Chapter 7 - Measuring and manipulating brain and behavior
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What instruments are used to examine humans with brain lesions?
Postmortem examination
Neuropsychological testing
What instruments are used to Manipulate brain-behavior interactions?
DBS
TMS
What instruments are used to measure the Brain’s Electrical Activity?
EEG
MEG
What are instruments are Anatomical Imaging Techniques?
CT
MRI
What instruments are for Functional Brain Imaging?
fMRI
fNIRS
PET
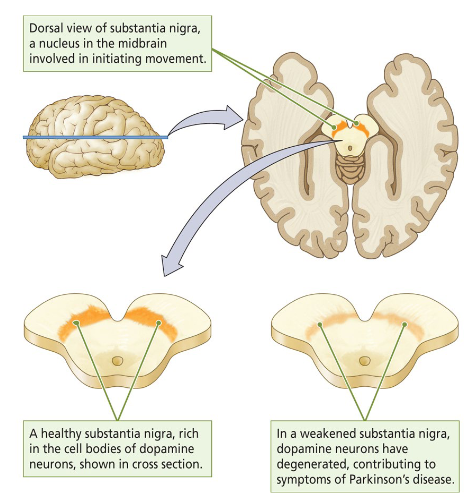
What do we look for in the brain when we look for brain lesions?
The substantia nigra, a nucleus in the midbrain involved in initiating movement.
A healthy substantia nigra = rich in the cell bodies of dopamine neurons.
A weakened substantia nigra = dopamine neurons have degenerated, contributing to symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
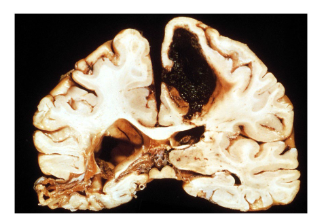
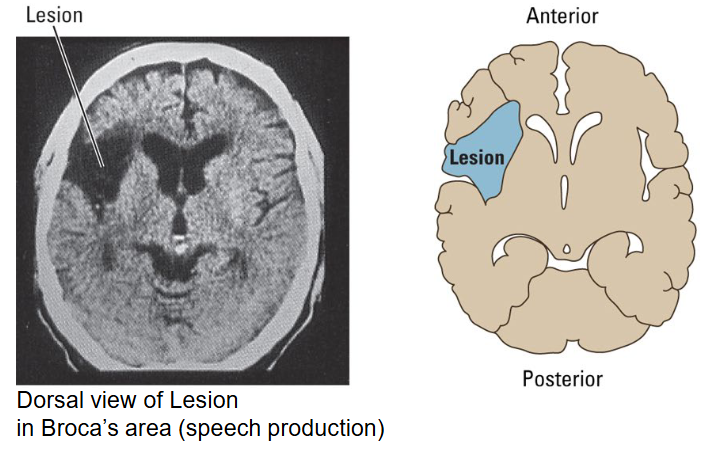
What type of brain lesion is this?
Hemorrhagic stroke
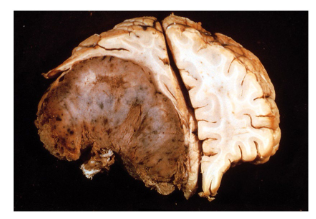
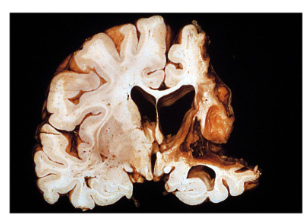
What type of brain lesion is this?
Meningioma: tumor is compressing right hemisphere and pushes the midline to the other side.
What type of brain lesion is this?
Ischemic stroke: blockage of blood, leads to brain tissue dying.
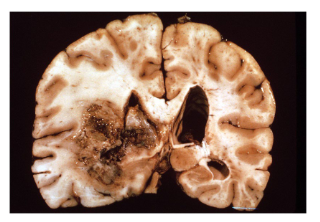
What type of brain lesion is this?
Glioma
What is the process of Neuropsychological testing of humans with brain lesions?
