spinal cord - part 4 (medical management, PT exam, strategies, motor levels)
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
stabilize spine, prevent complications
specialized medical management is a must; what are two goals for this?
accident
medical management:
- pre-hospital care
- starts at ___ site (stabilize spin and precent additional damage; emergency management)
neurological, immobilize, care
medical management - emergency management at accident site:
- enhance survival and ___ integrity
- ventilation
- circulation
- ___ spine (head to below buttocks)
- transport to acute ___
neurological, spine, ventilation, hemorrhaging, hypotension, ventilation
medical management - acute care:
- treatment to life threatening conditions
- preserve ___ function
- avoid motion to ___
- ___, oxygenation and circulation
- control ___
- cardiac: treat arrhythmias or ___
- respiration: ABG, intubation, ___
survival, neurological
medical management -
- goal is to enhance ___ and prevent any additional ___ damage
cognitive, sensation, voluntary, radiologic
medical management - neuro exam/assessment:
- ___ exam (level of consciousness, CN function, rule out head injury)
- ___
- ___ motion
- reflexes
- ___ tests (assess SC damage, standard xrays - lateral, AP, flex-ext and open mouth odontoid view, CT scans, MRI)
consciousness, cranial, head
cognitive exam:
- level of ___
- ___ nerve function
- rule out ___ injury
history, urinary, 8, 48
medical management - neurological exam:
- medical ___
- GI
- ___
- evaluate and treat associated injuries
- methylprednisolone (standard practice of care, given ___-___hours post injury)
methylprednisolone
what is the standard practice of care to be given 8-48 hours post injury?
reduction, immobilization
fracture management - ___ and ___ of SCI can be achieved via conservative or operative methods
neurological, alignment, spine, impingement, positioning
fracture management goals:
- minimize ___ damage
- restore vertebral ___
- stabilize ___
