Neurons and Neural Transmission
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Psychology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is a neuron?
cells of he nervous system that communicate with each other, as well as muscle and gland cells
What is the structure of a neuron?
cell body (soma)
Nucleus
Dendrites
Axon
Myelin sheath
Axon terminal
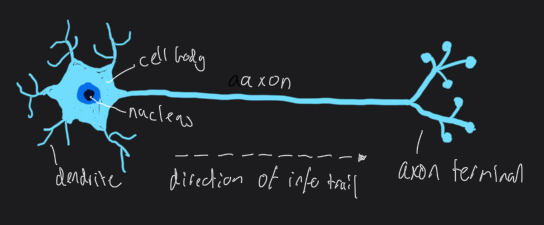
What is the cell body (soma)?
structure containing a nucleus that controls the activities of the neuron
Processes information received by dendrites
What is the dendrites?
extensions of the cell body that receive neurotransmitters from presynaptic neurons and convert them into electrical nerve impulses that are conducted towards the cell body
What is the axon?
long projection of a neuron that conducts electrical nerve impulses and carries them away from the cell body
What is the axon terminals?
enlarged end points of axon branches that store neurotransmitters and release them into the synaptic cleft
What is the myelin sheath?
fatty covering of the axon that acts as an insulator, protecting axon from stimuli that could interfere with electrical nerve impulse transmisson
What is Nerogenises?
The process of growing neurons
What is the process of neurogenesis?
Producing new neurons
the creation of new neurons from neural stem cells
Growing new branches
development of new dendrites or axon terminal branches
Establishing connections
forming connections between existing neurons to create neural circuits
What are the three main types of neurons?
Sensory
Motor
Interneurons
What do sensory neurons do?
process sensory information from the sense organs and carry the sensory messages to the spinal cord and brain (CNS)
Carry nerve impulses from receptor to CNS
Have long dendrites, and short axons
What do motor neurons do?
carry motor messages from the spinal cord and brain (CNS) to the muscles, glands and organs of the body.
carry nerve impulses from CNS to an effector gland (muscle or gland)
Short dendrites and long axons
What do interneurons do?
Act as a connection between sensory and motor neurons.
They transfer messages from the sensory neurons to motor neurons within the CNS
found completely in CNS
Provide link writhing CNS between sensory and motor neurons
Short dendrites, long or short axons
What are the three types of neurons (according to structure)
Unipolar
1 axon
Bipolar
1 axon, 1 dendrites
Multipolar
multiple dendrites and a single axon
Process of Neural Transmission (long)
Neurotransmitters within Nervous System that as as chemical messengers, allowing neurons to communicate info
Neurotransmitters DO NOT travel through the entire neuron. Only located in the Synapse
Electrical nerve impulses travels on only one direction, from dendrites to the cell body, where it is converted into an action potential
Action potential rapidly continues down the axon to axon terminals
Upon reaching axon terminals, triggers release of neurotransmitters into synaptic cleft, and attach to receptor sites on dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron
Dendrites then convert neurotransmitters into electrical nerve impulses that travels to cell body
What are neurotransmitters?
molecules found within the NS that act as chemical messengers
What is the synapse?
segment comprised of the action terminal of a presynaptic neuron, the synaptic cleft and the dendrites of a postsynaptic neuron
What is a presynaptic neuron?
neuron that transmits a signal into the synapse
What is the synaptic cleft?
space between 2 neurons
What is a postsynaptic neuron?
neuron that receives a signal from the synapse
What is an action potential?
electrical impulse that travels along the axon of neurons towards the axon terminals where it causes the release if neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft
What is an electrochemical signal?