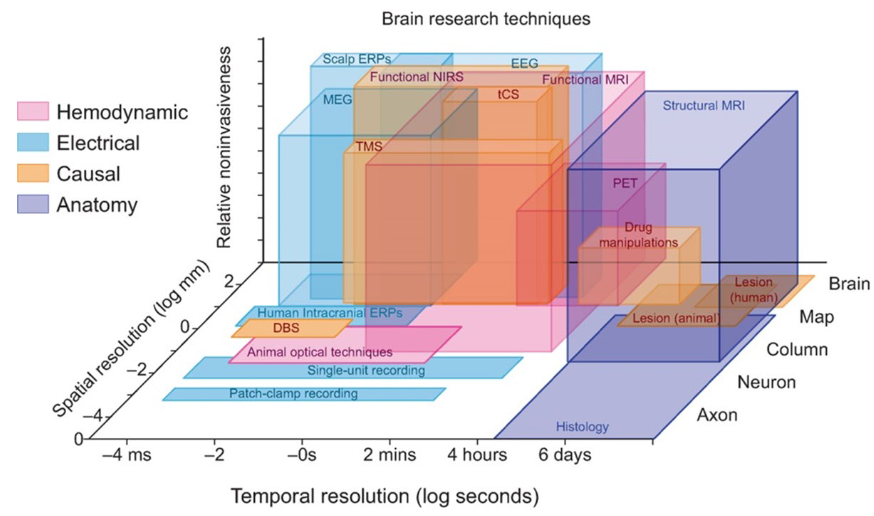
What are 3 Brain research techniques dimensions and what are the 2 imaging techniques?
Spatial resolution (the more megapixels, the more you can zoom in; mm is better than cm).
Temporal resolution (time, how accurate can you image what is going on in the brain; higher resolution is higher timing).
Invasiveness (how far do you have to go into the brain in order to apply the technique; more invasive, the deeper you have to go).
Anatomical (static) → focus on structure of brain (snapshot).
Functional (dynamic) → determine function of brain region.
What is Stereotaxic apparatus?
A device for Manipulating brain-behavior interactions which allows targeting of a specific part of the brain → fixates brain.
Psychosurgery (ablation, lesions, gamma “knife” radiation).
Deep brain stimulation (Parkinson’s disease).
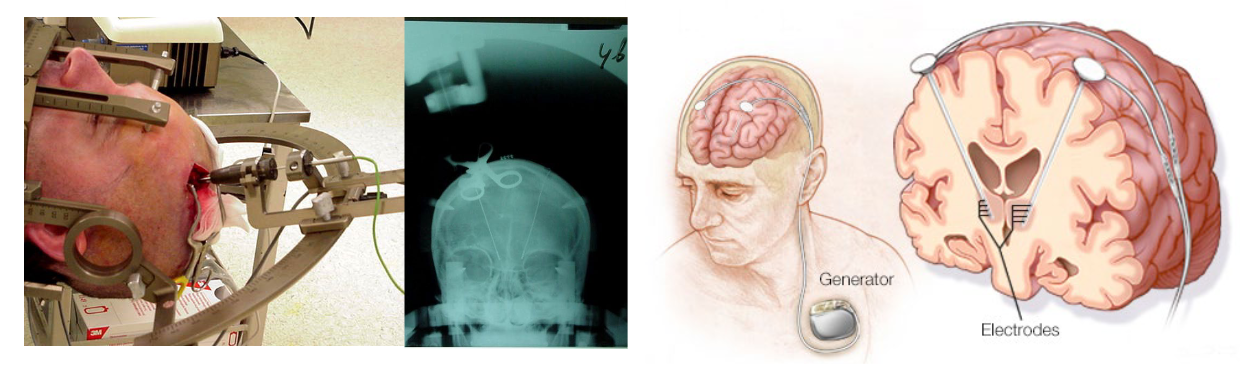
What are Irreversible lesion techniques for Psychosurgery?
Electrolytic: burning by passing current through electrode.
Neurotoxic: intoxication through infusion of neuron-killing chemical.
High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU): heating with focused ultrasonic beams.
NB: permanent lesions lead to compensation (neuroplasticity).
What are Reversible lesion techniques for Psychosurgery?
Regional cooling → cooling brain region makes it less active, neuroactive processes are decreased in these regions.
Local administration of a GABA agonist.
What happens in Deep-brain stimulation (DBS)?
Electrodes implanted in the brain stimulate a target area with continuous pulses of low-voltage electrical current to facilitate behavior.
Can be used for treatment of Parkinson’s disease, though not often used as it is invasive.
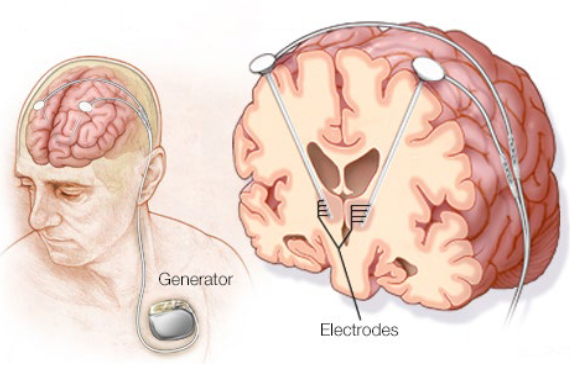
What is the target for Deep-brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease?
