Atomic structure
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What happens when electrons absorb electromagnetic radiation
They move to a higher energy level
What is atomic number
This is the number of protons in an atom
What is mass number
This is the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
What are isotopes
These are the atoms of the same element with equal number of protons but different number of neutrons
What is an ion
This is an atom or group of atoms that are electrically charged
What were the findings and conclusions of Rutherford scattering model
atoms are mostly empty space because most of the alpha particles passed straight through the gold foil
The nuclues of the atom is positively charge because a few particles were deflected from their path but continued thought the gold foil
The atoms contain a small heavy nucleus a small number of alpha particles rebounded
What were the features of the nuclear model
nearly all of the mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus
The nucleus is positively charged
Negatively charged electrons orbit the nucleus at a distance
What were the deductions of bohrs model
electrons orbit the nucleus at different distances
The different orbit distances are known as energy levels
when was the neutron discovered
1932 by James Chadwick
What are the differences between the plum pudding and nuclear model
In plum pudding atom is mostly positively charged dough which in nuclear model atom is mostly empty space
In plum pudding negative electrons are distributed throughout the atoms in nuclear model negative electrons orbit the nucleus at a distance
In plum pudding model mass of the atom is evenly distributed but in nuclear model mass is concentrated in the nucleus
What is radioactive decay
a random process that occurs when an unstable atomic nucleus breaks apart or changes, releasing radiation and creating a more stable nucleus
What is activity
This is the rate at which the unstable nuclei from a source of radiation decays
What instruments are used to detect radiation
photographic film changes colour when exposed to radiation
A Geiger-mullet tube
What is count rate
This is the number of decays recorded each second by a detector
What are the types of radiation
alpha
Beta
Gamma
Neutrons
Describe alpha particles
the same as helium nucleus. Two neutrons and two protons
Alpha particles have a charge of +2 this means they can be affected by an electric field
Describe beta particles
they are fast moving electrons
They are produced in nuclei when neutrons changes into a proton and electron
They have a charge of -1 so they can be affected by an electric field
Describe gamma rays
they are electromagnetic waves
They have the highest energy of the different types of electromagnetic waves
They have no charge
Describe neutrons
they have no charge
Found in the nucleus
What are the different properties of nuclear radiation
What are the uses of radiation
producing electricity through nuclear fission
Medical procedures during diagnosis
Testing material
Determine the age of artefacts
Smoke detectors
Checking the thickness of material
