Lesson 9: Price Controls
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Allocation
involves questions about WHAT goods a society produces and HOW it produces them
Rationing
is concerned with the FOR WHOM question
Why does the questions of allocation and rationing exist?
These questions exist because of scarcity- members of society cannot do everything they would like to do so some options must be chosen at the expense of others
Price system
Rationing system and allocation system
“Market Clearing” Outcome
When prices are unregulated, market forces (S&D) will exert strong and relentless pressure to move the price toward equilibrium. Market is in balance/equilibrium (NO SHORTAGES OR SURPLUSES)
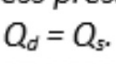
Shortages and Surpluses are
economically inefficient and undesirable
Two Types of Government Price Controls
Price Ceiling
Price Floor
Government Price Controls
Cases where prices are NOT allowed to freely fluctuate according to market prices, but are fixed above or below the market price due to a efficient market not being equitable (fair); prevents the market from reaching the equilibrium price and quantity
Price ceiling
Government regulation that places an UPPER limit on the price at which a particular good/service/resource may be traded (ex. Rent control, gasoline caps)
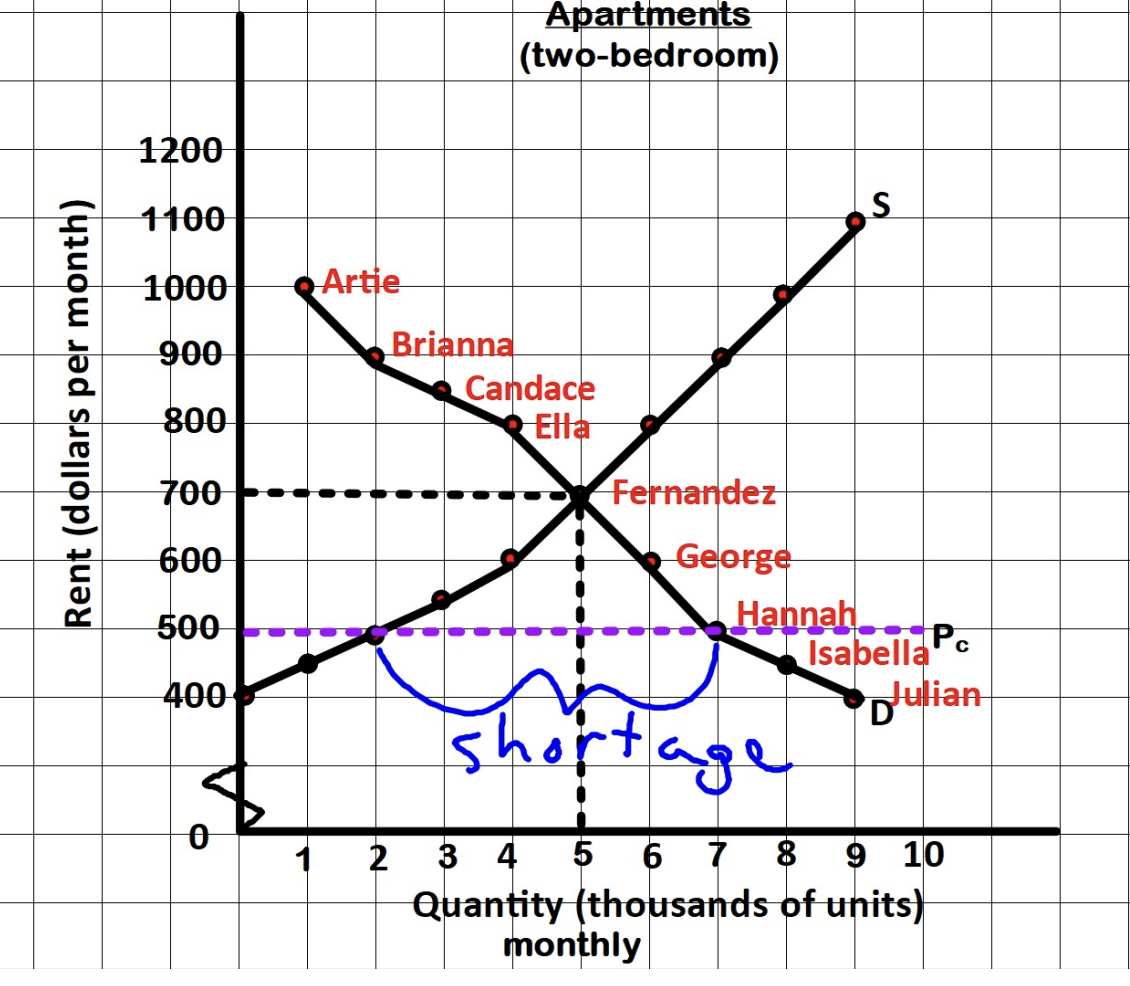
To have any effect, where does the ceiling need to be placed with relation to price?
