S3.2.4 Boiling points
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
1
New cards
Factors affecting boiling point of organic compounds
Boiling point is influenced by:
Molar mass
Chain structure (straight vs branched)
Functional group (intermolecular forces)
2
New cards
Effect of molar mass on boiling point
As molar mass increases, boiling point also increases due to stronger intermolecular forces
3
New cards
Why higher molar mass increases boiling point
Larger molecules are more polarizable with more electrons and larger surface area, enhancing London dispersion forces

4
New cards
Boiling point trend in alkanes
Methane to decane show increasing boiling point with increasing molar mass due to stronger dispersion forces
5
New cards
Why branched isomers have lower boiling points
Branched isomers have lower boiling points than straight chain isomers with the same formula
Branches reduce surface contact area between molecules, weakening London dispersion forces
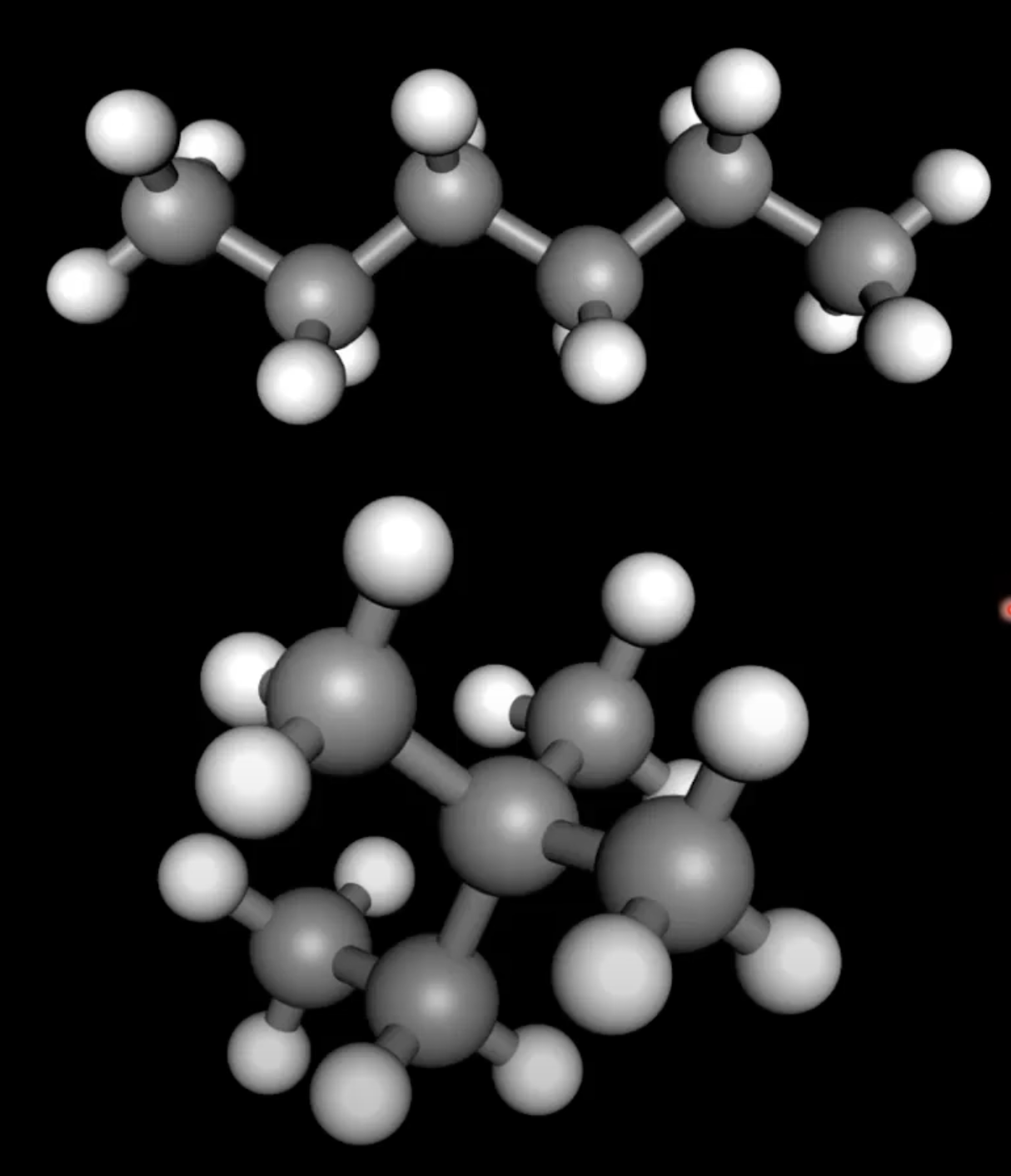
6
New cards
Effect of functional group on boiling point
Functional groups affect intermolecular forces
Stronger forces mean higher boiling points
7
New cards
Boiling point comparison: alcohols vs alkanes
Butan-1-ol (with hydrogen bonding) has a higher boiling point than pentane (only dispersion forces)
8
New cards
Functional groups with hydrogen bonding
