Week 8 Part 1 - Hematopoiesis
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Hematopoesis:
Formation and development of blood cells
The proliferation, differentiation and maturation
of blood cells
Primarily takes place in the bone marrow
Only mature cells are released into peripheral
blood
Formed elements of the blood go through developmental stages:
As cells mature, they are able to move through the sinusoids of the marrow because of decreased overall cell size, decreased nuclear cytoplasmic ratio, and increased flexibility and mobility.
Normal peripheral blood cells include lymphocytes, basophils, eosinophils, segmented neutrophils, monocytes, and band neutrophils.
Each cell type has a normal life span and function.
Normally, only mature cells are seen in the peripheral blood circulation
Immature cells may appear in the peripheral blood in certain disease states, called a shift to the left
Characteristics of Hematopoesis:
Replacement of circulating cells
Proliferation of precursor cells that retain mitotic
capability
Governed by multiple cytokines
Specialized microenvironment
Differentiation:
Process that generates the diverse cell populations
Appearance of different properties in cells which were
initially equivalent
Commitment:
When two cells derived from the same precursor take
a separate route of development
They commit to that path
Maturation:
The entire process from commitment to when the cell
has all of its characteristics
Two primary characteristics of hematopoesis:
The variety of distinct blood cell types produced
The relatively brief life span of the individual cells
Circulating cells are:
Mature
Incapable of mitosis
Exception: lymphocytes
Limited life span or terminally differentiated
Must be replaced by less differentiated, mitotically active precursor cells
Stages of Hematopoesis:
Divided into three phases:
Mesoblastic, Hepatic, Myeloid
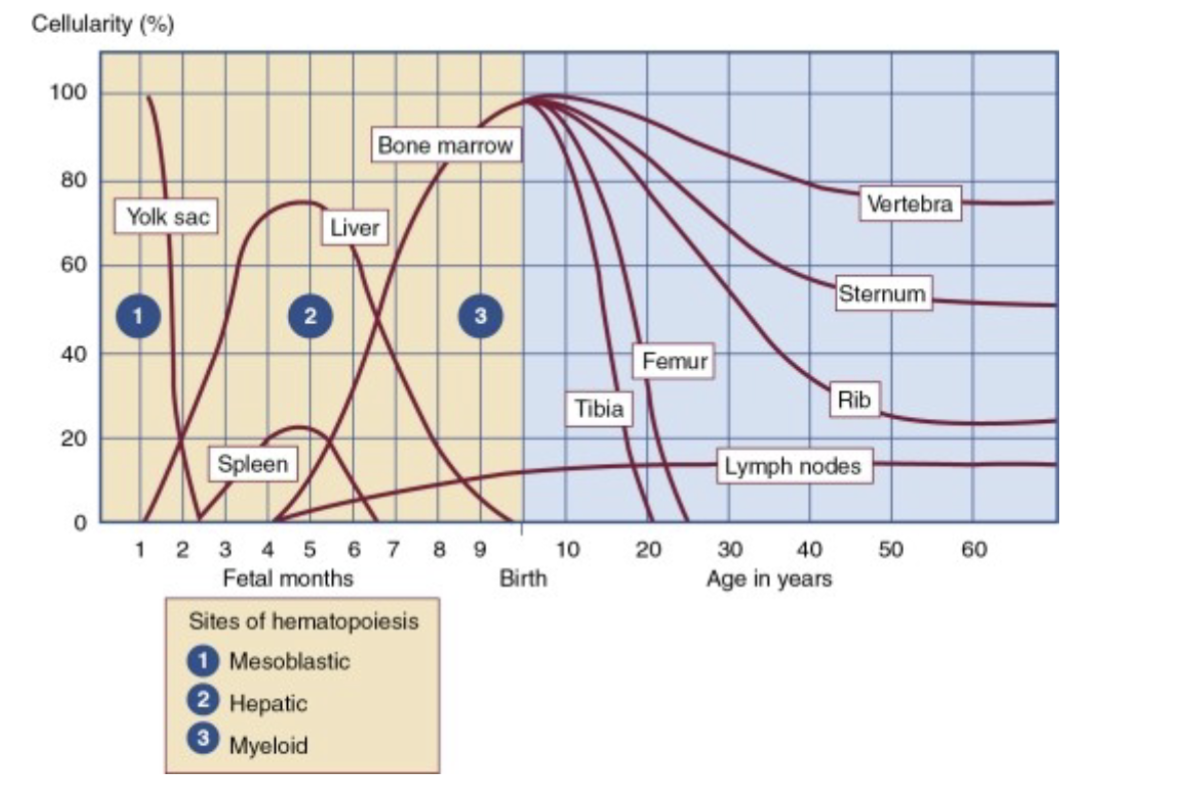
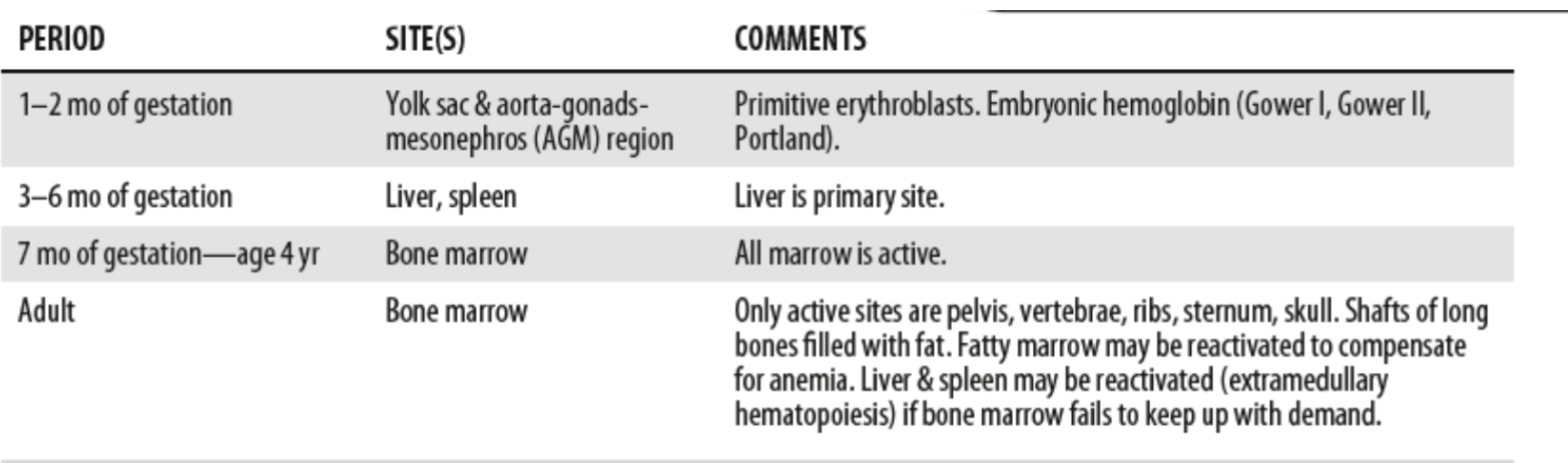
Sites of hematopoiesis by age
Mesoblastic stage:
Begins in early embryonic development
Starts with yolk sac, as early as 19 days after
fertilization
Confined to erythropoiesis from blood islands
Remains active for 8-12 weeks
Embryonic Hemoglobin: Gower 1, Gower 2, and
Portland
(do not carry oxygen well)
Differs from fetal and adult hematopoiesis because it occurs intravascularly – (within developing blood vessels)
Hepatic Stage:
Begins at 5-7 weeks gestational age
Reaches peak by third month.
Third month of fetal development liver becomes active along with kidney, spleen, and lymph nodes
Thymus (first fully developed fetal organ) becomes major site for T cell lymphocyte production
Kidney and Spleen produce B cell lymphocytes
Keep in mind cells differentiate in the lymph nodes, but aren’t produced there.
