lec 18. Malignant Tumors
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
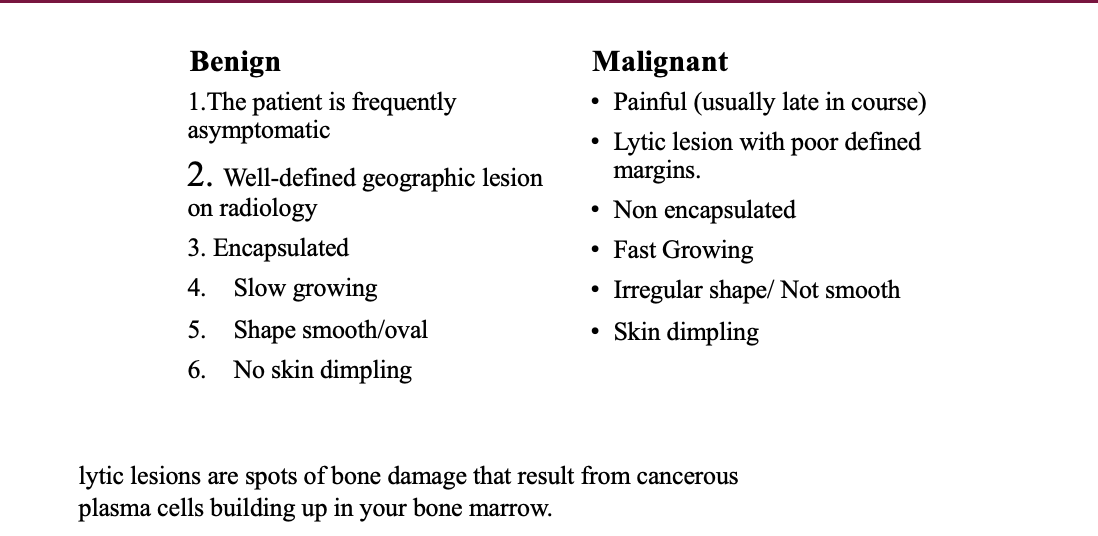
benign vs malignant

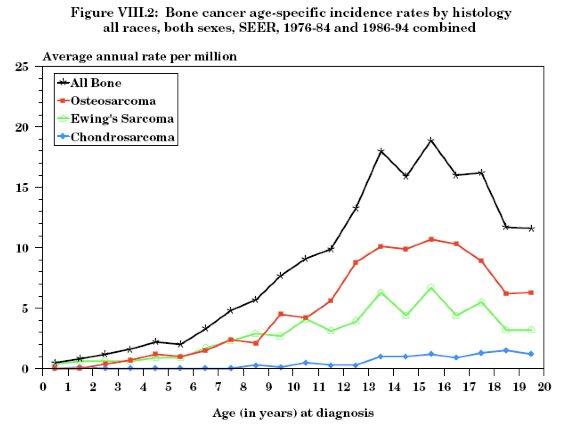
Age Distribution for bone cancer —peaks?
highest between 13 and 18 years
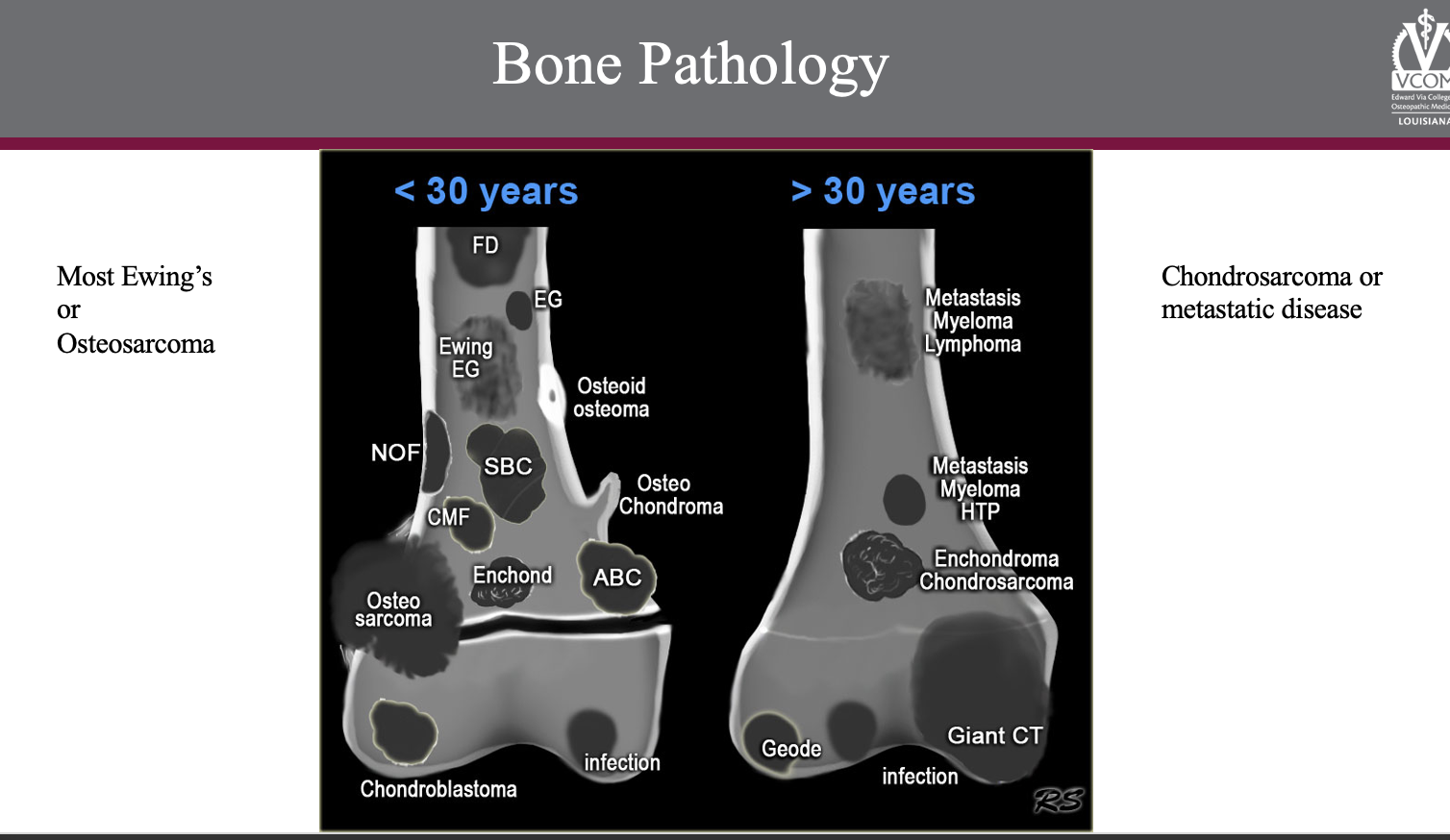
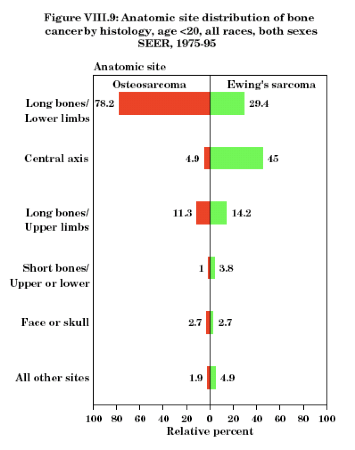
where is bone cancer mostly likely to be found?
