Newtons Laws of Motion
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Resistance of an object to change its motion
Inertia
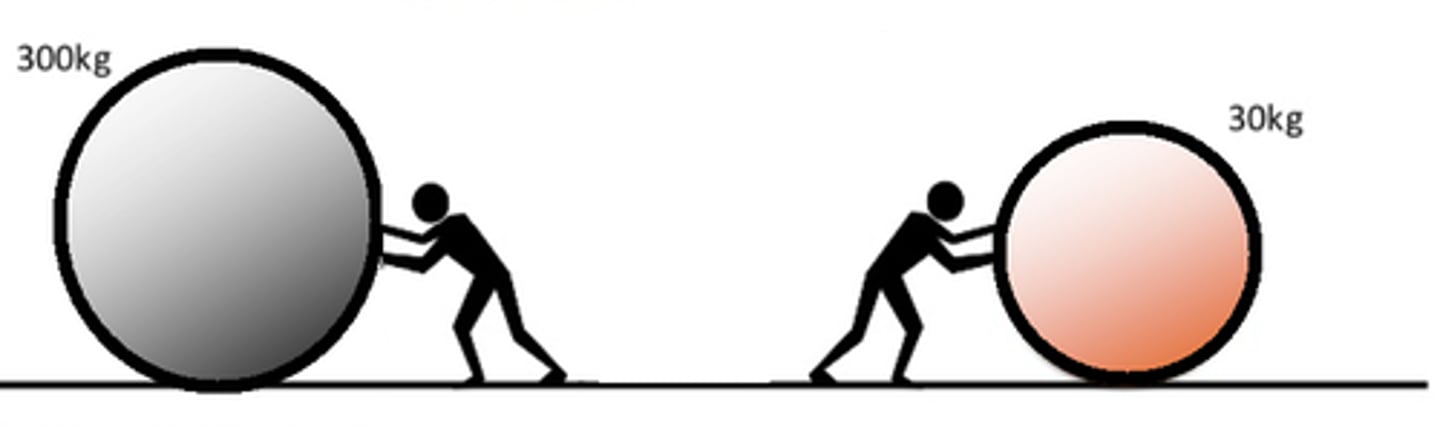
Objects that are moving want to keep moving
Inertia
Speeding up, slowing down or changing direction
acceleration
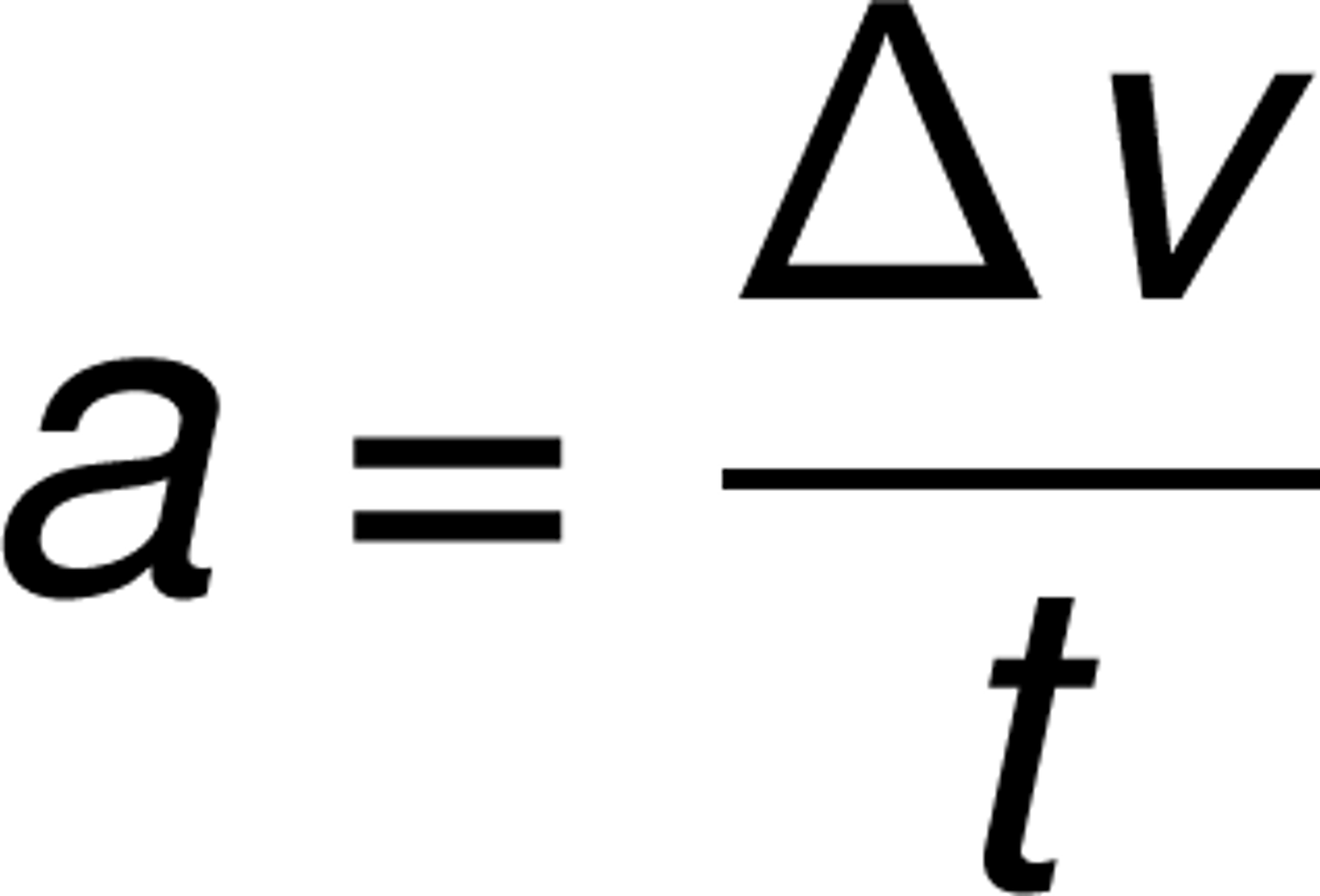
Acceleration of falling objects
9.8m/s
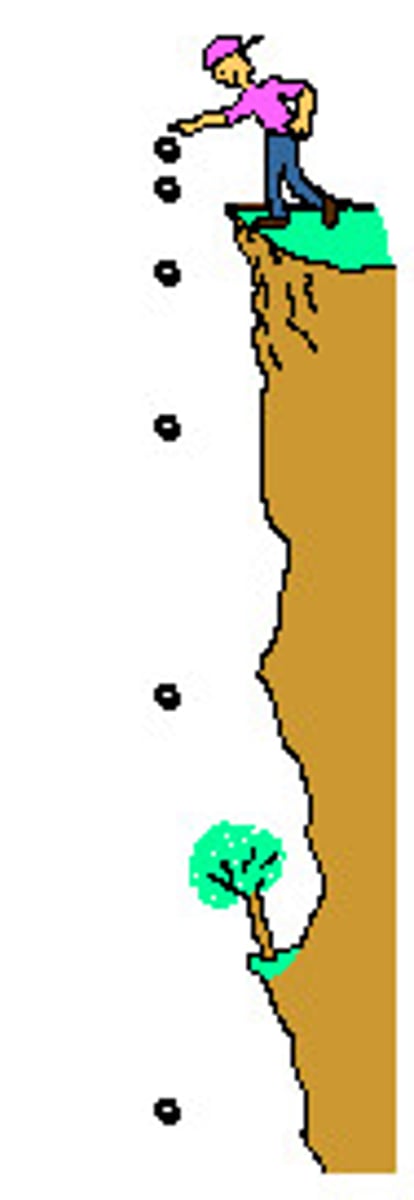
Gravity
This force pulls all objects to the ground with the same acceleration
Sir Isaac Newton