It must be placed BELOW the equilibrium price (a price above the ceiling is illegal; a price below is NOT)
What is the rationale for a price ceiling?
A price ceiling allows consumers to obtain some “essential” good/service that they could not obtain at the equilibrium price because the price was too high
Costs of a Price Ceiling
1st Effect (problem): Develops a shortage → creates an allocation problem (unequitable distribution of that good/service)
People who want the g/s badly and are willing to pay a high price may NOT be the ones to get the g/s… it may go to someone who’s not even willing to pay the market price
Methods to allocate limited units
Lottery (random selection)
First come, first served
Favoritism/ Personal Attributes
Black Markets
Contest/Competition
Need
Majority Rule (Vote)
Rationing (equal shares)
Tradition
Goal of Rent Controls
Meant to protect low-income families from rising rent prices caused by perceived housing shortages- however they actually create such shortages
intended to make housing affordable to the poor
Economic effect of Rent Control on Demand Side
Quantity Demanded increases and will continue to be high as long as the ceiling is in place and the price is below market
Economic effect of Rent Control on Supply Side
The lower price makes it less appealing to rent units
Short run: owners may leave the market; sell units or convert them to condos
Long run: growth of rental units will remain low and buildings may get rundown as owners neglect them.. could even turn into slums. Investors would rather put their money into real estate without rent controls (ex. office buildings, shopping malls)
Rent controls
disort market signals resulting with misallocated resources- too little resources are being allocated to rental housing and too many are allocated to other uses
