Unit 5: Absorption and Excretion - Anatomy & Physiology
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
In which of the following structures does chemical digestion not occur?
esophagus
Which of the following structures creates a substance that makes it possible for us to digest fats?
liver
The colon is another name for which structure?
large intestine
Which of the following correctly matches the subdivision of the small intestine with its role?
- Critical vitamins are mainly absorbed in the ileum.
- The majority of chemical digestion occurs in the duodenum.
- Nutrients are mostly absorbed into the blood from the jejunum.
all of the above
Which of the following structures secretes enzymes that help us digest carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins?
pancreas
The hepatic portal system includes the ___ which takes in nutrient-filled blood from the digestive tract and sends it towards the heart through the ___ to be oxygenated.
hepatic portal vein; inferior vena cava
Which of the following statements about the digestion of macromolecules is false?
Lipids get broken down into fatty acids and amino acids.
Which statement below correctly matches the structure with its function?
The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile that isn't immediately needed.
Which statement below correctly describes an endocrine function of the pancreas that aids in digestion?
Pancreatic islets release insulin and glucagon to aid in carbohydrate metabolism.
Which of the following accurately reflects the order in which the bolus travels through the small intestine?
Duodenum > jejunum > ileum
Which of the following organs does not serve as a temporary storage reservoir for a substance in the digestive or urinary systems?
pancreas
Which of the following statements about the large intestine is false?
It is the main site of absorption in the alimentary canal.
Which of the following is not considered an essential nutrient?
nucleic acids
Reactions that link simple molecules into more complex ones are __ and result in an overall __ of energy.
anabolic; absorption
Glucose serves as our body's main energy fuel during the __ nutritional state. Body reserves serve as our body's main energy fuel when the GI tract is __.
absorptive; empty
The portion of the kidney indicated by the arrow in the figure to the right between the pyramid like shapes is the ___.
renal column
Which of the following is not considered a major function of the kidney?
- Regulation of blood pressure.
- Red blood cell production.
- Regulation of blood pH.
- Retaining nutrients the body needs.
All of the above are functions of the kidney
Which of the following structures acts as a mechanical filter between the blood and Bowman's capsule?
Glomerulus
When a substance in the blood is moved from the capillaries into the filtrate, this is known as ...
reabsorption
A patient is admitted to the ER complaining of immense pain. An ultrasound indicates the presence of a kidney stone. Which of the following best describes the main location of the patient's pain?
In the dorsal body wall, lateral to the vertebral column.
List two accessory structures in the oral cavity and the specific role each plays in the digestive process.
1. Teeth - mechanical digestion/increasing surface area of food by making it into smaller pieces.
2. Tongue - muscle that moves food towards pharynx.
Describe the pathway that the bolus takes as it leaves the mouth in order to end up in the stomach, and how it differs from the pathway the air that we inhale through our mouth takes to get to our lungs.
The bolus leaves the mouth via the pharynx and travels down the esophagus to get to the stomach. This is different from air which travels from the oral pharynx down the larynx and the trachea to end up in the lungs.
Explain the importance of both mechanical and chemical digestion, including how one aids the other.
Mechanical digestion is critical for physically breaking down the food into smaller pieces to increase the surface area (to aid in absorption); it also helps to mix the broken down food with the enzymes to aid in their chemical breakdown.
Chemical digestion uses secreted enzymes to chemically break down food into its simplest forms to make them easier to absorb and be transported and used.
Explain the major function of the small intestine and two ways that its structure aids it in accomplishing this function.
The small intestine is known for being the main site of chemical digestion and nutrient absorption. The folds and villi aid to maximize the surface area for nutrients being absorbed into the blood, and the lining contains smooth muscle tissue to aid in the propulsion of the chyme through the very long intestines.
The majority of the steps in the digestive process happen in multiple structures in the alimentary canal at the same time. What two steps only occur in one organ? List the step and where it occurs beside it.
1. Ingestion - occurs only in the mouth
2. Defecation - occurs only in the large intestine
Where is the gastroesophageal sphincter located and what is its role?
It is located where the esophagus and the stomach connect and its role is to close once the bolus is in the stomach to prevent regurgitation.
Describe one example of how the digestion process is regulated.