British scientist that developed the three laws of motion

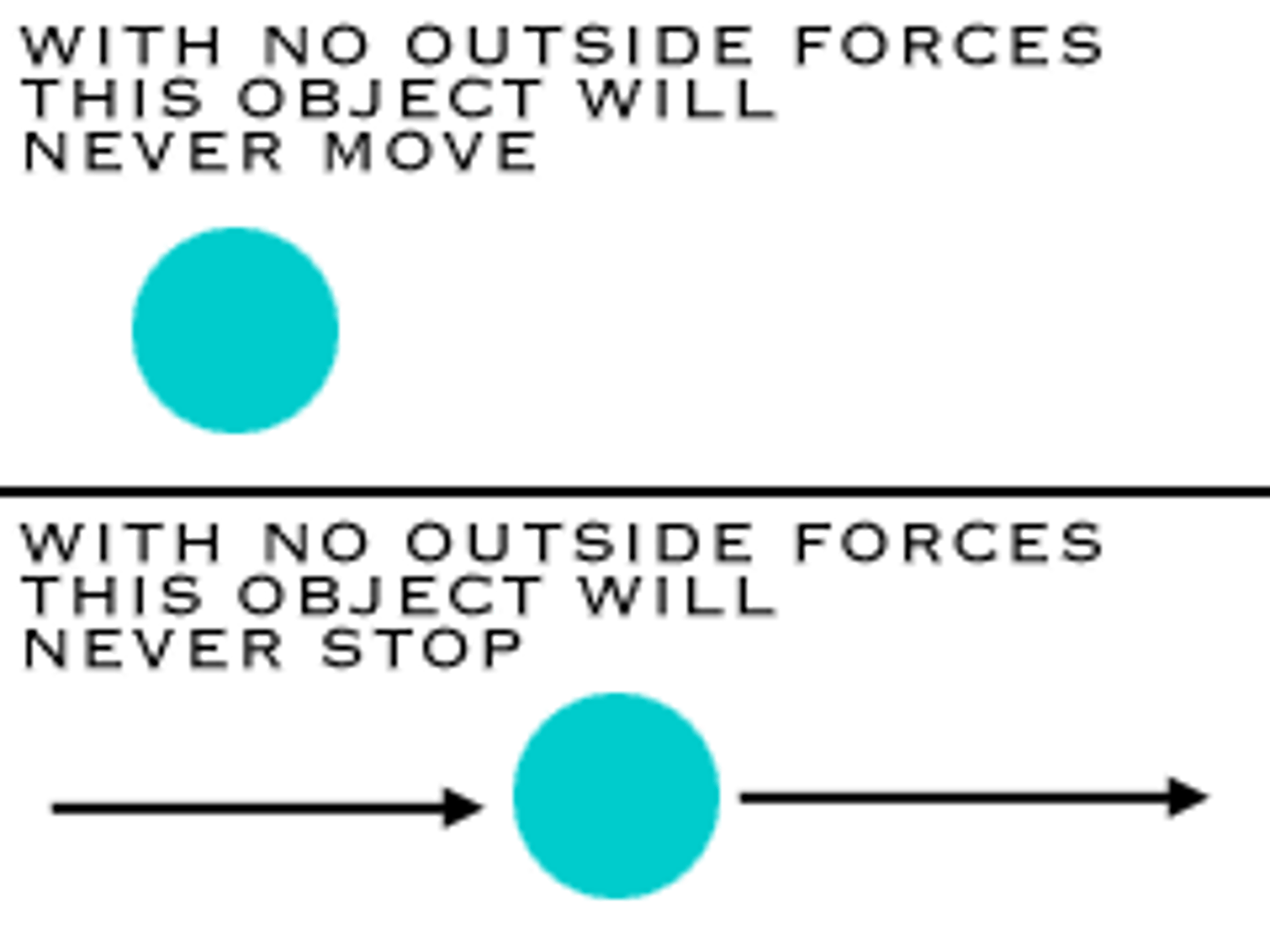
1st Law of Motion
an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force

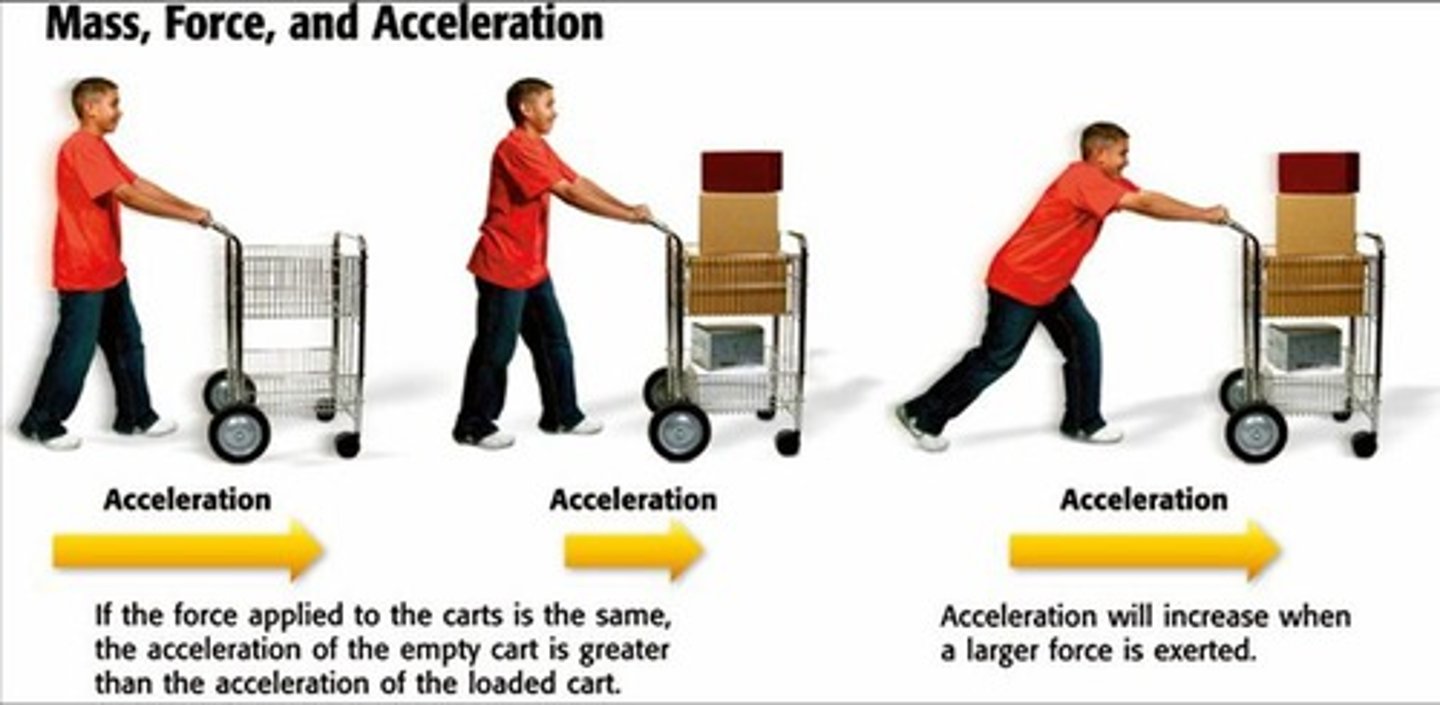
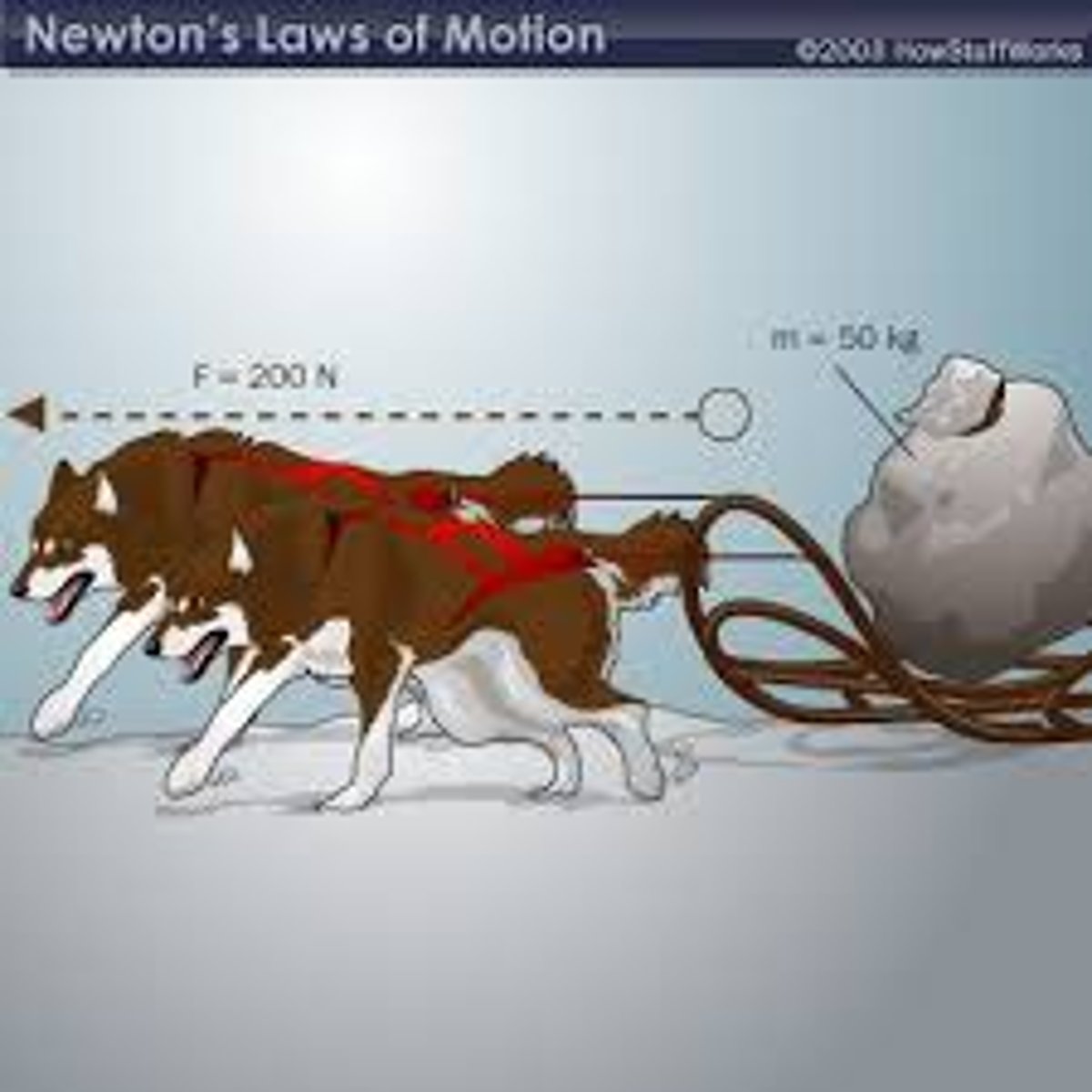
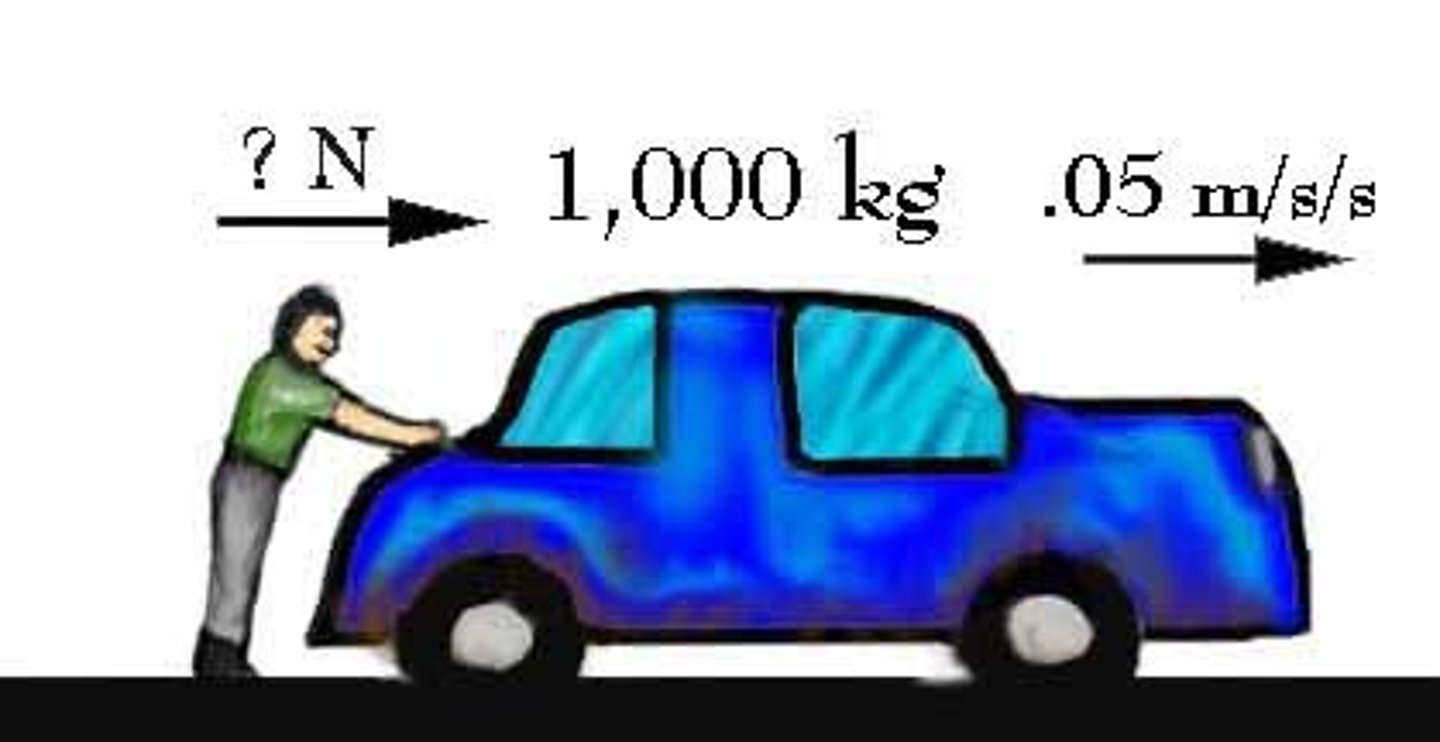
2nd Law of Motion
an object with an unbalanced force acting on it will accelerate in the direction of that force...f=m(a) ; force = mass times acceleration
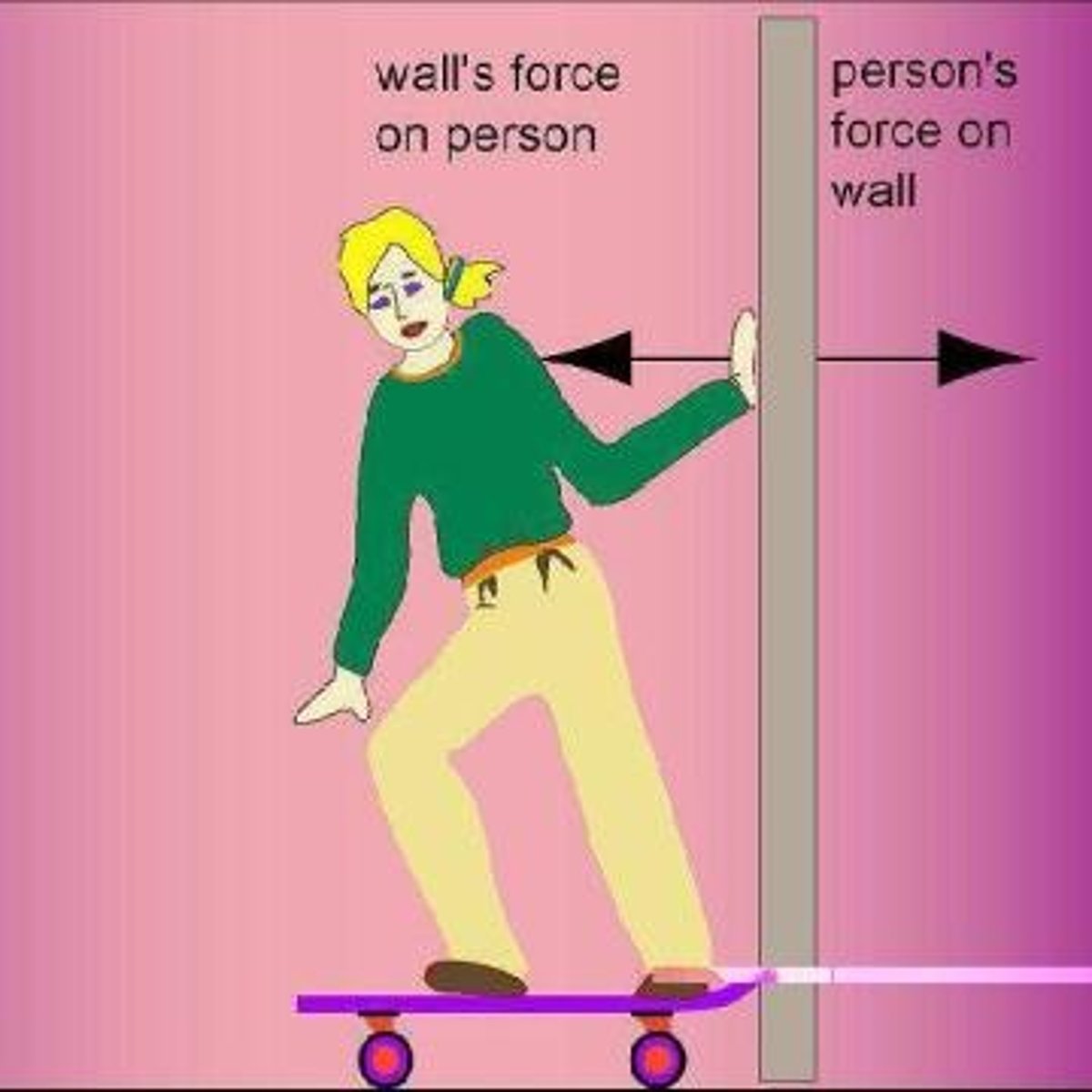