Granulocytes and lymphocytes are at a minimum
Hemoglobin production: A, A2 and F
Continues to about the fifth month
Myeloid Stage:
Occurs in bone marrow (called medullary) because it occurs in medulla
Begins in 4th and 5th month of fetal development
6th month the bone marrow becomes the primary
site for hematopoiesis and continues throughout
life
Measurable levels of EPO, G-CSF, GM-CSF,
HgbF, HgbA can be detected
Cells at various stages of maturation (for all cell
lineages) can be seen
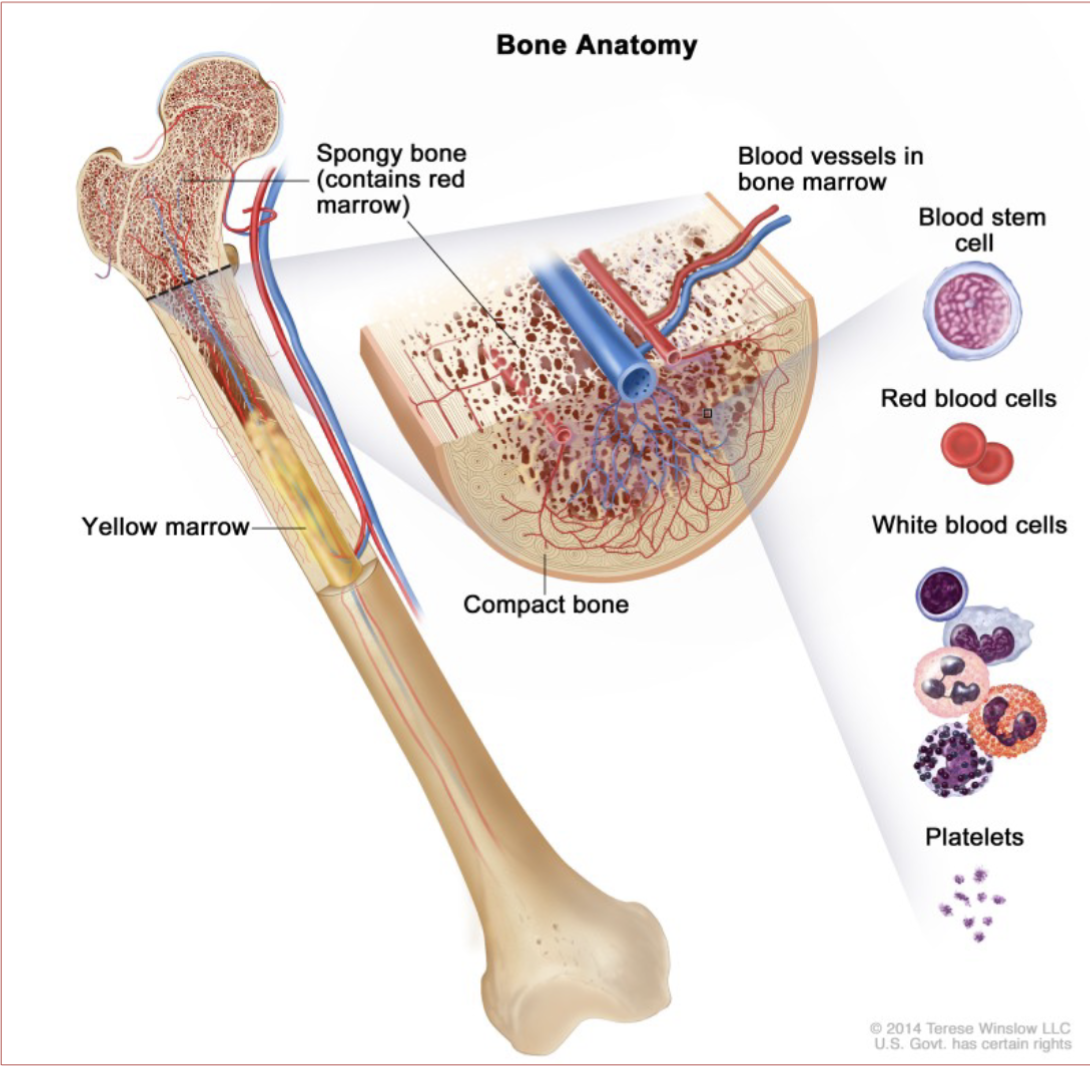
Bone Marrow:
One of the largest organs in the body
Composed of yellow and red marrow
Intricate supply of nutrients and blood vessels
Consists of vessels, nerves, differentiated and undifferentiated hematopoietic cells, reticuloendothelial cells
Bone Marrow Structure consists of:
Vascular Compartment
Hematopoietic Compartment
Vascular Compartment:
Consists primarily of venous vessels referred to as sinuses
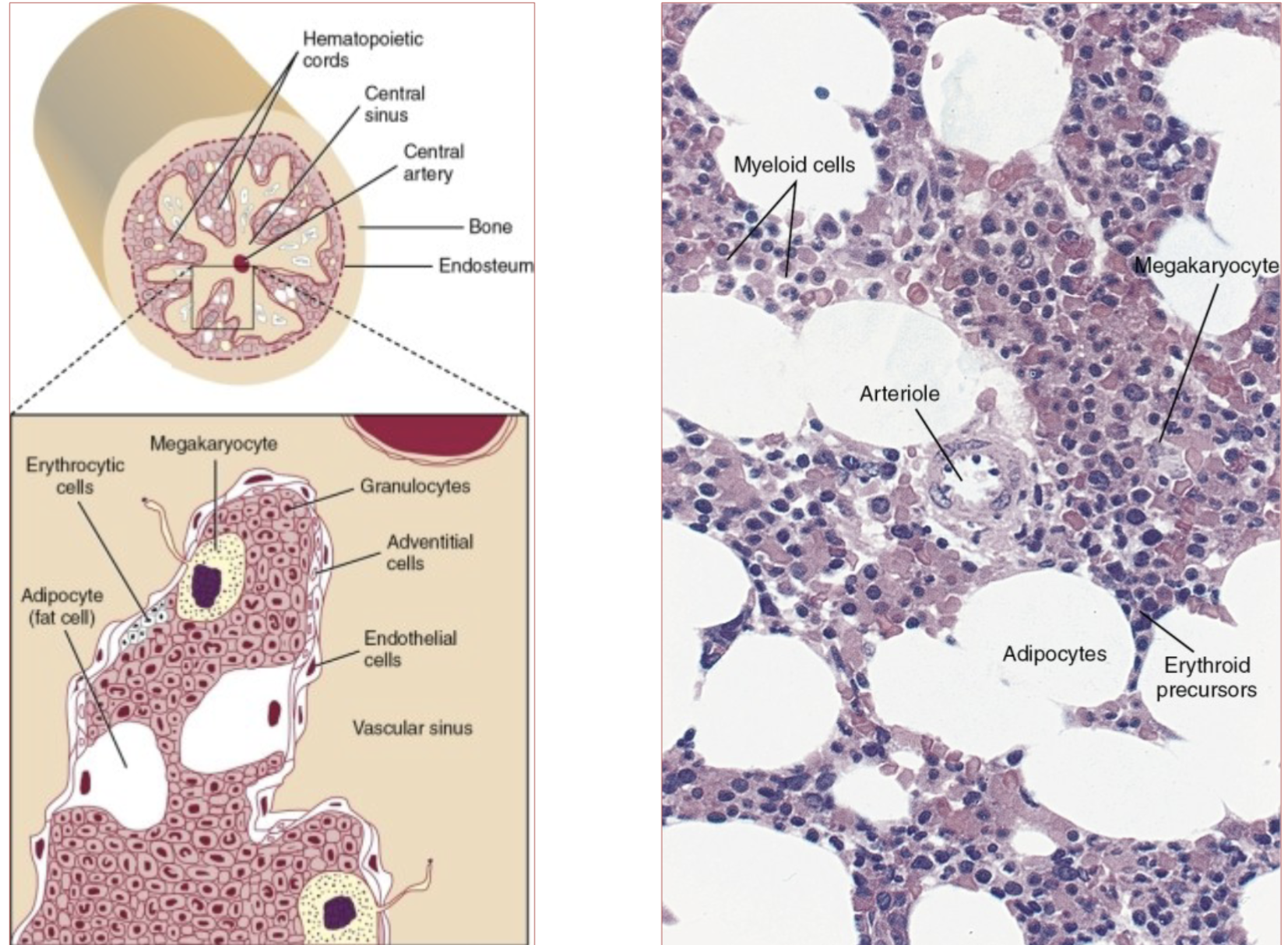
Hematopoietic Compartment:
Hematopoietic stem cells residing in this compartment
proliferate and differentiate into the lymphocytic,
granulocytic, monocytic, megakaryocytic and
erythroid lineages
All cells go into sinus before going to peripheral
blood
Megakaryocytes – cytoplasm pinches off to
become platelets
Bone Marrow Activity:
During first few years of life the marrow of all
bones is red and cellular