Basal ganglia (globus pallidus internal, subthalamic nucleus).
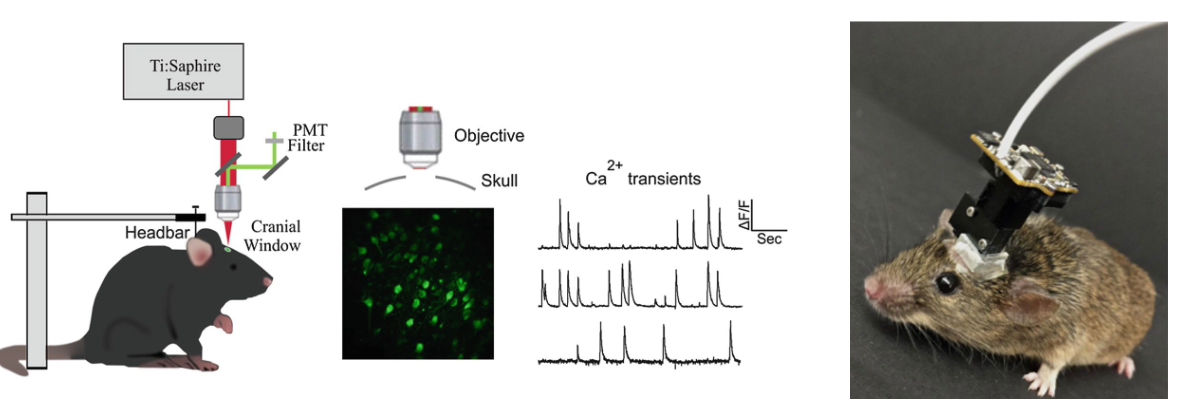
What happens in Optogenetics?
Manipulate and record neural activity in awake, ‘freely’ moving mice.
What happens in Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)?
Manipulate brain activity in living subjects. Injecting magnetic fields inside brain tissue which then trigger opening up of ion channels → key factor in neurotransmission.
You can alter neuroactivity by injecting magnetic fields.
TMS in muscle brain area stimulates muscles move.
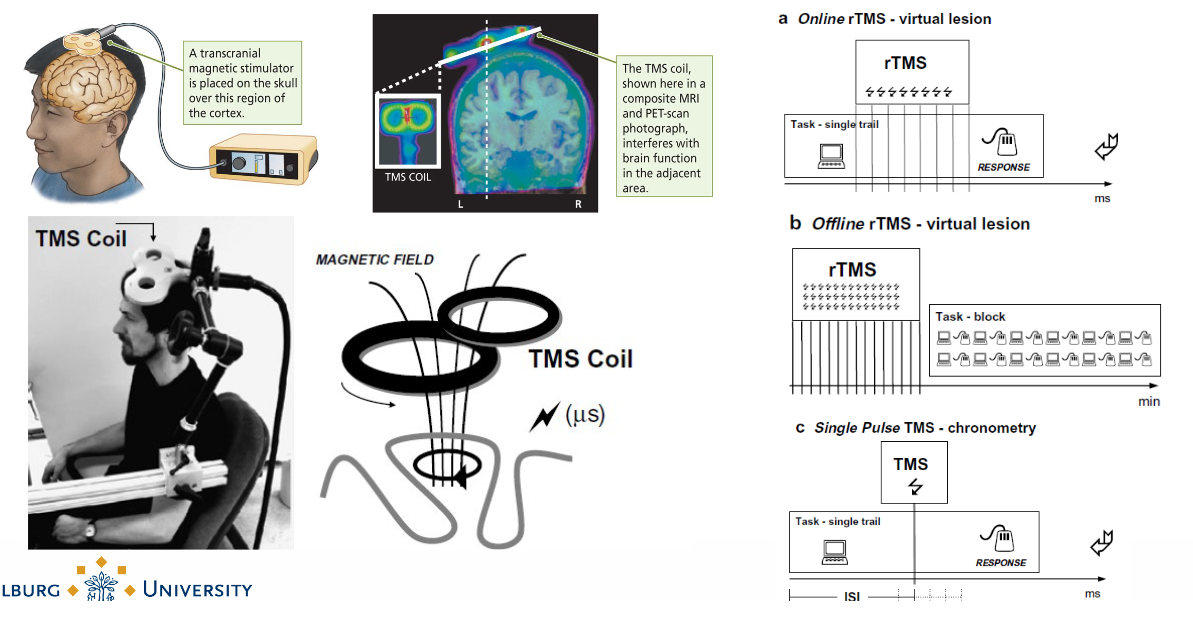
What are the 4 major techniques for Measuring the Brain’s Electrical Activity?
