Glycolysis, Acetylcholine, Krebs
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Glycolysis
A metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, producing a net gain of 2 ATP and 2 NADH.
Acetyl-CoA
A molecule formed from pyruvate that enters the Krebs cycle for further energy production.
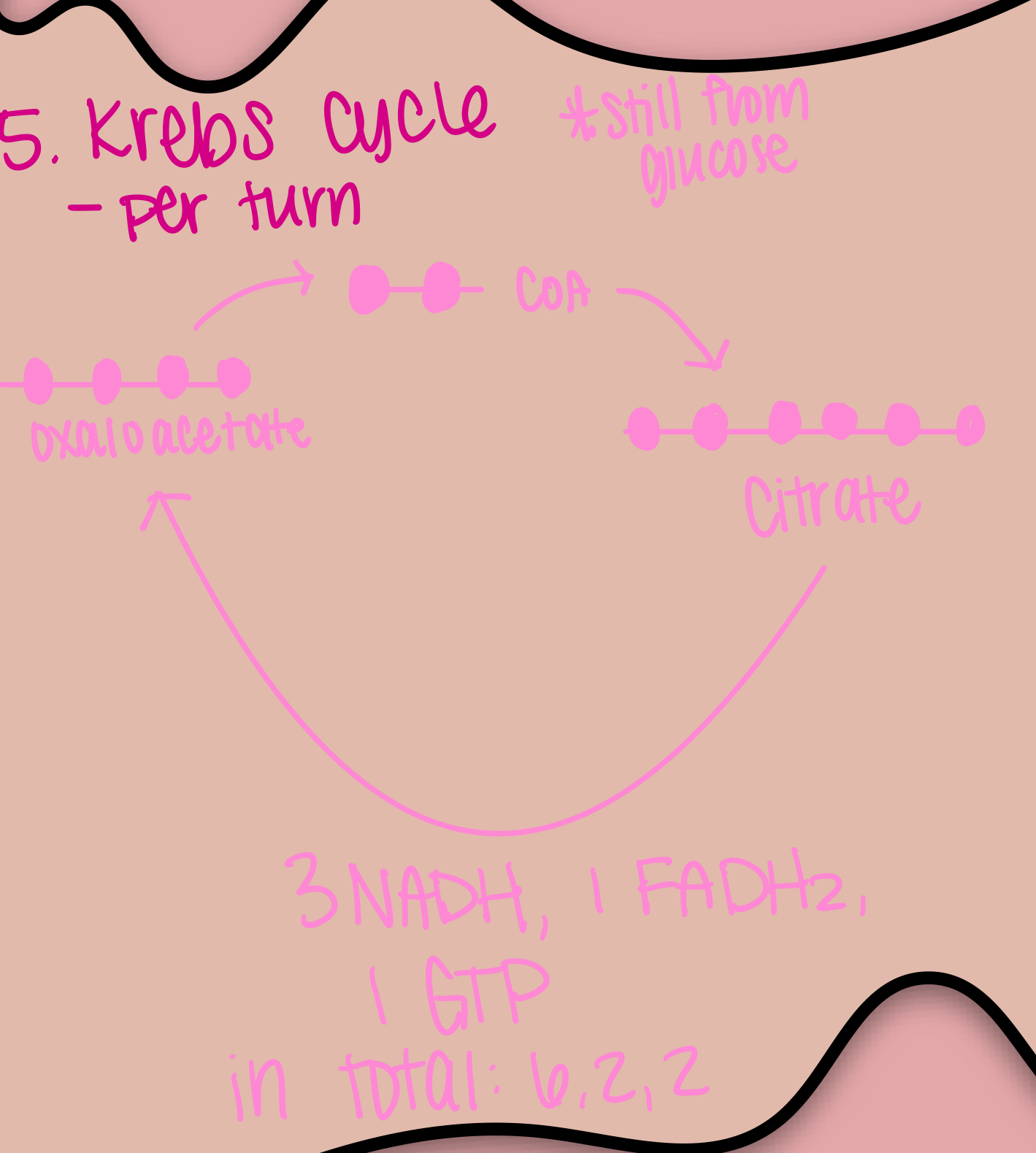
Krebs Cycle
A series of reactions that produce ATP, NADH, FADH2, and CO2 from the oxidation of Acetyl-CoA.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The process in which ATP is produced from ADP using energy derived from electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
ATP Synthase
An enzyme that synthesizes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate, driven by the flow of protons across the mitochondrial membrane.
NADH
A reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, which acts as a carrier of electrons in cellular respiration.
FADH2
A reduced form of flavin adenine dinucleotide, which also serves as an electron carrier in the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
Facilitated diffusion
The process of transporting molecules across a cell membrane via protein channels without the expenditure of energy.
GTP
Guanosine triphosphate, similar to ATP, and can be converted to ATP during the Krebs cycle.
Substrate-level phosphorylation
A metabolic process that generates ATP by directly transferring a phosphate group to ADP from a phosphorylated intermediate.