central axis or long bones
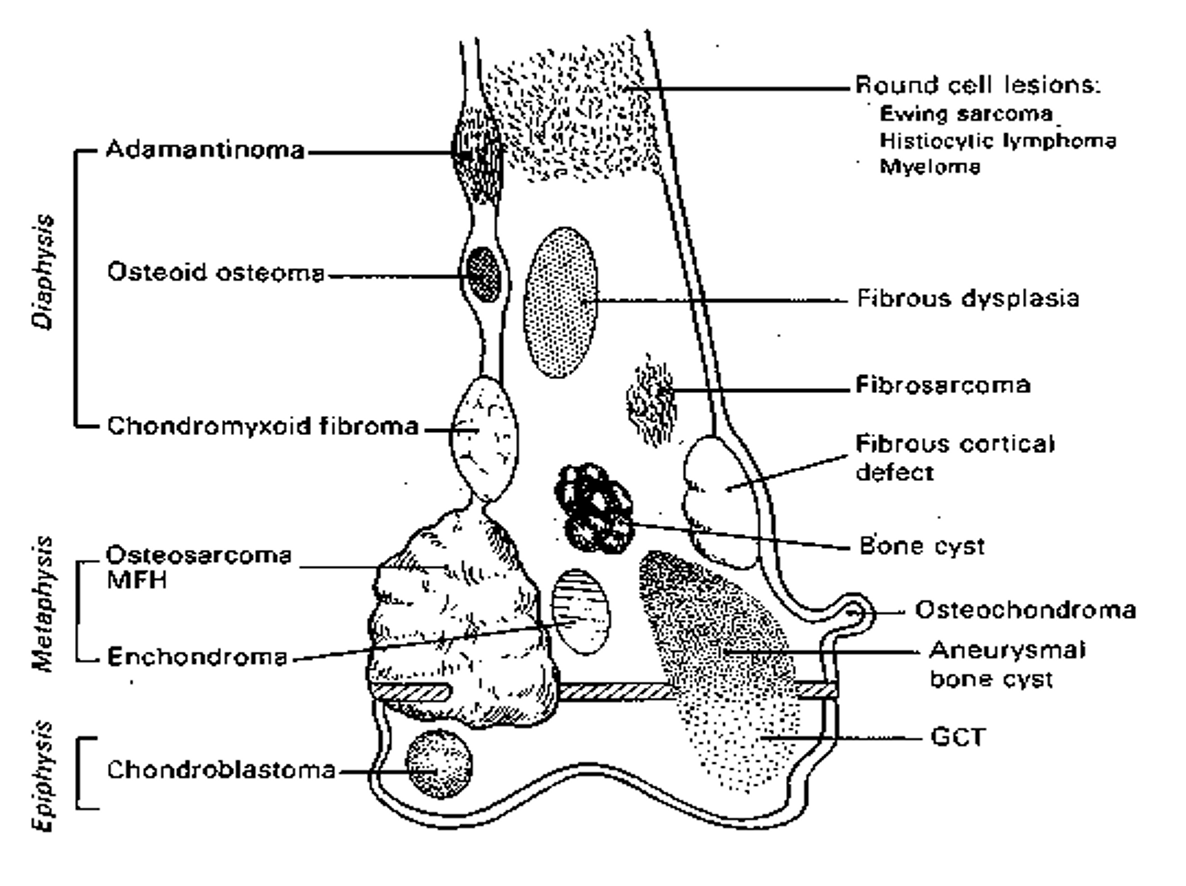
Sarcoma Cellular Genesis/ Histology
Osteosarcoma Clinical Presentation
what do we see in primary?
what do we see on plain films?
Painful swelling around the knee (and sometime humerus),
RARE: joint effusion or ROM problems
Night pain and limping
Firm/soft mass fixed to underlying bone
Serum alkaline phosphatase (bone fraction) elevated
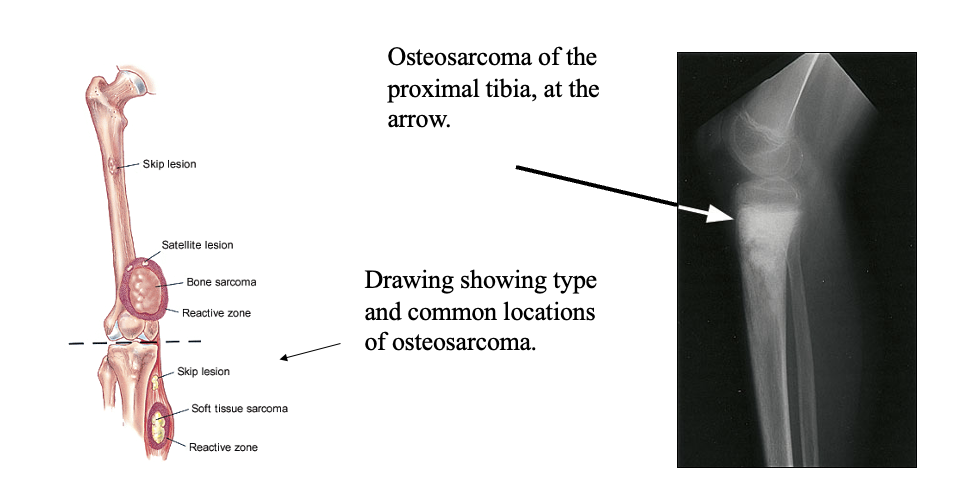
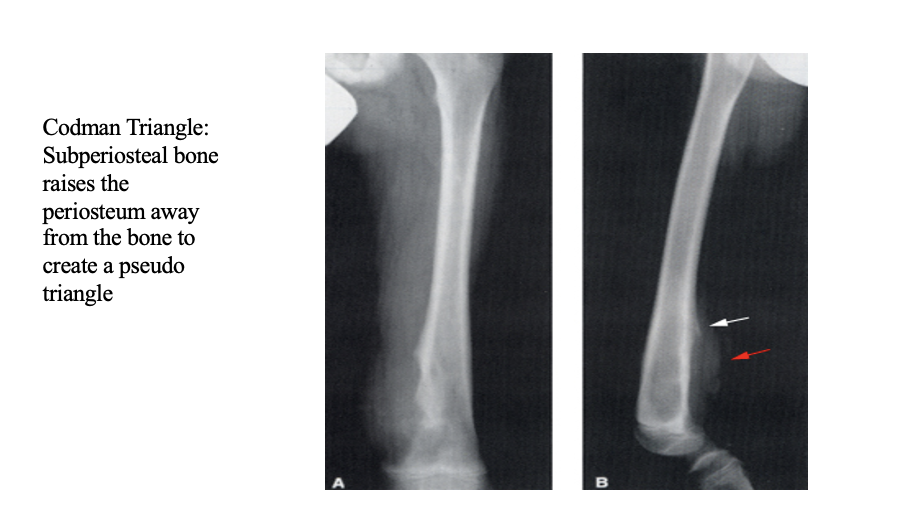
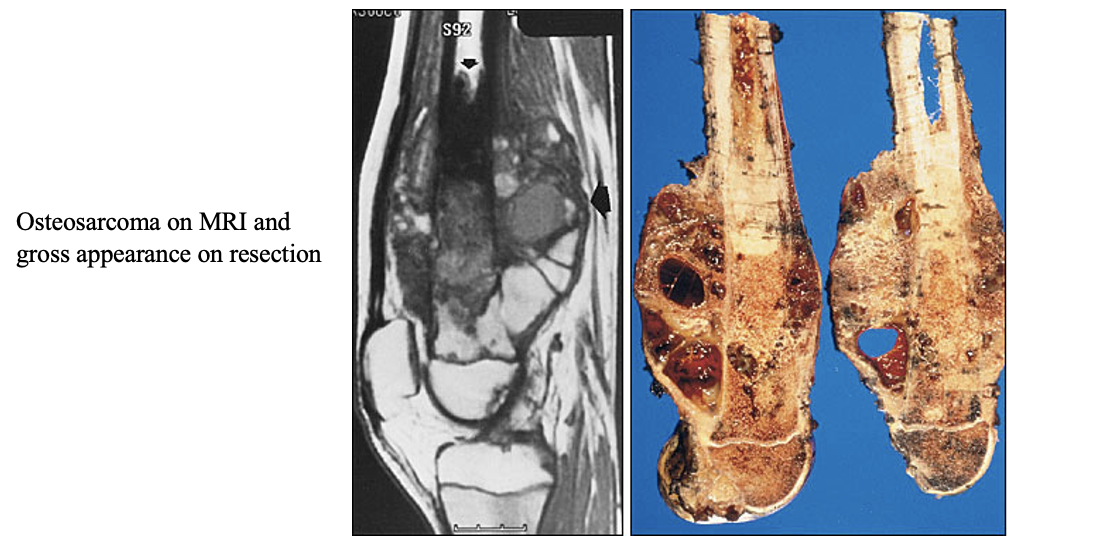
Osteosarcoma Clinical Presentation
secondary usually affects what age group and previous of what disease?
Usually in individuals > 40
Area of previous Paget’s or radiotherapy
Osteosarcoma — PROGNOSIS STATS?