- eliminate ___ on neuronal tissue
- minimize deformity
fracture management:
- traction
- ___
- orthoses
- surgery
subluxation
non surgical management - radiologic exam:
- vertebral angulation or ___
lateral, traction, decompress
immobilization cervical - tongs:
- ___ side of skull
- ___ rope with pulley
- ___ spine
- reduction confirmed with x-ray ... if not surgery
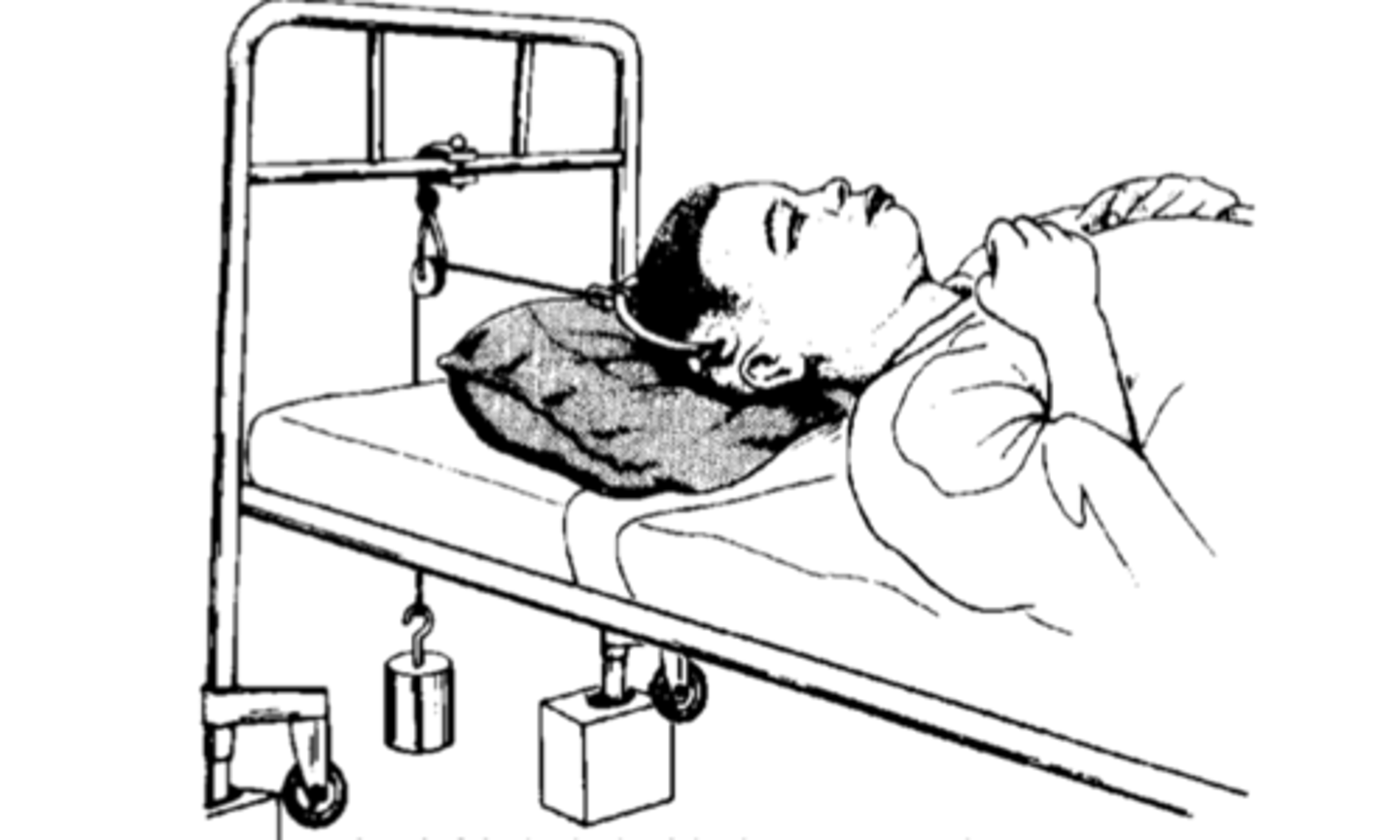
fracture, respiratory, stable
immobilization cervical - halo:
- for cervical ___
- halo ring with 4 steel screws attached to outer skull
- body jacket with 4 vertical posts
- contraindicated with severe ___ involvement
- most ___
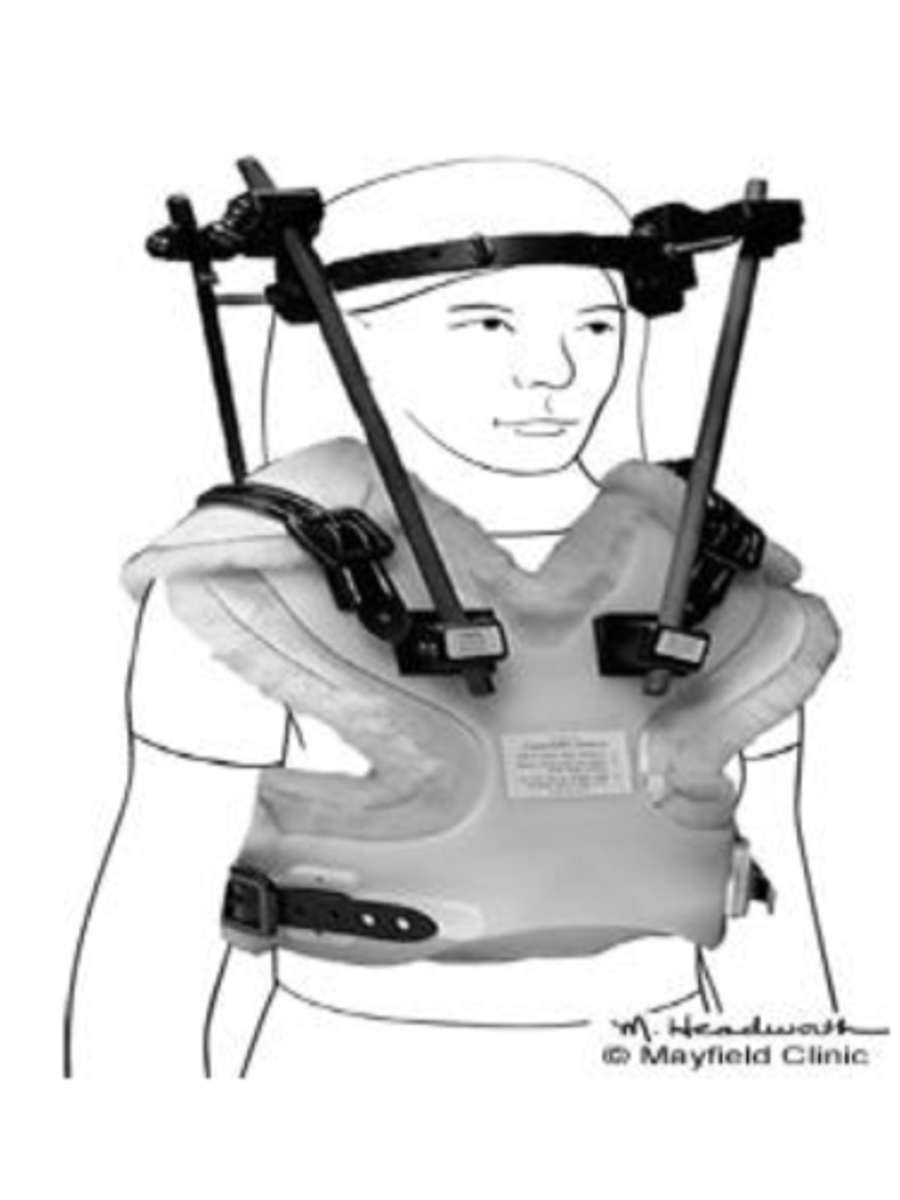

posterior, pelvis, planes
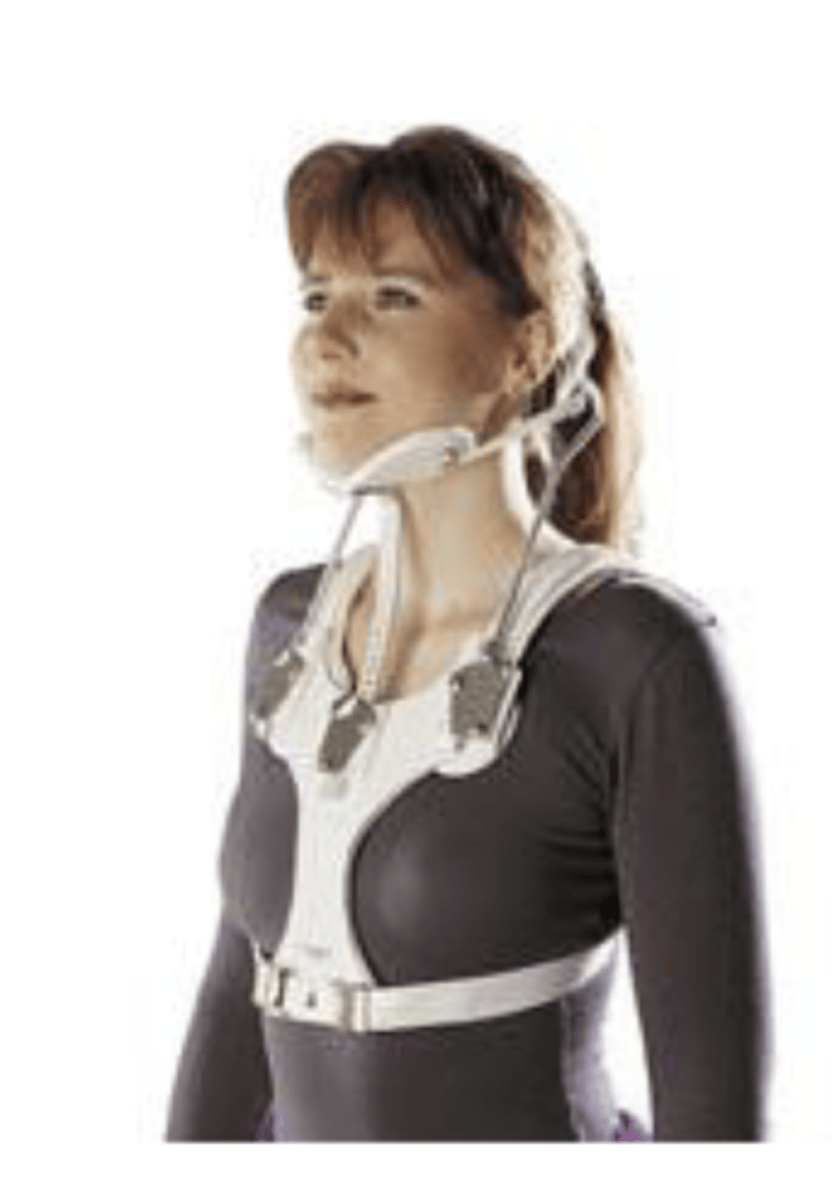
immobilization cervical - minerva body jacket:
- thermoplastic encases chin and ___ aspect of skull
- extends down to ___
- headband around skull
- restricts cervical motion in all ___

cervical motion in all planes
what does the minerva body jacket restrict?
