ECON 248 16.1 How Fiscal Policy Influences Aggregate Demand
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
The setting of government spending and taxation by government policy makers.
Fiscal Policy
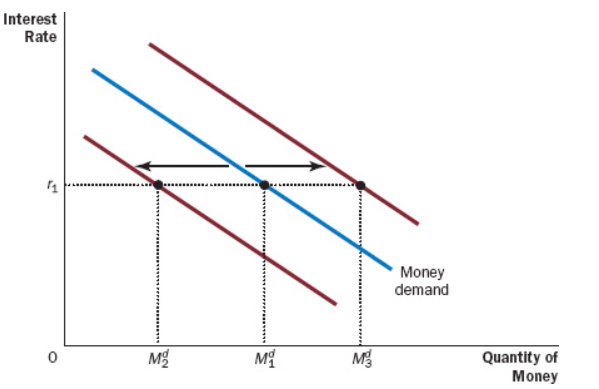
An () in the dollar value of transactions causes the demand for money to shift right and vice versa.
Increase
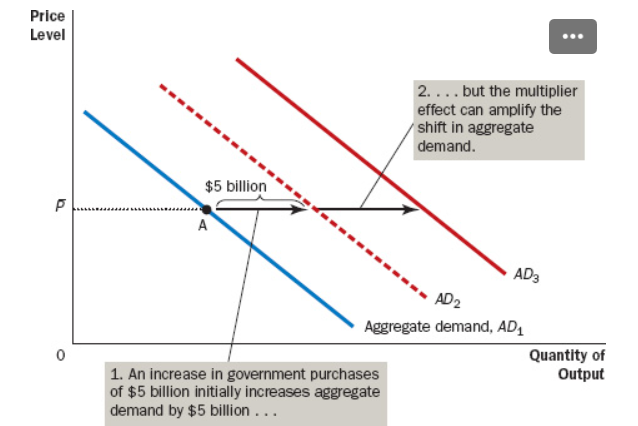
When government spending increases, aggregate demand for goods and services shifts ().
Right
The additional shifts in aggregate demand that result when expansionary fiscal policy increases income and thereby increases consumer spending.
Multiplier Effect
() is a term referring to an increase in investment as a result of an increase in demand for goods and services.
Investment Accelerator
The fraction of extra income a household consumes rather than saves is called the (1). For example, if someone earned 1 dollar and spent 0.75$ of it, then the (1) is ().
Marginal Propensity To Consume(MPC), 3/4
The relevant formula for government purchases in a closed economy is the following:
1/(1-MPC) = Multiplier
The fraction of extra income that a Canadian household spends on imports is called ().
Marginal Propensity To Import(MPI)
The relevant formula for the government-purchases multiplier in an open economy is:
1/(1 - MPC + MPI) = Multiplier
The government purchases multiplier is smaller in a () compared to a (2), since a (2) doesn’t have MPI.
Open Economy, Closed Economy
A high MPC () the multiplier while a high MPI does the opposite.
Increases
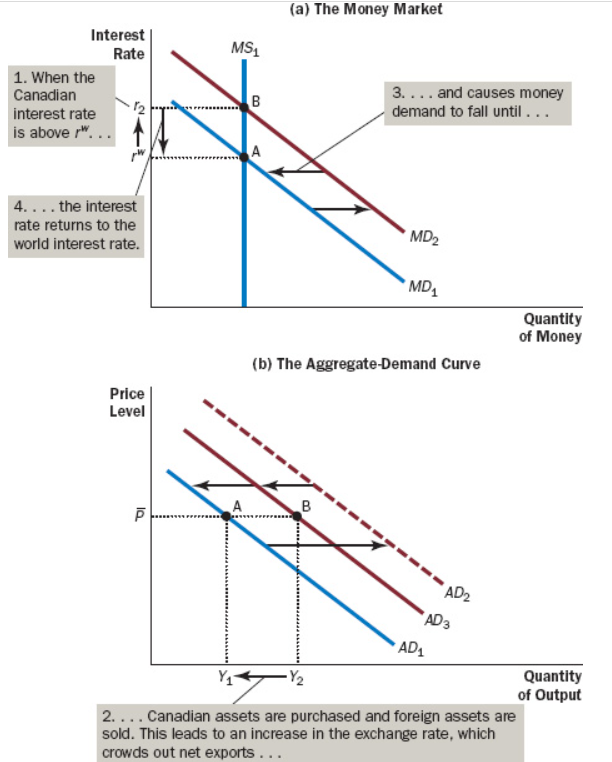
Due to a fiscal expansion, () also increase to keep the expanding demand in check, causing a ().
Interest Rates, Crowding-Out Effect on Investment
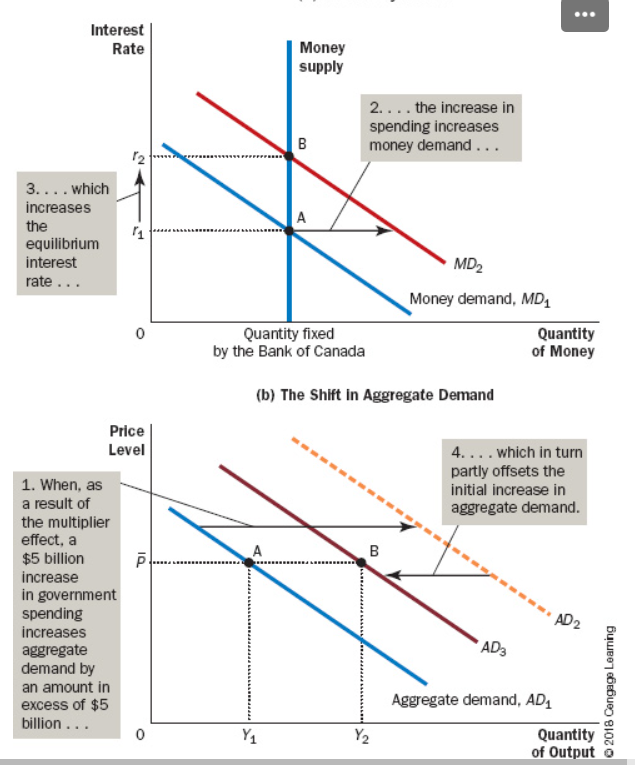
The offset in aggregate demand that results when expansionary fiscal policy in a small open economy with a flexible exchange rate raises the real exchange rate and thereby reduces net exports
Crowding-Out Effect On Net Exports