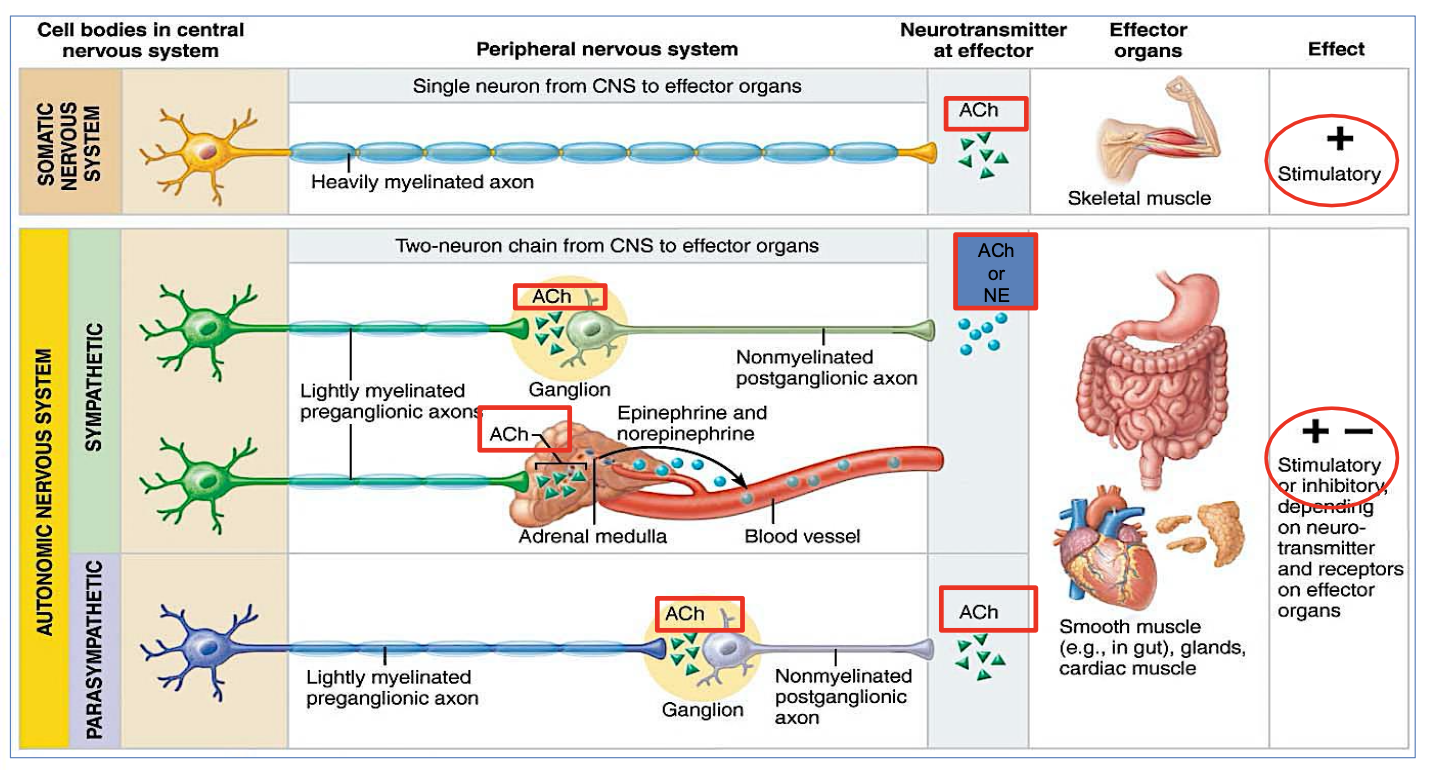
Differences between Efferent Somatic Vs Autonomic Nervous System?
Describe their Effector organ, control, neurotransmitter, effect & efferent pathway (5 answers for each)
Somatic Nervous System:
Controls voluntary movements (like moving your arms or legs)
Targets skeletal muscles
Uses 1 neuron
Uses acetylcholine (ACh)
Always excitatory
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS):
Controls involuntary actions (like heartbeat, digestion)
Moves cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands
Uses 2 neurons
Uses ACh and norepinephrine (NE)
Can be excitatory or inhibitory
What is the effector of the somatic nervous system?
Skeletal muscle.
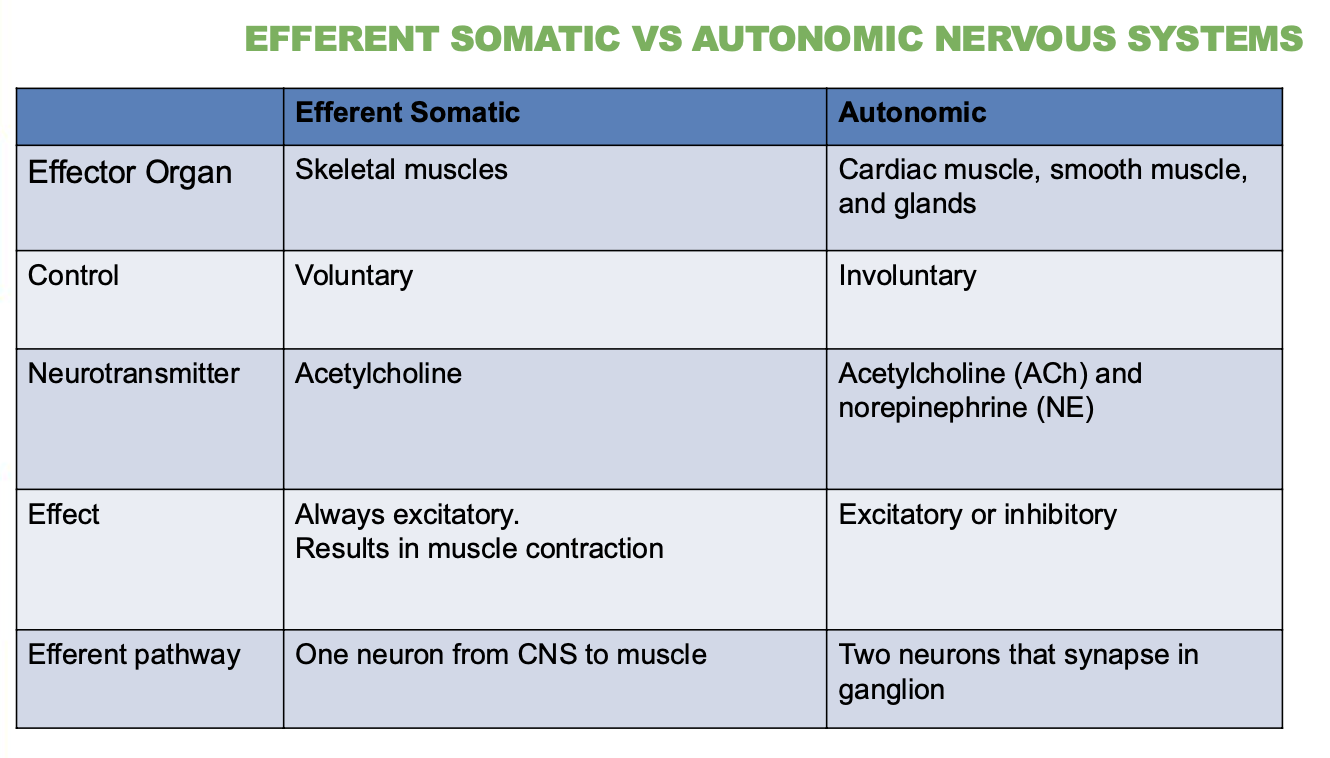
What type of control does the somatic system have?
Voluntary
What type of control does the autonomic system have?
Involuntary
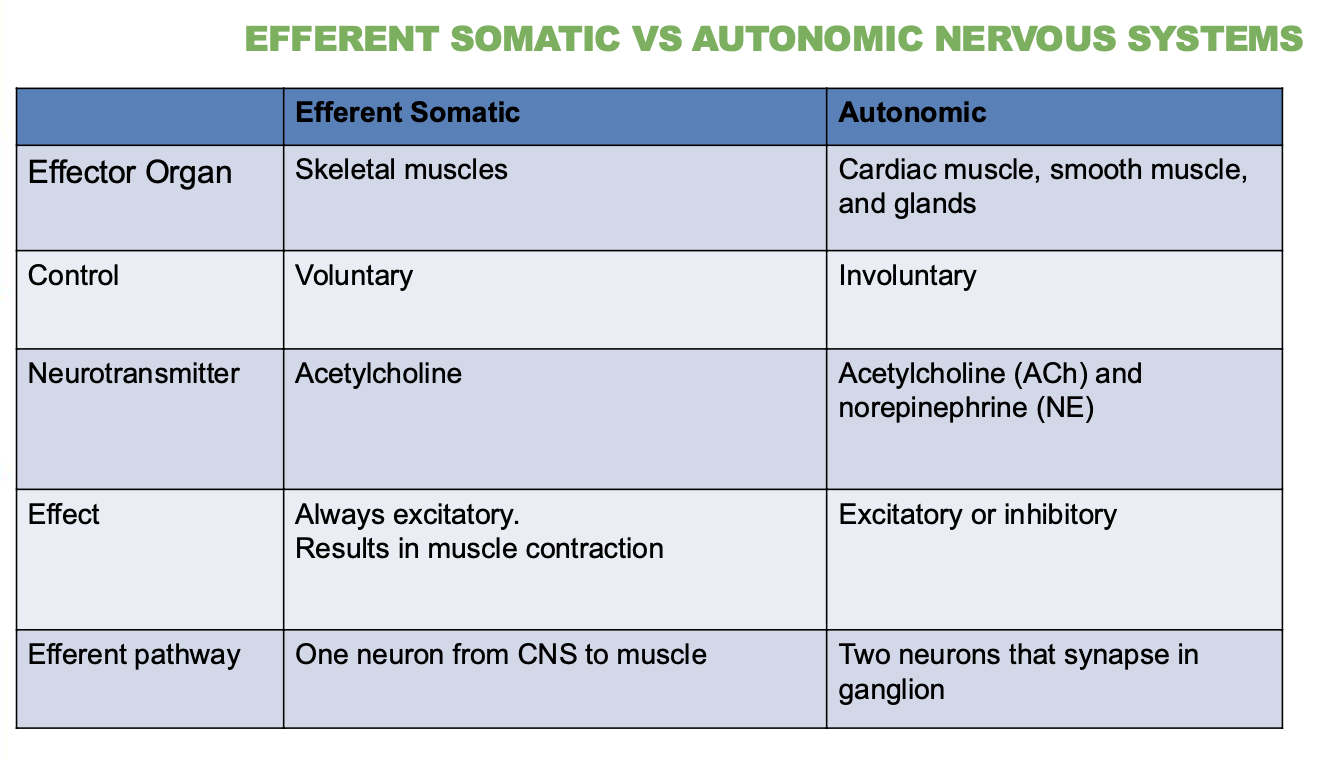
What neurotransmitters are used by the somatic system?
Just 1, Acetylcholine (Ach)
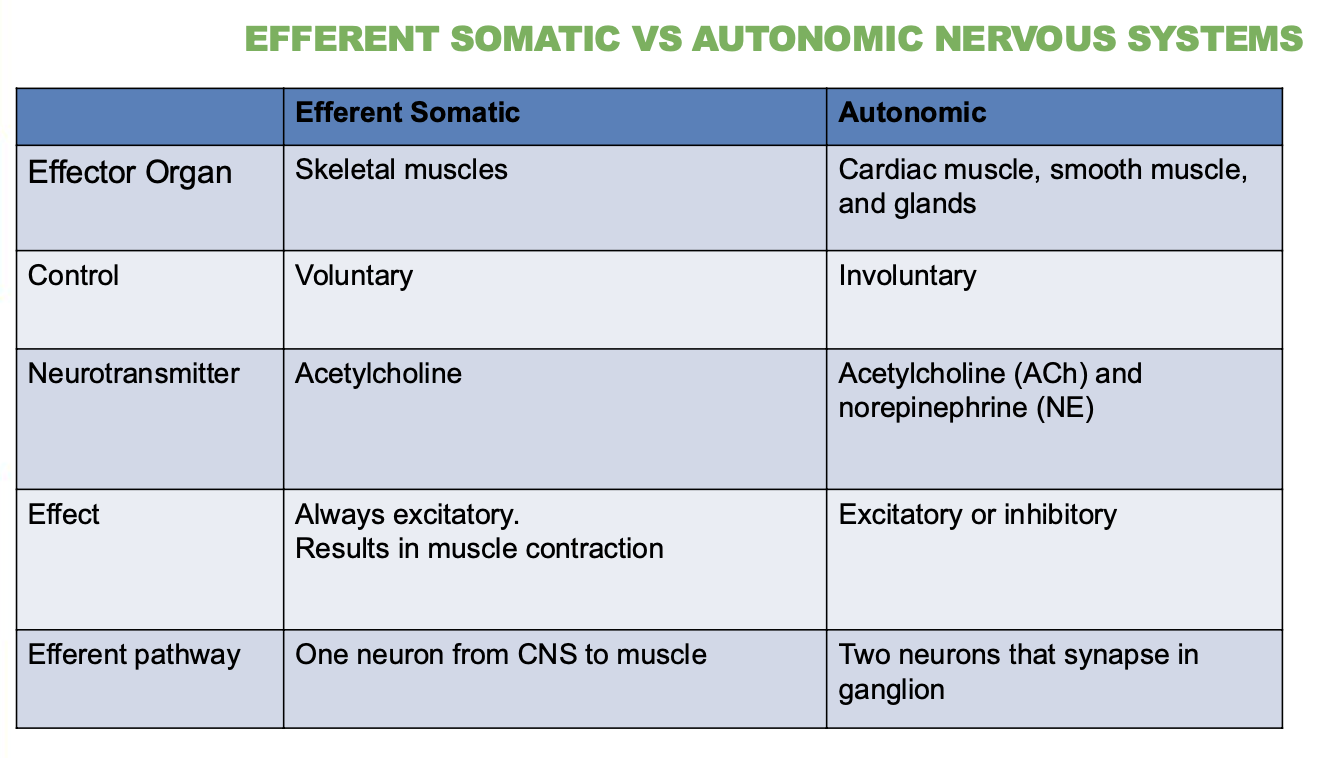
What neurotransmitters are used by the autonomic system?