The combination of electrical nerve impulses and neurotransmitters found within and between neurons
Process of Neurotransmission (simple)
NEUROTRANSMISSION IF AN ELECTRO-CHEMICAL PROCESS
Electrical nerve impulses (action potential) travel to the axon terminal in the presynaptic neuron
Action potential triggers neurotransmitter release from vesicles in the axon terminal
Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft
Neurotransmitters bind to receptor sites on the dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron
Dendrites converts neurotransmitters into electrical nerve impulses which travel to the cell body
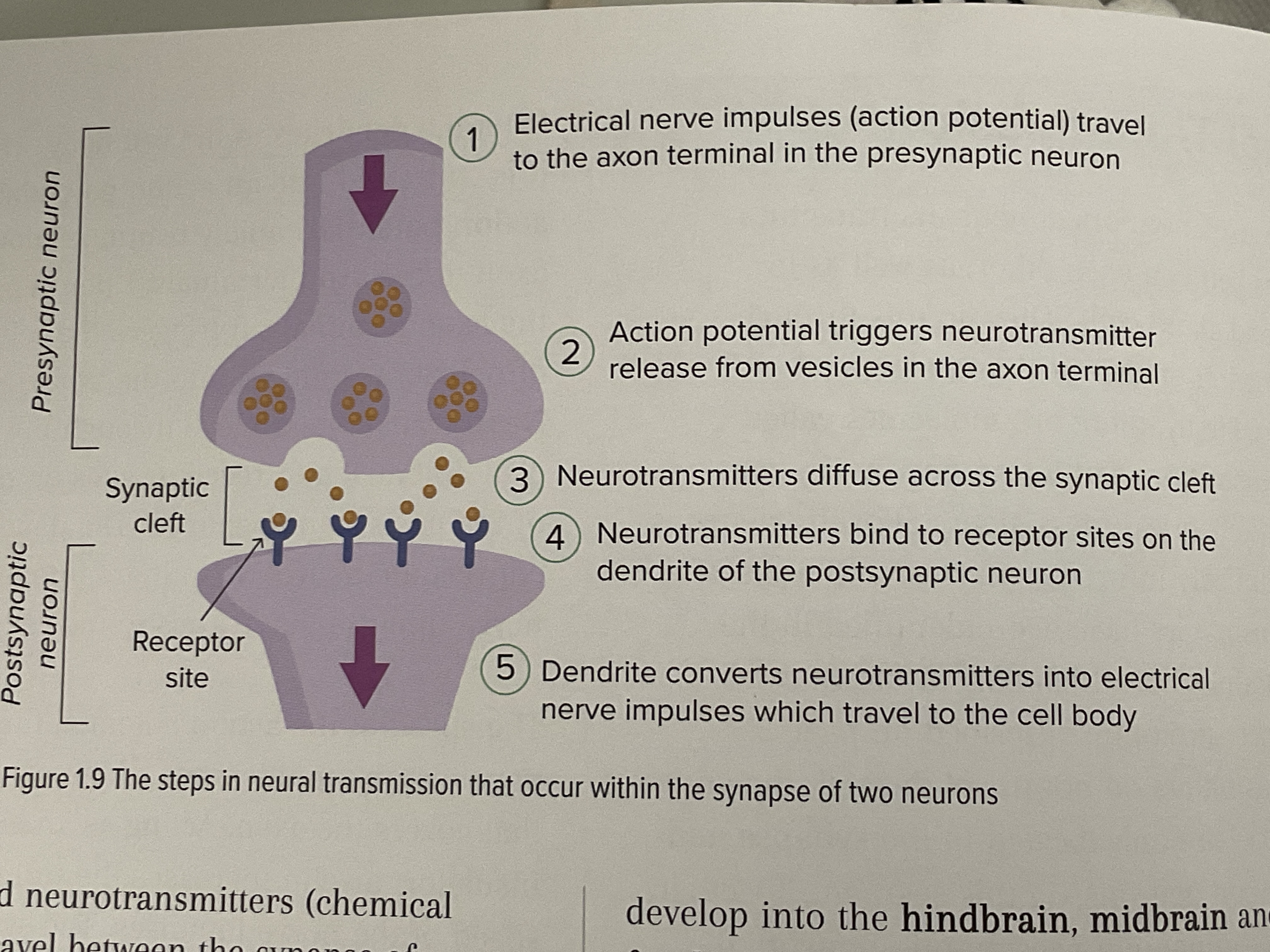
How are neural impulses transmitter/ what is the electro-chemical signal?
Resting state
neuron maintains negative charge inside, relative to outside
Depolarisation
stimulus causes sodium channels to open, positive ions flow in
Action potential
if threshold is reached, electrical signal travels down axon
Depolarisation
potassium channels open, restoring negative internal charge
What are receptors?
specialised proteins on postsynaptic neuron that bind to specific neurotransmitters
What happens at the synapse? Stage 1
Axon terminals connect with receptors on neighbouring dendrites
What happens at the synapse? Stage 2
When hit with electrical impulse (action potential), axon terminals of sending neuron release neurotransmitters
What happens at the synapse? Stage 3
Neurotransmitters travel across tiny gap called synapse and attach to receptor sites on target dendrites of receiving neuron
What happens at the synapse? Stage 4
Attached neurotransmitters generate action potential in receiving neuron’s short dendrites (neural impulse has been transmitted)
What happens at the synapse? Stage 5
Most neurotransmitters return to their original axon terminal, a ‘re-uptake’ process
What happens at the synapse? Stage 6
Other neurotransmitters are broken down by enzymes and need to be replenished.
By: -food, excessive sleep
Affected: drugs, toxins, emotional states
What happens at the synapse (simple)
Release
neurotransmitters are released into synaptic gap
Binding
neurotransmitters bind to receptors
Signal
Postsynaptic neuron is excited or inhibited (depending on the emotion etc..)
Removed
excess neurotransmitters are removed
What is he direction of transmission?
Electrical never impulse travels ONE WAY
From dendrites down to axon
Once reached axon terminals, causes release of neurotransmitters
What is the role of the synapse?
allows neural transmission to occur by converting electrical nerve impulses from one neuron into chemical signal and then back into electrical