Thermodynamics, energy, heat, work
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is a system?
The part which is of interest
What is an open system?
Can exchange both energy and matter with its surroundings
What is a closed system?
Can exchange energy but not matter with its surroundings
What is an isolated system?
Can exchange neither matter nor energy with its surroundings
Example of open system?
Biological cell→ open system because nutrients and waste can pass through the cell wall
Example of closed system?
A stoppered flask → energy can be exchanged with the contents of the flask because walls may be able to conduct heat.
Example of isolated system?
A sealed flask that is thermally, mechanically and electrically insulated from its surroundings.
What is the energy of the system?
Its capacity to do work, energy can be exchanged between a closed system and its surroundings by doing work or by the process ‘heating’
When is work done?
When motion occurs against an opposing force
Why is measuring of absolute values of internal energy not possible? What is possible?
Because it includes the kinetic and potential energies of all the electrons and all components of the atomic nuclei
It is possible to measure changes of internal energy (^U)
^ is a triangle - change in
Change in internal energy equation?
^U = w + q
w is the energy transferred to the system by doing work.
q is the energy transferred to it by heating
What equipment can be used to calculate the change in internal energy?
Calorimeter
The first law of thermodynamics?
The internal energy of an isolated system is constant.
What does U stand for?
Internal energy → the sum of all the kinetic and potential energies
U is a state function
Change in internal energy equation? And what do the letters stand for?
Change in U = w+q
w- Energy transferred to the system by doing work
q- The energy transferred to it by heating
What is internal energy?
A state function
A physical property that only depends on the present state of the system and is independent of the path by which that state was reached
What happens to the internal energy when the temperature and pressure is changed and then adjusted back to the original values?
It will also return to its original value
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
The internal energy of an isolated system is constant
What is the enthalpy change calculation for a reaction at constant pressure?
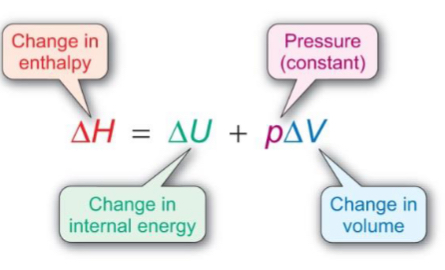
How to calculate enthalpy change using products and reactants?
Change in H = H(products) - H(reactants)
Change in H > 0 is endothermic or exothermic?
Endothermic
Change in H < 0 is endothermic or exothermic
Exothermic
What isi change in rH dependant on?
Temperature, pressure and physical state of the component
What are standard conditions?
A pressure of 1 bar (1×10^5 Pa)
298K
A substance at a specified temperature in its pure form
△fH⦵ definition?
Enthalpy of formation
△cH⦵ Definition?
Enthalpy of combustion
△atH⦵ Definition?
Enthalpy of atomisation
△iH⦵ Definition?
Enthalpy of ionisation
△eaH⦵ Definition?
Enthalpy of electron affinity
△LH⦵ Definition?
Enthalpy of lattice dissociation
△hydH⦵ Definition?
Enthalpy of hydration
△solH⦵ Definition?
Enthalpy of solution
△vapH⦵ Definition?
Enthalpy of vaporisation
△fusH⦵ Definition?
Enthalpy of fusion