2, Acetylcholine (ACh) and norepinephrine (NE).
Is the effect of the somatic system excitatory or inhibitory?
Always excitatory—causes muscle contraction.
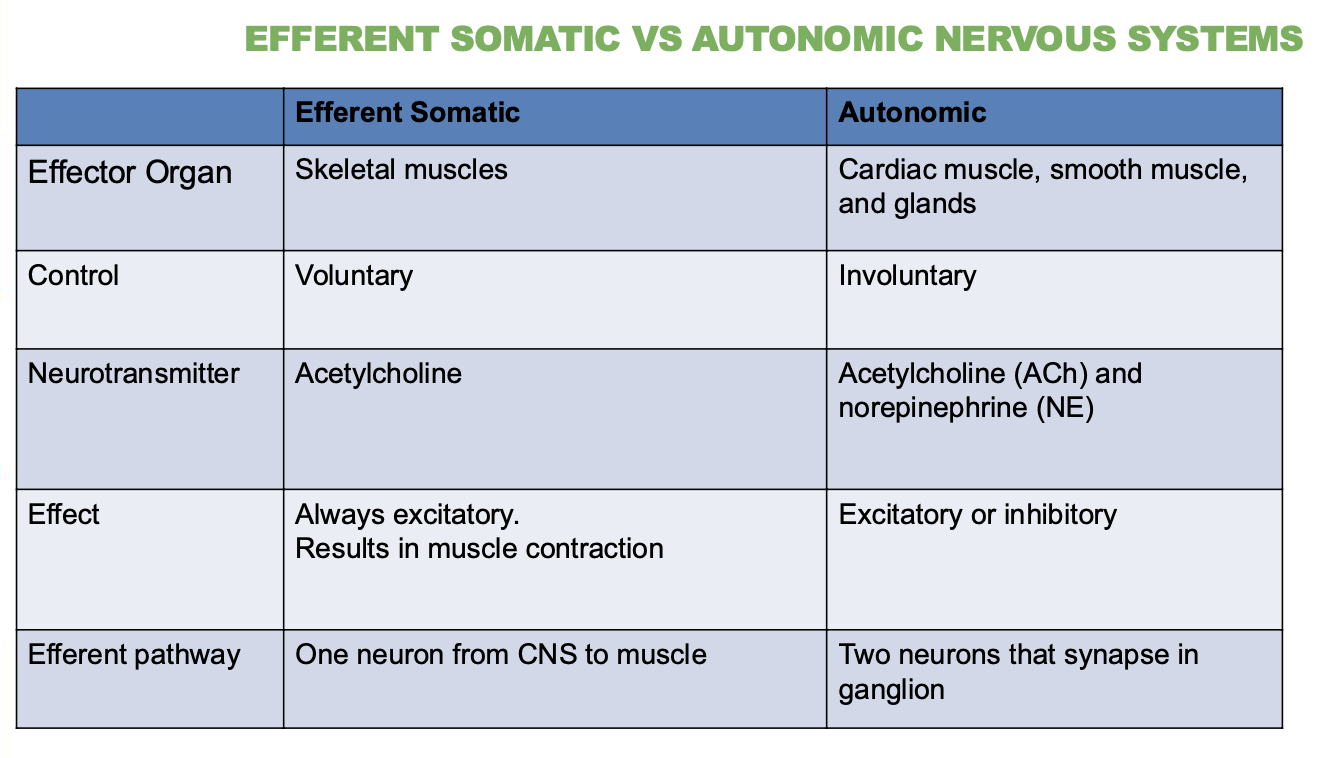
Is the effect of the autonomic system excitatory or inhibitory?
Can be either, Excitatory or inhibitory.
How many neurons are in the somatic motor pathway?
1 neuron from CNS to muscle
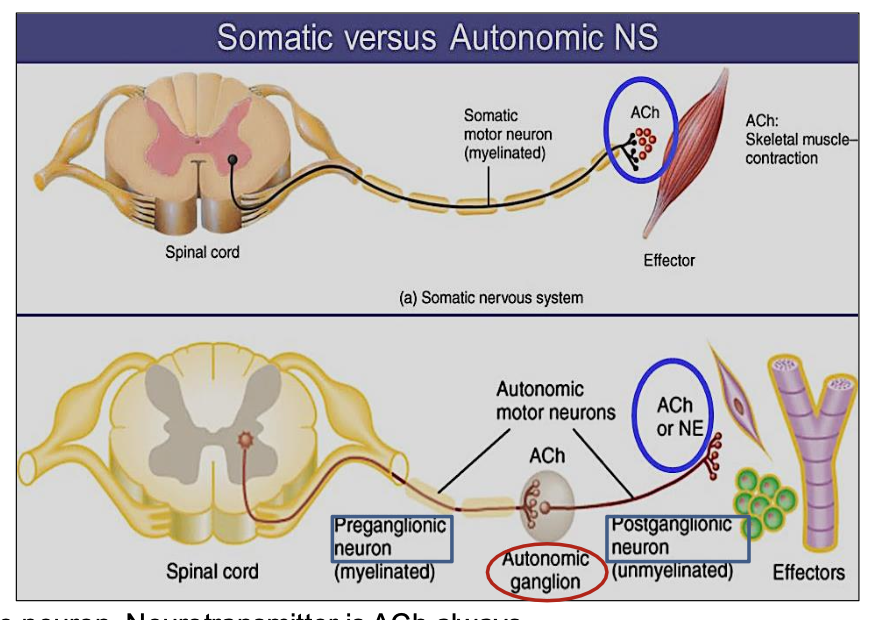
How many neurons are in the autonomic motor pathway?
2 neurons that synapse in a ganglion.
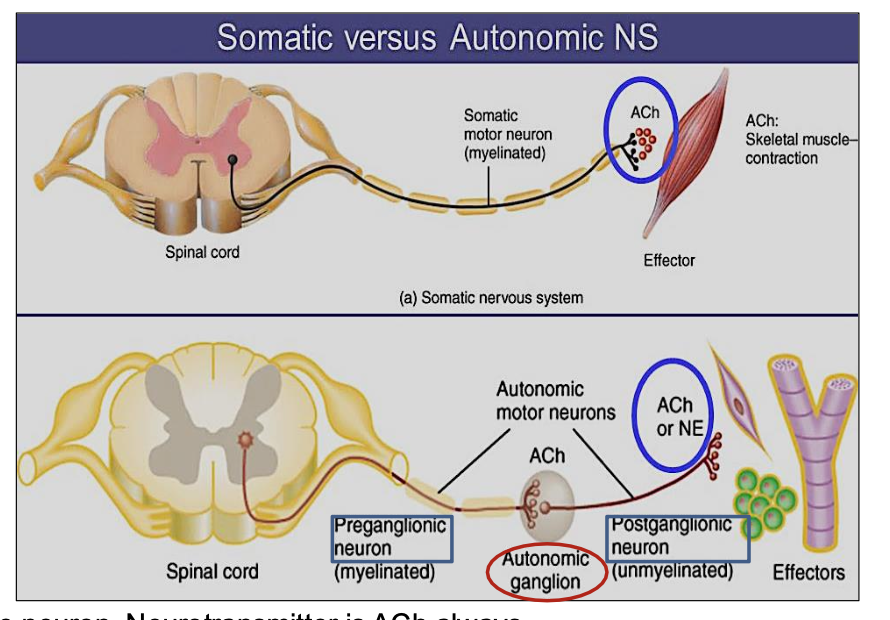
How many neurons are in the somatic nervous system pathway?
1 neuron from CNS to target organ.
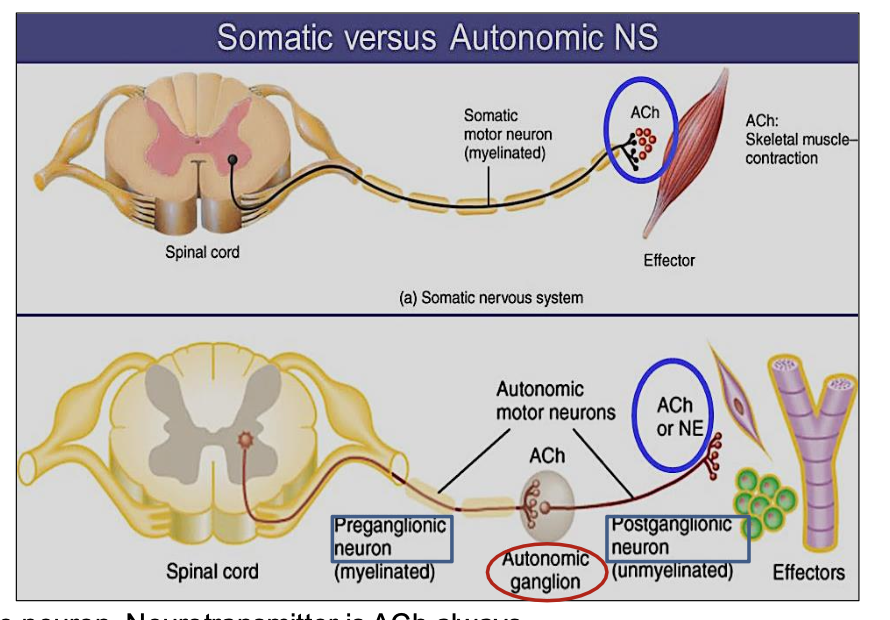
What neurotransmitter does the somatic nervous system use?
always Acetylcholine (ACh)
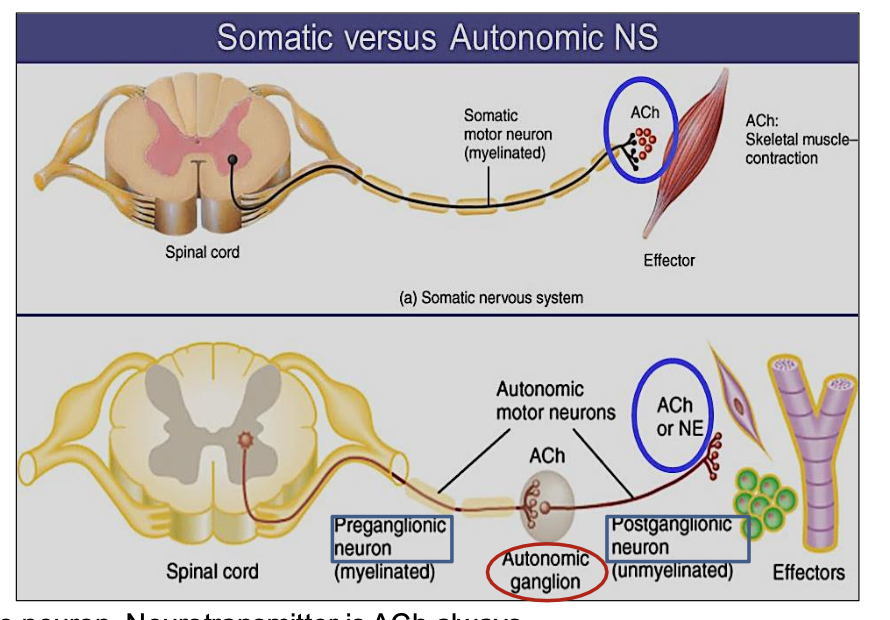
How many neurons are in the autonomic nervous system pathway & their names ?