By age 18 the red marrow is found in the vertebra, ribs, sternum, skull, and pelvis
Past the age of 40, marrow in the sternum, ribs, pelvis, and vertebra are composed of equal amounts of red and yellow marrow
Medullary Hematopoiesis:
Hematopoiesis that takes place in the bone marrow
Extra-Medullary Hematopoiesis:
When there is an increased demand for hematopoiesis it may (again) begin in the spleen and liver (as a last resort kind of)
Bone Marrow Procedure:
Iliac crest of pelvis site preferred site for bone marrow analysis
200 cell differential is performed (new recommendation is 500 cell differential)
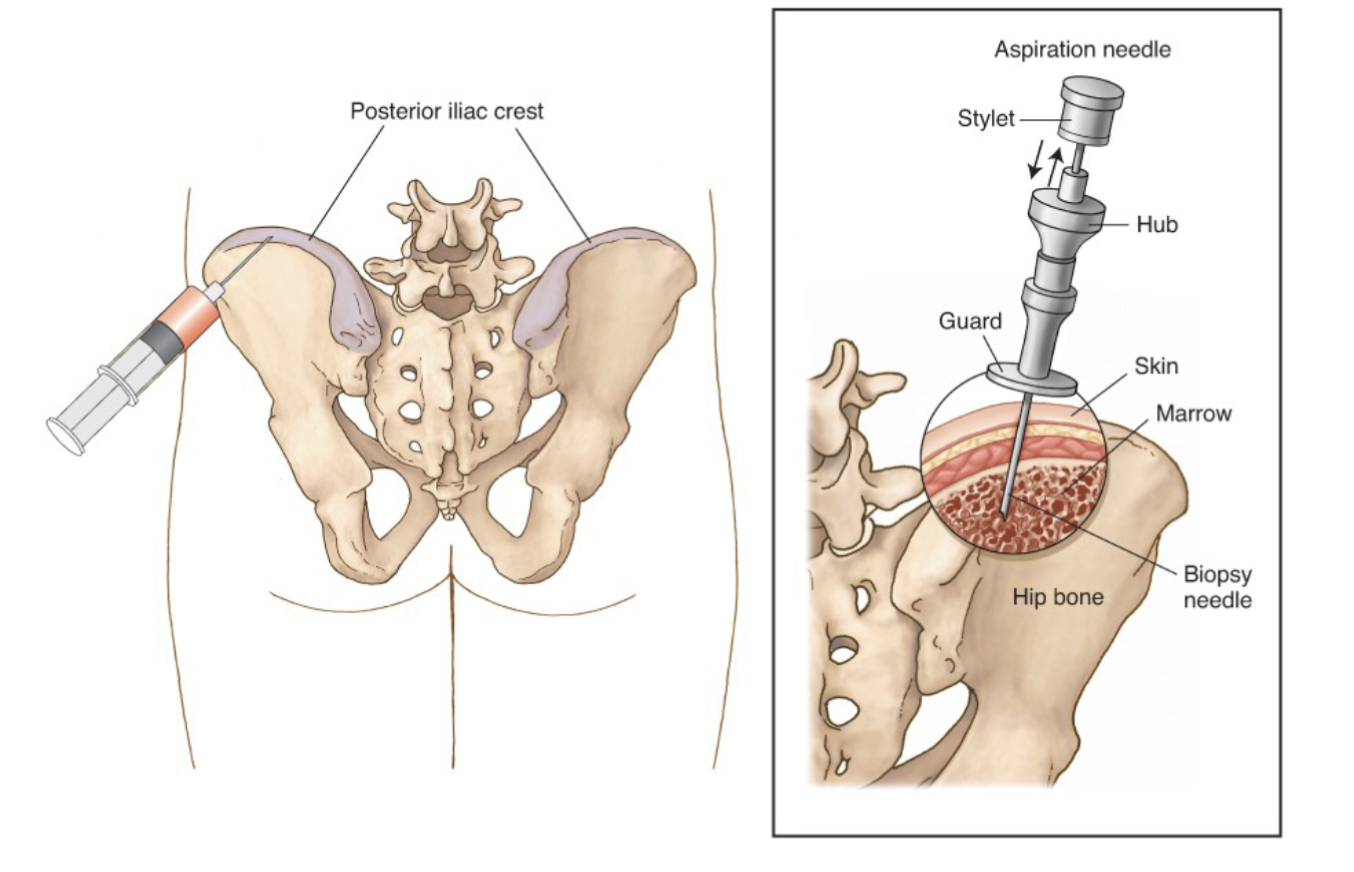
Bone Marrow Biopsy or Core:
To identify placement of cells to see where each cell belongs and the cellularity
Touch preparation used to study cellular details.
(Sample applied to several coverslips)
Takes a whole piece of bone marrow
Bone Marrow Aspirate:
To identify morphologically, cells are not in natural architecture
Gives poor estimation of marrow cellularity
Takes fluid from the bone marrow
Bone Marrow Differential Count:
Birth: Predominance of granulocytes (first line of defense)
One Month: Switch to lymphocytes
Adult: Granulocytes and Erythrocytes predominate
Stem Cell Cycle:
Bone Marrow is capable of producing massive
amounts of cells daily
Per kilogram of body weight
The determining factor controlling the rate of production is physiologic need.