How are alpha particles used in smoke detectors
the alpha radiation will normally ionize the air within the detector creating a current
The alpha emitter is blocked when smoke enters the detector
The alarm is triggered by a microchip when the sensor no longer detects alpha particles
Why is alpha particles used in smoke detectors
alpha is the most weakly penetrating and strongest ionizer
Beta and gamma have stronger penetrating power and weaker ionizing power
If beta or gamma were used in this situation then they would pass straight through the smoke and the alarm wouldn’t go off
Therefore since alpha is absorbed by smoke this makes it the most suitable for use
What is half life
This is the amount of time it takes for a number of nuclei of a sample of radioactive isotopes to decrease by half
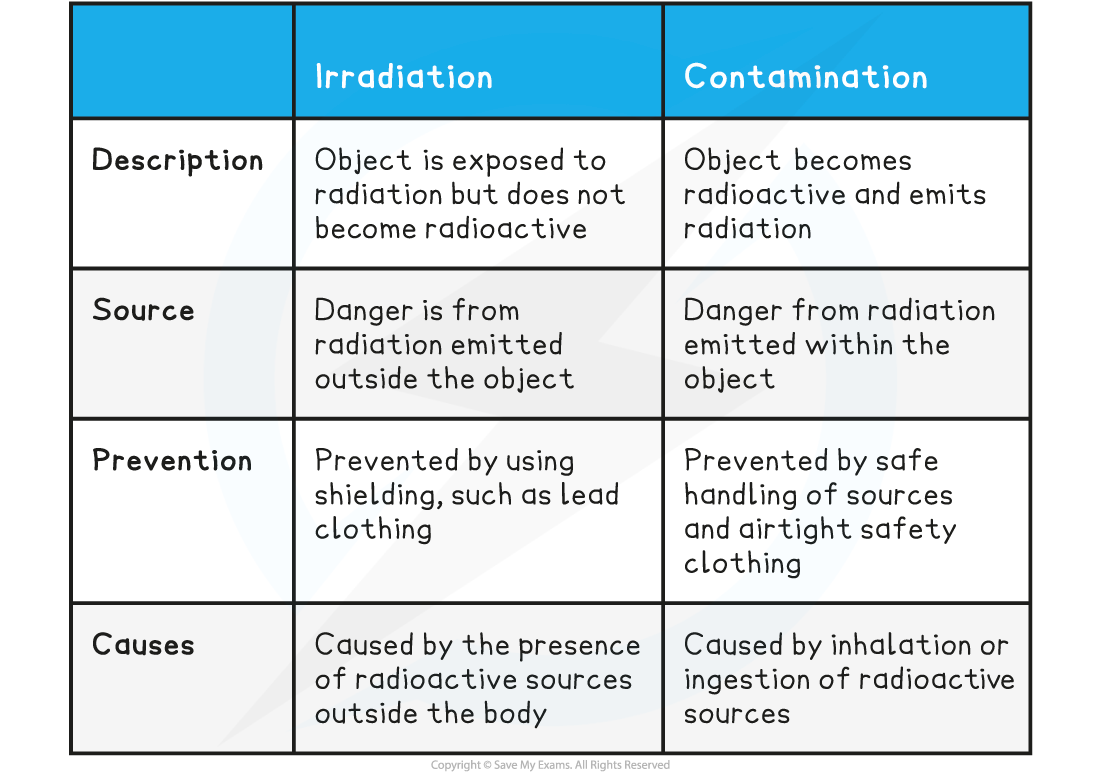
What is contamination
The unwanted presence of materials containing radioactive atoms on other materials
What is the irradiation
This is the process of exposing a material to nuclear radiation the material does not become radioactive
Describe the nature of radioactive decay
Random
Which nuclei decays and when is only determined by chance
It is impossible to determine what nuclei will decay and when
Compare irradiation and contamination
What is background radiation
this is radiation that exists around us all the time
What are the sources of background radiation
natural
Man made sources
What are the natural sources of radiation
rocks
Cosmic rays from space
Foods
What are the man made sources of background radiation
exposure from medical testing
Fallout from nuclear weapons testing
What is becquerels
This measures the amount of radiation emitted by a source every second
What is counts per second
Measures the rate at which radiation hits a particular location
What is sieverts
This measures the received dose of radiation
What are the medical uses of radiation
tracers: used to track the movement of substances- gamma
Radiotherapy- gamma
Sterilizing medical equipment- gamma
What are the risks of nuclear radiation
kill or damage living cells
Cause cancer
Cause mutations
What is nuclear fusion
This is when two light nuclei join to form a heavier nucleus
What is nuclear fission
This is the splitting of a large unstable nucleus into two smaller nuclei
What is a chain reaction
During fission it produces two or three neutrons which move away at high speeds each of these neutrons can start another fission reaction which again creates excess neutrons
Why is nuclear fussion so hard to reproduce
This process requires extremely high temperatures
Why are high temperatures needed for nuclear fission
So two hydrogen nuclei have a repulsive force between them so high temperatures are required to give the nuclei enough energy to overcome the repulsive force
Describe the process of nuclear fission
neutron absorbed by a uranium nucleus nucleus splits into two parts and (2 / 3) neutrons (are released) and gamma rays (are emitted) | ||
What is the advantage of radioactive waste have short half life
activity decreases quickly
Risk of harm decreases quickly