mandibular, flexion
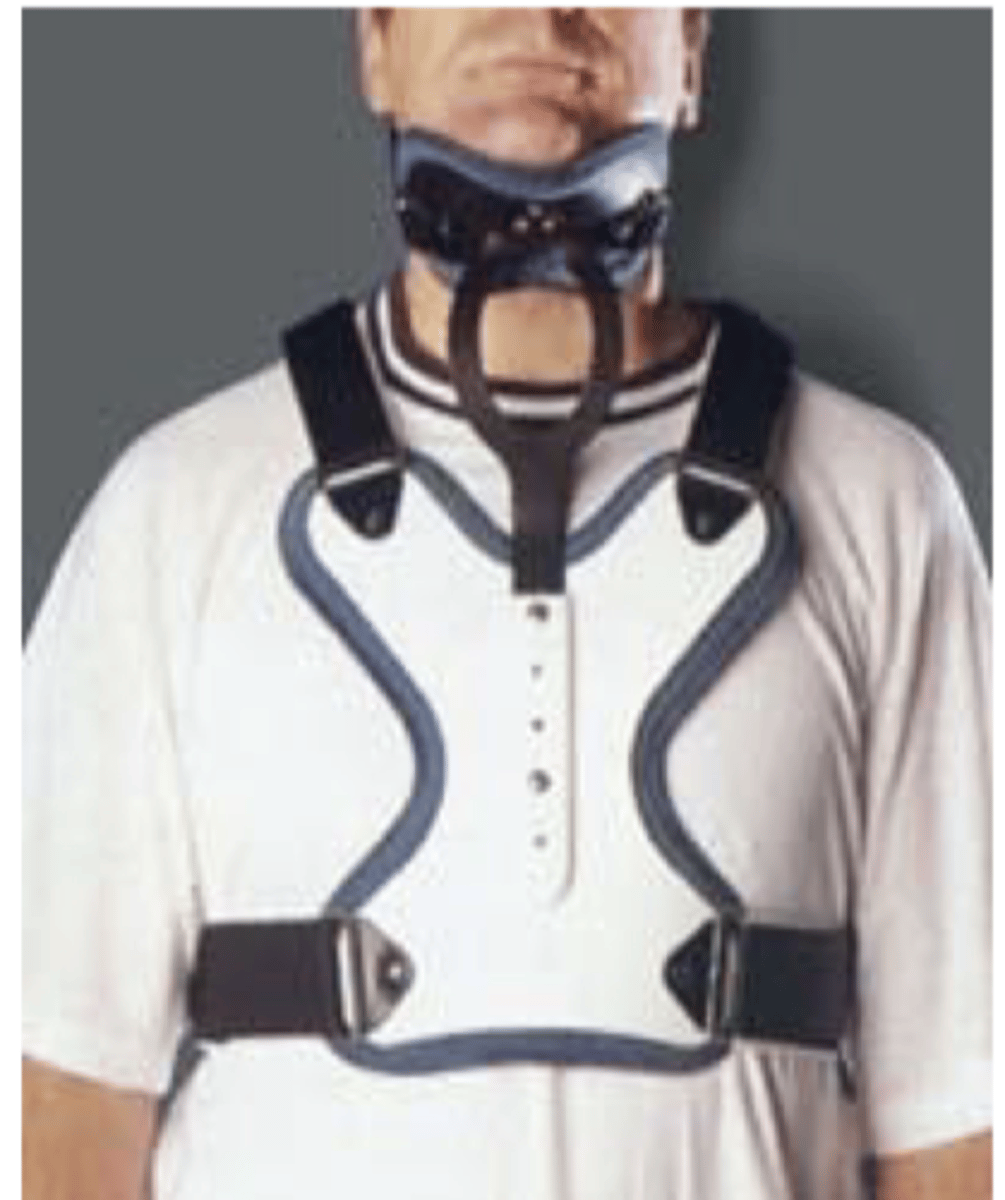
immobilization cervical - somi:
- sterno occipital ___ immobilizer
- padded sternal plate attached to 3 uprights
- most effective restricting ___ at C1 to C5

flexion at C1 to C5
what is the somi most effecting at restricting?