Stem cell ratio in Bone Marrow
1:1000 (1 stem cell per 1000 nucleated RBC)
Origin of Marrow Cells:
Bone Marrow contains pluripotent stem cells
These cells have ability to differentiate and proliferate with self renewal.
Influenced by growth factors and cytokines
Stem cell division:
One reverts to stem cell
Other becomes a colony forming unit (CFU)
CFU stimulated to proceed in any direction
Growth factors or cytokines regulate
proliferation
differentiation
maturation of hematopoietic precursor cells
Cell Cycle":
G0 Resting Stage
G1 RNA and Protein Synthesis
S DNA Synthesis
G2 Pre-mitotic
M Mitosis
Apoptosis: programmed cell death
* In leukemia – no apoptosis
Growth factors & Cytokines:
Often interchanged terms
Growth Factors:
Proteins that bind to receptors on the cell surface of cells and result in proliferation or differentiation of the affected
cells.
Cytokines:
often compared with growth factors, affect primarily the cells of the immune system and orchestrate immune responses.
Soluble protein, cellular products, that influence the
function or activity of other cells.
Have important functions in hematopoiesis and other
cellular activities (especially immunology)
Cytokines include:
Colony stimulating factors
Interferons
Interleukins
Lymphokines
Monokines
Chemokines
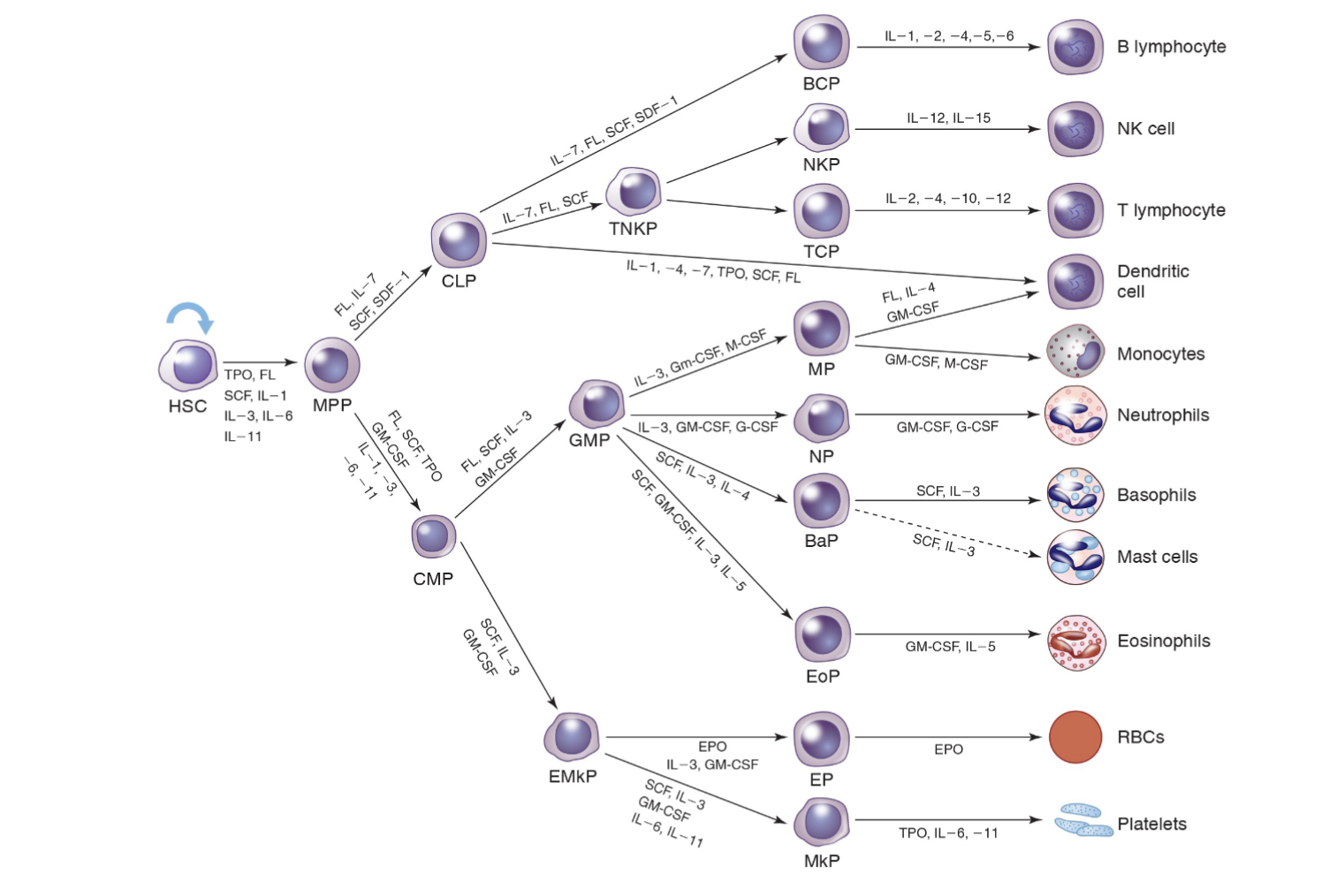
Cytokine Influence
How are cytokines & growth factors produced:
By stromal cells in hematopoietic microenvironment
Exception is erythropoietin (EPO)
Produced mainly in the kidney
EPO specifically targets synthesis of RBC
Most are not lineage specific
Each has multiple functions acting on more than one cell type (pleiotropy)
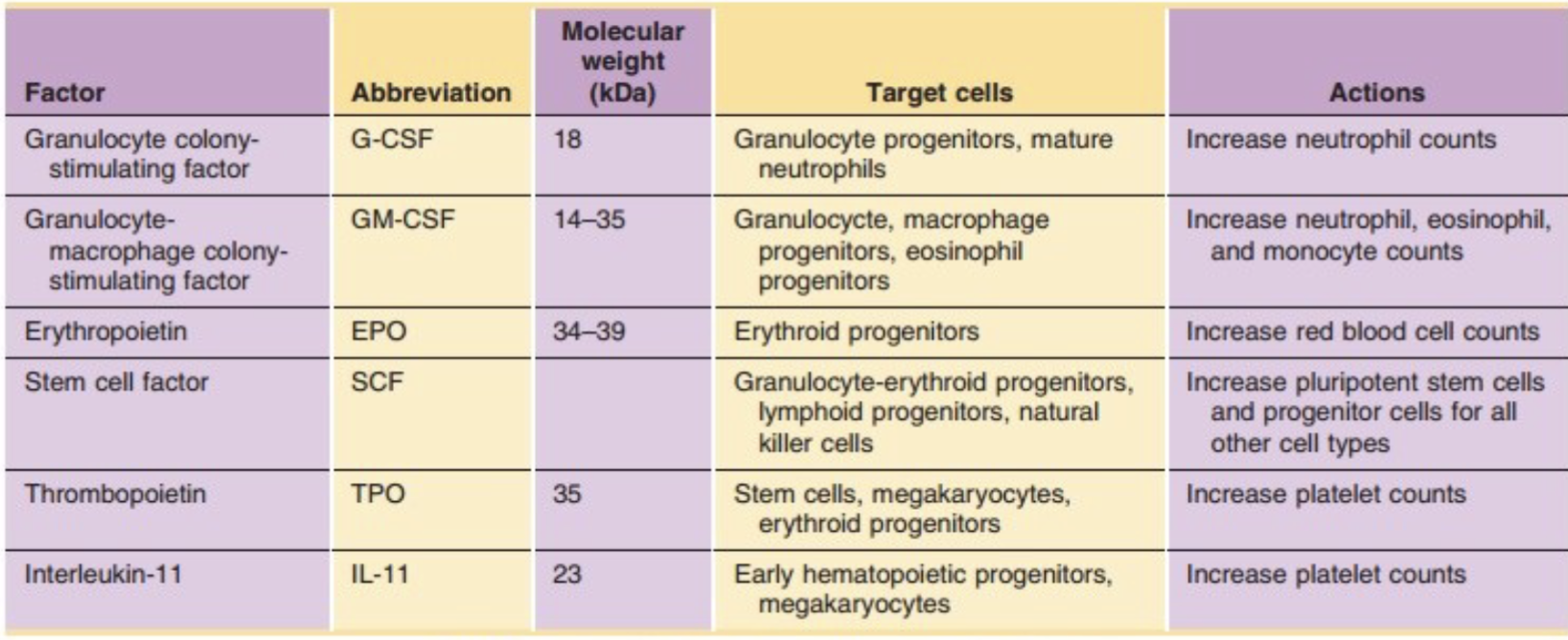
Hematopoietic Growth Factors
SCF also called kit ligand
G-CSF:
(Granulocyte colony stimulating factor)
Produced by monocytes/macrophages, placenta, endothelial cells and stimulates development of the granulocytic lineage
GM-CSF:
(Granulocyte Macrophage CSF)
Produced by T lymphocytes, stromal cells, and macrophages and is an essential cytokine for development of granulocytic and monocytic lineages
Eythropoietin:
Glycoprotein produced by kidney for the stimulation of red cell production
Thrombopoeitin:
Glycoprotein produced by kidney, stromal cells, and
hepatocytes to stimulate platelet production
KIT Ligand:
(stem cell factor or SCF)
Tyrosine-protein kinase expressed on HSC (Hematopoietic Stem Cell) , gets down regulated during differentiation, stimulates proliferation.