Single-cell recording → action potentials.
Electroencephalography (EEG) → graded potentials.
Event-related potentials (ERPs)
repeatedly harassing patient by stimulating with same things, then measuring EEG.
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
What are the 2 types of Single-cell recording for Action potentials?
Extracellular → record electrical activity of multiple neurons at once (clusters).
Intracellular → allows study and recording of electrical activity of a single neuron.
e.g. low vs high pitch sensitive cells in auditory cortex, place cells in hippocampus (spatial location).
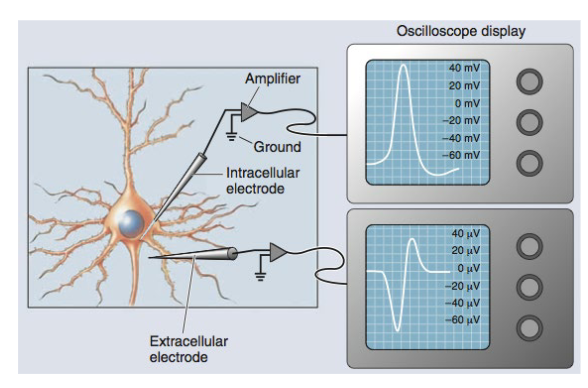
What is the main disadvantage of Single-cell recording for Action potentials?
It works well for dish-grown neurons (in vitro), but requires surgery when recording brain cells in living organisms (in vivo).
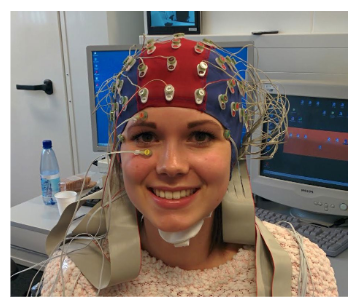
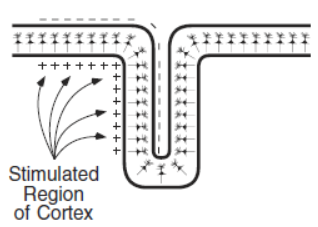
What does Electroencephalography (EEG) do?
It measures graded potentials (EPSPs and IPSPs) of similarly orientated neurons that are simultaneously active.
High temporal resolution (~1ms)
Poor spatial resolution (~1cm)
inexpensive, noninvasive
shown as scribbly lines (^~~^~^~~).
dynamic imaging technique: record activity in the brain over time.
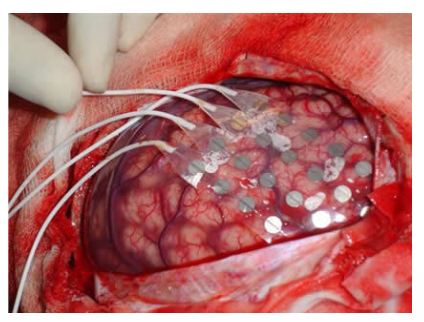
What is Electrocorticography?
Cutting skull open and putting electrodes straight onto the cerebral cortex.
Why can EEG not record action potentials? (extracurricular).
Potentials can only be recorded at the scalp if they occur at approximately the same time across thousands or millions of neurons.
action potentials have a very short duration (1 ms)
neurons rarely ‘fire’ at exactly the same time
axons are relatively randomly orientated (i.e. not spatially aligned
Why can Postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs and IPSPs) be recorded with EEG? (extracurricular).
EPSPs and IPSPs typically last longer (10’s -100’s ms).
EPSPs and IPSPs occur instantaneously (rather than travel along axons).
EPSPs and IPSPs occur at dendrites and cell bodies, which are typically orientated perpendicular to the surface of the cortex.
NB: graded potentials recorded at the scalp reflect summed EPSPs and IPSPs.
What does a high frequency of the EEG mean?
The higher the frequency of the EEG, the more active the brain is.
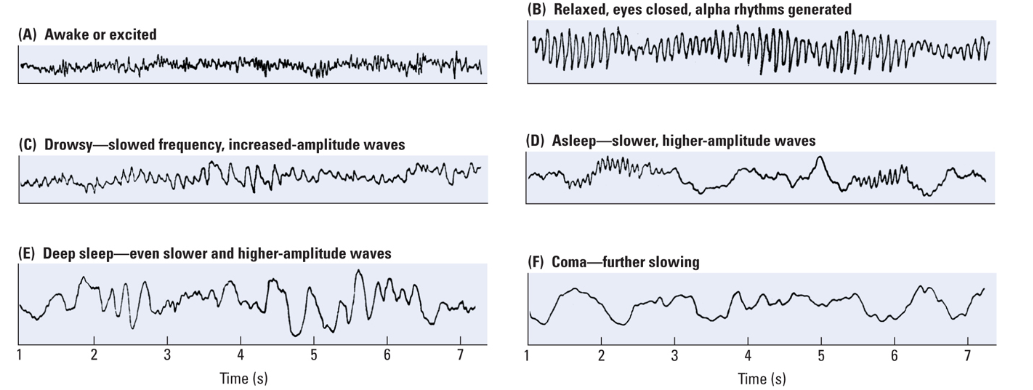
What happens in an Epileptic seizure?