2 neurons: preganglionic and postganglionic
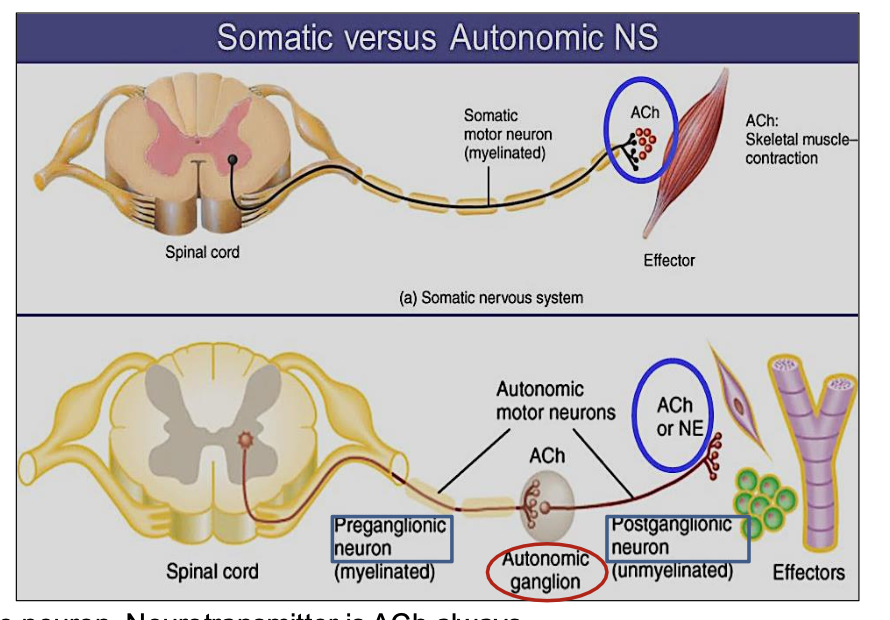
What neurotransmitter is used by the preganglionic neuron in the autonomic system?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
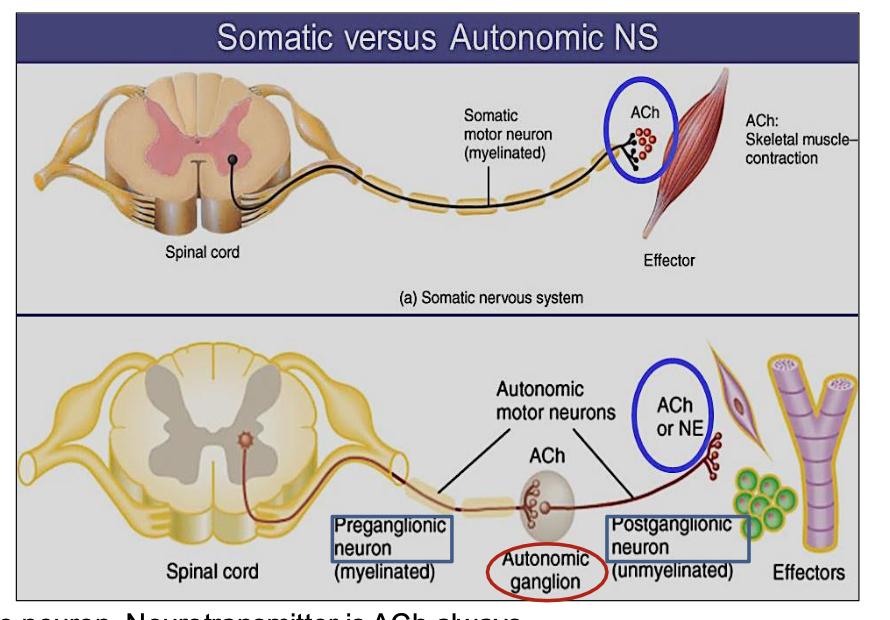
What neurotransmitter is used by the postganglionic neuron in the autonomic system?
ACh or norepinephrine (NE)
What are the Parasympathetic & Sympathetic divisions a part of?
The autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary physiological functions.
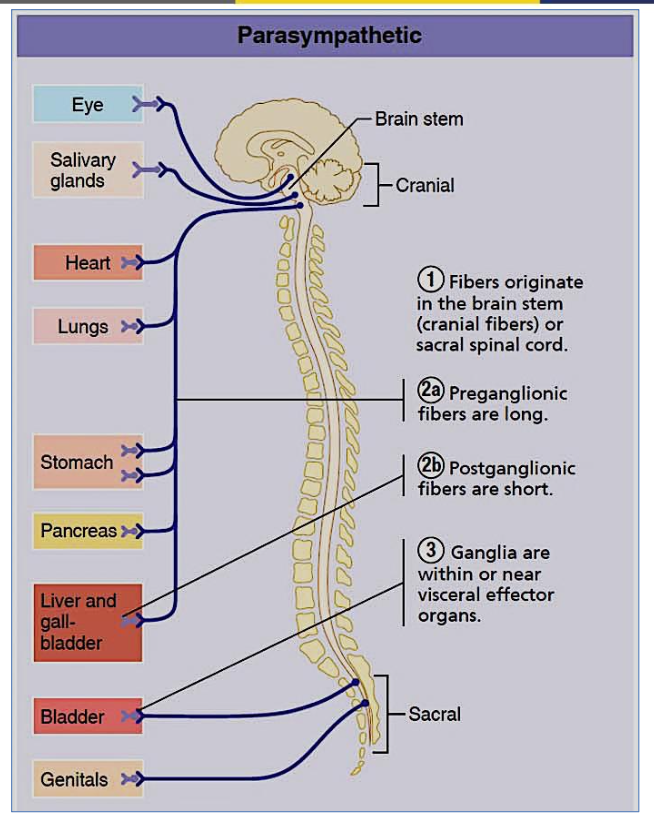
What is the main function of the parasympathetic division?
"Rest and digest" – conserves energy, aids digestion
What are 2 example effects of the parasympathetic division?
Slows heart rate, increases digestion
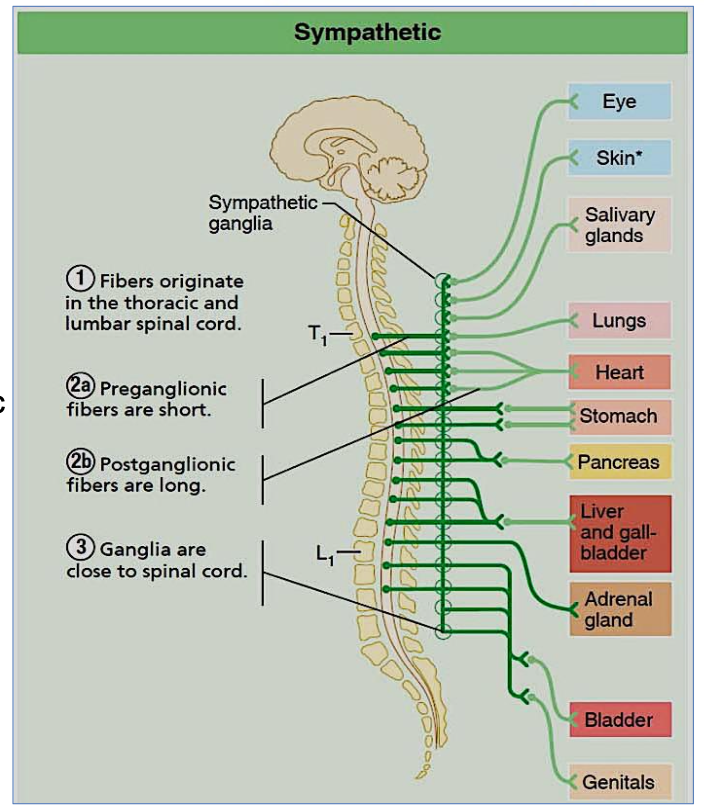
What is the main function of the sympathetic division?
"Fight or flight" – prepares the body for action
What are 2 example effects of the sympathetic division?
Increases heart rate, slows digestion
(opposite from parasympathetic)
How many neurons are used in the parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions?
Both use 2 neurons: preganglionic and postganglionic
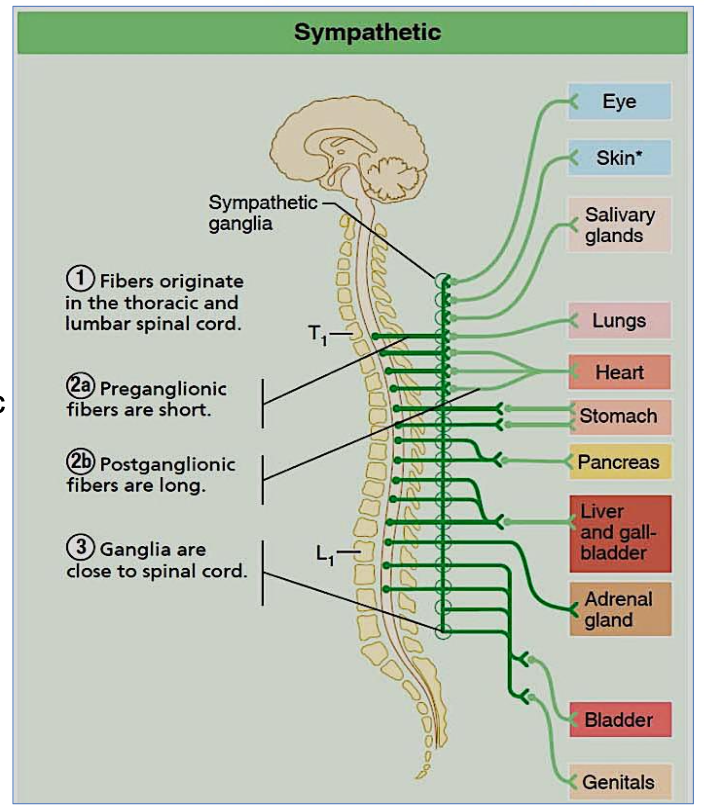
What is the origin of the sympathetic nervous system?
Thoraco-lumbar
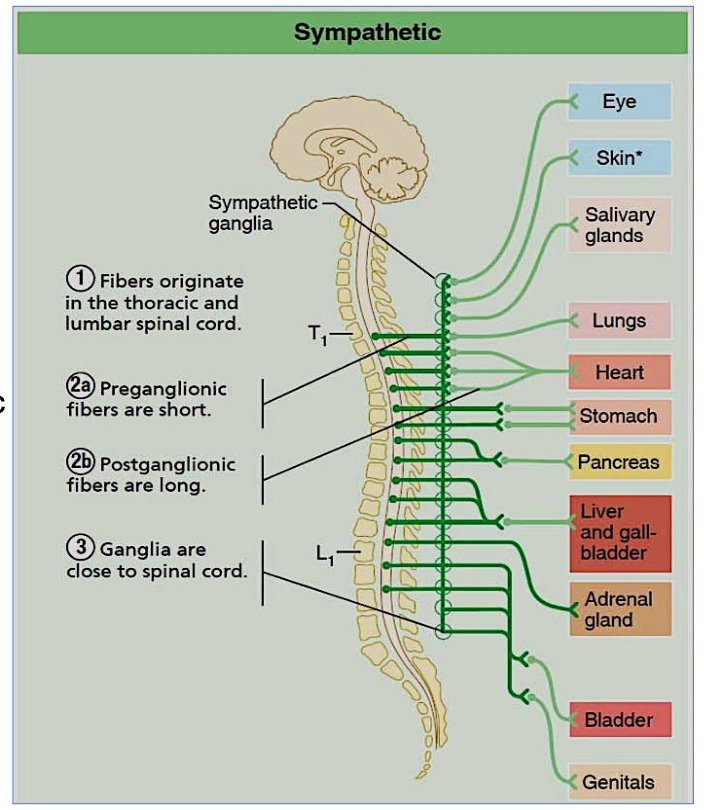
Describe the neuron length in the sympathetic nervous system.
Short preganglionic, long postganglionic
Where are sympathetic ganglia located?
Near the spinal cord
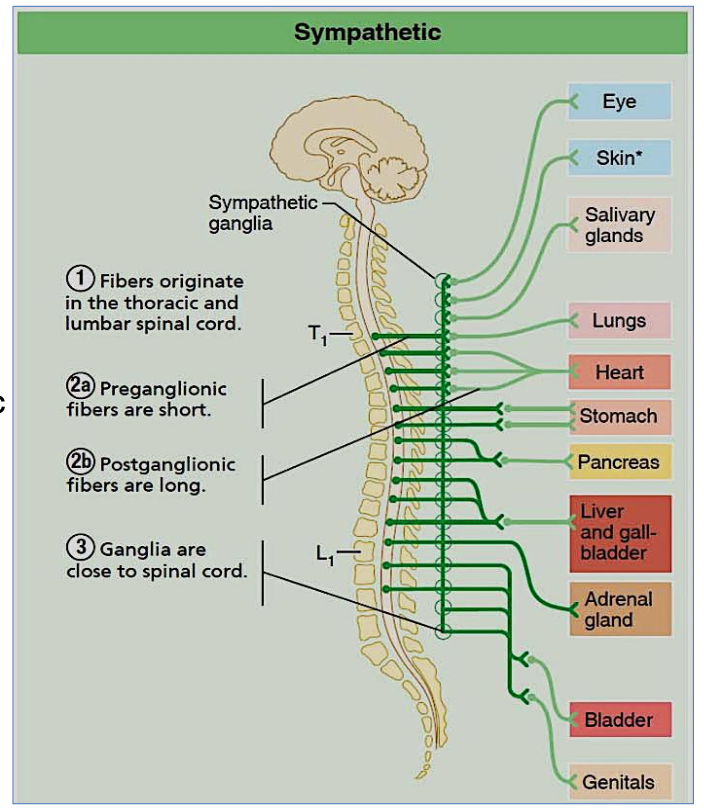
What is the origin of the parasympathetic nervous system?