Price floor
Government regulation that imposes a LOWER limit on the price at which some good/service/resource may be traded (ex. minimum wage laws; agricultural price supports)
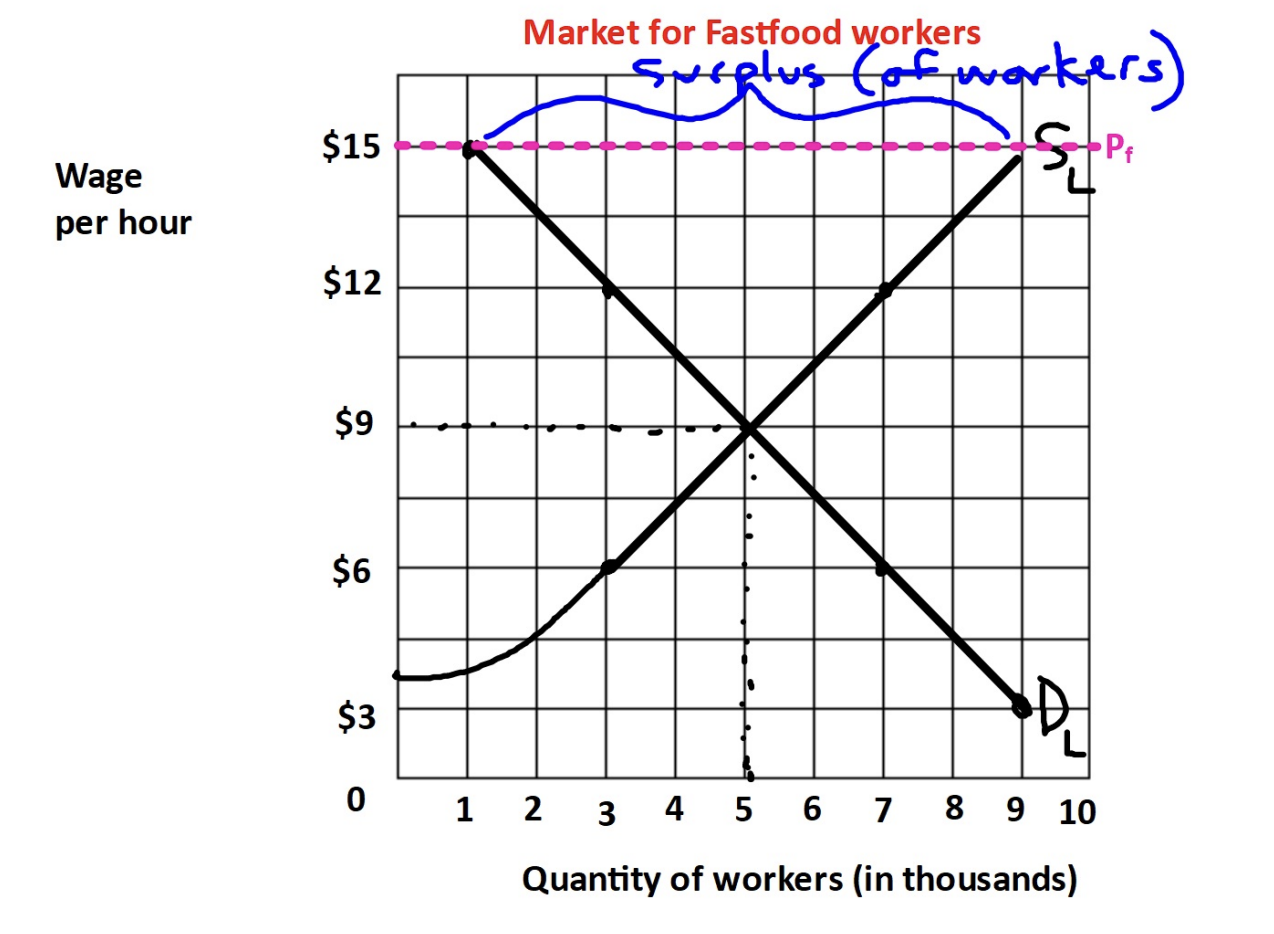
To have any effect, where does the floor need to be placed with relation to price?
It must be set ABOVE the market equilibrium price (price below the floor is illegal; a price above is NOT)
What is the Rationale for a price floor?
To protect the welfare of certain suppliers by maintaining a higher price and thus maintain a sufficient income
Costs of a Price floor
1st effect (problem): a surplus → creates an allocation problem
More quantity supplied than quantity demanded (for labor)- this distorts resource allocation (it’s inefficient)
Goal of minimum wage
to maintain a higher wage so workers have sufficient income
Economic Effects of Minimum Wage
Surplus of workers creates higher unemployment rates
There’s some inflation as employers raise prices to cover additional costs
There’s increased search activity as more people search for work
It may create some discrimination
Black Markets
Effect of Price ceilings
Although theyre usually imposed to help buyers, they only help buyers who are actually able to buy (get) the good at the mandated lower price while hurting any buyer NOT able to get the good due to the shortage, especially if they are willing to pay at market price
Effect of Price floor
Although theyre usually imposed to help sellers, they only help sellers/suppliers who are able to “sell” the g/s or resource at the higher mandated wage while hurting any supplier/seller NOT able to sell the g/s or resource, especially those willing to sell for a low price