Very high frequency of the EEG, the brain is overactive.
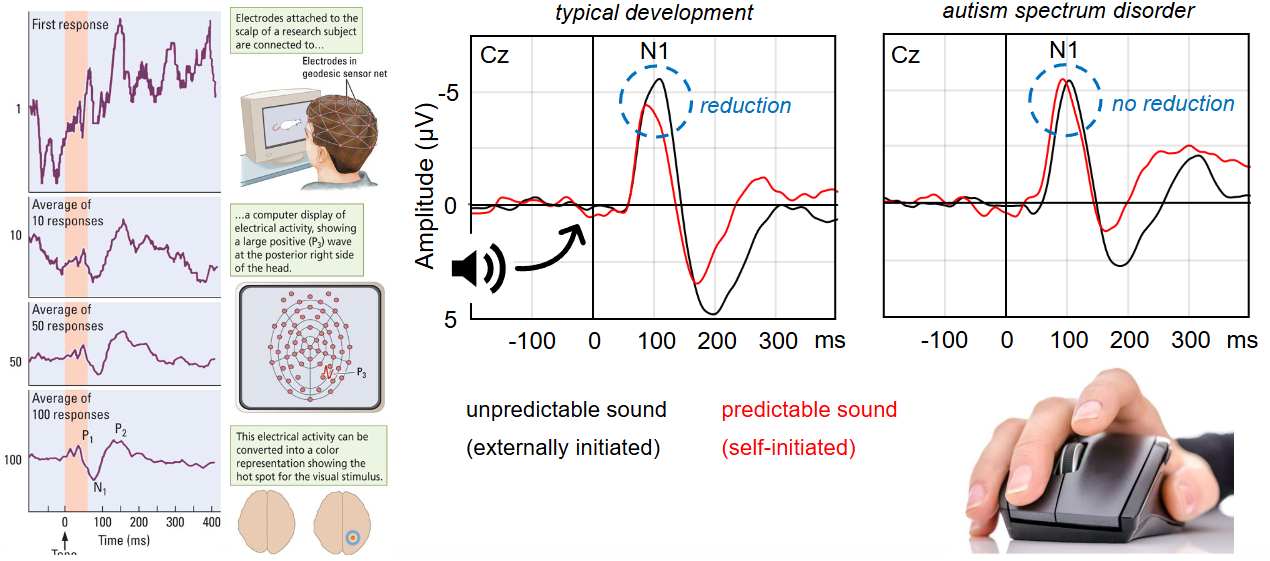
What are Event-related potentials (ERPs)?
Repeatedly show stimulus to patient and measure average brain activity (should be about 0) with EEG.
What is Magnetoencephalography (MEG)?
Magnetic counterpart of EEG, ERP.
High temporal resolution (~1ms)
High spatial resolution (~2-3mm)
Very expensive, so not often used.
Measure magnetic field.
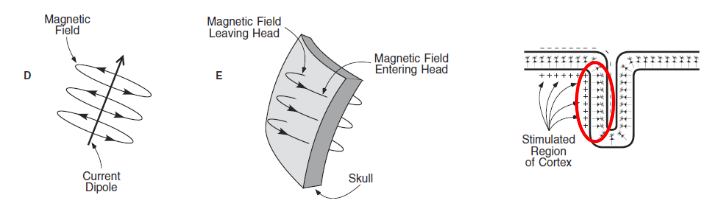
Why does MEG have higher spatial resolution than EEG?
Magnetic waves (MEG) undergo less distortion through brain tissue and scalp compared to electric signals (EEG, ERP).
NB: main disadvantage is that MEG is more expensive than EEG, ERP.
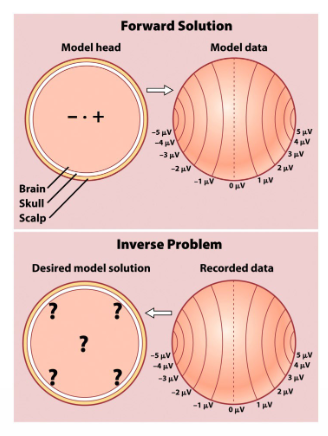
How do you localize the source localization in EEG + MEG?