Cranio-sacral
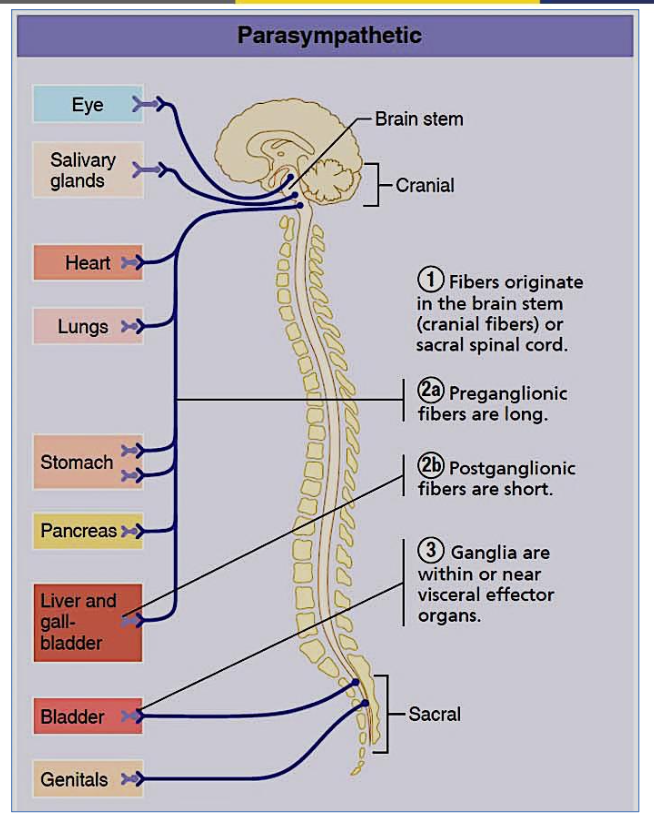
Describe the neuron length in the parasympathetic nervous system.
Long preganglionic, short postganglionic
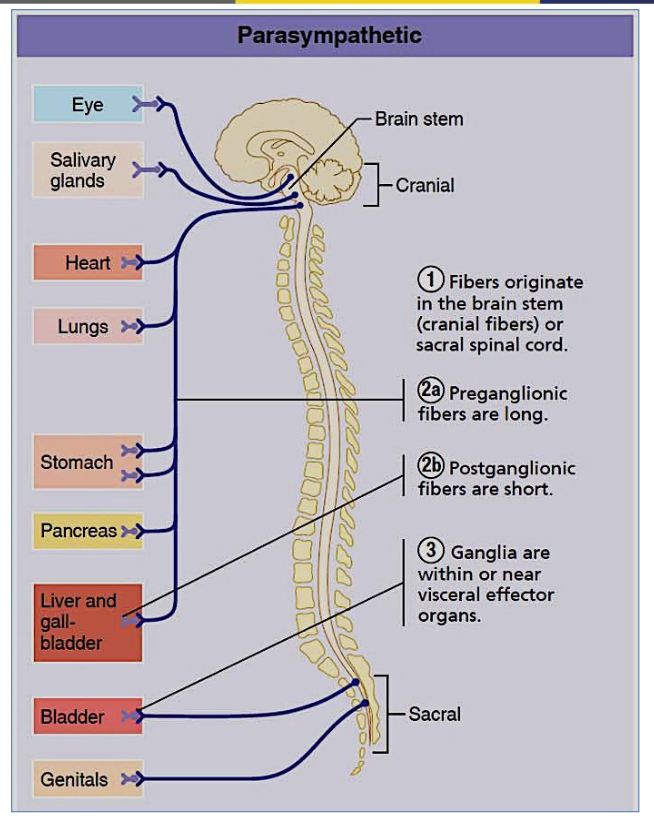
Where are parasympathetic ganglia located?
Near the effector organ
What are the postganglionic neurotransmitters in the Sympathetic system?
Norepinephrine (NE) or ACh
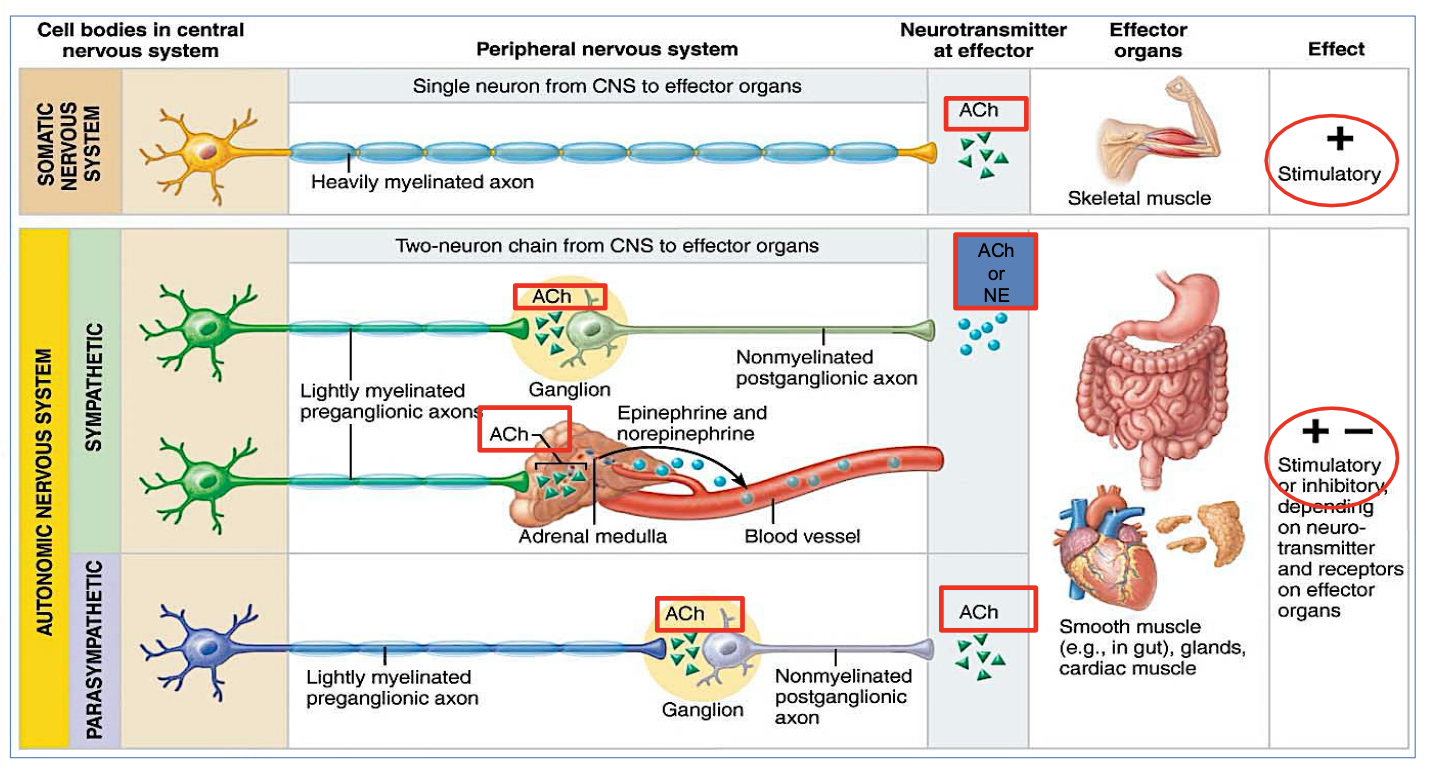
What is the Pre-ganglionic neurotransmitters in the Sympathetic system?
Just ACH
What is the postganglionic neurotransmitter in the Parasympathetic system?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
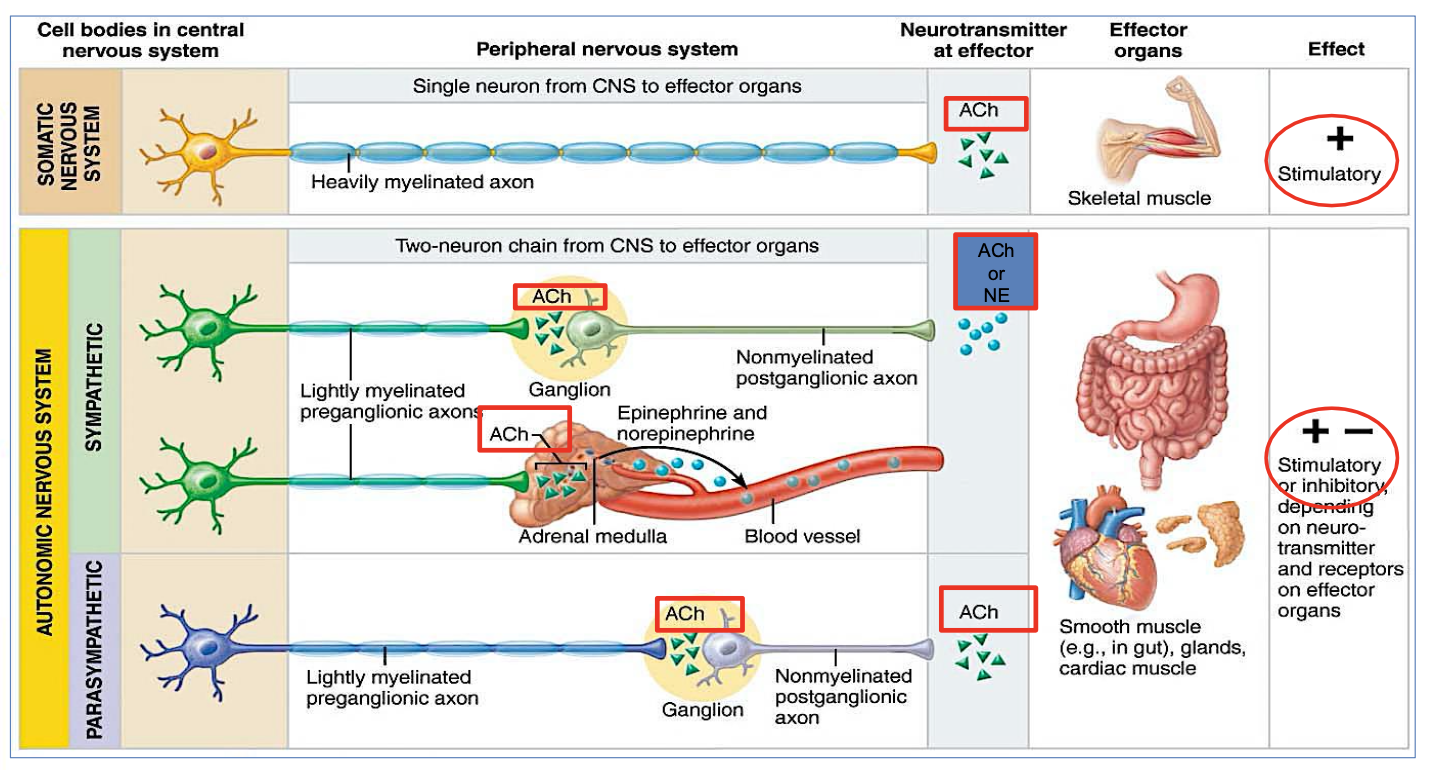
What effect does the Sympathetic system usually have?
Excitatory or inhibitory
Excitatory
→ typically increases heart rate, dilates the airways, and prepares the body for 'fight or flight' responses.