G cells produce gastrin and other hormones activate the release of HCI into the stomach breaks down the proteins in our stomach to prepare them for digestion
What causes heartburn? Include where it occurs and why the name of this health issue is misleading.
Occurs when stomach acid backs up into your esophagus (through the gastroesophageal sphincter); it's misleading because it isn't in your heart, but since your esophagus runs posterior to your heart, the burn can be felt in your chest cavity.
Suppose you are a GI doctor and you discover one of your patients cannot make bile salts. Which organ is malfunctioning?
Liver
Suppose you are a GI doctor and you discover one of your patients cannot make bile salts. The digestion of which macromolecule will be most affected?
Fats/lipids
Suppose you are a GI doctor and you discover one of your patients cannot make bile salts. List three ways the inability to digest this specific type of macromolecule will affect your body's ability to
function properly.
Protective cushioning, insulation, and energy storage.
Name the dietary sources of carbohydrates.
Fruits, grains, vegetables
starches, sugars, fibers
Name the dietary sources of lipids.
Meat and dairy foods
fats oils
Name the dietary sources of proteins.
Eggs, milk, fish, meat, beans, and nuts
What is the monomer for carbohydrates?
monosaccharides
What is the monomer for lipids?
glycerol and fatty acids
What are carbohydrates' use in the body?
Glucose fuels body cells with ATP
What are lipids' use in the body?
Cushioning of organs
What are proteins' use in the body?
transport, enzymes, hormones, etc.
What is the monomer for proteins?
amino acids
It is rare to have a health issue from taking too much of a given water-soluble vitamin, but that isn't the case for fat-soluble ones. Why do you think that is?
Water-soluble vitamins are not stored in the body and fat-soluble vitamins are. Because of this, if you have excess of a water-soluble vitamin it will just be excreted from the body, whereas fat-soluble vitamin excess could result in a build up that causes a health issue.
Give an example of one vitamin and one mineral and a role each plays in the body. What are neither of them used for?
Vitamin k helps bloofd clotting. k Potassium used for nerve function and acid base formation. Neither of them are used for fuel for the body.
Oxygenated and nutrient-filled blood gets sent to the ___.
Cells in our body
Two things can then happen to these nutrients, depending on the body's present needs. What are they?
Can be built into other molecules that are needed for storage or to be used for energy
If the nutrients go through glycolysis, where will be they be sent next and what will happen to them?
To the mitochondria to go through aerobic cellular respiration to make ATP
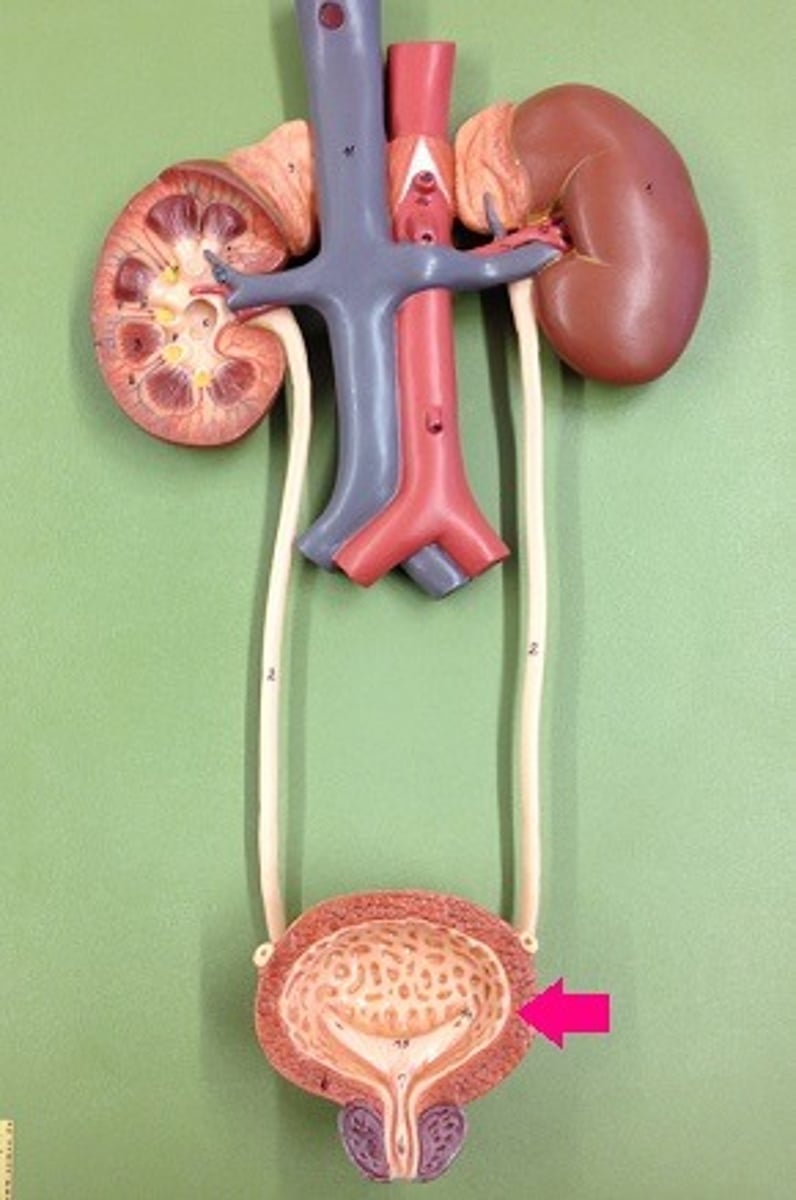
Where is the bladder?