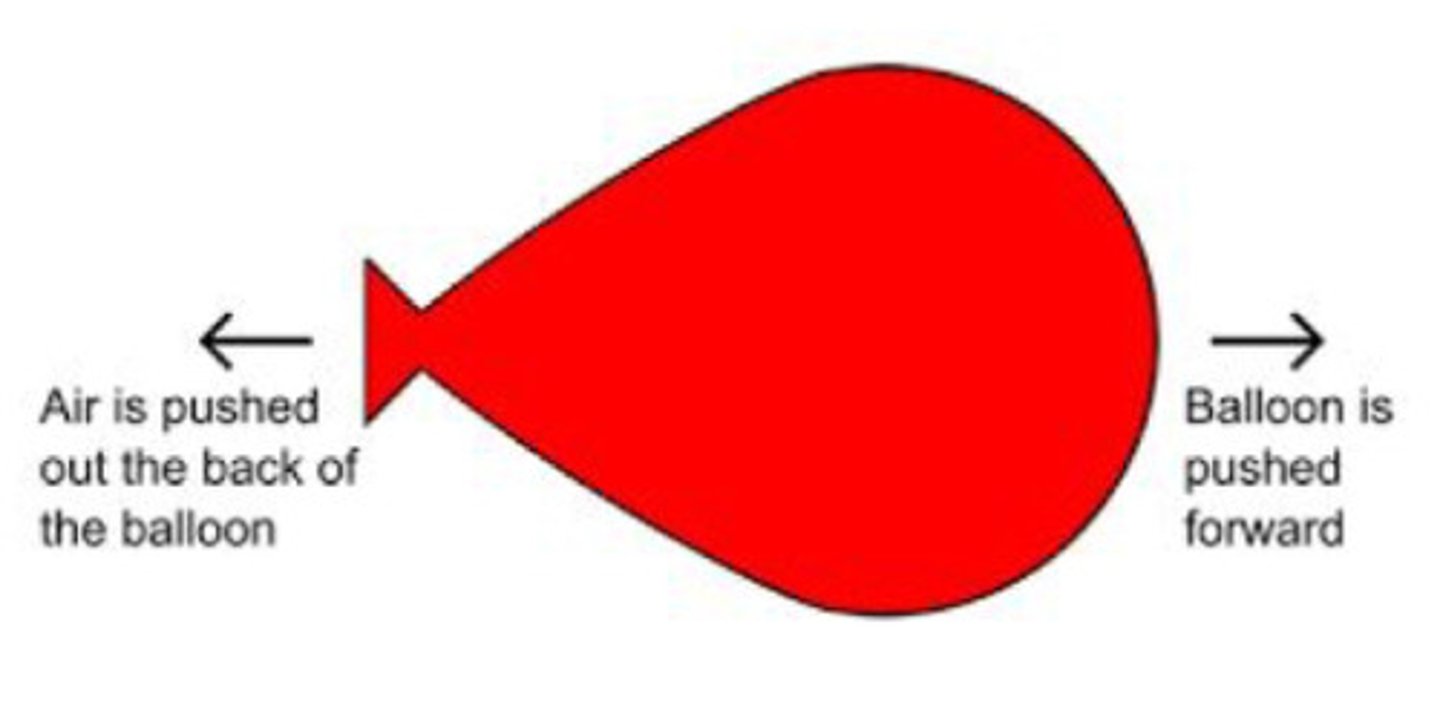
3rd Law of Motion
for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
friction
A force that opposes the motion of objects that touch as they move past each other
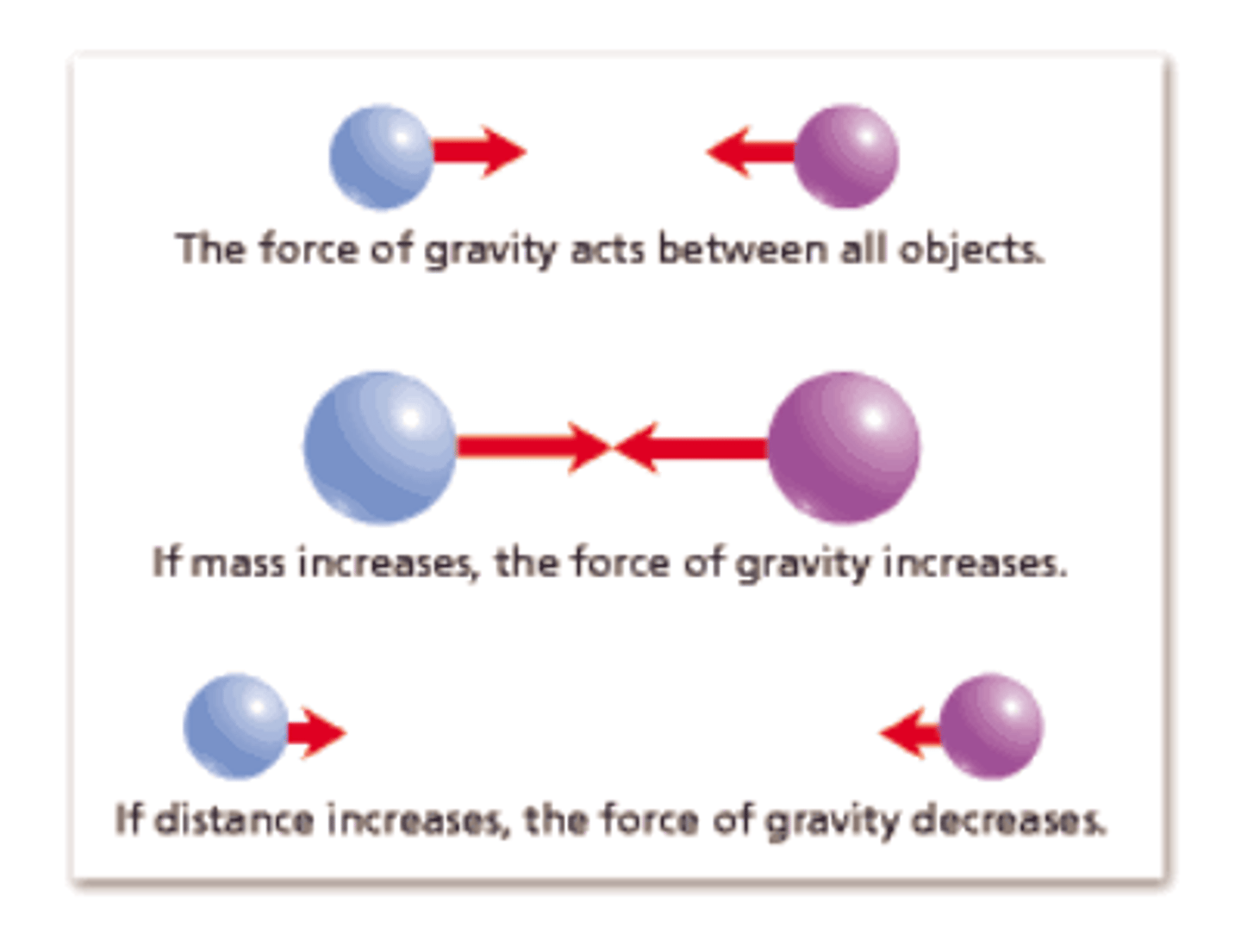
gravity
A force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses.
motion
A change in position over time

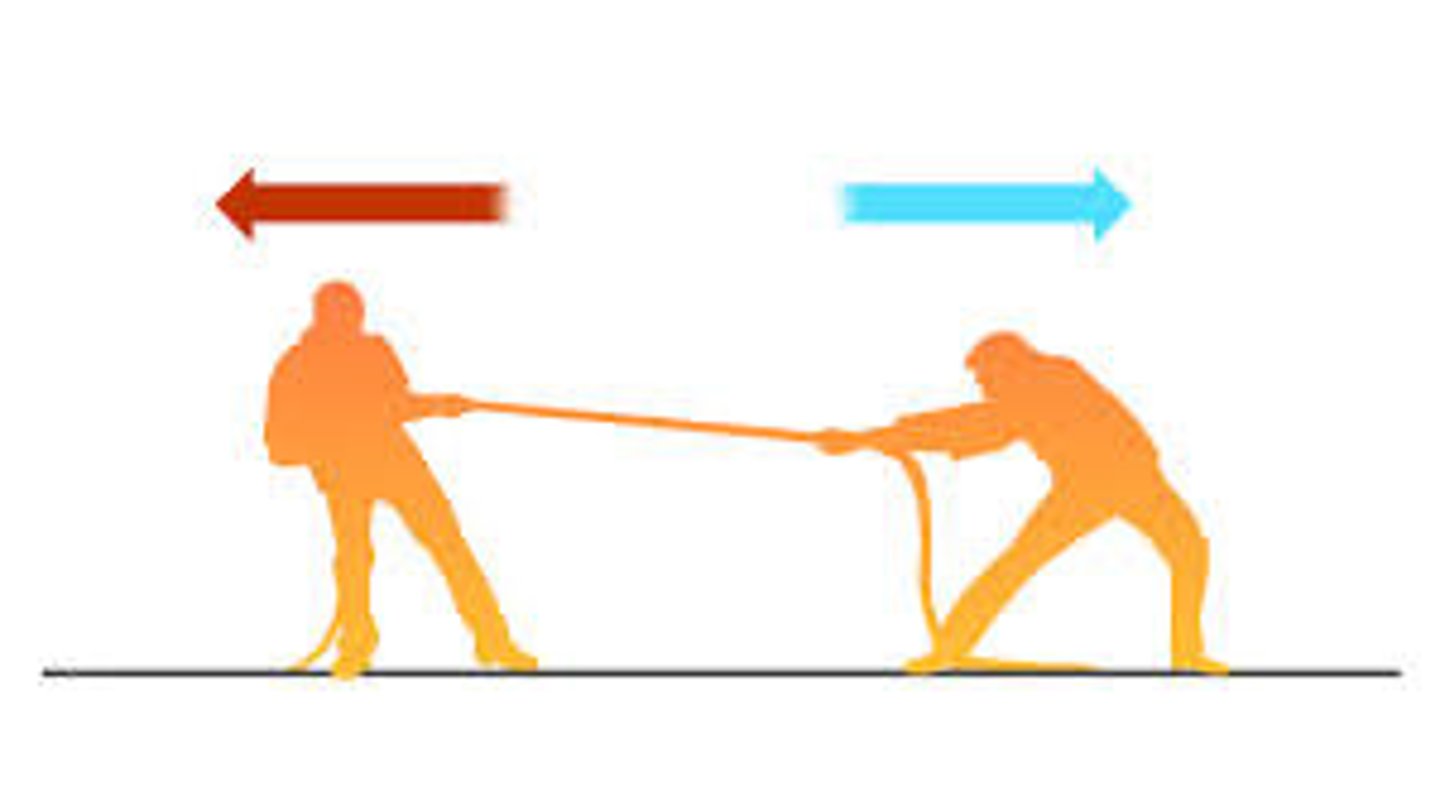
balanced force
Equal forces acting on an object in opposite directions

newtons