Record data first, then try to infer what sources ‘caused’ data.
What is the main problem of Source localization in EEG + MEG? How can it be solved?
No unique solution i.e. multiple sources might yield the same data.
inverse problem
Possible solutions can be derived using models involving prior knowledge of brain functioning.
What happens in the process of Staining?
Histology = slicing of the brain. Then add dye to the brain to visualize the brain cells.
Clarity (makes brain tissue transparent).
Brainbow (transgenic technique).
What is the main disadvantage of staining?
It only works in fixed brain tissue (ex vivo, in vitro, post-mortem).
What is the main advantage & disadvantage of the Anatomical Imaging Techniques: Computed Tomography (CT)?
Main advantage = relatively inexpensive.
Main disadvantage = uses X-ray radiation (may damage DNA).
And cannot distinguish between white / grey matter.
What is the Anatomical Imaging Technique Computed Tomography (CT) used for?
It is appropriate for localizing bone fractures, brain tumors and lesions.
Low temporal resolution (~1sec)
High spatial resolution (~1mm)
How does X-ray absorption vary with tissue density?
High-density tissue (e.g. bone) absorbs a lot of radiation → light regions.
Low-density tissue (e.g. CSF, blood) absorbs little radiation → darker regions.
Neural tissue absorption lies in-between.
Can grey and white matter be distinguished on CT scan?
No; grey and white matter cannot be distinguished on CT scan.
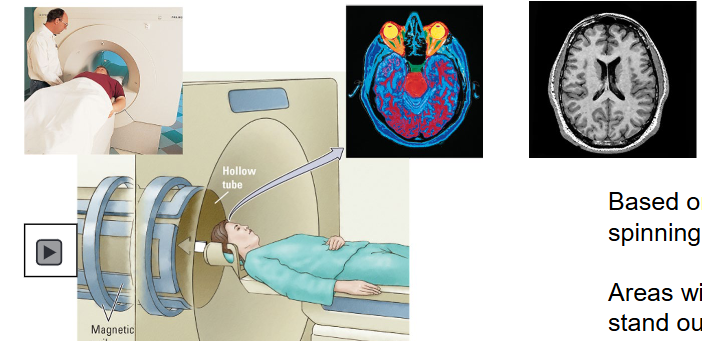
What does the Anatomical Imaging Techniques: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) do?
= magnetic counterpart of CT.
more expensive, slower compared to CT → MRI: 20-40 mins, CT: 5-10 mins.
Low temporal resolution (1-4sec)
High spatial resolution (~1-5mm).
Gives more information about distribution of white and grey matter.
Another disadvantage: subjects must lie motionless in an (extremely) noisy tube for a long time.
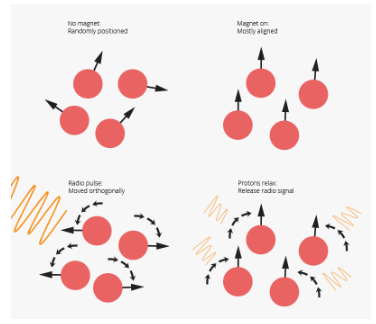
What principle is the Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) based on?
Based on the principle that hydrogen atoms behave like spinning bar magnets in the presence of a magnetic field.
Areas with high water (H2O) content (cell-body rich areas) stand out from areas with low water content (axons).
white matter has less density of H2O so it appears differently from grey matter in the MRI.
Why is it handy that grey and white matter can be distinguished with MRI?
It is appropriate for examining neural tissue.
What does the Anatomical Imaging Techniques: Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) do?
= MRI method that detects the directional movements of water molecules.
Water can move relatively free along the axon but less freely across cell membranes.
Used to create virtual images of nerve fiber tracts in the brain and identify changes in axon myelination (e.g. myelin loss in MS).
Tells you the structure inside the brain??