...
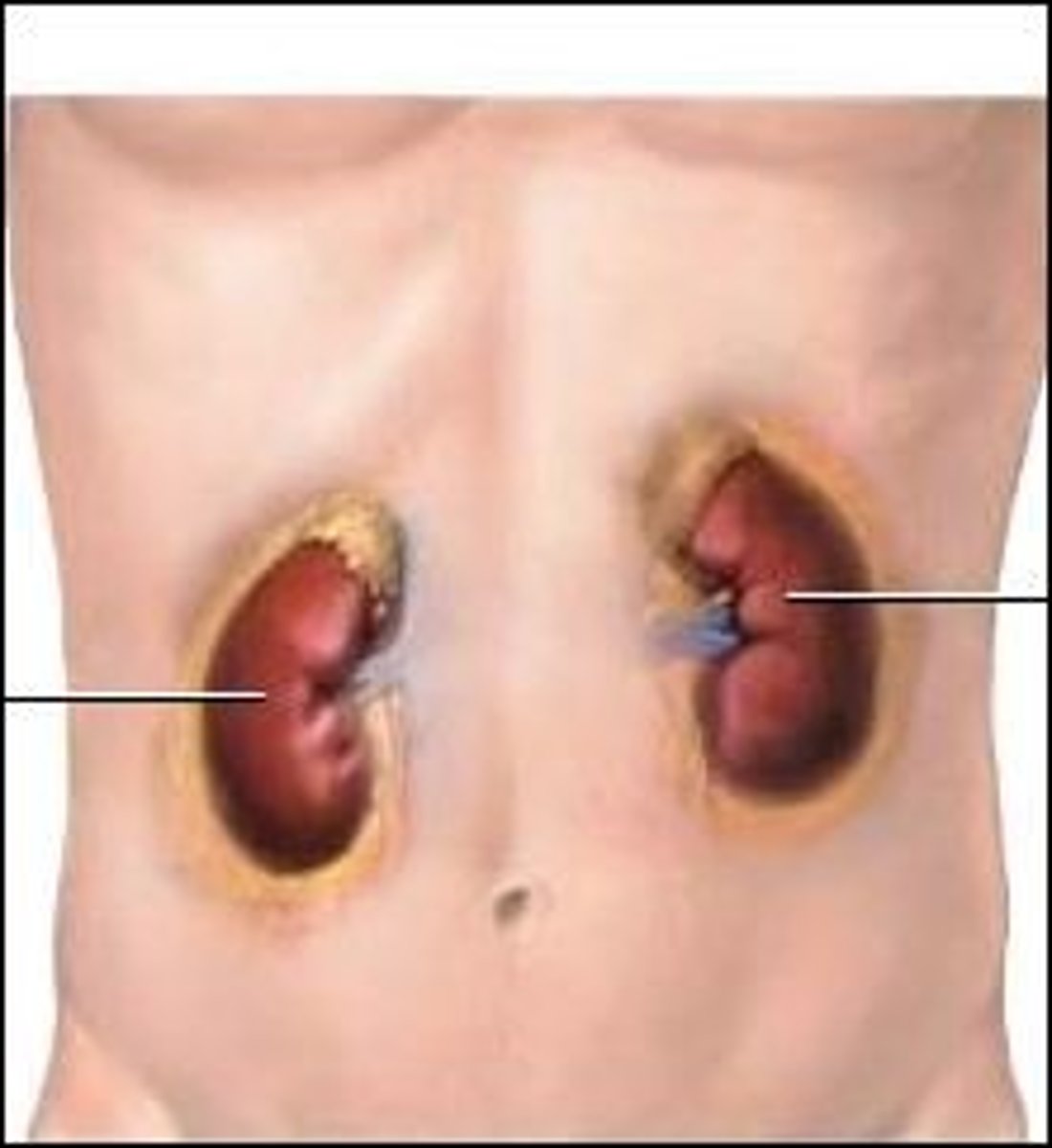
Where are the kidneys?