Unit for force
Mass
Amount of matter in an object

Forces
A push or a pull that causes objects to move
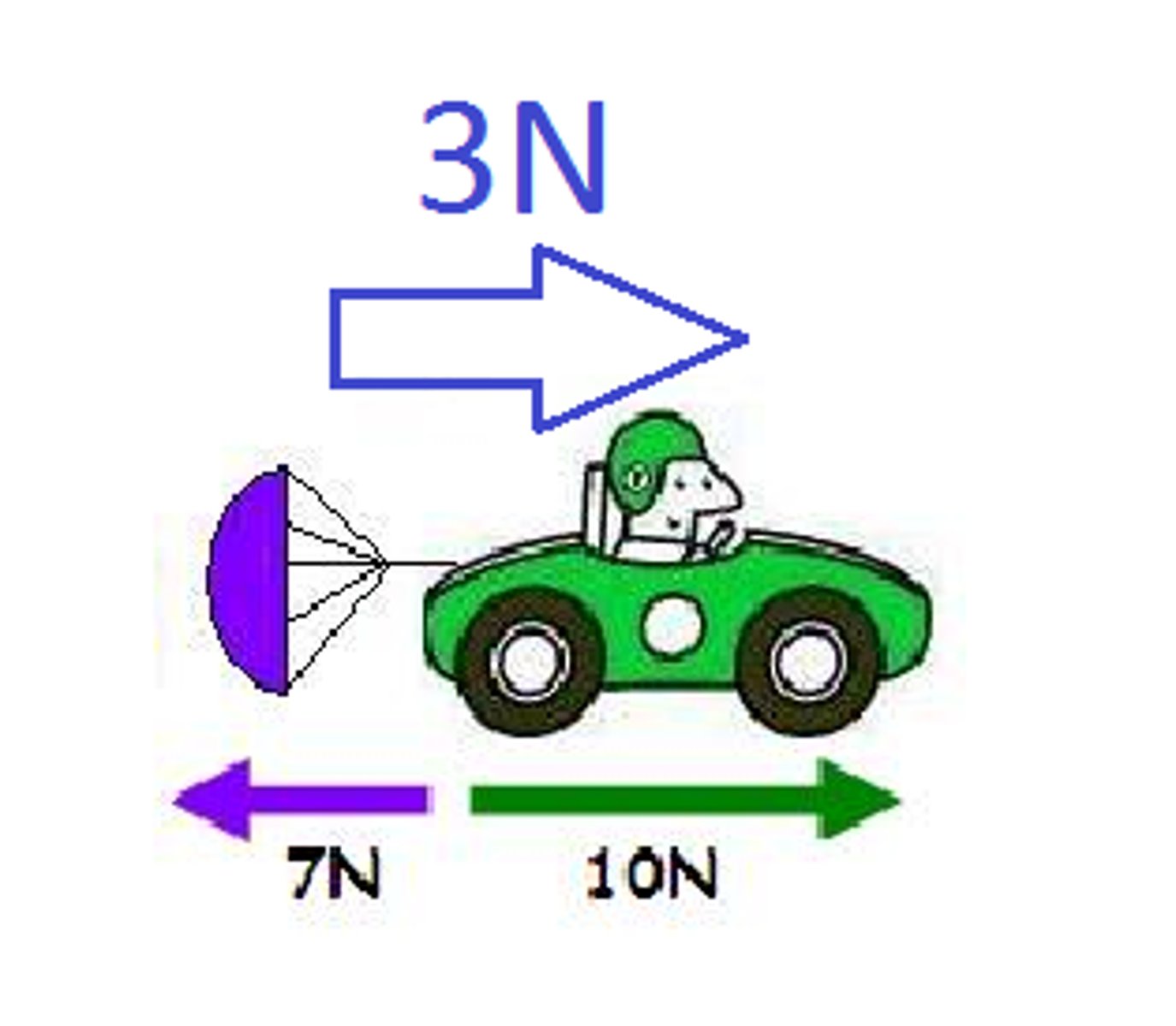
Unbalanced force
When the forces on an object are pushing harder in one direction than in another, causing movement

Net force
The sum of all forces acting on an object
Weight
Amount of gravity pulling down on an object's mass

Gravitational force
The attractive force that exists between all objects with mass
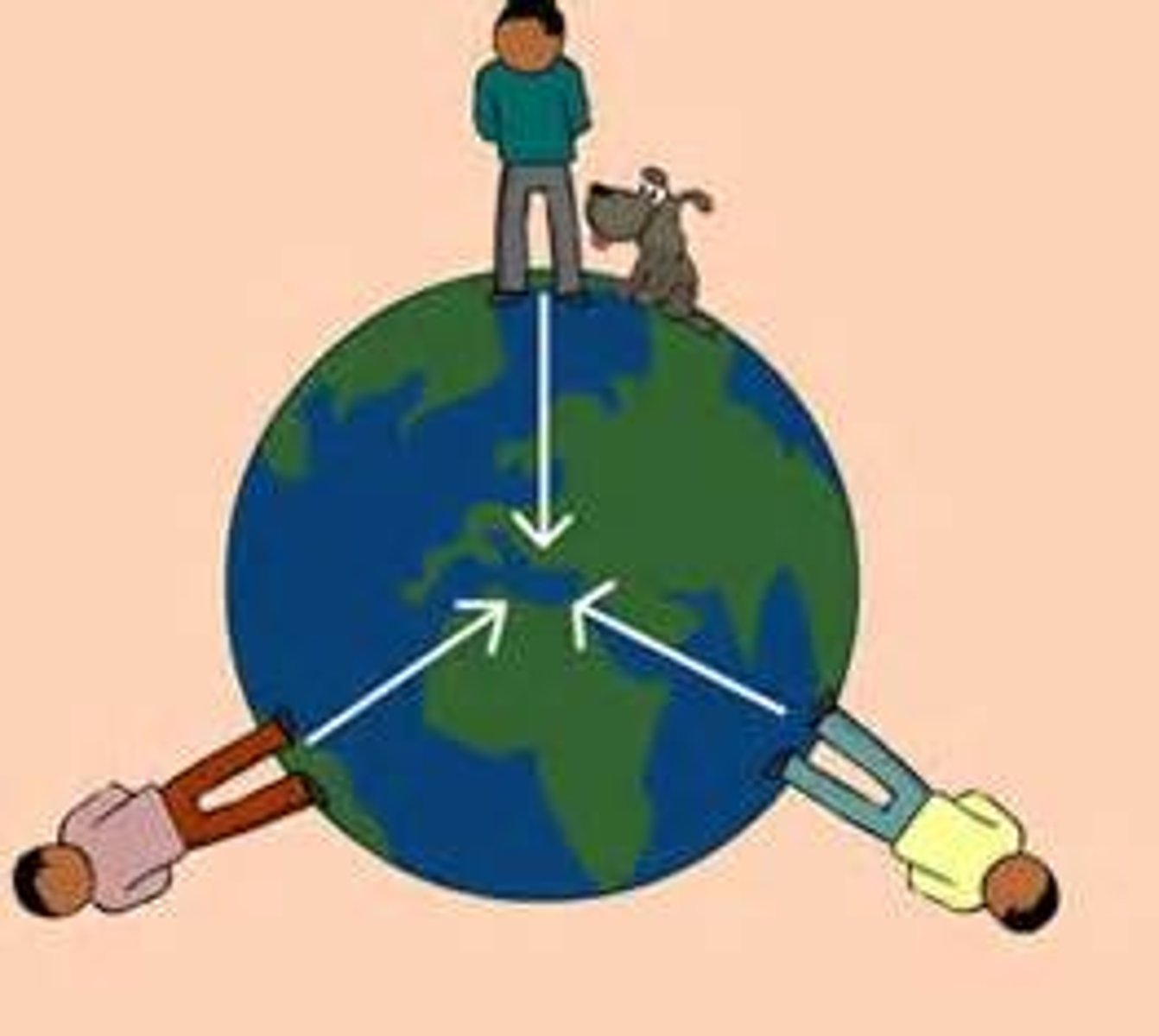