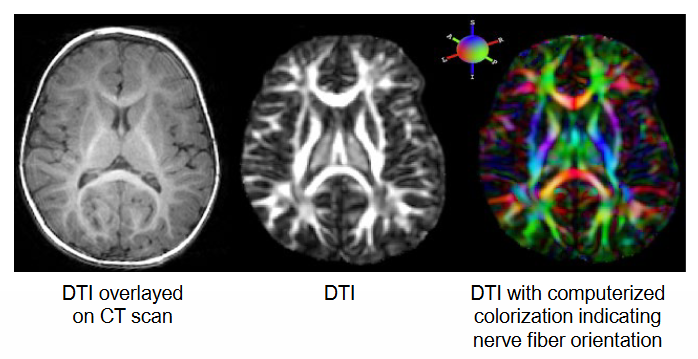
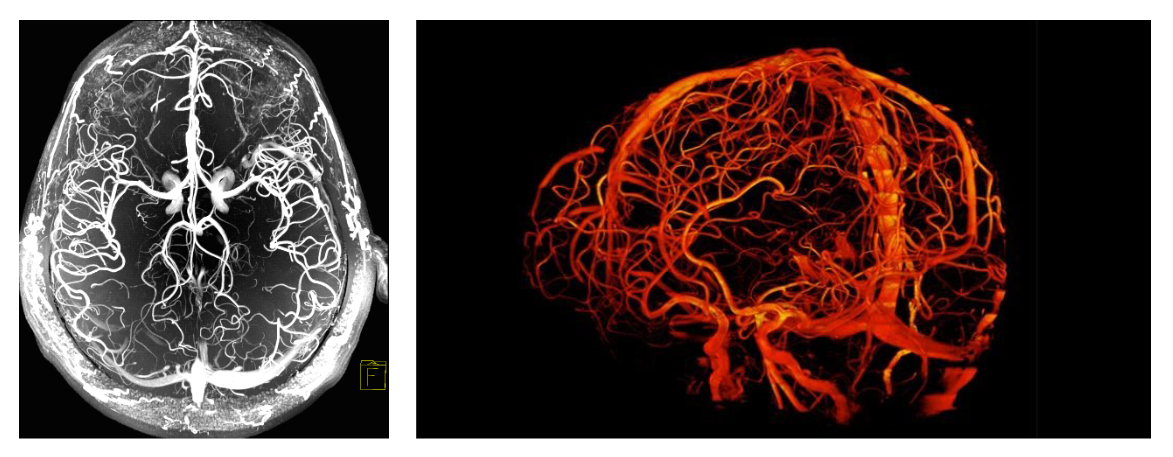
What is the Anatomical Imaging Technique: MRA?
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) = MRI focused on blood vessels.
Image of the blood flow.
What is fMRI?
Functional Imaging Techniques = Functional MRI
Low temporal resolution (~10 sec)
High spatial resolution (~1-5mm)
What does fMRI record and how?
When a brain region is active, the amount of blood, oxygen and glucose flowing to the region increases.
fMRI records changes in brain activity by measuring either blood flow or levels of the blood constituents such as oxygen, glucose and iron.
NB: Oxygen-rich blood is less magnetic than oxygen-poor blood.
Tells you how the brain responds to certain things (ex. visual information) at specific times (time intervals) → similar to ERP.
you measure functional state of the brain (we’re not looking at the structure of brain tissue, but the functions).
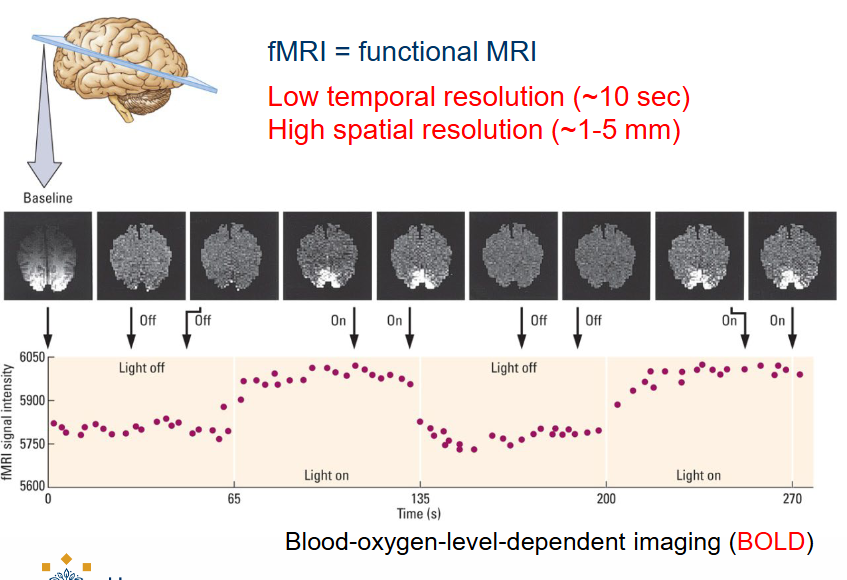
What do you measure in fMRI?
We measure the fuel (blood) that is used by brain activity.