~20% survived 5 years before chemotherapy era
60-70% five-year survival currently
Limb-sparing in 80%+ currently
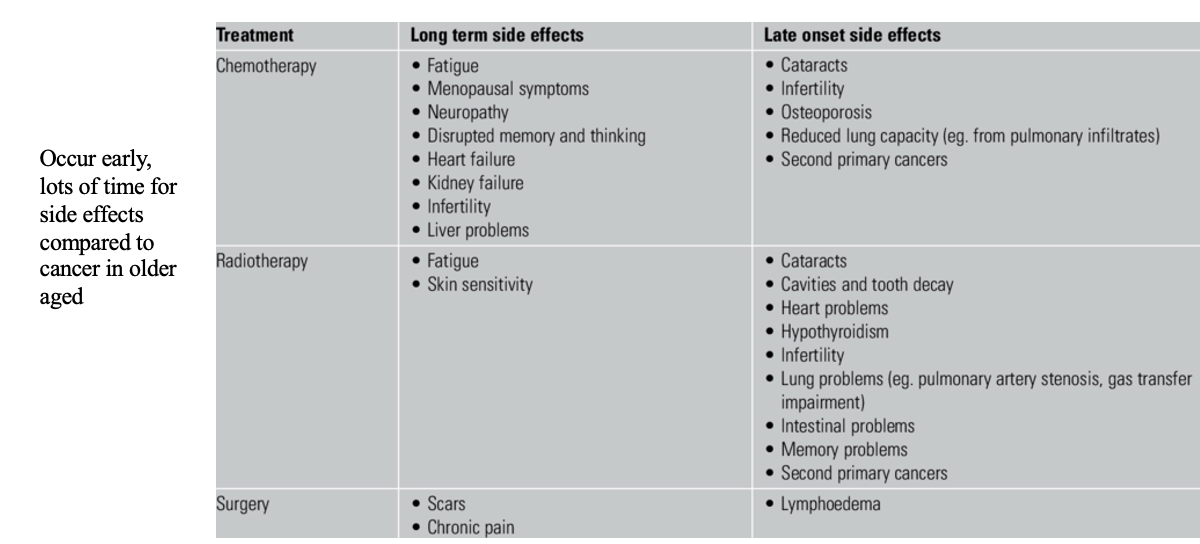
what are the main Long term morbidities from chemotherapy (3)
Heart disease
Second cancers
Early menopause and infertility
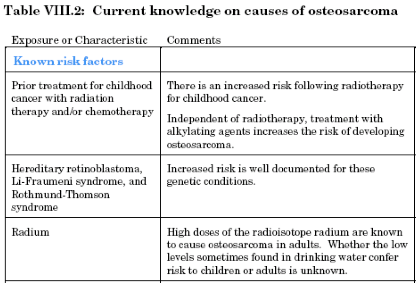
Risk Factors Osteosarcoma
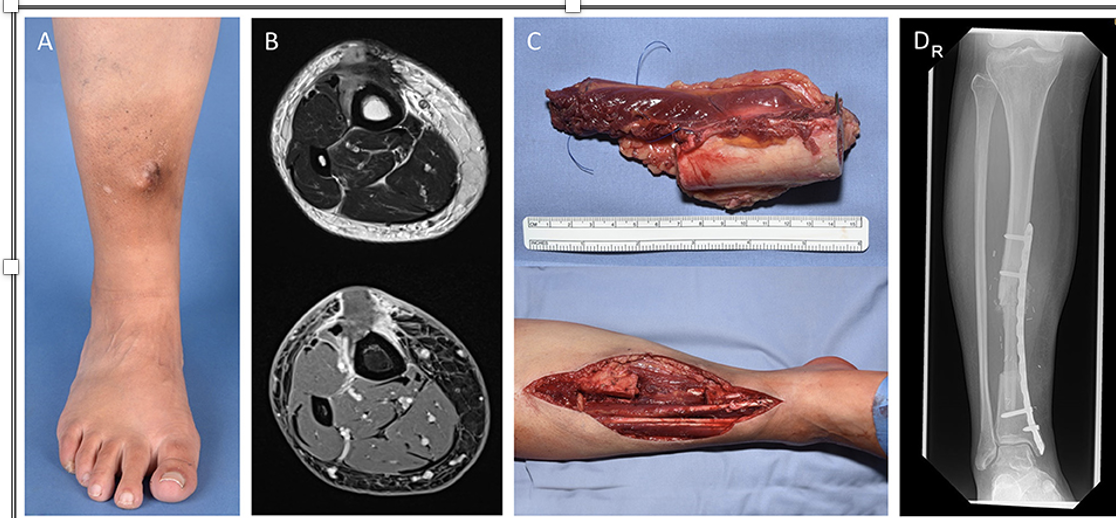
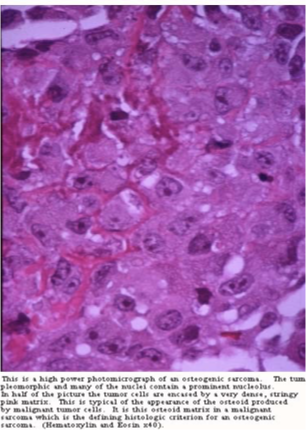
Osteosarcoma
CASE STUDY: 15 YO MALE, KNEE PAIN 15-year-old African American male notices pain in his left knee during gym class
Pain is associated with redness, warmth, tenderness and swelling
Pain is worse at night
ROM of his knee is normal and not tender
RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) is employed w/ some improvement
Over the next several days he begins to limp and have progressively more pain and swelling
A mass is palpable in the lateral aspect of the distal femur
He sees the school nurse who recommends he see a physician
His mother had breast cancer at age 33
You order a plain film and MRI
WHAT DO YOU DO FIRST (after work up)?
DX?
TREATMENT? — long term effects??
refer him immediately to an orthopedic (Ped) oncologist
An orthopedic surgeon trained in removal of tumors and reconstructive surgery
tx:
referred to a pediatric oncologist
to begin neoadjuvant (before surgery) chemotherapy {to try and select him into limb sparing}
He begins treatment with cisplatin/Adriamycin and high dose methotrexate [Chemotherapy]
After several weeks limb-sparing surgery is performed
OUTCOME: 5 years later he is doing well without recurrence
CASE STUDY: 15 YO MALE, KNEE PAIN 15-year-old African American male notices pain in his left knee during gym class
Pain is associated with redness, warmth, tenderness and swelling
Pain is worse at night
ROM of his knee is normal and not tender
RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) is employed w/ some improvement
Over the next several days he begins to limp and have progressively more pain and swelling
A mass is palpable in the lateral aspect of the distal femur
He sees the school nurse who recommends he see a physician
His mother had breast cancer at age 33
WHATS YOUR WORKUP?
Radiographic studies —> possible osteosarcoma
MRI shows neurovascular structures involved – precluding (Limb sparing) surgery
CT chest shows no lung metastases
Bone scan shows no skip lesions
Orthopedic oncology does an open biopsy
labs: Alkaline phosphatase is elevated
Presents similar to osteosarcoma
Pain and constitutional symptoms (mimics osteomyelitis)
Metastatic disease in 25% at presentation —> Lungs, Bone, Bone marrow
Ewing’s Sarcoma
(more common in white people)
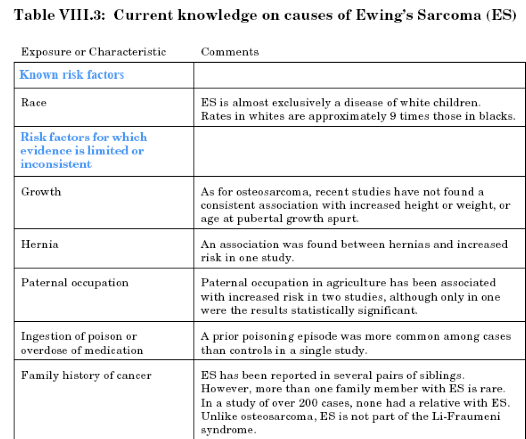
“Onion Skinning”
is seen in?