...
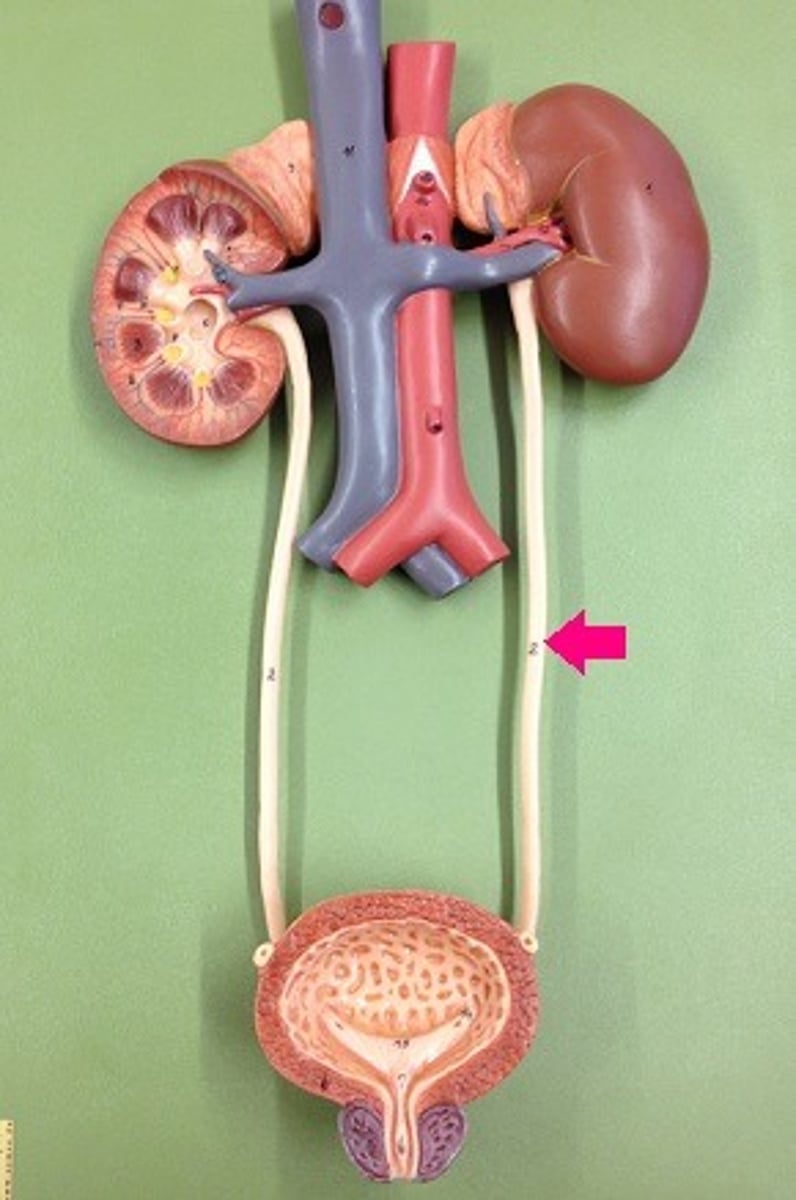
Where are the ureters?
...