soft, rigid
immobilization cervical - cervical collars:
- ___
- ___: miami J, philadelphia, aspen
alignment, traction, respiratory, obese, coma
immobilization positioning - turning beds/frames:
- stryker
- allow positional changes while maintaining ___
- turn without disruption of ___
- supine or prone
- need to be careful with cardiac or ___ involvement
- unsuitable for ___ or ___ pts
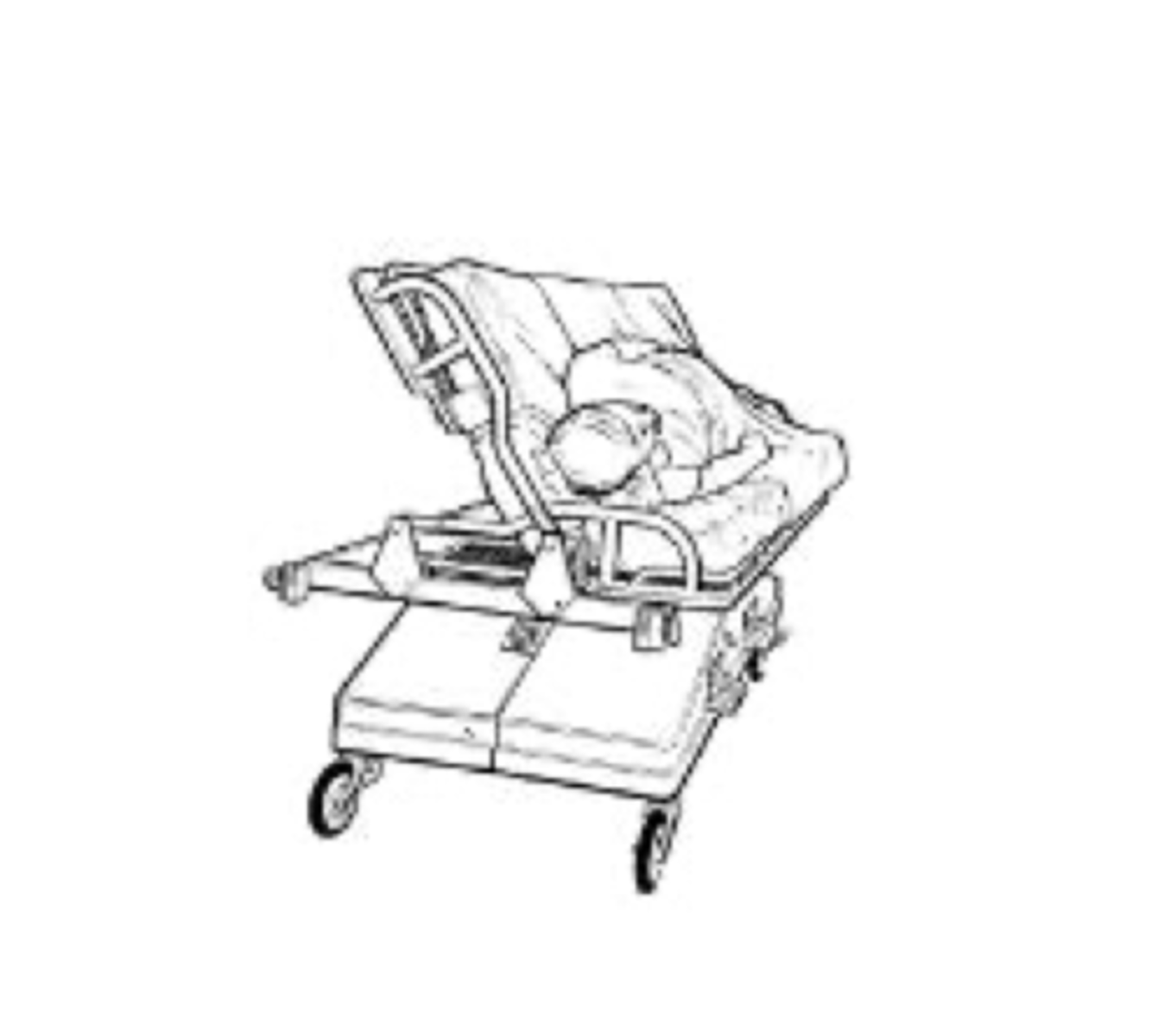
allow positional changes while maintaining alignment
what is the purpose of turning beds/frames?
stability
immobilization - thoracic/lumbar - thoracolumbosacral orthoses (TLSO):
- molded plastic body jacket
- clam shell
- maximum ___ (knight-taylor, jewett - prefabricated metal frame)
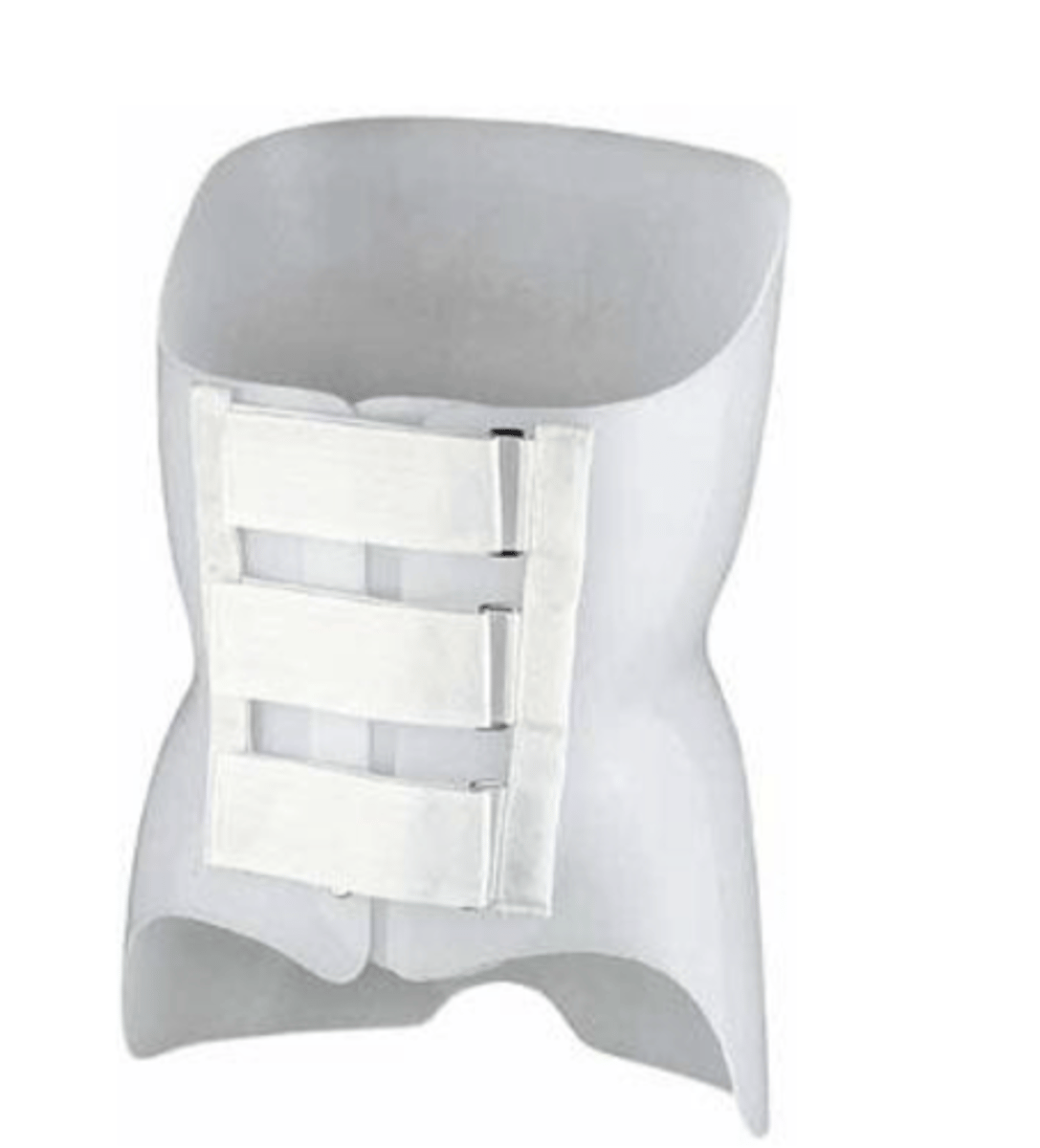
fracture, malalignment, compression, neurological, instability, mobility, facet
surgical management - indications:
- unstable ___ that will not reduce with closed reduction
- gross spinal ___
- evidence of continued cord ___
- deteriorating ___ status
- continued ___ following conservative management
- remove boney fragments in the canal
- remove foreign bodies impinging cord
- assist with earlier ___
- bilateral ___ dislocation
reduction, stabilization, anterior
surgical management-
optimal timing of surgery:
- hours vs days vs weeks
surgery:
- decompression
- ___
- ___ with rod and plates
approaches:
- ___
- posterior
- combination
level, instability, impingement, neurological
surgical approach - factors that affect surgery approach and internal stabilization:
- ___ and type of SCI
- extent of spinal ___
- number of vertebral levels
- location of bone and soft tissue
- ___ of SC
- extent of ___ impairment
- length of time since injury
subjective, goals