Plain film Ewing’s Sarcoma
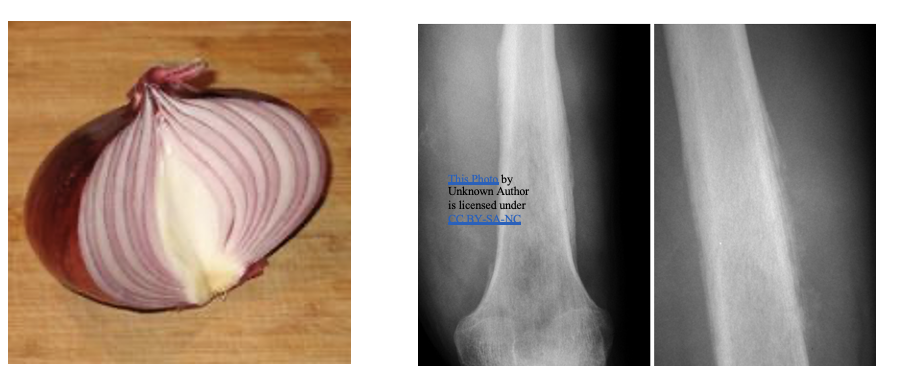
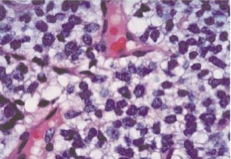
Ewing’s Sarcoma
CASE 2: 19YO F, PAIN IN FOOT
HISTORY:
19-year-old white female college student has pain in her foot presents to student health with small nodule seen over her metatarsal on the plantar side. Diagnosed with plantar fasciitis and given stretching exercises.
Pain worsens, especially at night
Develops low grade fevers, malaise and anorexia
Returns to student health for further evaluation
Plantar nodule is larger(enlarged quickly) and tender to touch
No purulence is expressed, nor is there lymphadenitis
Temperature is normal
workup:
No recent trauma, No neurologic diseases
Individuals with neuropathy cannot feel trauma/puncture wounds as well
Xray's show moth eaten appearance to 2nd metatarsal
MRI shows possible osteomyelitis
Referral to orthopedic surgeon is made
imaging:
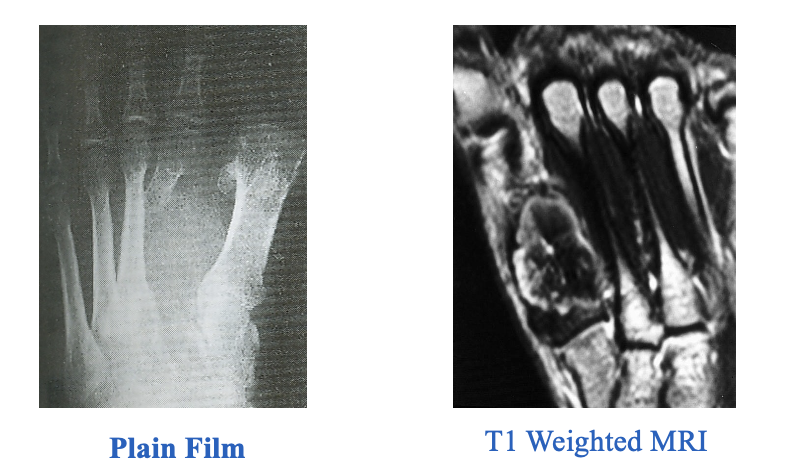
biopsy:
Area of radiographic abnormality is curetted
Wound Culture is negative
Pathology shows Ewing’s sarcoma
Serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is high
TREATMENT:
She undergoes radiation to the site
Pain improves
F/U films show remission
Staging CT Chest is negative for metastatic disease
Bone scan is negative for metastatic disease
OUTCOME:
She is lost to follow up for 2-3 years
After graduation she develops dry cough and progressive dyspnea
She also has progressive back pain
She presents to urgent care and sees you
What tests would you order?
To whom would you refer her?
1st —> imaging
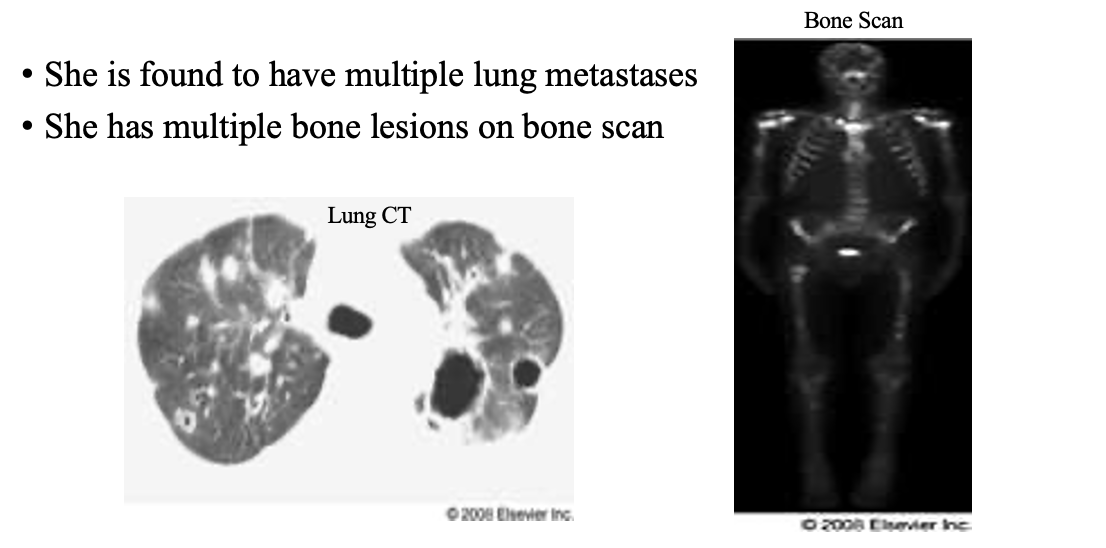
treatment:

top 3 places Distribution Chondrosarcoma
is located at?
pelvis > femur > shoulder
Epidemiology (Chondrosarcoma)
Slight male to female predominance
Children fare worse than adults
Peripheral lesions lower grade than central
5-year survival is ~50%
Tumor grade has largest impact on survival (stages)
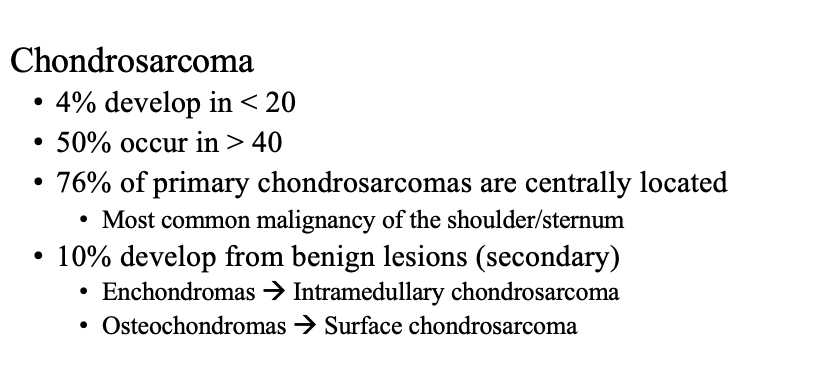
50% of chondrosacarcomas are in what age group?
>40 years
what is this tumor?
Pain is related to location of mass lesion, typically in the shoulder
Previous site of enchondroma
Suspect if tumor involves shoulder/sternum**
Rapid expansion suggests higher grade or de-differentiation(=malignant transformation)
Chondrosarcoma
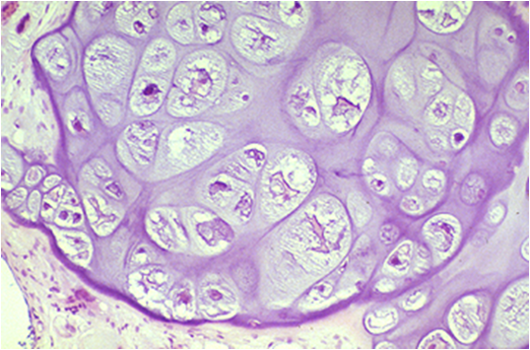
case 3
history:

image
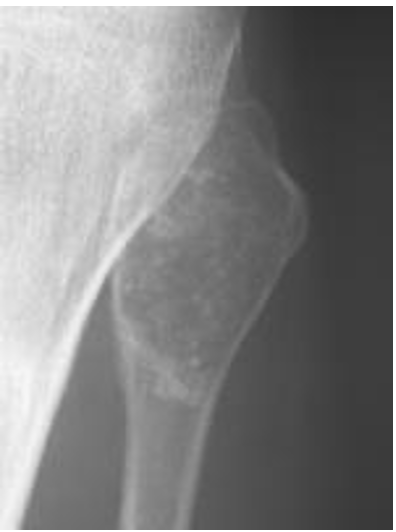
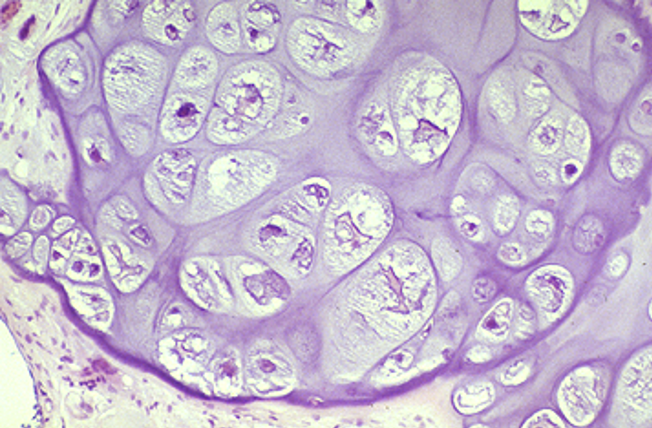
result:
You refer him to an orthopedic oncologist
Needle biopsy (diagnostic) confirms suspected chondrosarcoma
Humerus is resected and replaced with titanium implant
images Evaluation of Bone Malignancies
x rays are for
Anterior-Posterior and orthogonal views
images Evaluation of Bone Malignancies
CT is used for?