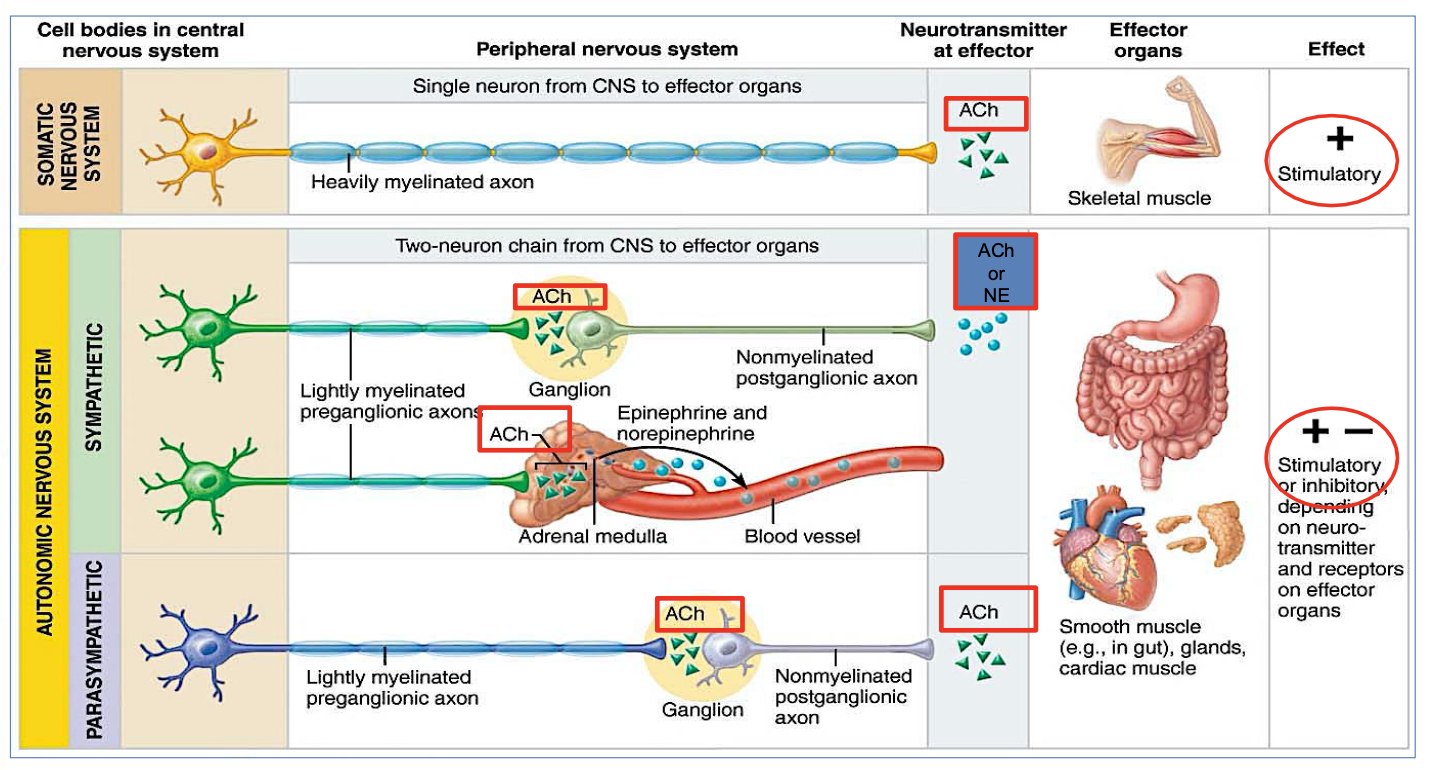
What effect does the Parasympathetic system usually have?
Inhibitory
→ generally promotes relaxation, slows heart rate, and increases digestive processes.
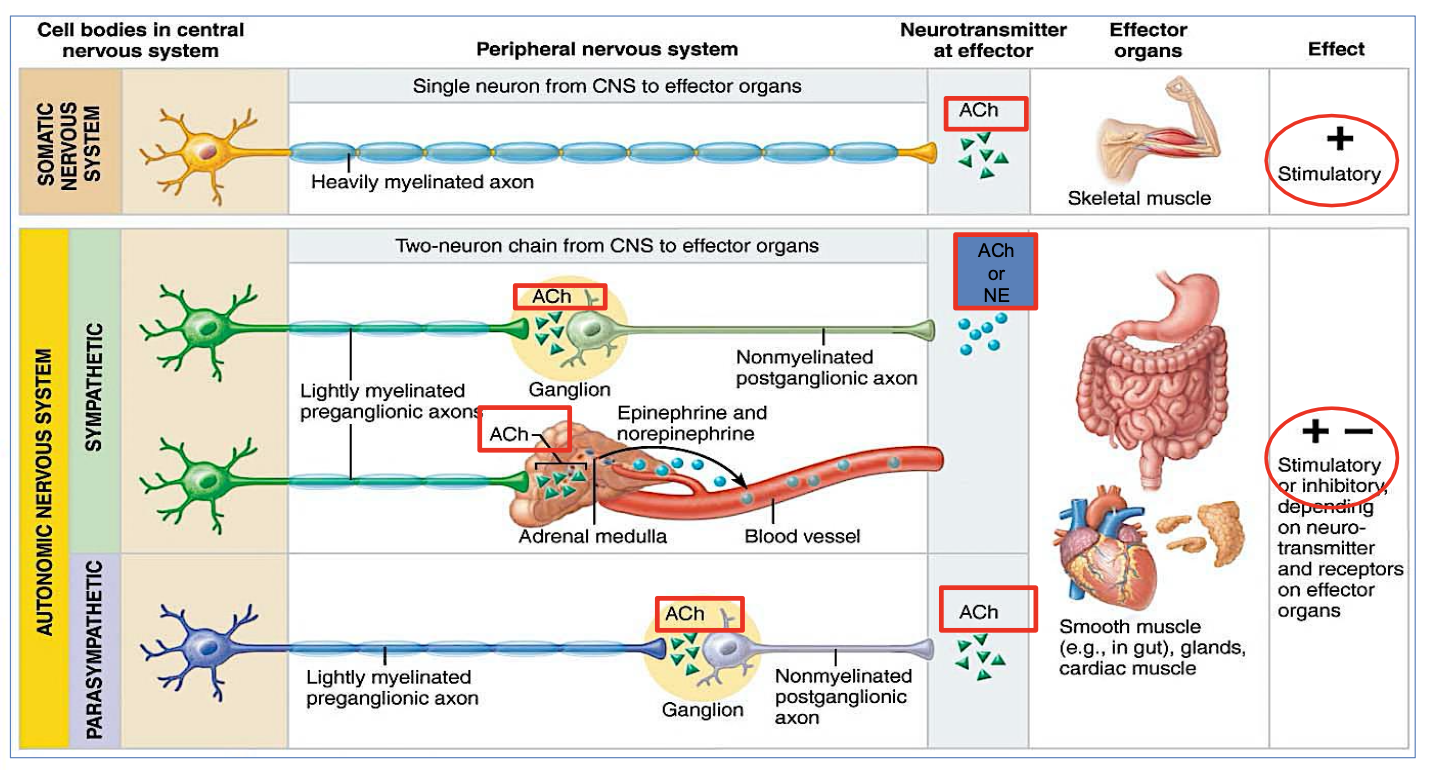
What are the Preganglionic & Postganglionic Neurotransmitters of the Sympathetic nervous system?
Pre-ganglionic : ACh
Postganglionic: ACh or NE
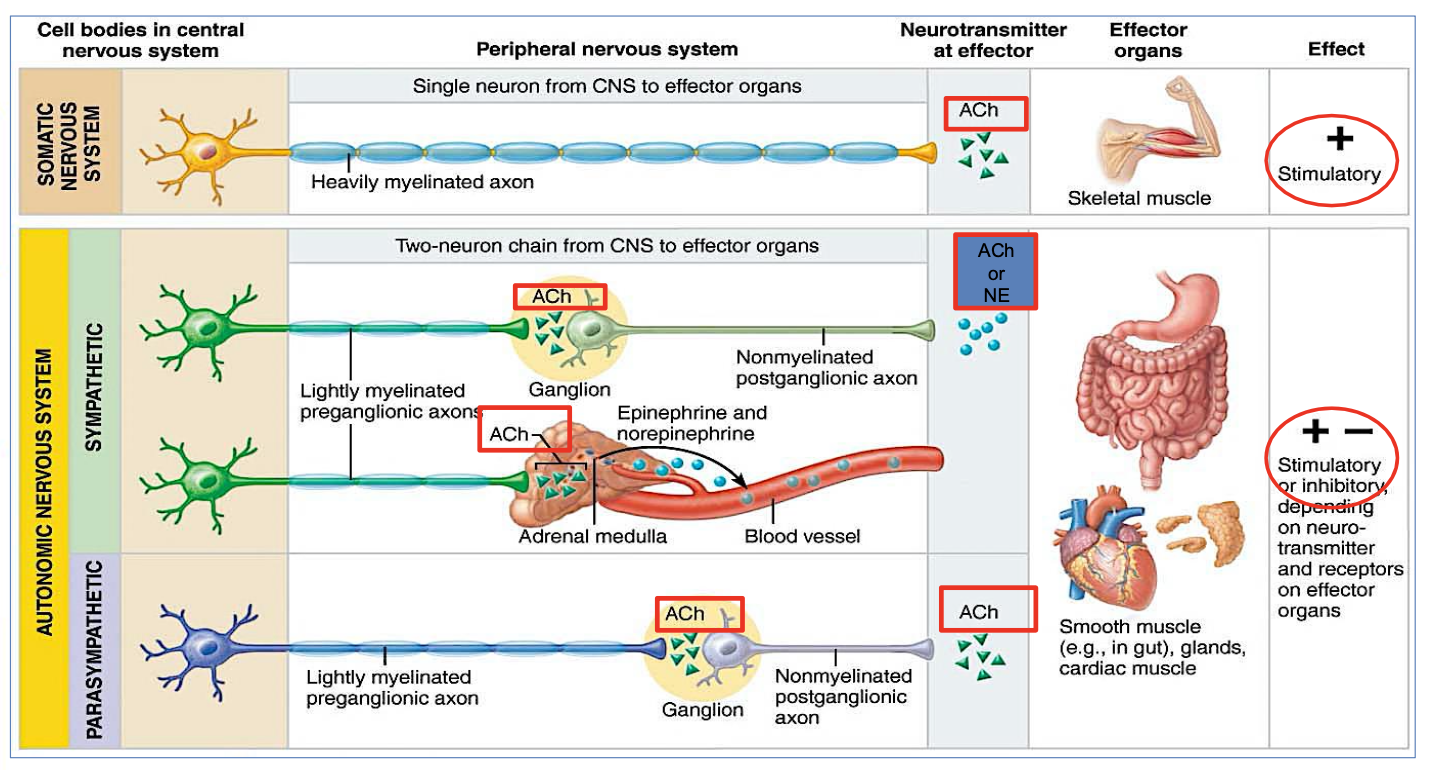
What are the Preganglionic & Postganglionic Neurotransmitters of the Parasympathetic nervous system?
Preganglionic : ACh
Postganglionic: ACh
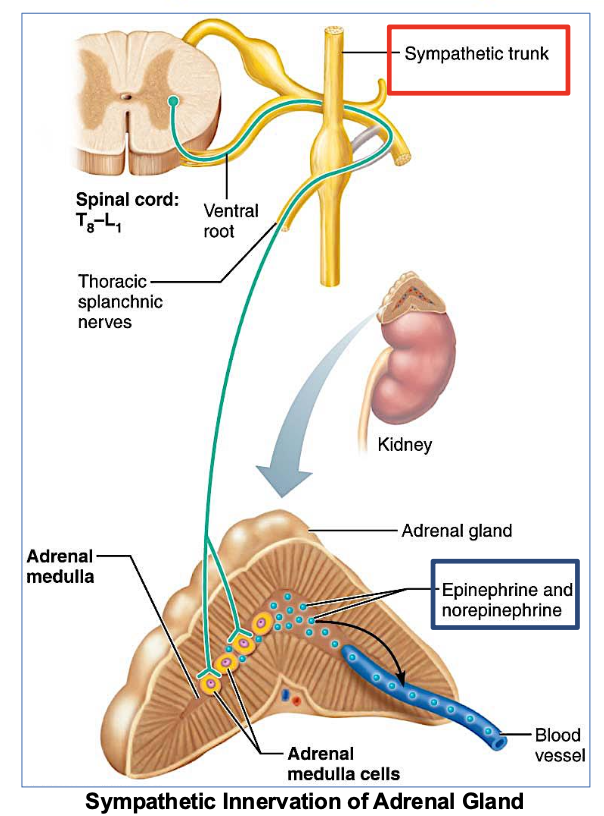
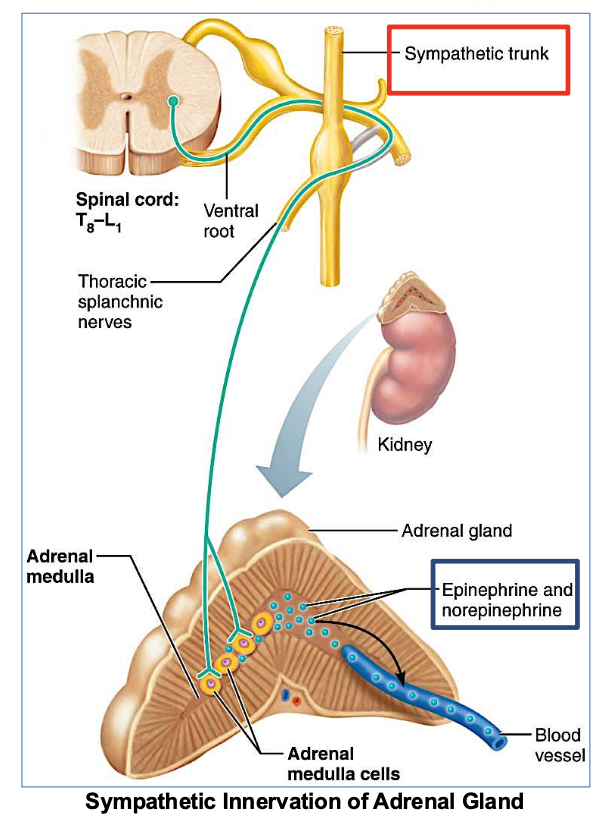
Where is the Adrenal Gland?