Newton's 1st Law

Newton's 1st Law

Unit for Mass
kg (kilograms)

Unit for Acceleration
m/s/s
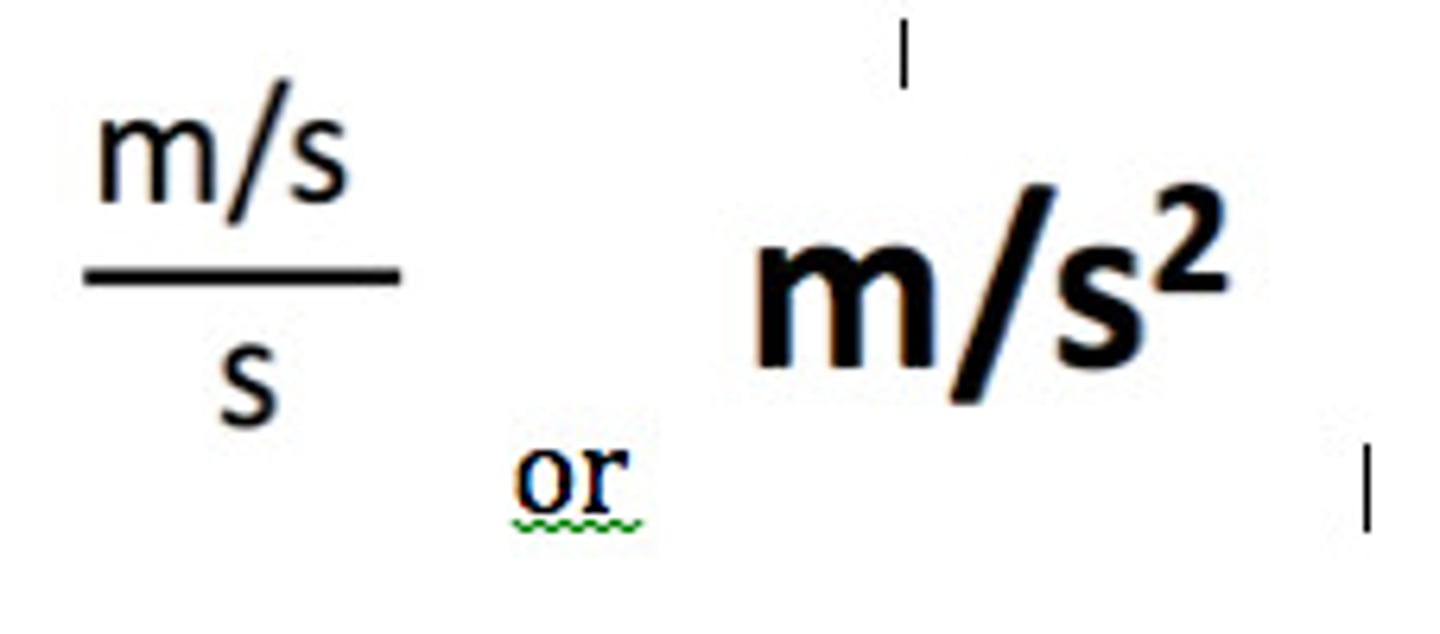
Newton's 2nd Law of Motion
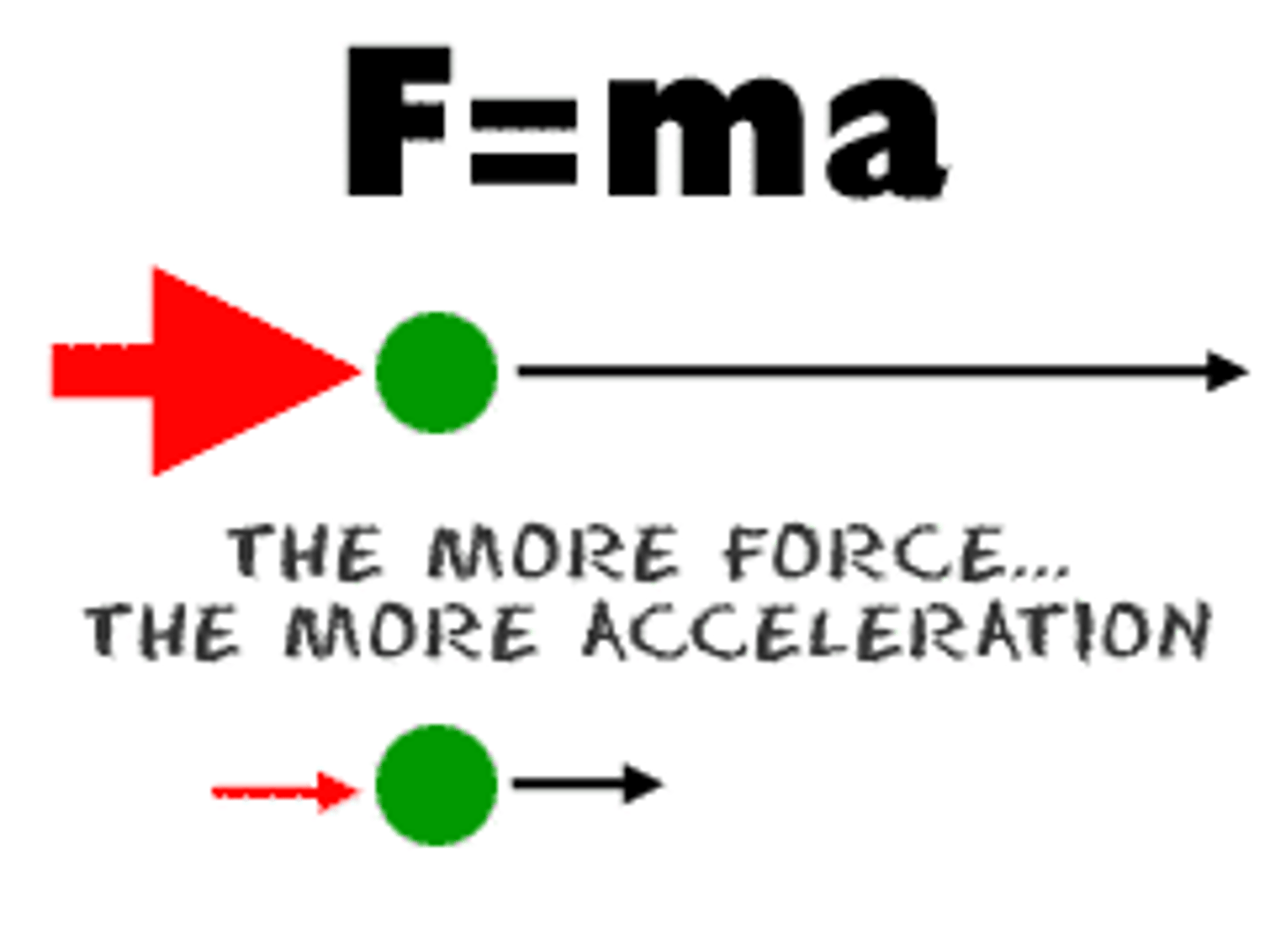
Force = mass x acceleration
Newton's 3rd Law

Action Reaction
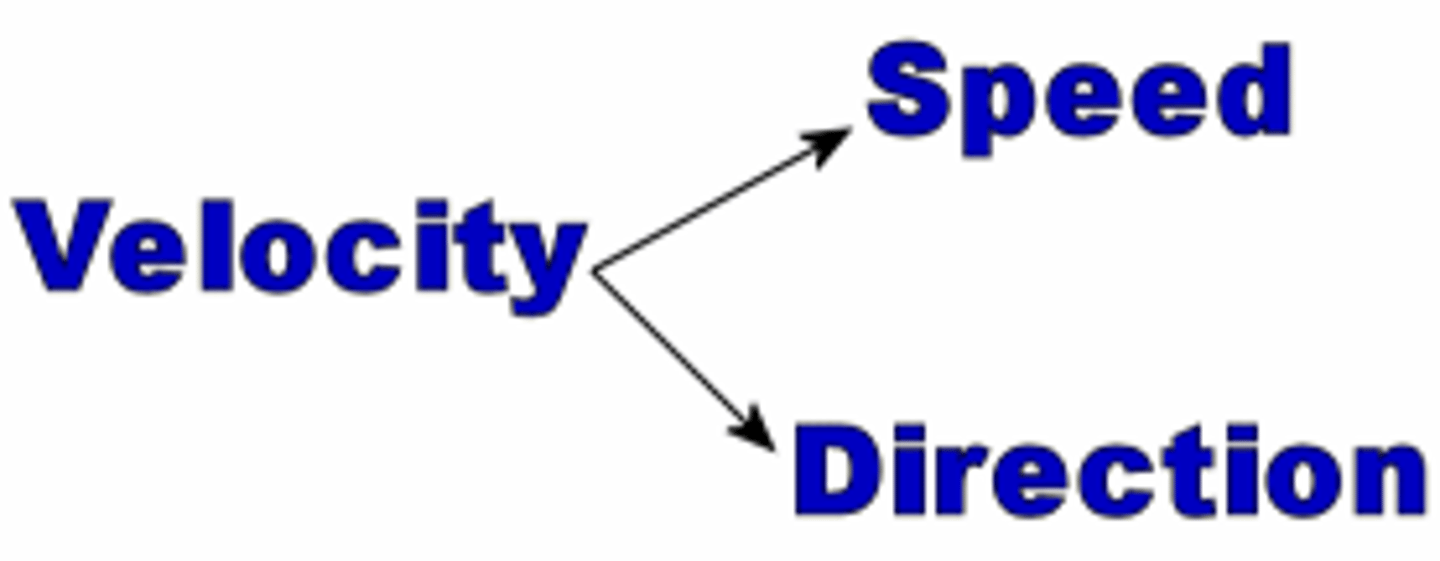
Velocity
Speed in a given direction
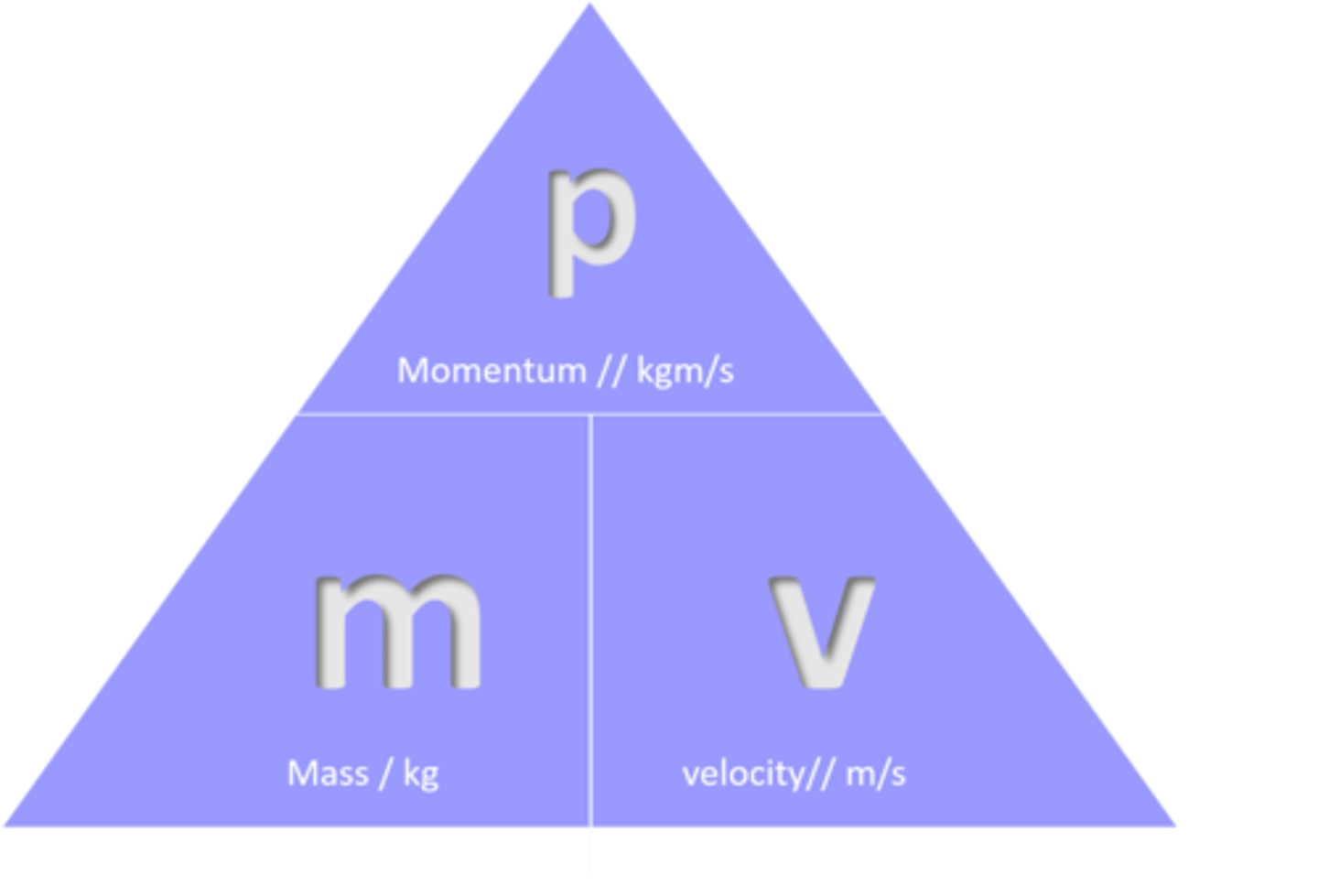
Momentum
mass in motion

momentum formula
momentum = mass x velocity
p = mv
Isaac Newton
An English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, and author, widely recognized as one of the most influential scientists of all time.
Laws of Motion
Three physical laws that together form the foundation for classical mechanics, describing the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it.
Universal Gravitation
A law stating that every point mass attracts every other point mass in the universe with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.
Calculus
A branch of mathematics that studies continuous change, which Newton co-developed independently of Leibniz.
Optics
The study of light, which Newton explored through experiments with prisms, demonstrating that white light is composed of various colors.
Principia Mathematica
A work published in 1687, laying the groundwork for classical mechanics and containing the laws of motion and universal gravitation.
Cambridge University
The institution where Newton studied and later became a professor, significantly influencing his scientific career.
Alchemical Studies
Newton's secretive research into alchemy, which he pursued alongside his scientific work, reflecting his interest in the transformation of matter.
Royal Society
A prestigious scientific institution in London where Newton served as president and contributed to the advancement of scientific knowledge.
The Apple Story
A popular anecdote suggesting that Newton formulated his theory of gravitation after observing an apple fall from a tree.