PT exam:
- ___ information
- history (document from acute care)
- relevant information
- pts ___ (be specific, know their definition of walking)
information, goals, evaluation
PT examination:
- foundation of PT program
- need thorough and accurate ___
- basis for development of realistic ___ and POC for pt
- ongoing ___ process
level, contraindications, injuries, social
PT exam - history - damage to SCI:
- date of injury
- ___ of injury
- extent of injury
- etiology
- specific ___
- additional ___ sustained
- summary of medical and surgical management
- pre-existing conditions
- ___ issues (need to know about their situation)
potential, functional independence
PT exam - voluntary motor function:
- important factor that affects ultimate ___
- results of MMT predict level of ___ ___
ASIA, control
PPT - MMT:
- ___
- conventional
- motor ___ vs MMT
- maybe limited secondary to mobility and/or surgical precautions
all, function
MMT - standardized MMT:
- test ___ muscles
- do not assume there is no ___ even if they say they have none
function
MMT - ASIA:
- calculate upper and lower limb motor scores
- useful for documenting changes in motor ___
use functioning muscles to perform actions of muscles that are weak or absent
describe substitution
extend, wrist extension, toe extension, abdominals
MMT substitution - use functioning muscle to perform actions of muscles that are weak or absent:
- ___ elbow in absence of tricep
- gross grasp with ___ ___ (tenodesis)
- ankle DF with ___ ___ (can mimic especially if pt has tone)
- hip flexors by ___ or adductors
- need to eliminate motions and carefully palpate muscles for MMT
biceps, ER
what muscles if the UE is fixated can mimic elbow extension if a pt lacks triceps?