Located on top of each kidney
responsible for producing hormones like adrenaline and cortisol.
In which ANS division is the Adrenal Gland located?
in the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, playing a key role in the body's fight-or-flight response.
Which NS does the adrenal medulla receive stimulation from?
from the sympathetic nervous system only
→ specifically from preganglionic sympathetic fibers.
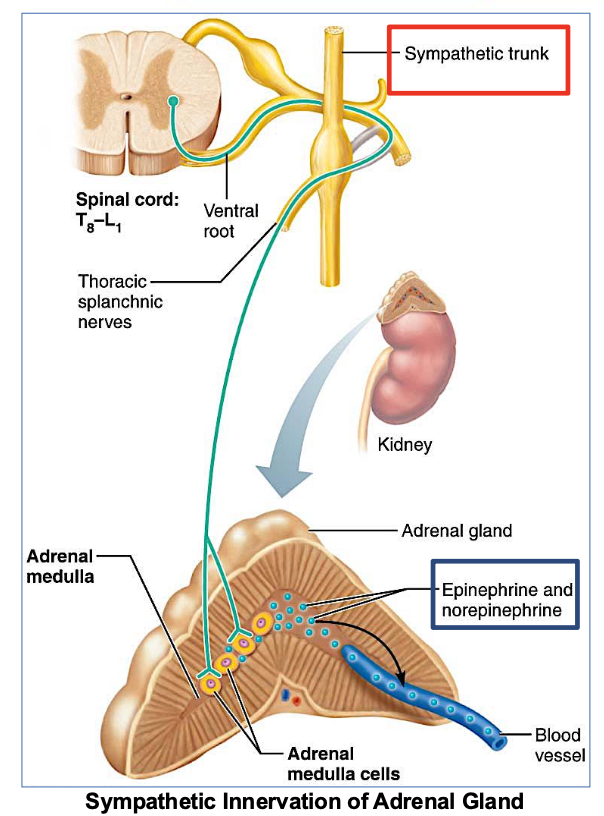
What does the Adrenal medulla secrete when stimulated?
(2 answers)
It secretes adrenaline
(NE) norepinephrine
& epinephrine
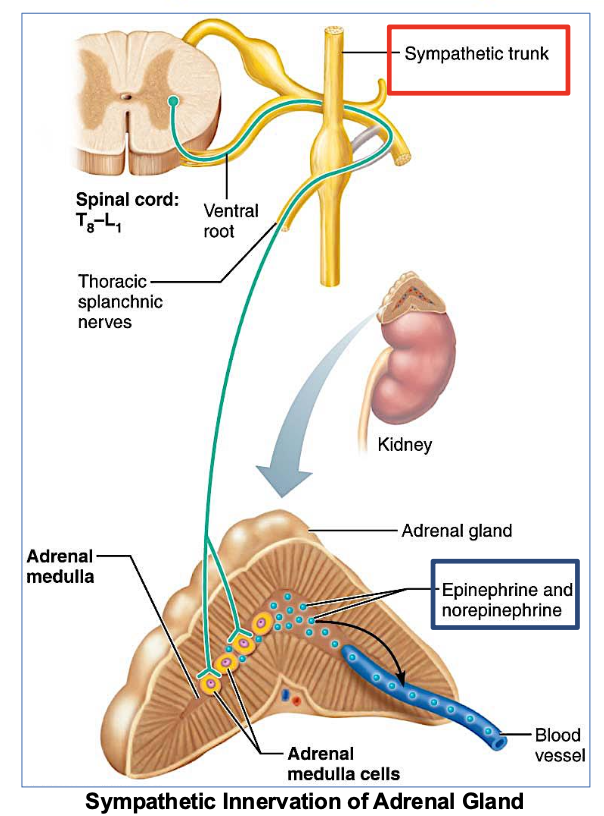
Functions of adrenal medulla and sympathetic nervous system are ____.
different/similar
similar
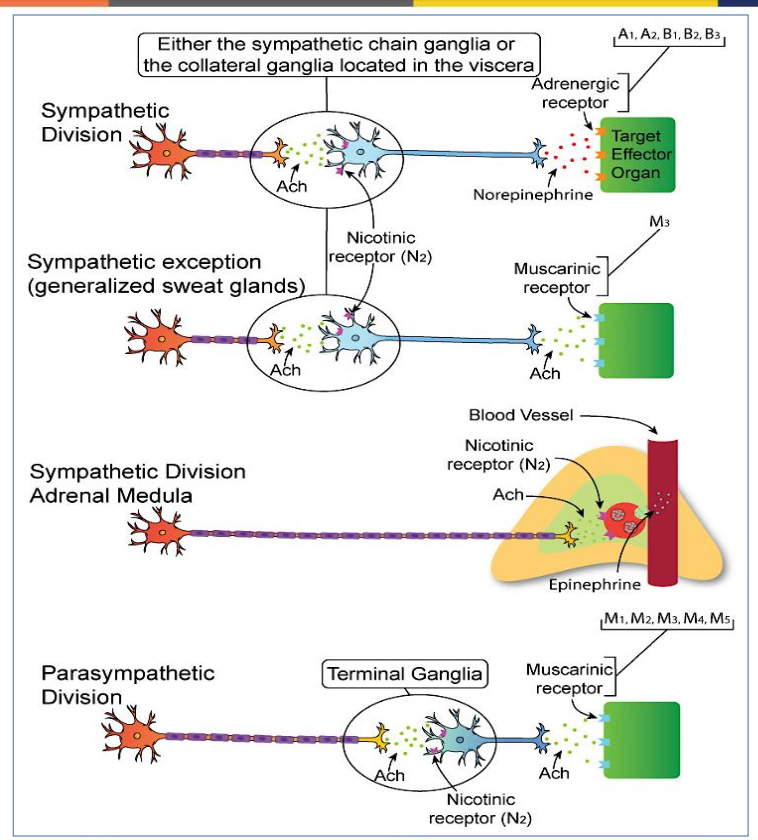
What are neurons that secrete specifically Acetylcholine called?
Cholinergic neurons
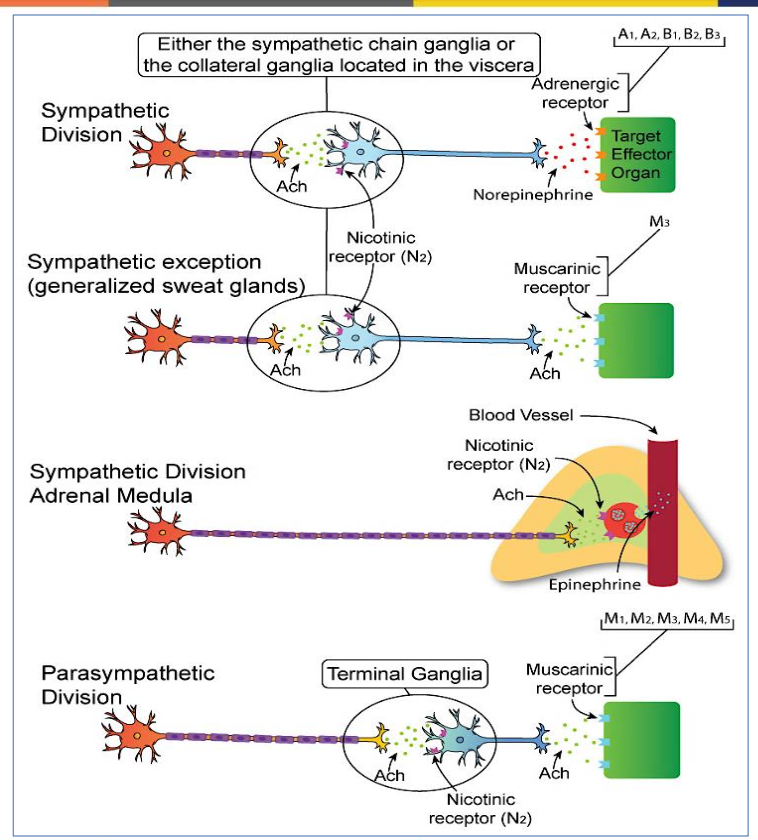
What are neurons that secrete Norepinephrine (adrenaline) called?
Adrenergic neurons
What are the two types of Cholinergic receptors & what do they do?
Muscarinic and Nicotinic, which are activated by acetylcholine.
(Neurons that secrete Acetylcholine are called cholinergic)

What are the two types of adrenergic receptors?
Alpha and Beta, which mediate responses to norepinephrine.
(it means they are activated by norepinephrine- a neurotransmitter)
→ (Also, Neurons that secrete Norepinephrine (adrenaline) are called adrenergic)
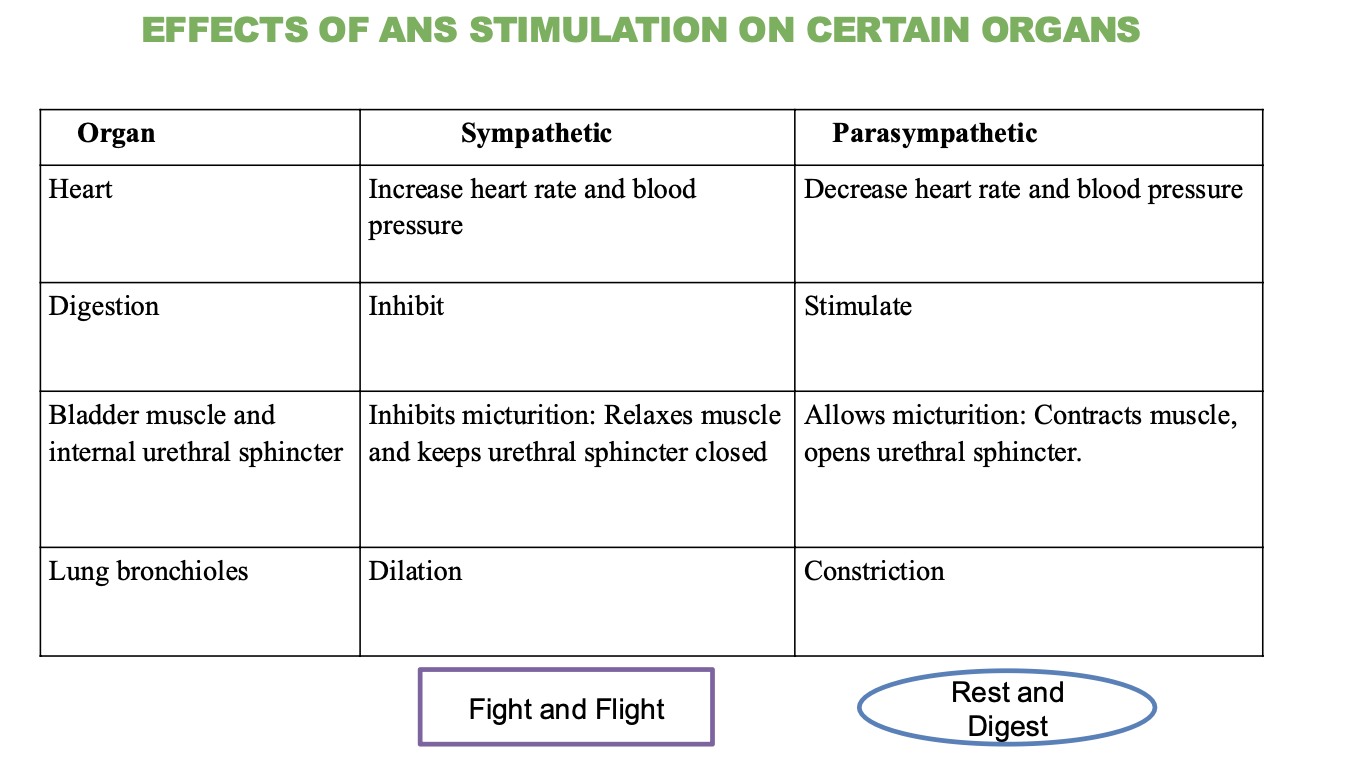
What is the effect of the sympathetic nervous system on the heart?