Small cortical lesions
Lung Windows (metastases)
images Evaluation of Bone Malignancies
Angiogram is used for?
Used to image vascular structures
Helps determine resect ability
images Evaluation of Bone Malignancies
Magnetic Resonance (MRI) used for
Gold standard for work up
Soft tissue and bony structures
Neurovascular bundle à “resect ability”
images Evaluation of Bone Malignancies
Bone Scintigraphy (Scan) used for?
“Skip” Metastases
Determines margins
Misses –lytic lesions
gold standard image for bone cancer
MRI
General Treatment Principles for bone cancer
try to save the limb
Need good margins
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy +/ -radiation therapy, if primary resection difficult
have a diverse team
idisciplinary and tertiary/university-based team
Surgeons, Radiation Oncologists, and Medical Oncologists
Physical Therapy/Occupational Therapy (PT/OT)
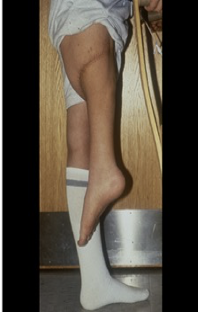
what type of reconstruction is this?
Rotationplasty
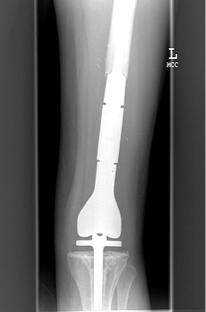
what type of reconstruction is this?
Endoprosthesis
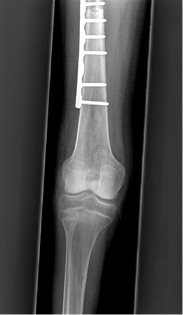
what type of reconstruction is this?
Allograft
3 forms of reconstruction are?
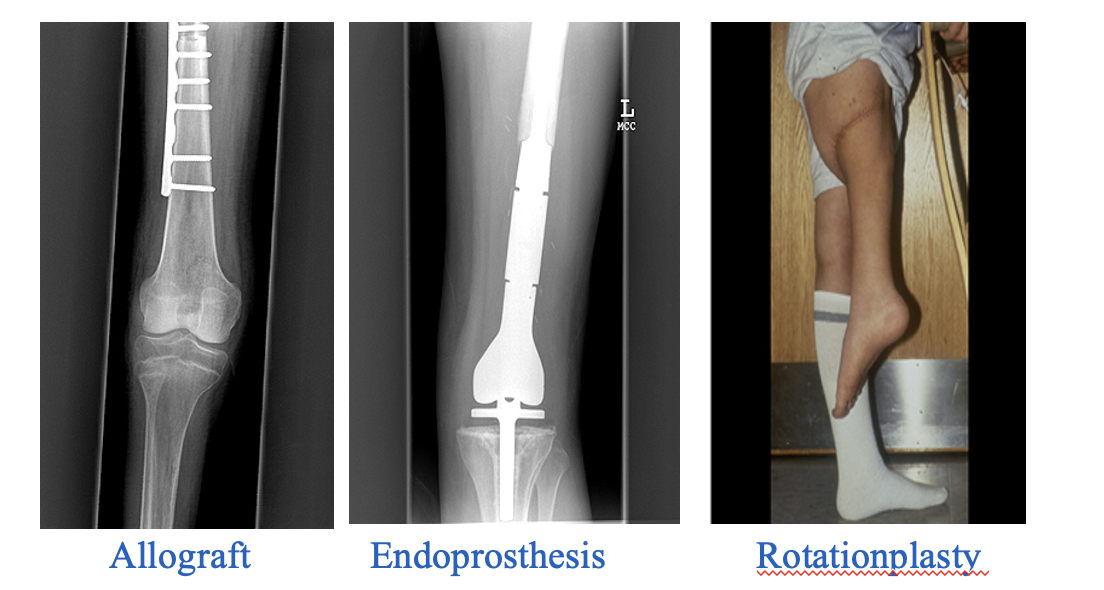
treatment
Generally, radio-resistant & Chemo-sensitive
Osteosarcoma
treatment
Radio- and chemo-sensitive
Ewing’s sarcoma
treatment
Radio- and chemo-resistant typically
Chondrosarcoma
Axial (axial skeleton) lesions problematic to resect with __________?