Essential for early stage hematopoiesis
FLT3:
Tyrosine-protein kinase expressed on HSC. Works
synergistically with SCF and IL-3, GM-CSF to early stage hematopoiesis
IL11 (Interleukin 11):
Produced by stromal cells and IL-1 stimulated fibroblasts to stimulate proliferation/differentiation of myeloid lineage
IL3 (Interleukin 3):
Produced by activated T cells, eosinophils, and mast cells,
stimulates colony formation for myeloid lineage WBC, RBC, PLT (but not lymphs)
IL7 (Interleukin 7):
Produced by stromal cells stimulates proliferation/differentiation of lymphoid lineage
Colony Forming Units:
Influenced by colony stimulating factors (CSF)
CSF produced by many cells and have high specificity for target cells
Highly active at low concentrations
Capable of influencing multiple cell linages
Different types of CSF such as:
G-CSF (Granulocytic CSF)
GM-CSF (Granulocytic/Monocytic)
Lymphoid Stem Cell CFU-L:
Gives rise to two types of lymphocytes
B cell: in the bone marrow, these transform to plasma cells
Participate in humoral immunity by synthesizing immunoglobulins
T cell: migrate to thymus
Regulate humoral immunity through T-helper cell and T-suppressor cells subpopulations
Helper to suppressor – 2:1 ratio
Myeloid Stem Cell CFU-GEMM:
Granulocytes – From myeloblast to the release
of the mature cell is about 9 days
Remain in circulation 3-6 hours, later moving to tissue for 1-4 days
Neutrophils: primary function to phagocytize
extracellular pathogens
Eosinophil: defense against parasites, also plays
role in allergic reaction
Basophil: plays role in hypersensitivity
Monocyte maturity:
3-5 days
Circulate 16-36 hours
Move to tissue where they transform to macrophages (or histiocytes)
Histiocytes (macrophage) resides in tissues, aids in phagocytosis as part of innate immune response
Megakaryocytes maturity:
4-5 das
Function in hemostasis, through production of platelets
Platelets are small pieces of megakaryocyte cytoplasm
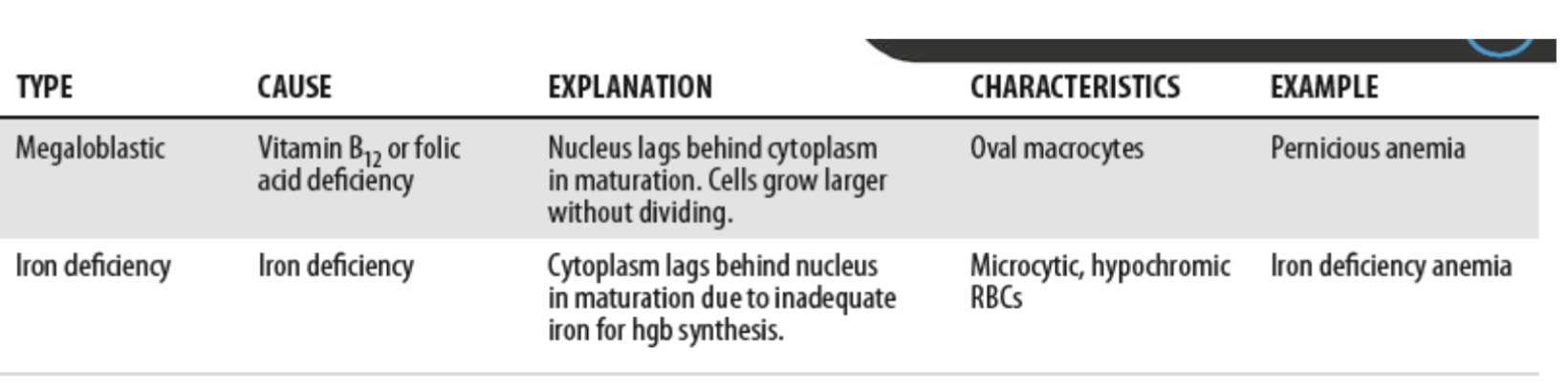
Erythroid Cells:
arise from the BFU (burst forming unit)
Mature in about 3-5 days
Remain in circulation for 120 days
Filled with hemoglobin (oxygen carrying protein)
Myeloid:Erythroid Ratio (M:E):