Increases heart rate and blood pressure
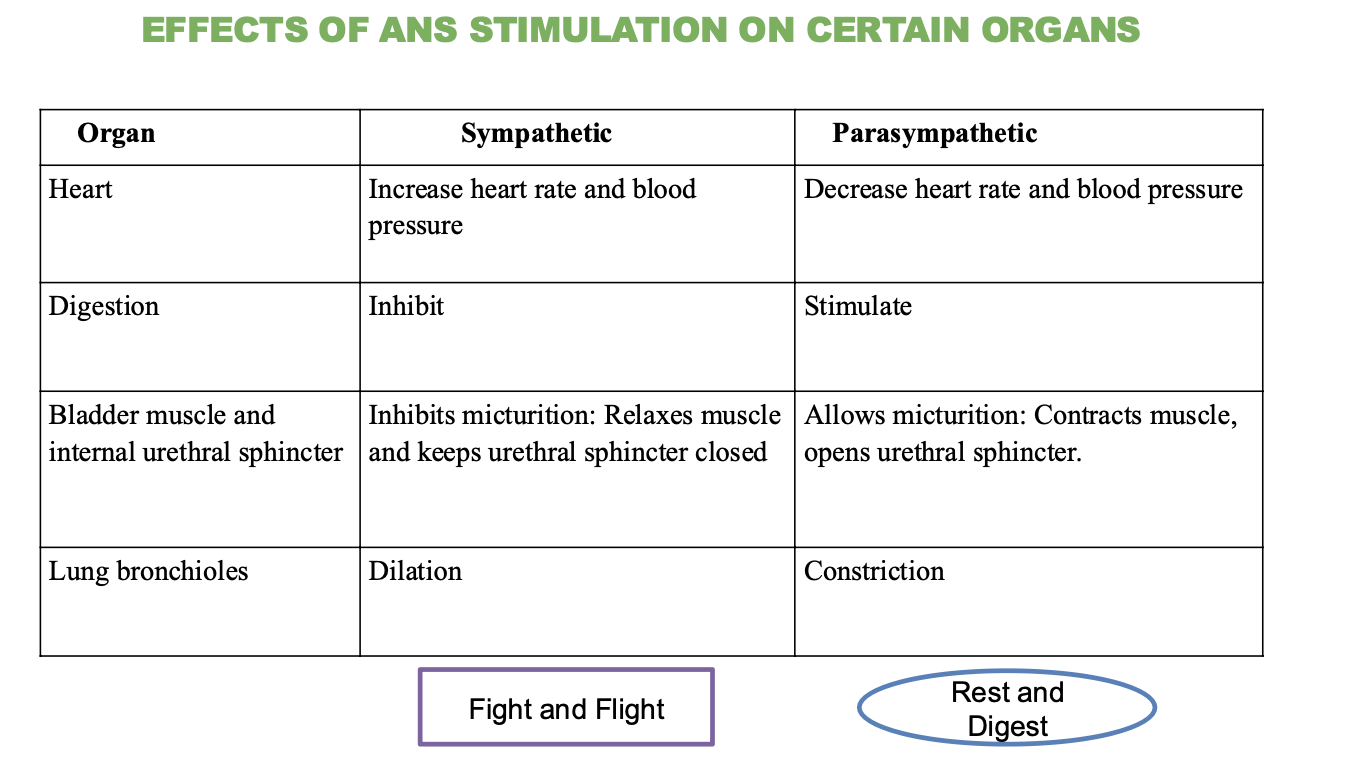
What is the effect of the parasympathetic nervous system on the heart?
decreases heart rate and blood pressure
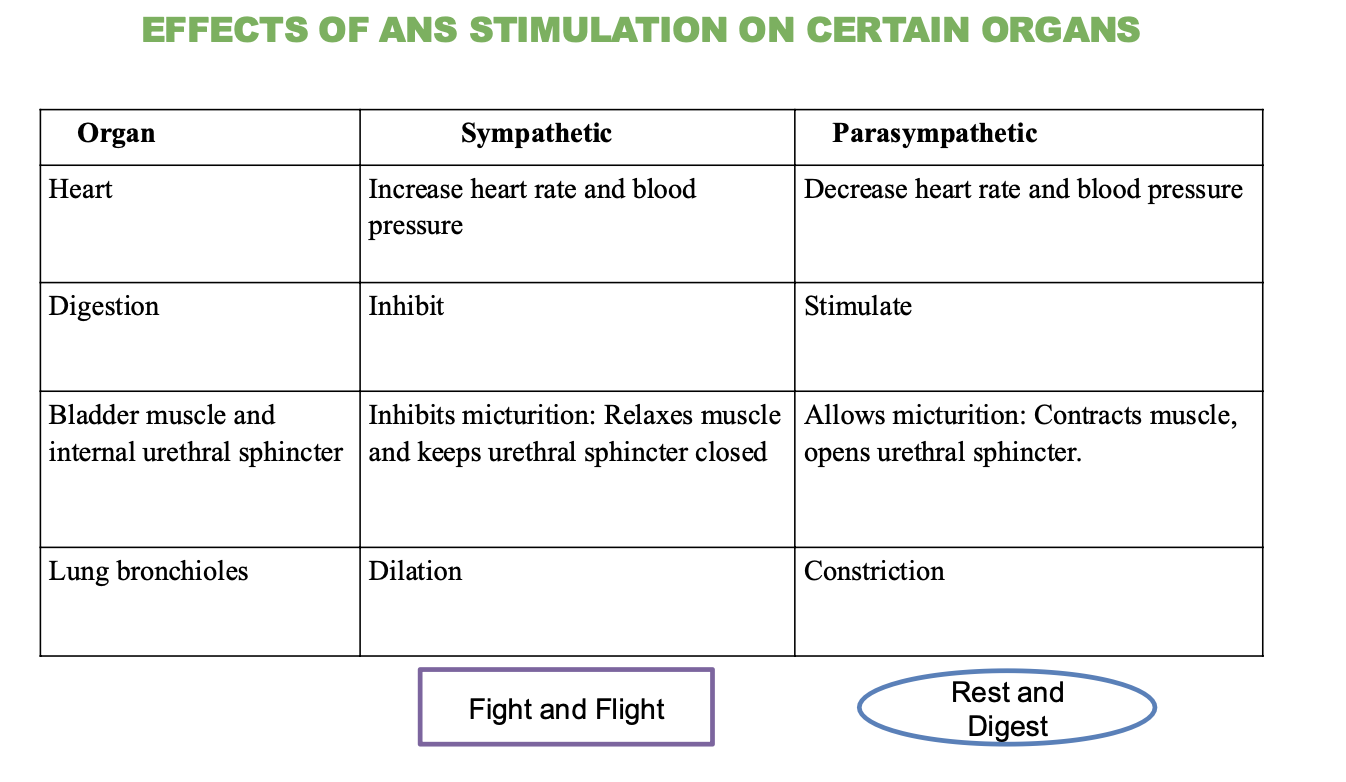
What is the effect of the sympathetic nervous system on digestion?
Inhibits (stops) digestion
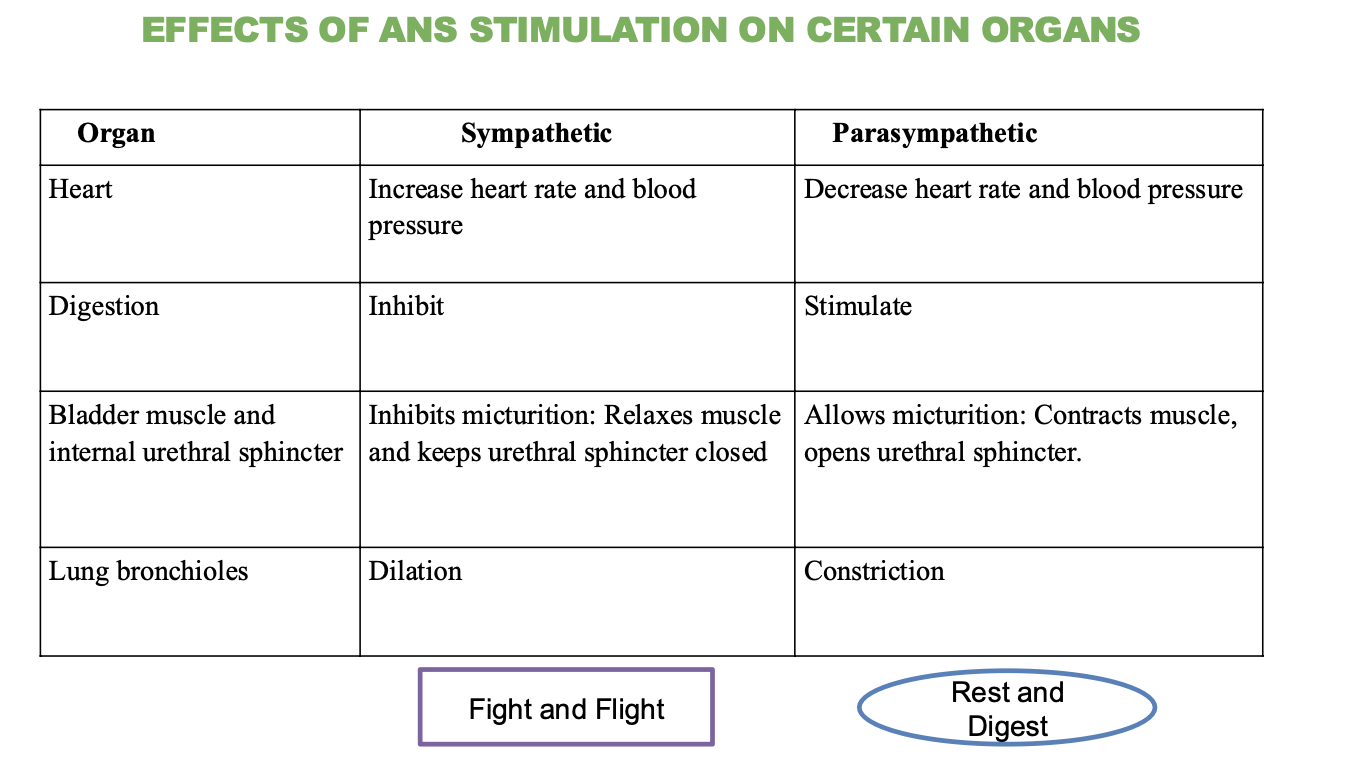
What is the effect of the parasympathetic nervous system on digestion?
Stimulates (promotes) digestion
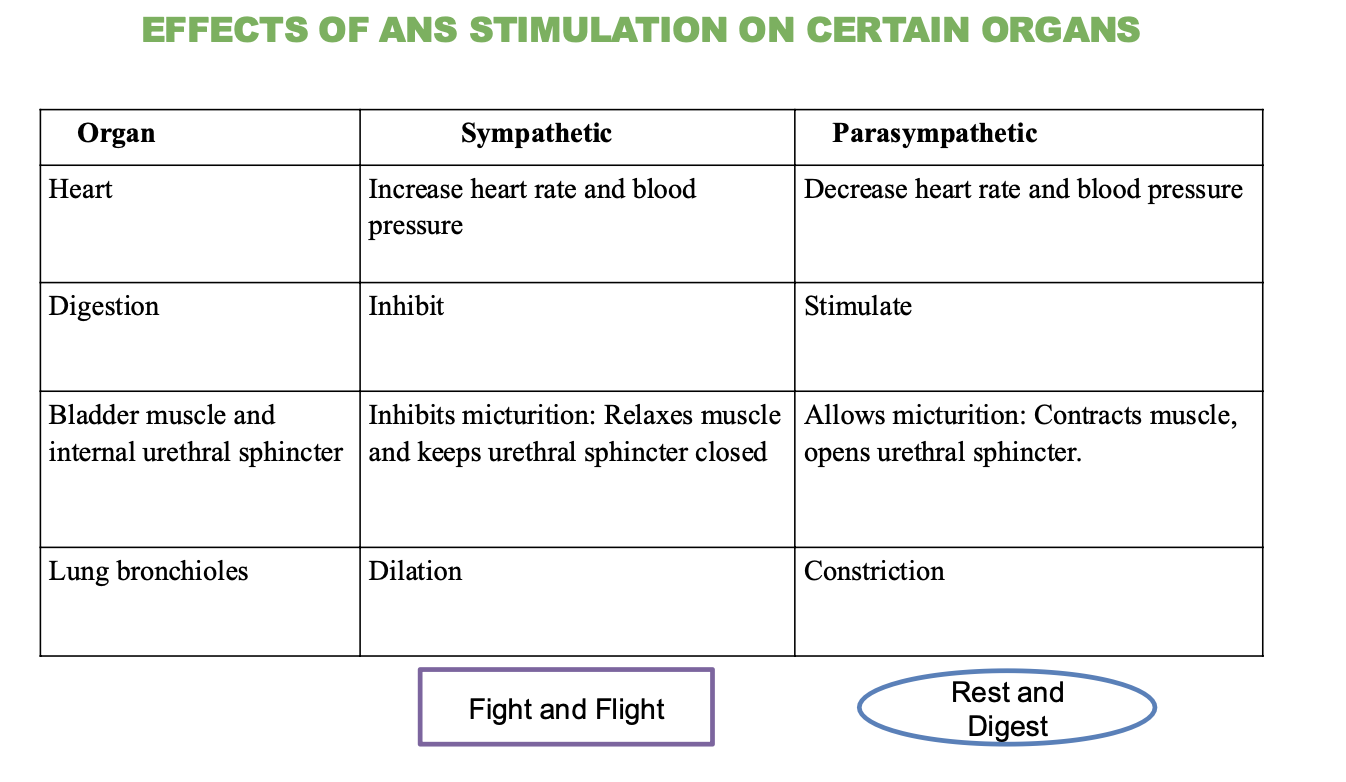
What is the effect of the sympathetic nervous system on the bladder and urethral sphincter?