Intraoperative Radiation Therapy
Proton beam therapy
good margins
Less than 1% of malignancies involve mesenchymal tissue
Over 50 histopathologic subtypes
75% involve the limbs
Can originate from muscular, vascular, adipocytic (fat), or other connective tissue elements
examples:
Myosarcoma
Angiosarcoma
Liposarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Soft Tissue Sarcoma
case 4
history:

PE:
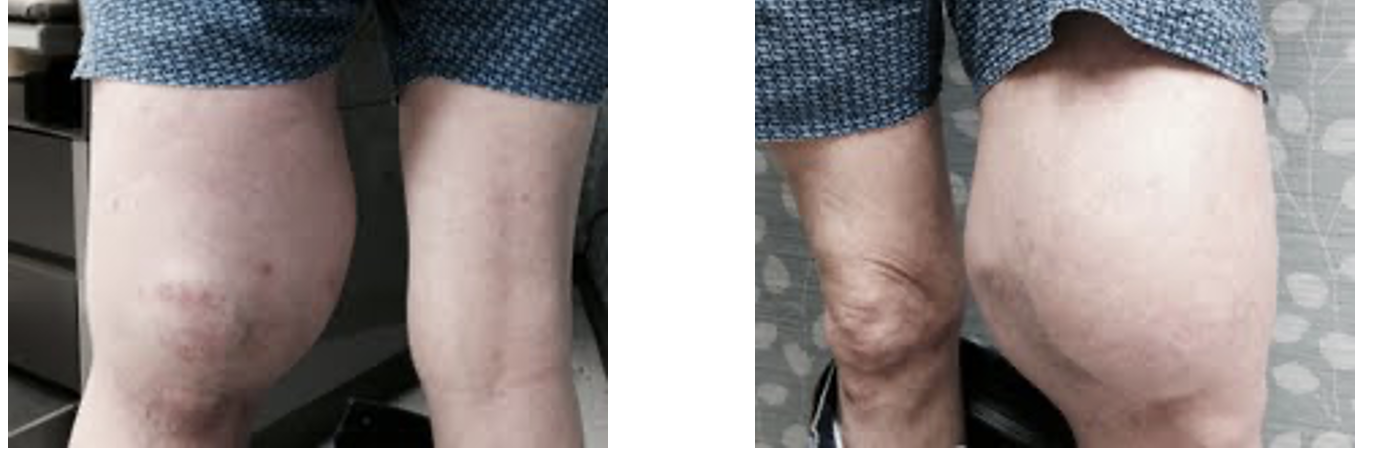
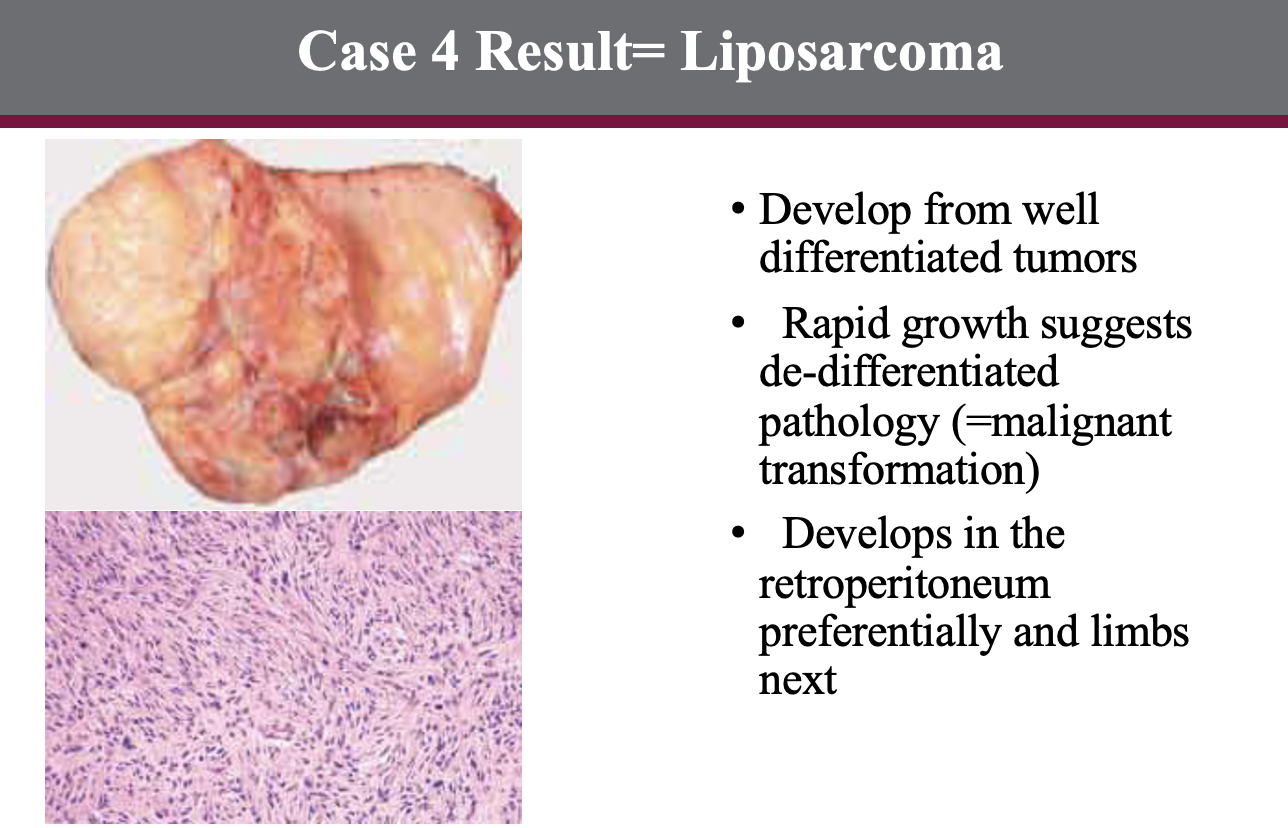
RESULT?
treatment:

case 5
history :

image:
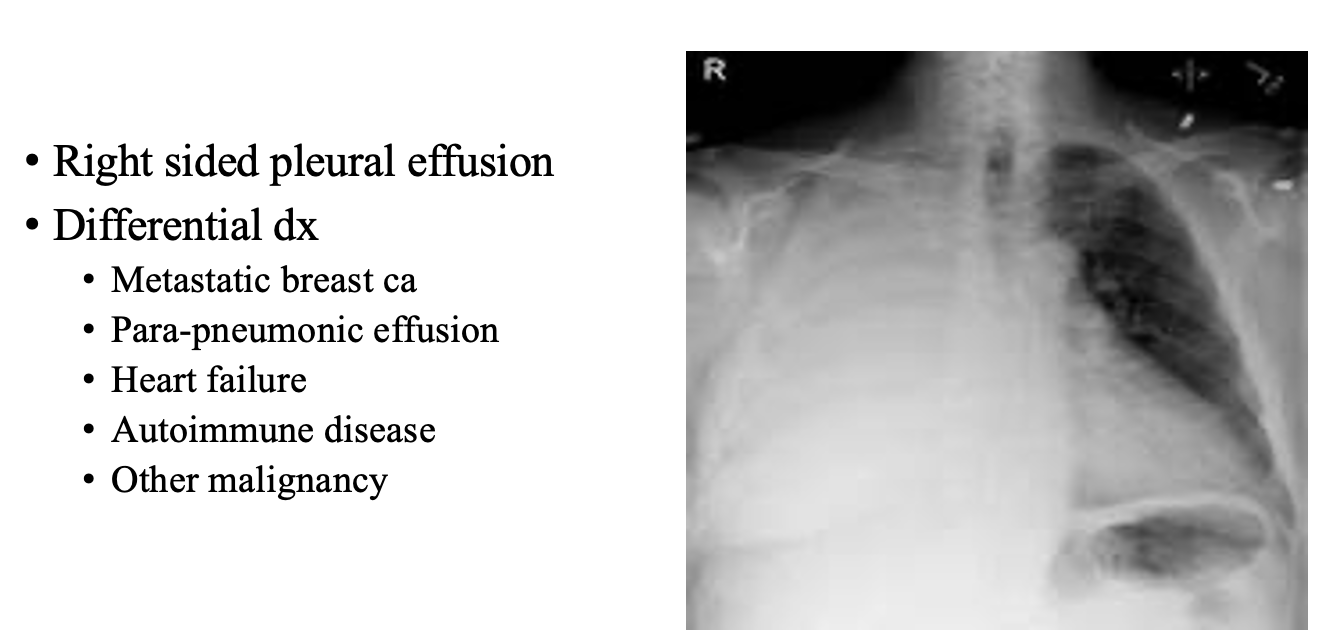
DX?
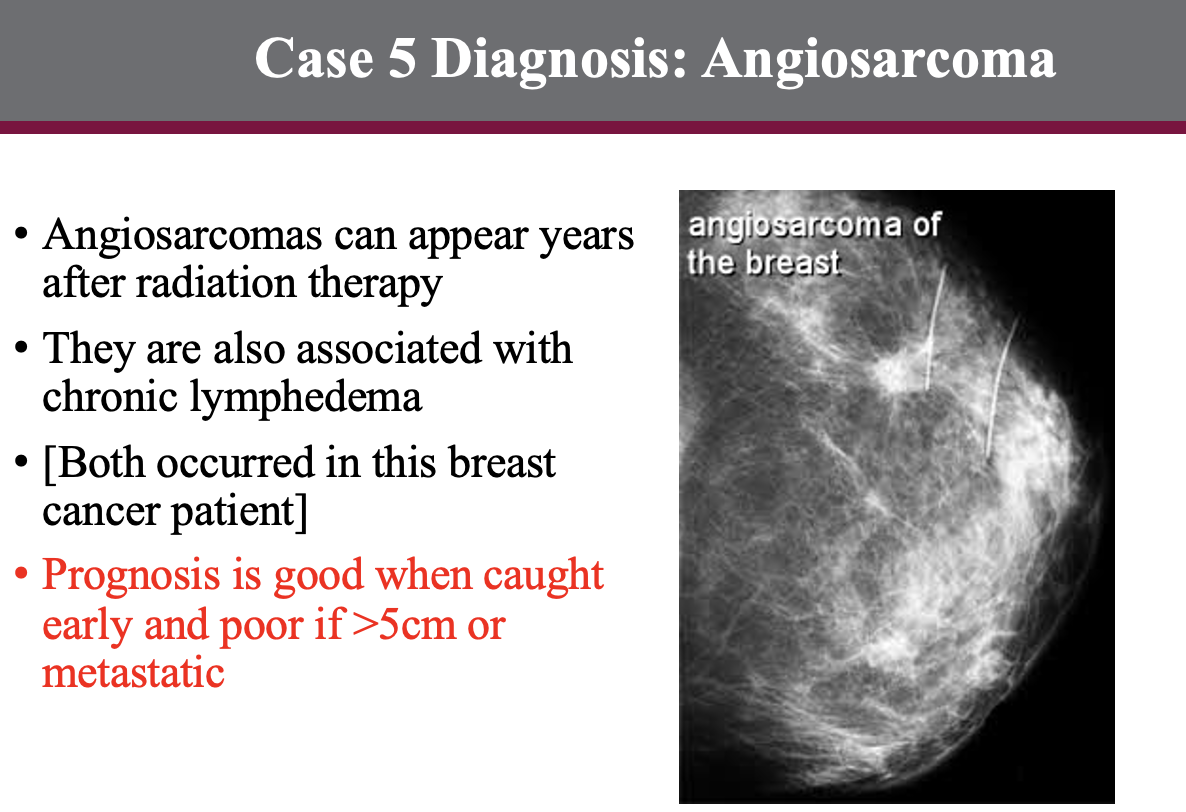
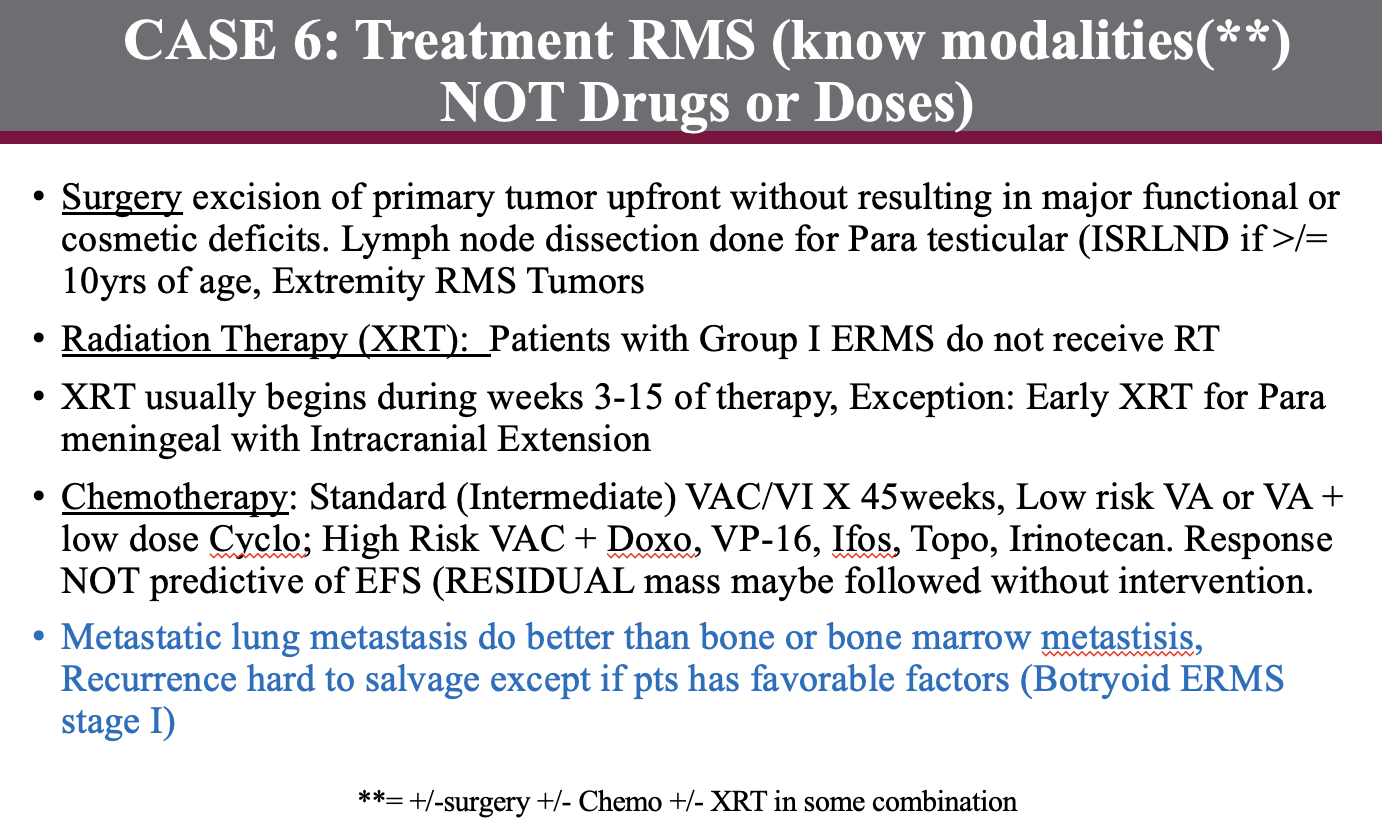
case 6
history:

work up:
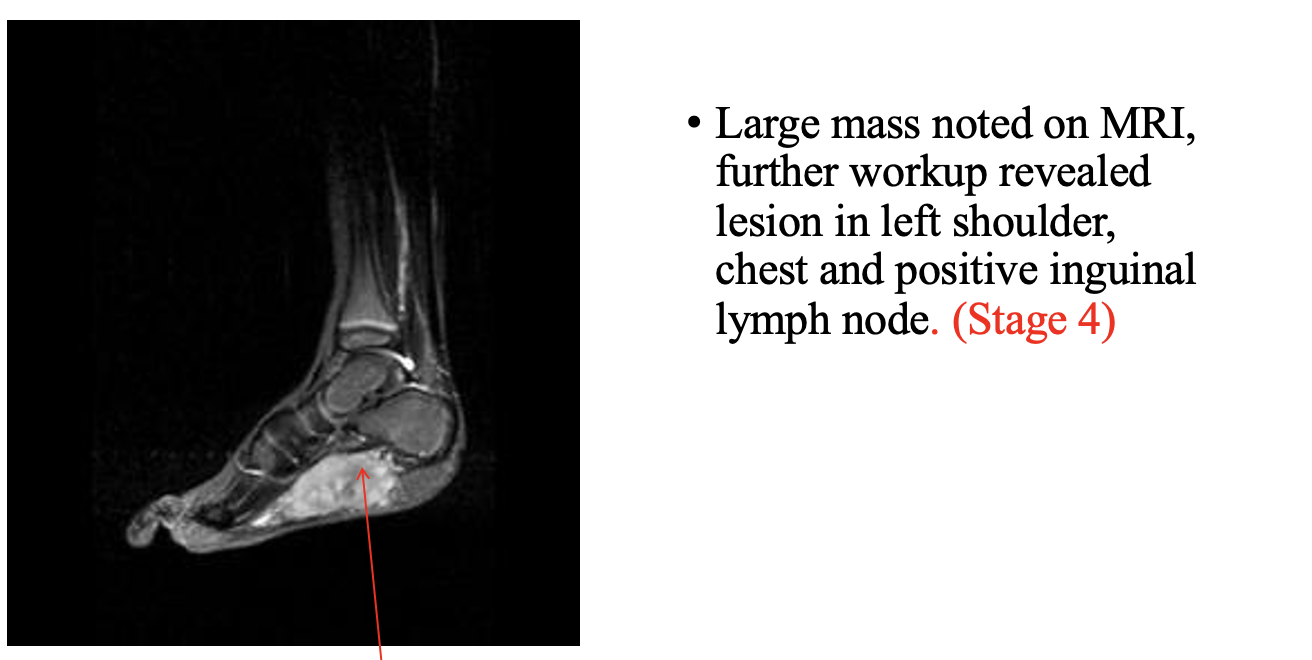
DX?
