Egans CH 37 Airway Maintenance, Suction, and Airway Trauma
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary-style flashcards covering suctioning, airway management, placement confirmation, humidification, infection control, and emergency troubleshooting.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Suctioning
Application of negative pressure to airways through a collecting tube.
Upper airway suctioning
Suctioning of the oropharynx (upper airway).
Lower airway suctioning
Suctioning of the trachea and bronchi (airways below the larynx).
Tracheal suctioning through the mouth
Suctioning into the trachea via the mouth; should be avoided due to gagging/reflex irritation.
Coude tip catheter
Suction catheter with a bent tip to facilitate entry, and suction left mainstem bronchus.
Open endotracheal suctioning
Sterile technique with disconnection from the ventilator; one-time-use catheter, must maintain sterile technique.
Closed endotracheal suctioning
Sterile, closed, in-line suction catheter attached to the ventilator circuit; allows reuse and no disconnection from ventilator and therefore O2.
In-line suction catheter
A suction catheter designed to stay in the circuit during suctioning.
Ballard suction catheter
A commonly used closed suction catheter platform.
What is step 1 of Endotracheal Suctioning?
Check the patient for indications for suctioning
When the patient cannot clear secretions (e.g., unconscious, sedated, paralyzed, intubated, trach); indicated by poor airway clearance and abnormal breath sounds.
Relative contraindication for endotracheal suctioning?
High intracranial pressure
There are no absolute contraindications; high ICP is a relative consideration.
Abnormal breath sounds indicating suction
Coarse crackles, rhonchi, or crackles suggesting need for suctioning.
Cough reflex as indicator
A need for suctioning is suggested when the patient should cough but cannot.
What is step 2 of Endotracheal Suctioning?
Assemble and check equipment
Catheter size formula (ID × 3)/2
Estimate proper suction catheter size in French; choose size equal to or smaller than (ID × 3)/2.
Example: 8.0 ETT → 12 Fr catheter
For ID 8.0, catheter size = (8 × 3)/2 = 12 Fr.
What is step 3 of Endotracheal Suctioning?
Hyperoxygenation
Give 100% oxygen before suctioning (30–60 seconds; neonates get 10% more).
Total suction time
Keep suctioning passage time to less than 15 seconds per pass.
Suction pressures (adult)
120–150 mm Hg for adults.
Suction pressures (child)
100–120 mm Hg for children.
Suction pressures (infant)
80–100 mm Hg for infants.
What is step 4 of Endotracheal Suctioning?
Insert catheter
Introduce the suction catheter into the endotracheal tube as part of the procedure.
What is step 5 of Endotracheal Suctioning?
Apply suction / clear catheter
Activate suction while withdrawing to collect secretions; clear catheter as needed.
<15 seconds total suction time
What is step 6 of Endotracheal Suctioning?
Re-oxygenation after the suctioning episode.
What is step 7 of Endotracheal Suctioning?
Monitor patient and assess outcomes
Repeat steps (3–7) as needed.
Tracheostomy suctioning
Similar to endotracheal suctioning but with a shorter, sometimes deeper, catheter; avoid deep suction with an open catheter use the tip of the tracheostomy tube.
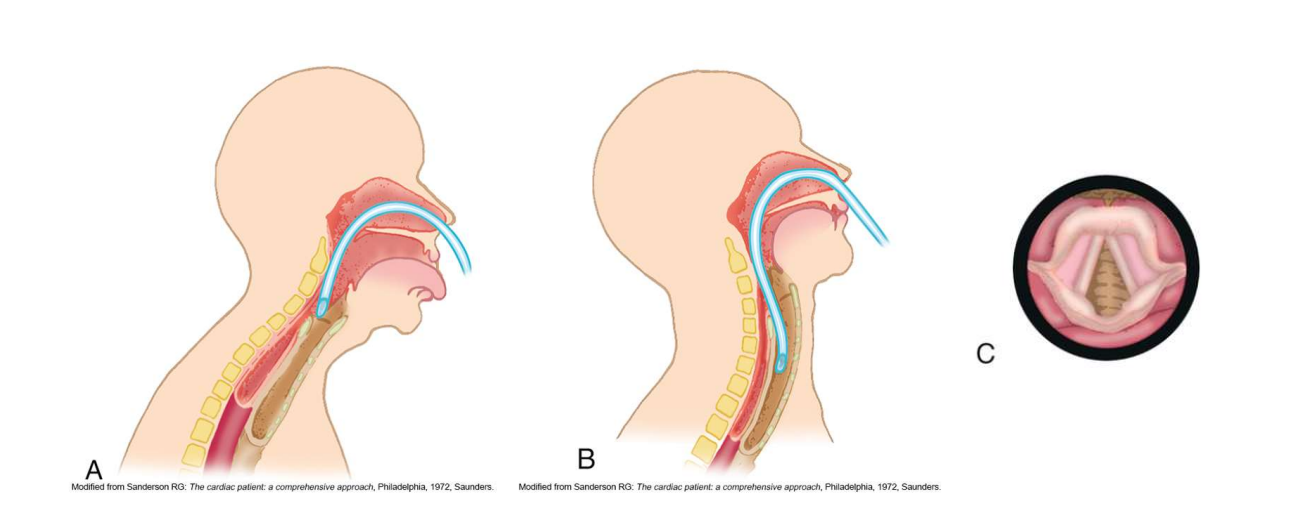
Sniffing position
Position used to facilitate nasotracheal suctioning; head position aids catheter passage.
Nasotracheal suctioning
Suctioning through the nose into the trachea for patients with secretions but no artificial airway.