Blood-oxygen-level-dependent imaging (BOLD)
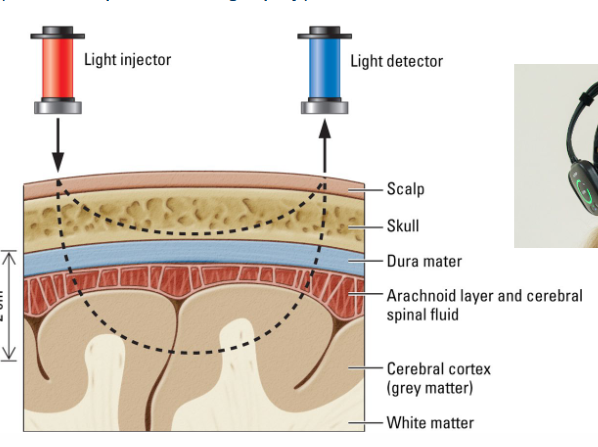
Functional Imaging Techniques: fNIRS; what is it and what are its advantages / disadvantages?
= Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (form of optical tomography).
Good temporal resolution (~100ms)
Fairly high spatial resolution (~1cm)
Main advantage: inexpensive, noninvasive.
Main disadvantage: max. depth ~2cm (so only superficial layers) → light doesn’t traverse the whole brain, just the upper layers.
How does fNIRS work? What does it measure?
Reflected infrared light is used to determine blood flow because oxygen-rich blood and oxygen-poor blood differ in their absorption spectra.
By measuring the blood’s light absorption it is possible to measure the brain’s average cortical oxygen consumption (~like fMRI, but more superficial.
Light is absorbed differently depending on the type of structure.
What is PET?
A Functional Imaging Technique = Positron emission tomography.
Low temporal resolution (~2 mins).
Fairly high spatial resolution (~4-6mm)
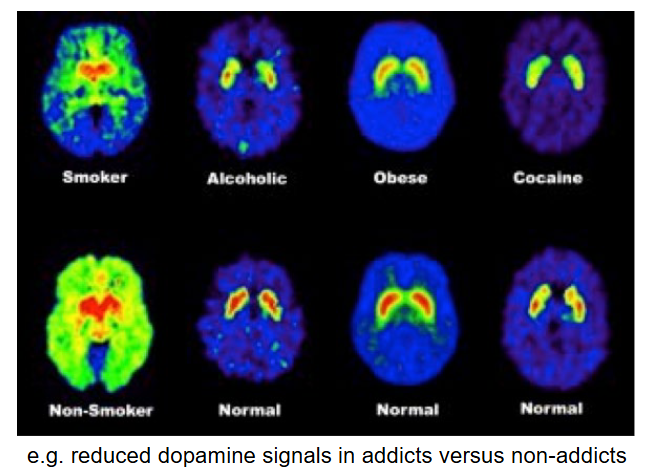
What is PET used for? What is the process of this measurement?
To study metabolic activity (use of neurotransmitters; ex. dopamine) of brain cells by injecting a small amount of water labeled with radioactive molecules into the blood stream.
Radioactive molecules emit positrons, which collide with electrons in brain tissue.
These collisions cause gamma rays to be emitted from the head, which is registered by the PET scanner.
What does PET detect?
It detects changes in the brain’s blood flow by measuring changes in the uptake of compounds such as oxygen, glucose, neurotransmitters, proteins (indirectly measures neural activity).
Often combined with CT, MRI (better imaging) or EEG (better timing).
What is the biggest disadvantage of PET?
It requires preparation of radiochemicals = very expensive.
What temporal resolution & spatial resolution does Simultaneous EEG-fNIRS recordings have?
High temporal resolution (EEG)
Fairly high spatial resolution (fNIRS)
NB: max. depth is ~2 cm so only superficial layers.
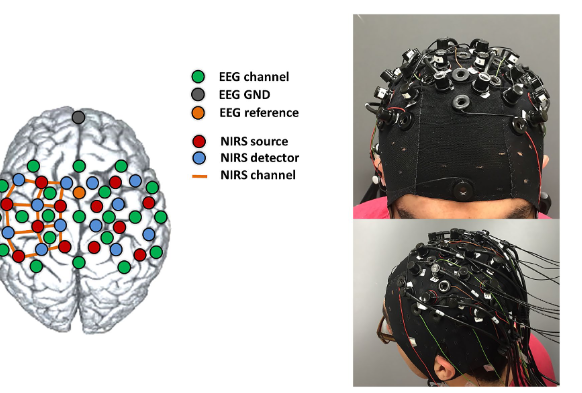
What temporal resolution & spatial resolution does Simultaneous EEG-fMRI recordings have?
High temporal resolution (EEG)
High spatial resolution (fMRI)
Requires MRI compatible EEG amplifiers and electrodes.