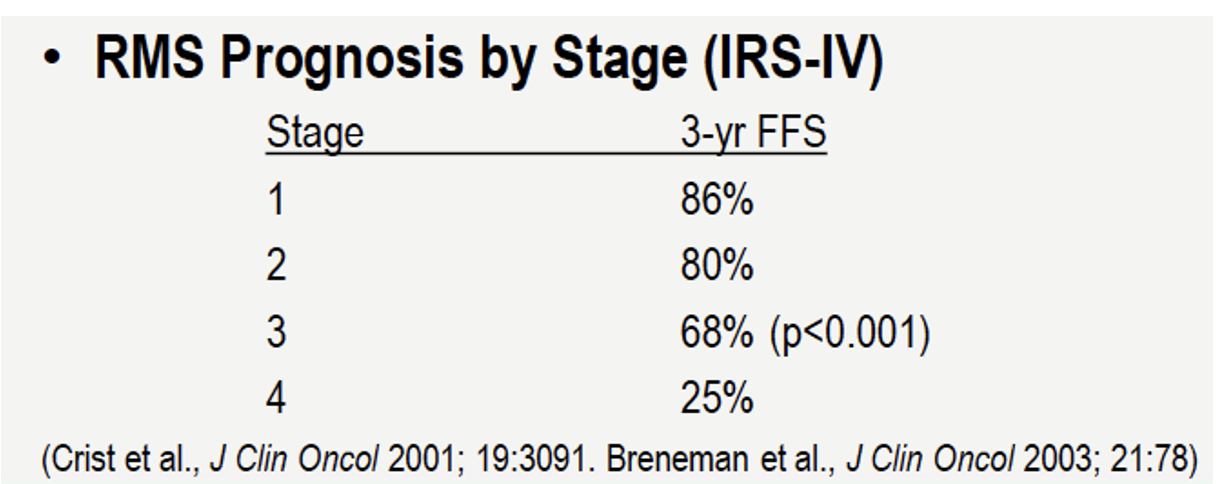
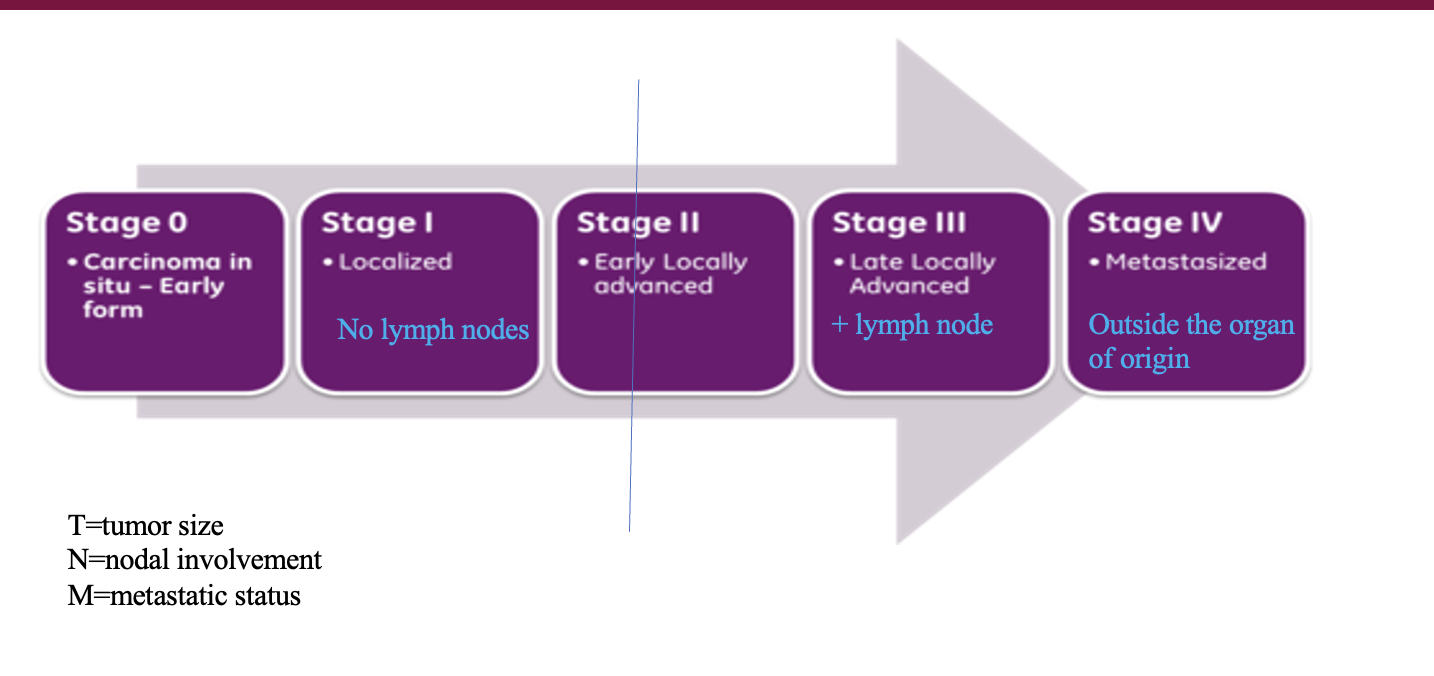
cancer stages :
stage 0 -?
stage 1- ?
stage 2 -?
stage 3 -?
stage 4 -?
for RMS
Epidemiology:
40% of soft tissue sarcomas in children <5 yo
Clinical presentation/Staging:
May arise in any part of the body, most commonly the extremities and trunk; metastatic spread to lungs, bone, nodes
Prognosis:
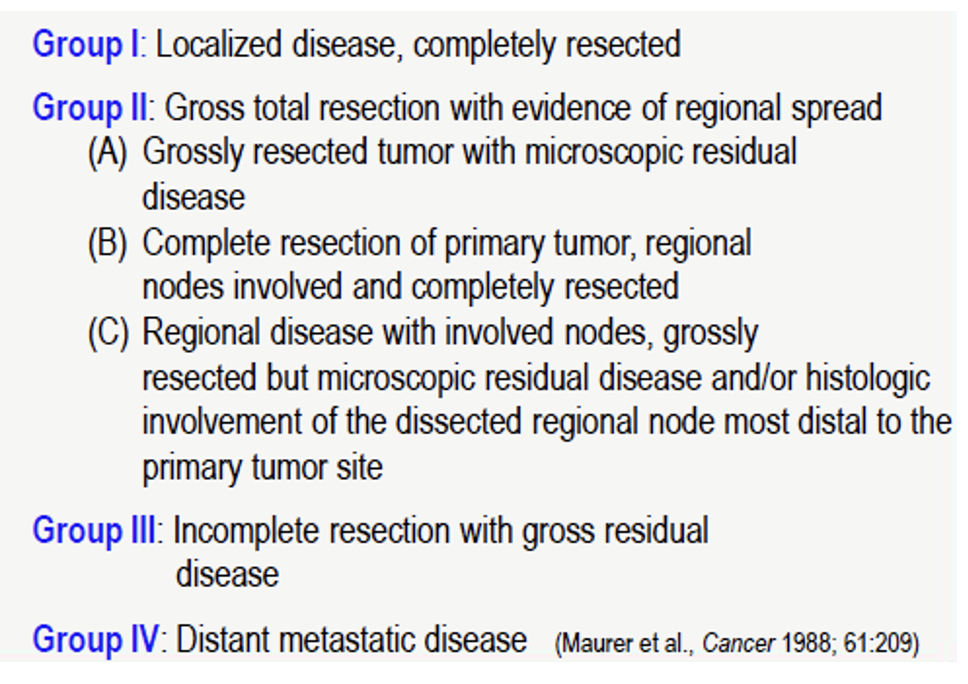
depends on tumor type, metastasis, age, extent of resection (Group), tumor size, and grade
Treatment: Surgery, XRT for residual, +/- Chemotherapy
Group I; observe unless grade 3 and > 5 cm, then consider XRT and/or chemotherapy (Dox + Ifos)
Group II; XRT alone unless grade 3 and/or > 5 cm, then consider chemotherapy (Dox + Ifos)
Group III-IV or grade 3 and > 5 cm any group; chemotherapy (Dox + Ifos), RT, delayed surgery
Non-RHABDOMYOSARCOMA SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA (NRSTS)
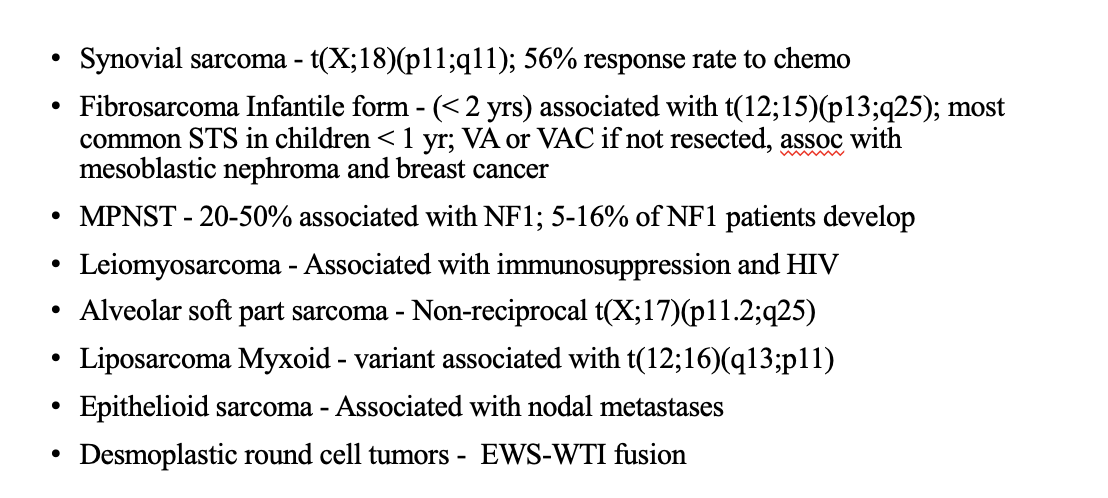
case 7
history