May cause gagging or regurgitation; avoid after meals
Sputum sampling
Collection of sputum to identify airway organisms; use sterile technique.
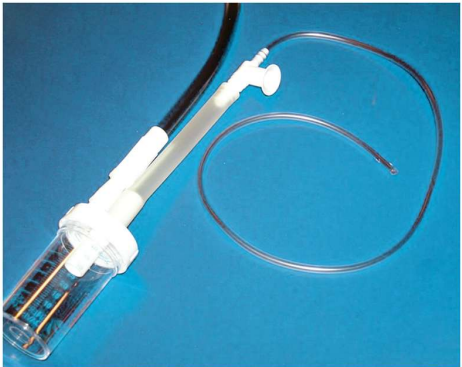
Lukens trap
Sterile collection device used to collect sputum without contaminating the sample.
Sterile technique needs maintained when touching connection points on sterile Lukens trap
Securing the airway
ETT holders (ICU), tape (OR), commercial stabilizers, or cloth ties for tracheostomy to secure the airway.
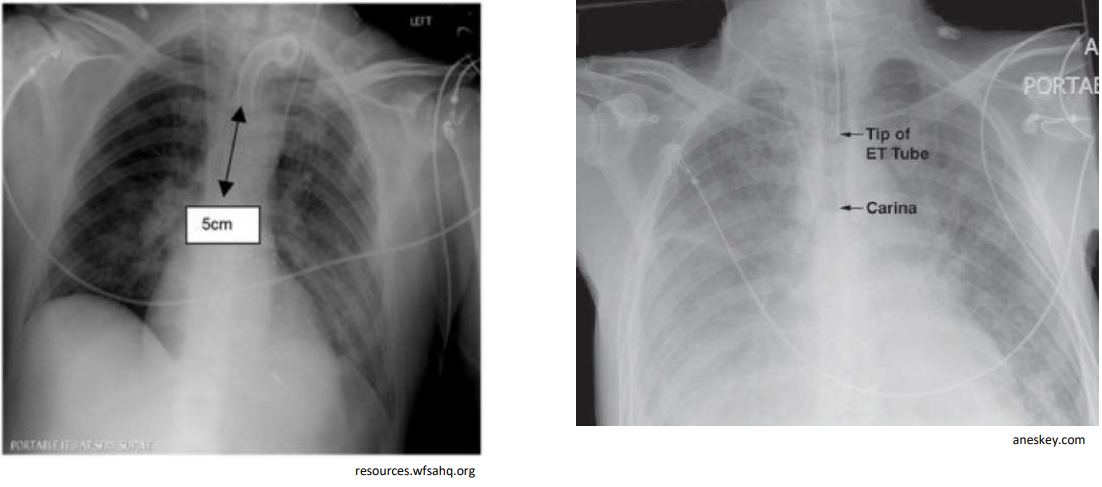
How is proper placement of an ET or Tracheostomy tube confirmed?
Chest X-ray confirmation
Carina distance (ETT tip)
ETT tip should be 3–5 cm above the carina in adults, or between the second and fourth tracheal rings
Humidification
Artificial tracheal airways bypass upper airway humidification, filtration, and heating; device choice based on needs, assessment of airway, and volume and thickness of secretions/history of mucous plugging or tube occlusions of the pt.
Nosocomial infections
Pts. w/ ETT/Tracheal airways are susceptible to bacterial colonization and infection of lower respiratory tract
Risk of lower respiratory infection; emphasize hand hygiene and sterile technique during suctioning, and only aseptically clean/sterile respiratory equipment used for each pt.
Tube obstruction
Blockage of the airway tube; fix by repositioning head/neck or tube; suction as needed.
Kinking or biting tube
Tube obstruction from bending or biting; fixed by moving the pt’s head and neck or repositioning the tube.
Cuff herniation
Cuff protrudes over the tube tip; deflate cuff and/or pass suction catheter through tube if deflating cuff fails; reassess.
Mucus plugging
Obstruction due to mucus; clear with suction if instillation of sterile normal saline is not necessary.
Cuff leaks
Primary problem for pts receiving mechanical ventilation, causing reduction delivery of tidal volume
Leak around the cuff due to pilot/valve issues; may require tube change or ETT exchanger.
Endotracheal tube exchanger
Semirigid guide which damaged tube can be removed and new tube inserted.
Extubation
Process of removing an oral or nasal endotracheal airway.
Decannulation
Process of removing a tracheostomy tube.
Readiness for extubation/decannulation
OG problem is not present,assessment of secretions (quantity and thickness), upper airway patency, presence of gag reflex, and ability to clear secretions before removal.
What type of endotracheal suctioning is useful on high levels of PEEP?
Closed endotracheal suctioning
How do you minimize complications and adverse responses while suctioning?
Pre-oxygenation reduces inccidence of hypoxemia
Limit the amount of negative pressure used
Keep the time of suctioning duration low
Use appropriate size suction catheter
Avoid disconnection from ventilator
Use sterile technique during suctioning and manually ventilate pt. to minimize bacterial colonization
Don’t routinely instill sterile normal saline into artificial airway prior to suctioning unless needed to mobilize thick secretions
What do you do if secretions are thick and difficult to suction?
Ensure suction pressure in right range
Increase to maximum size suction catheter (not going over)
Increase suction pressure (not exceeding range)
Increase suction time
May also need to check canister of sputum, if too full will not suction properly
What is this picture of nasotracheal suctioning showing?
Sniffing position
What is this picture of sputum sampline showing?
Lukens trap
What type of tubes are these on the chest x-ray?
Left: Tracheostomy tube
Right: Endotracheal tube