Alcohols, amides, carboxylic acids can form hydrogen bonds, raising boiling point
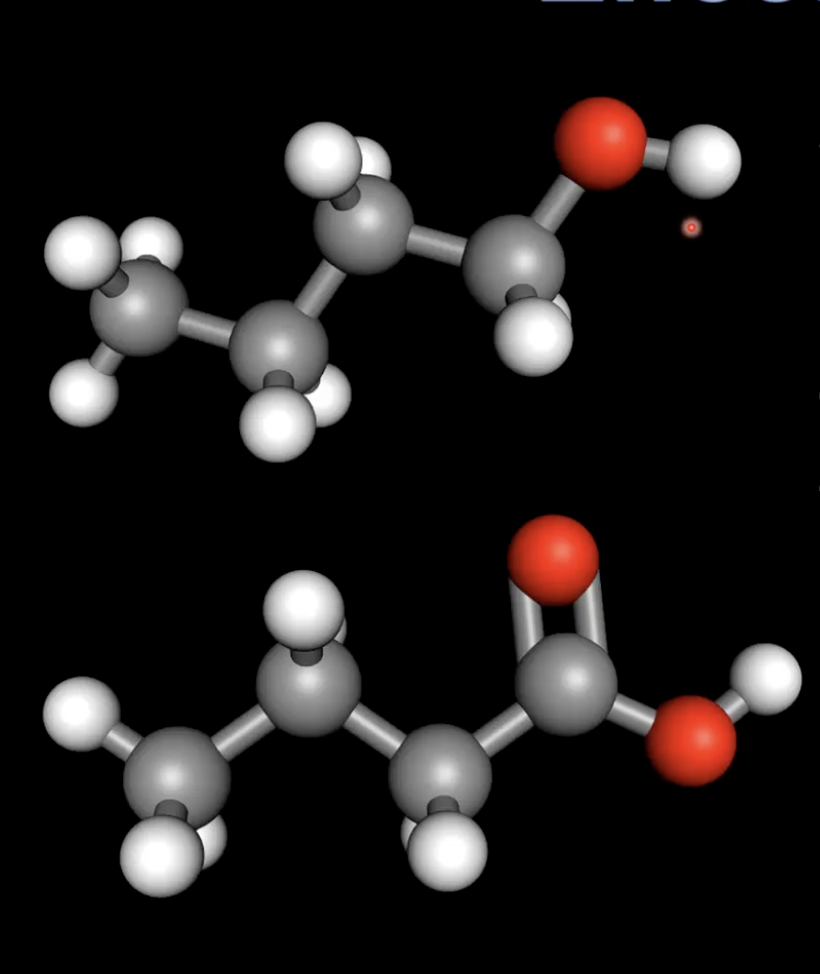
9
New cards
Functional groups with dipole-dipole forces
Aldehydes, ketones, esters have dipole-dipole forces, weaker than hydrogen bonding
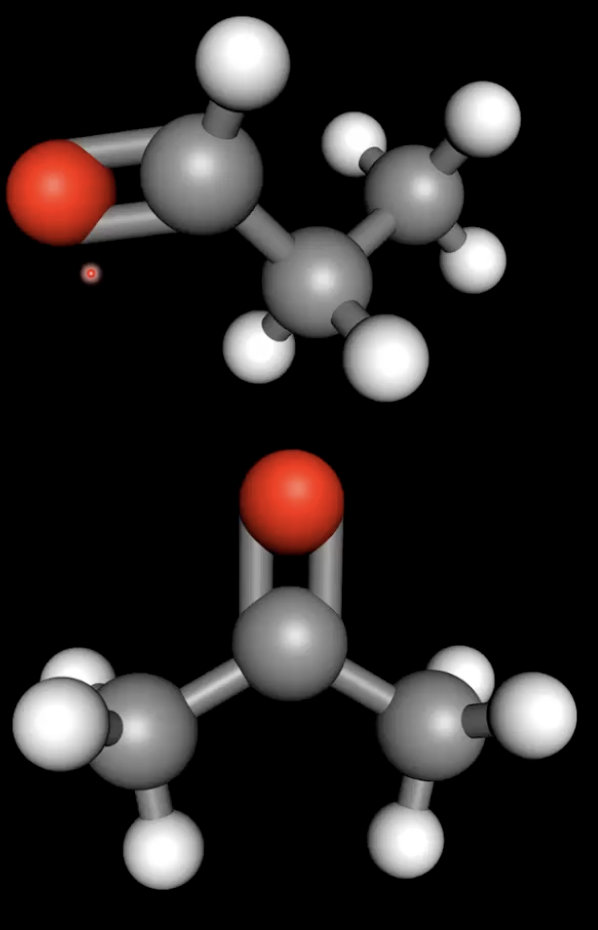
10
New cards
Functional groups with only London dispersion forces
Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes are nonpolar and rely only on weak London dispersion forces
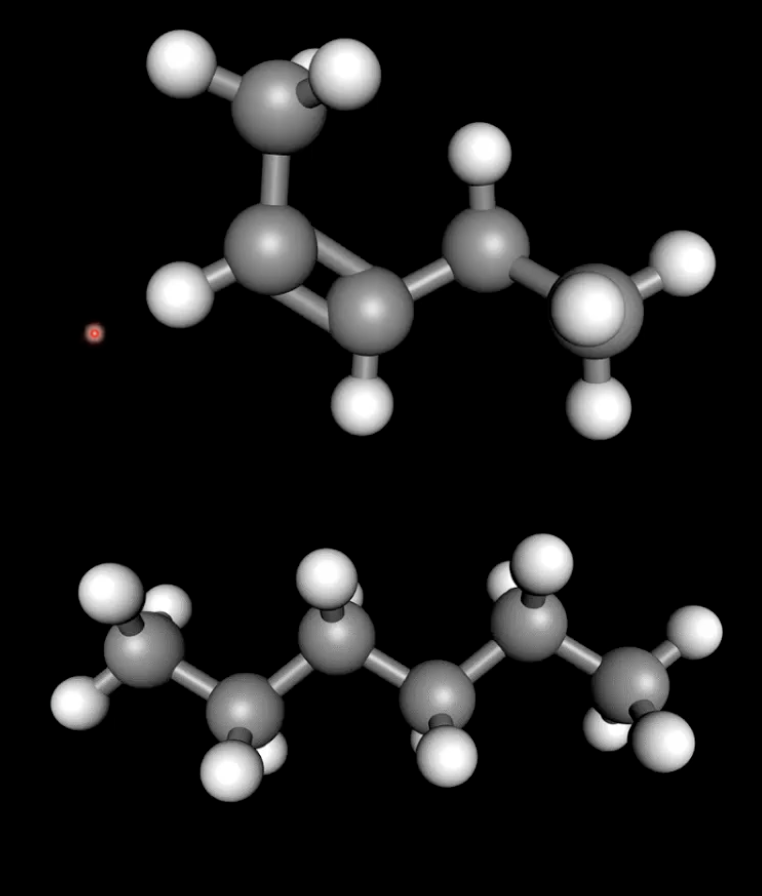
11
New cards
Ranking organic compounds by boiling point
From lowest to highest boiling point:
alkanes/alkenes/alkynes < ketones/esters < alcohols/amides