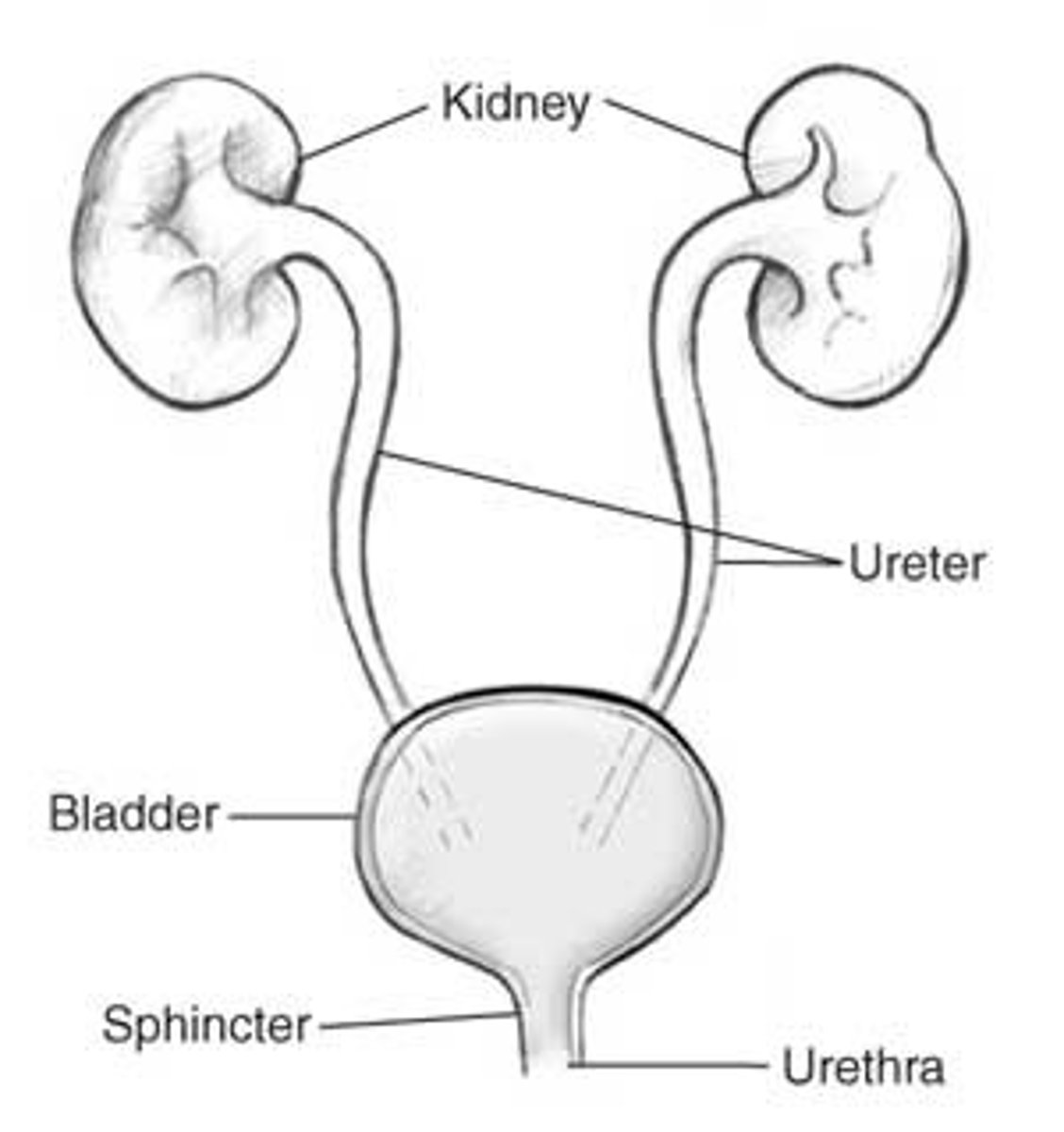
Where is the urethra?
...
Where is the renal pelvis?
...