absent, weaker
MMT - stabilization:
- muscles used to stabilize during MMT may be weak or ___
- need to accommodate for this or muscle tested may appear ___ than it is (ex- periscapular muscles, trunk/abdominals, quads)
trunk
MMT - ___ is difficult to assess:
- standard tests test entire length of muscle
- sit ups are often contraindicated
abs, T12
position of umbilicus stays central and uniform pull:
- ___ either totally function or are absent
- injury above T5 or below ___
beevors sign, T5, T12
position of umbilicus move cephalad ___ sign:
- muscle pull greater above umbilicus than below
- lesion between ___ and ___
beevors sign
what is it called when the umbilicus moves cephalad? - muscle pull greater above umbilicus than below
muscle pull greater above umbilicus than below
what does beevors sign mean?
injury above T5 or below T12
if the umbilicus stays central and uniform pull, what does this imply about injury?
lesion between T5-T12
if the umbilicus moves cephalad, what does this imply about injury?
voluntary, reflexive, synergistic, factors, ashworth
PT exam - tone:
- distinguish between ___ and not
- ___ movement
- associative motions
- quality
- muscle groups
- ___ patterns
- positions
- ___ that influence tone (ex- noxious stimuli inc)
- modified ___ to measue
0
modified ashworth - no increase in muscle tone
1
modified ashworth - slight increase in muscle tone, manifested by a catch and release or by minimal resistance at the end of the range of motion when the affected part(s) is moved in flexion or extension
1+
modified ashworth - slight increase in muscle tone, manifested by a catch, followed by minimal resistance throughout the remainder (less than half of the ROM)
2
modified ashworth - more marked increase in muscle tone through most of the ROM, but affected part(s) easily moved
3
modified ashworth - considerable increase in muscle tone; passive movement difficult
4
modified ashworth - affected part(s) rigid in flexion or extension
functional, contractures, skin, severity, noxious
PT exam - muscle tone:
- positive or negative (how is ___ movement affected?, pain, ___, ___ breakdown)
- constant or fluctuating
- ___
- provides info re medical status (___ stimuli may inc tone)
proprioception, neurological
PT exam:
- ___
- sensation
- directly affected by a SCI
- reflection of ___ status
pinprick, light, deep, pain
PT exam - sensation - reflection of neurological status:
- improvement or deterioration evident by change in sensation
- ___ (important bc so close to motor)
- ___ touch
- ___ pressure
- temperature
- ___ (protects skin; if decreased more vulnerable to trauma)
voice, words, sensory
PT exam - sensory substitution - pt watches PT for possible hints:
- ___ intonation
- choice of ___
- eliminate any ___ clues (don't brush up against them by accident)
bicep, ECRL, tricep, quad, gastroc
PT exam - DTR:
- ___ (C5)
- ___ (C6)
- ___ (C7)
- ___ (L3)
- ___ (S1)
LE, vertebral, functional, measurements
PT exam - ROM:
- general ___ ROM
- avoid stress to areas of ___ instability
- mild restrictions can have huge ___ impact
- specific ___ needed
hip, elbow, SLR, flexion, DF
PT exam - ROM:
- avoid stress to areas of vertebral instability
- lumbar fx (limit ___ ROM to when resistance to motion occurs)
- mild restrictions can have huge functional impact
- ___ (needs to be hyperextended for mat mobility)
- shoulder
- ankle
- specific measurements needed
- ___ (test supine with pelvis stabilized at top)
- hip ___ (can go into lumbar lordosis and think they have more)
- ___ (may affect ability to walk if impaired)
positional, pressure, inspection
PT exam - skin:
- ___ changes in bed and wc
- ___ relief techniques
- ___ of at risk areas
rate, cough, posture, breath, expansion, strength
PT exam - respiratory:
- respiratory ___
- ___
- vital capacity
- ___ (abdomen protrusion, poor diaphragm rest position, lowers/sags)
- ___ pattern (accessory motions noted)
- chest ___ (measure at axilla and xiphoid process; difference between max expiration and max inspiration)
- ___/tone (diaphragm, abdominals, intercostals)
abdomen protrusion, diaphragm lowers/sags at rest
describe posture in terms of respiratory exam with SCI pt?