Inhibits micturition (relaxes muscle and keeps sphincter closed)
→ not worried about using the bathroom
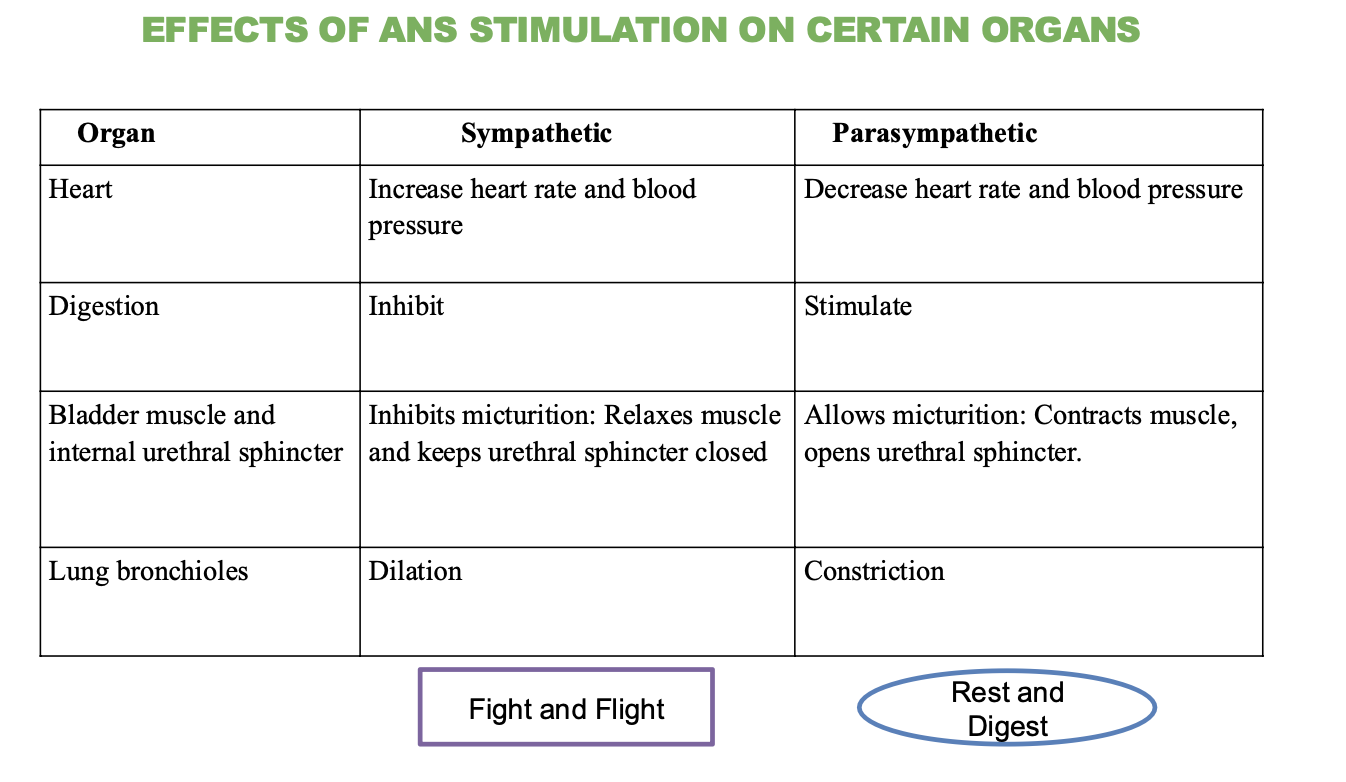
What is the effect of the parasympathetic nervous system on the bladder and urethral sphincter?
Stimulates micturition (contracts muscle and opens sphincter)
→ promotes bathroom usage
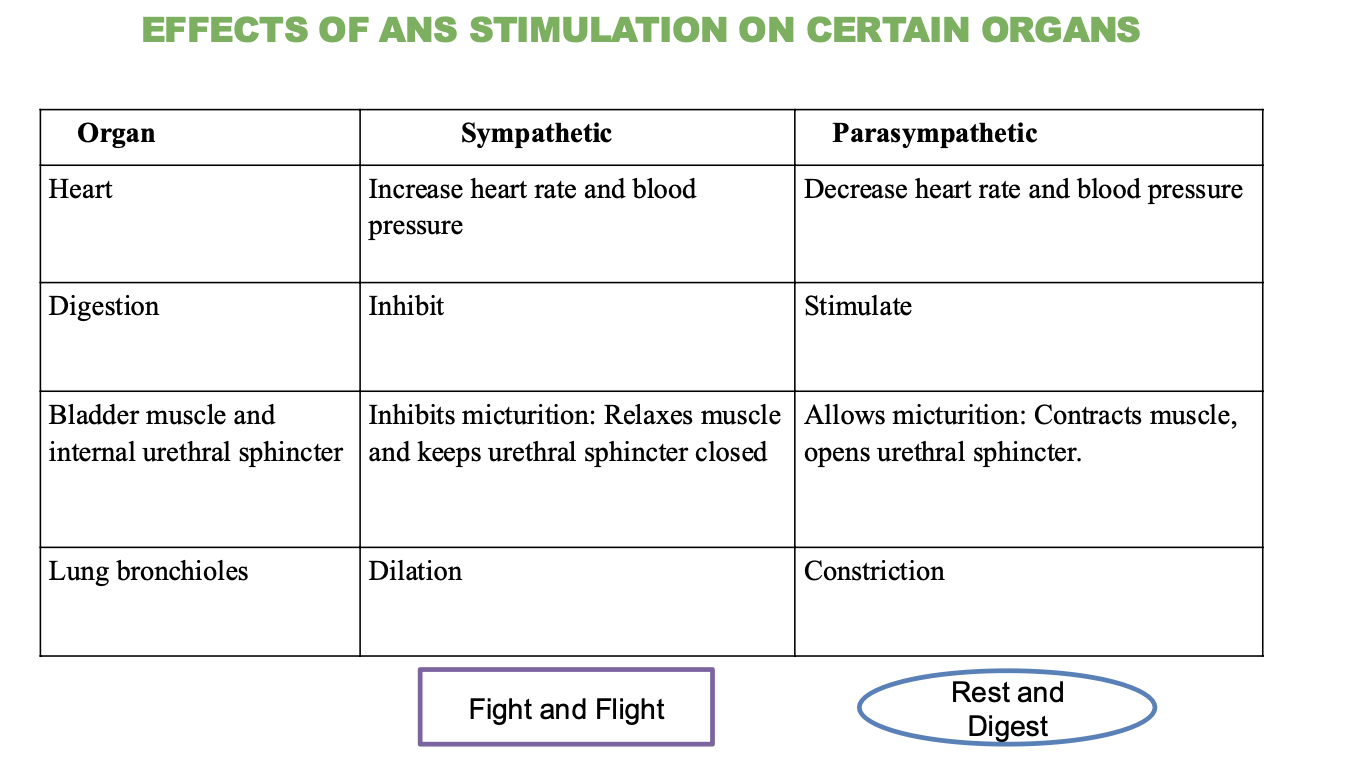
What is the effect of the sympathetic nervous system on the lungs?
Dilation of bronchioles
→ increases airflow and oxygen intake
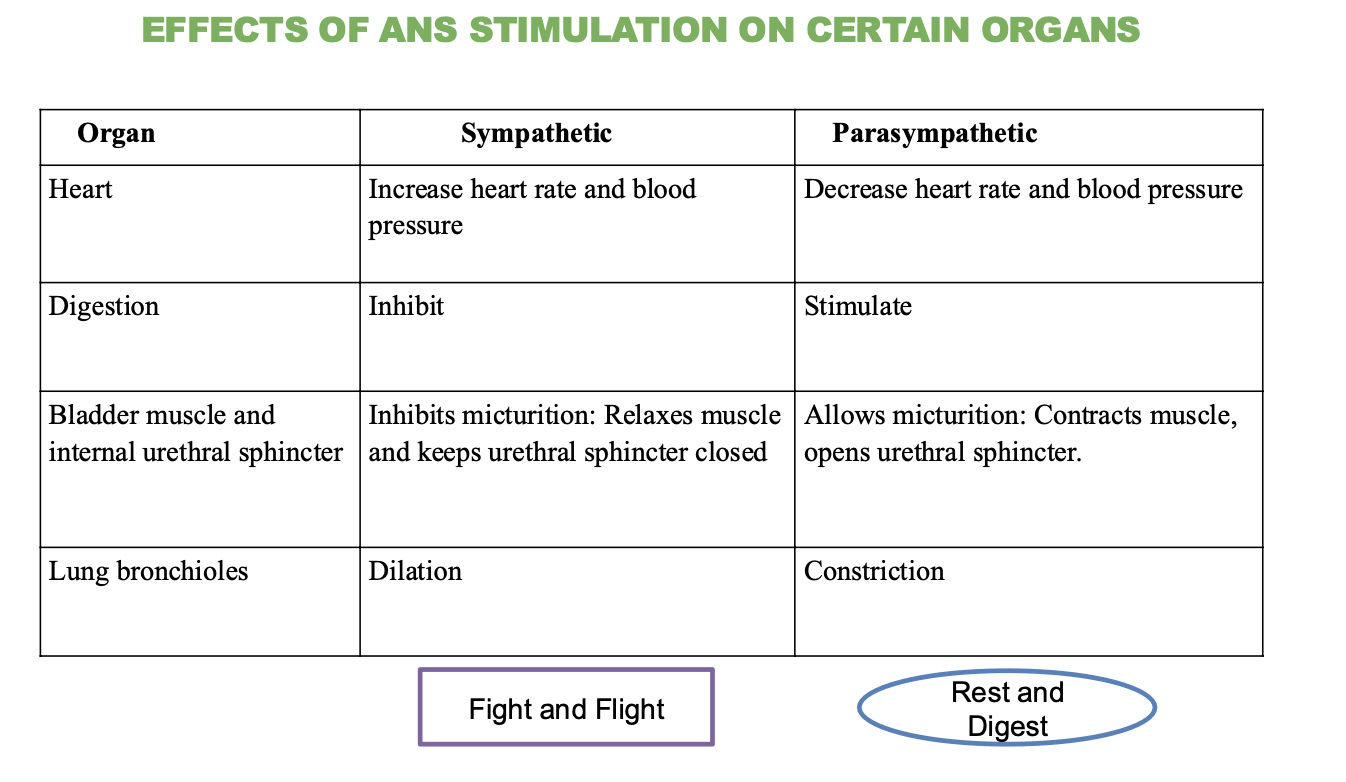
What is the effect of the parasympathetic nervous system on the lungs?
Contraction of bronchioles
→ promotes less airflow and easier breathing during rest.
What effect does the Sympathetic nervous system have on blood vessels?
Vasodilation of blood vessels to skeletal and cardiac muscle and brain
Vasoconstriction of blood vessels in the digestive system and skin
Where does Vasodilation occur in the Sympathetic nervous system & why?
(3 areas)
In skeletal and cardiac muscles and brain
→ to increase blood flow and oxygen delivery during stress or activity.
Where does Vasoconstriction occur in the Sympathetic nervous system & why?
(2 areas)
In the digestive system and skin
→ to redirect blood flow away from less urgent areas and toward muscles and the brain during a "fight or flight" response. It helps the body focus energy where it’s most needed in emergencies.
What is the Autonomic Ganglion?
place where two nerves preganglionic & postganglionic neurons meet in the autonomic nervous system and pass the signal.
helps carry messages from the brain and spinal cord to organs like the heart, stomach, and glands