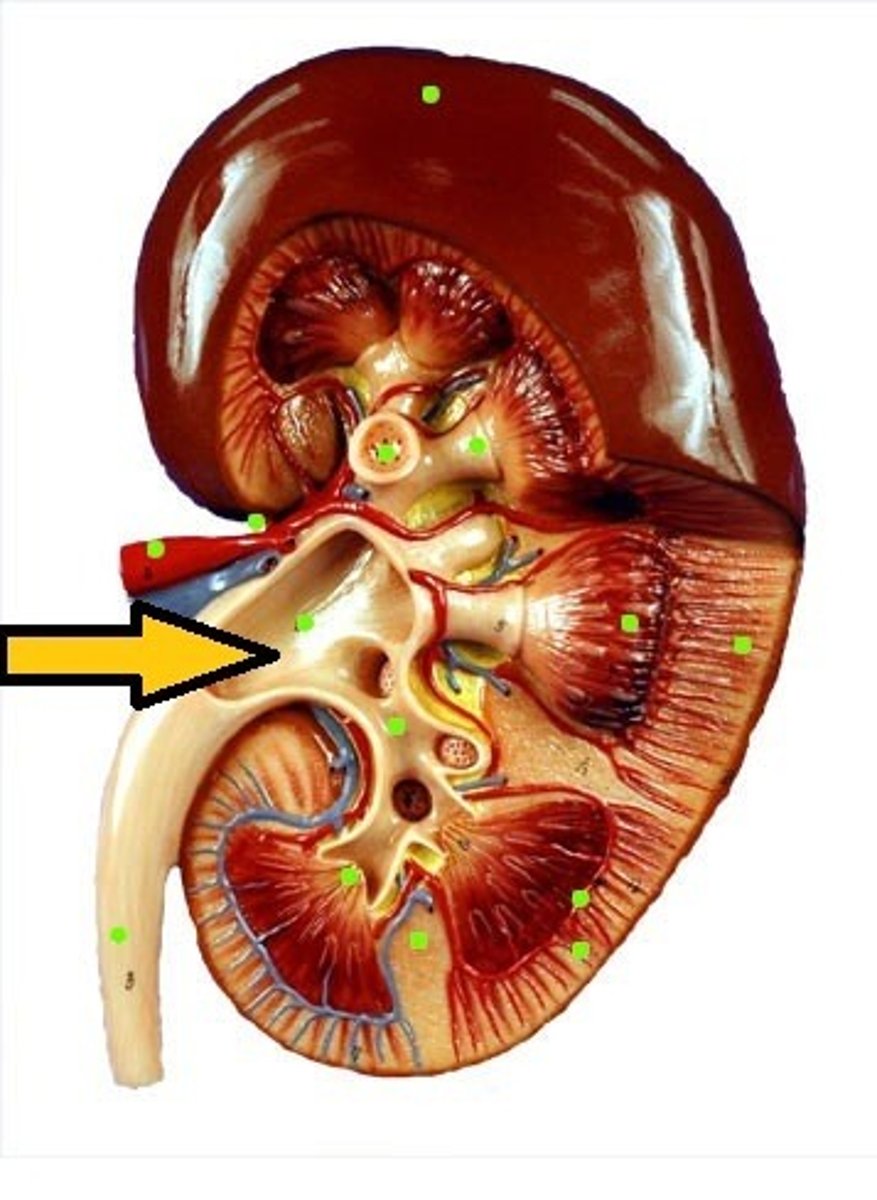
How would homeostasis be disrupted if the renal pelvis was damaged?
Homeostasis would be seriously disrupted because this structure is a funnel-shaped tube with walls made of smooth muscles that propel urine into the ureters and then on to the bladder to be excreted.
List three things that can be tested in a urinalysis test and what they can potentially indicate about a patient's health.
1. The presence of glucose being an indicator for diabetes.
2. The presence of hCG being an indicator for pregnancy.
3. The presence of ketones being an indicator for fat being used for energy and starvation/fasting
What is the name of the structural and functional unit of the kidneys?
the nephron
What is the purpose of nephrons?
Filtering blood and making urine
What is the first step in the process of how the nephrons accomplish this purpose?
1. Glomerular filtration: a passive process where the glomerulus acts as a mechanical filter between the blood and glomerular capsule to push fluids and solutes through it in order to create a filtrate.
What is the second step in the process of how the nephrons accomplish this purpose?
2. Tubular reabsorption: when the majority of the filtrate's contents get reabsorbed back into the blood if the body needs them.
What is the third step in the process of how the nephrons accomplish this purpose?
3. Tubular secretion: when any unneeded substances get removed from the blood and secreted into the filtrate to be excreted as urine.