The relative proportions of the two principle
bone marrow cells
Compares the relative numbers of developing
granulocytes with the relative number of
erythroid precursors
Normal M:E ratio in adults is 2:1 to 4:1
Birth – 3:1 to 4.5:1
Granulopoietic tissue occupies 2 to 4 times greater
marrow space than the erythropoietic precursors
Hematopoietic Maturation Process:
Overall size of cells
As a rule, primitive cells are large but as they mature their size decreases
Exceptions to the rule are megakaryocytes
Hematopoietic Maturation Process: Nuclear to cytoplasm ratio (N:C):
N:C ratio decreases as cell matures
Blasts contain about 4:1 ratio
Nucleus gets smaller with maturation
Exceptions: platelet (cytoplasm) RBC (loses nucleus) and lymph ratio aprox. 3:1
Hematopoietic Maturation Process: Chromatin Pattern:
Nucleus is made up of DNA
Young cells have very fine and loose chromatin
As the cell matures the chromatin becomes dense, clumped and typically stains dark blue
Hematopoietic Maturation Process: Nuclear Shape:
Younger cells have round to oval nucleus
Monocyte has a folded shape
Granulocyte nucleus is segmented
Hematopoietic Maturation Process: Nucleolus or Nucleoli:
Made up of RNA with indicates metabolic activity and
growth
Stains light blue and as the cell matures they are not
visible
Blasts typically have between 1-5
Hematopoietic Maturation Process: Cytoplasmic RNA:
Young cells have a large amount of RNA and typically
stain dark blue, as the cell matures they become a
light blue to pink
Hematopoietic Maturation Process: Golgi Zone:
Immature cells demonstrate a clear zone adjacent to
the nucleus
Golgi apparatus is responsible for transporting,
modifying, and packaging proteins
When visible, often indicates a younger cell
Hematopoietic Maturation Process: Granulation:
Progresses from no granules to non-specific, to specific granules
Granulocytes are noted for their distinctive granules
Primary are big and burgundy color
Secondary are more common and are small
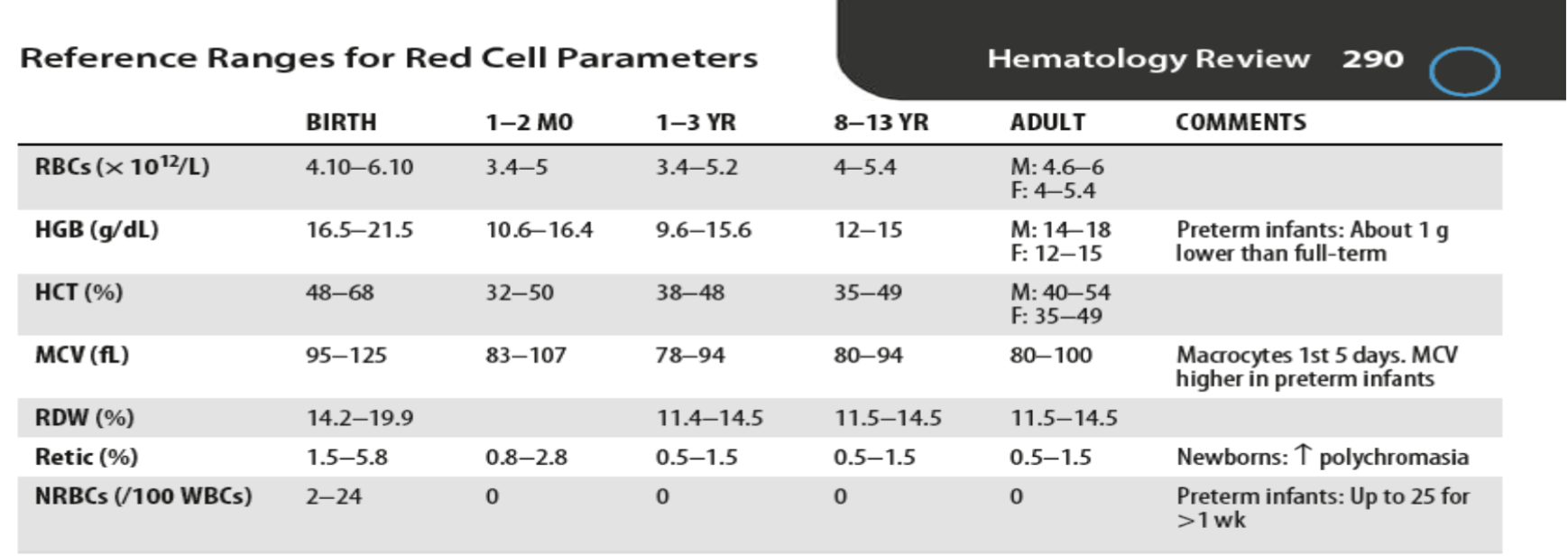
Reference Ranges for Red Cell Parameters
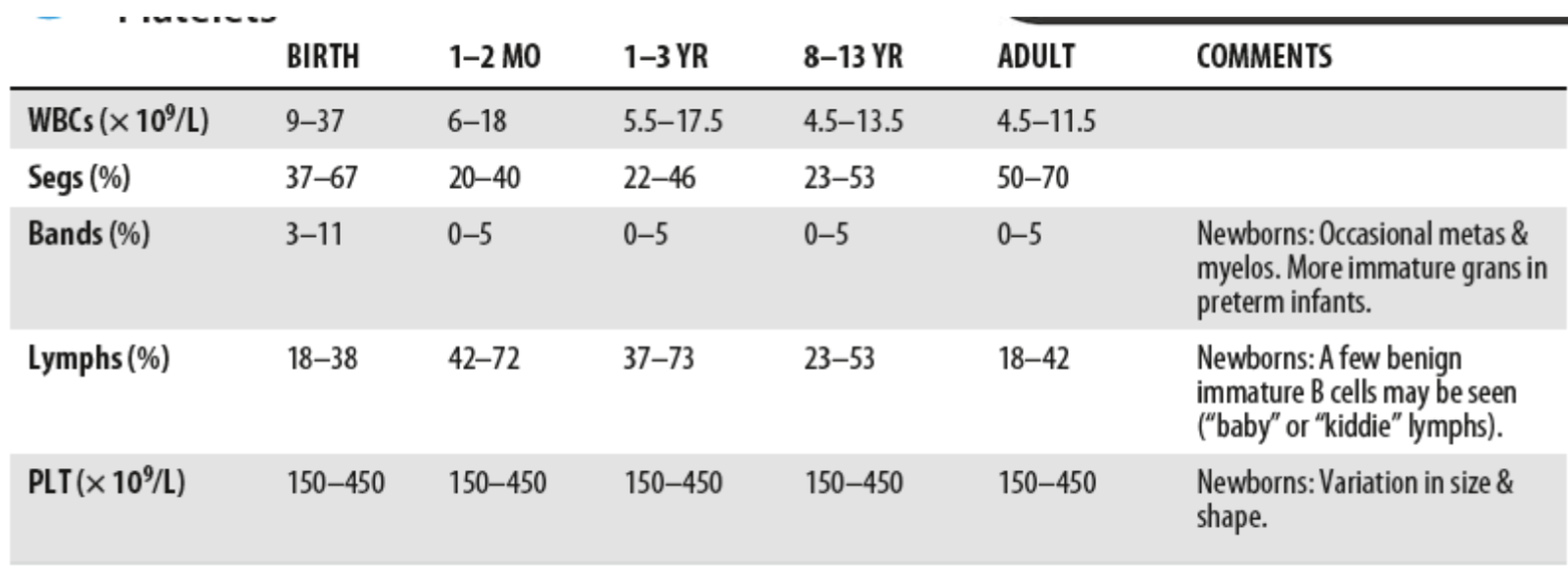
Reference Ranges for WBC Parameters
Erythropoiesis
Asynchronous Erythropoiesis