accurate, equipment, cues
PT exam - functional abilities:
- important to be ___ and specific (starting point, measure of success)
- during functional mobility evaluation - assistance need, ___ need, amount of ___ needed (verbal and manual)
incontinence, programs, equipment, digital
PT exam - bowel/bladder:
- ___
- type of ___ they're on and timing
- ___ needed
- meds may soften stool
- ___ stimulation (finger around anal area to stimulate bowel movement)
management, propulsion
PT exam - wc skills:
- ___ (can they remove armrests, put on breaks, get up if they fall, etc)
- ___ (indoor, community, advanced)
bed, transfers, balance, ambulation
PT exam - functional status:
- ___/mat
- ___ (even, uneven, functional)
- ___ (static and dynamic) - sit, stand
- ___
- wc skills
- instruction of others
true
t/f: the seating evaluation for wc is comprehensive, specialized, and expensive
FIM, wc, max, preferred, berg, modified CTSIB
PT exam - standardized tests:
- ___ (measures functional ability, both reliable and valid)
- ___ skills test (57 specific skills)
- WISCI/WISCI II (ranks ability of a person to walk 10 m; 0-20 most to least severe impairment)
- 10 m walk test (___ and ___ gait speeds)
- ___ for balance
- ___ for balance
effectiveness, meaningful, functional, measurable
PT exam - goal setting:
- gives direction
- used to measure ___
- involves the patient
- should be ___ goals
- ___ outcomes
- specific and ___
- set target date
what does walking mean to you? what activities do you want to be stronger for?
what are two examples of questions to ask the patient to make their goals more specific (about ambulation and strength)?
compensation, restoration
strategies for functional rehab - ___ vs ___:
- dependent on voluntary motor function
- neuroplasticity
- need to know neurologic levels for proper treatment
muscle substitution, substitution with gravity, substitution using tension in passive structures, substitution using fixation
what are 4 methods of substitution as strategies for functional rehab?
TFL for hip ABD
provide an example of muscle substitution in the LE as a strategy for function rehab
specific position of extremity used
describe how substitution with gravity is used as a strategy for functional rehab
tenodesis
provide an example of substitution using tension in passive structures for functional rehab
tighten finger flexors
if a pt intends on using tenodesis as substitution method, what should be done length wise to what muscle group?
short sit elbow extension
provide an example of substitution using fixation for functional rehab
place head in opposite direction of where you want the hips to go (hips should go in opposite direction as head)
describe head to hips ratio (use ratio to assist with movement for transfers and weight shifting)
momentum, velocity
strategies - ___/___
- throw extremity
- rolling
- keeping head forward when doing a supine to EOB transfer
functional, movement
mobility progression:
- ___ outcomes
- CPG outcomes
- ___ strategies
complications, obesity, trunk, arm, cognitive, fear
factors affect outcome:
- medical ___
- ___
- body type
- ___/___ ratio
- age
- ___ status
- proprioception
- ___ (want them to be comfortable)
- culture
athletic, adjustment, pain, spasticity, expertise
factors affect outcome:
- ___ ability
- motivation
- ___ to disability (suicide/depression screen)
- ___
- ___/tone
- fractures
- ___ of clinical team!
cervical flexors/extensors, diaphragm rhomboids, supraspinatus, SCM, levator scap, anterior/middle scalenes
what are the key muscles innervated by C4?
C4
the following functions are available with which motor level? -
- head control, neck movement, mouth movement, ability to breathe
rotator cuff, deltoids, biceps, brachialis, brachioradialis, serratus anterior, teres major
what are the key muscles innervated by C5?
C5
the following functions are available with which motor level? -
- movement of the deltoid, shoulder ABD/flx/rotation and some extension/depression, bicep
pec major, ECRB, ECRL, supinator, lats
what are the key muscles innervated by C6?
C6
the following functions are available with which motor level? -
- strong bicep, wrist extension, tenodesis, shoulder rotation/adduction/abduction and extension/depression
triceps, pronators, supinators, pec major/minor
what are the key muscles innervated by C7?
C7
the following functions are available with which motor level? -
- full shoulder movement, strong scapular stability, elbow extension, strong wrist, moderate grasp
FDP
what are the key muscles innervated by C8?
interossei
what are the key muscles innervated by T1?
intercostals, abs
what are the key muscles innervated by T2-L1?
C8-L1
the following functions are available with which motor level? -
- improved/normal grasp, trunk musculature/trunk stabilizers
iliopsoas
what are the key muscles innervated by L2?
quads
what are the key muscles innervated by L3?
tib ant, glute med
what are the key muscles innervated by L4?
EHL
what are the key muscles innervated by L5?
gastroc/soleus
what are the key muscles innervated by S1?
sphincter
what are the key muscles innervated by S2-5?
L2-S5
the following functions are available with which motor level? -
- pelvic stabilization, LE motion, bowel/bladder
C1-4
these are the functional outcomes and equipment for injury to what level?
