invertebrates 2
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
mollusca
three universal features: mantle, radula, nervous system
benthonic and nektonic organisms
most are motile, although some are sessile
found in all oceans, as well as freshwater environments
four classes: bivalvia, gastropoda, polyplacophora, cephalopoda
bivalvia
key feature is possession of a pair of hinged valves secreted by the mantle
variable sizes
suspension feeders, can filter large amount of water
some infaunal, other epifaunal
infaunal bivavles
bury themselves in sand or soft sediment
epifaunal bivalves
attach themselves to a surface and never leave
boring bivalves
can bore and feed upon wood
able to digest cellulose
destroy wooden ships and piers
looks more worm than bivalve
shells almost disappear
gastropoda
recognized by their spiral shell and muscular foot
shell has a single opening protected by a hard structure called operculum
internal torsion of the body
all members of this call possess a radula
ex snails, sea slugs

gastropods radula
anatomic structure unique to gastropods
a modified tongue used for scraping food off a hard substrate
contains hundreds of identical teeth
creates a characteristic feeding track
modified into a harpoon in some species
cone and limpets
carnivorous organism, active hunters
radula modified into a harpoon containing venom
large specimens can be lethal to humans
have flattened shell
common in intertidal zone
feeds on coralline algae
interspecific relations with cca
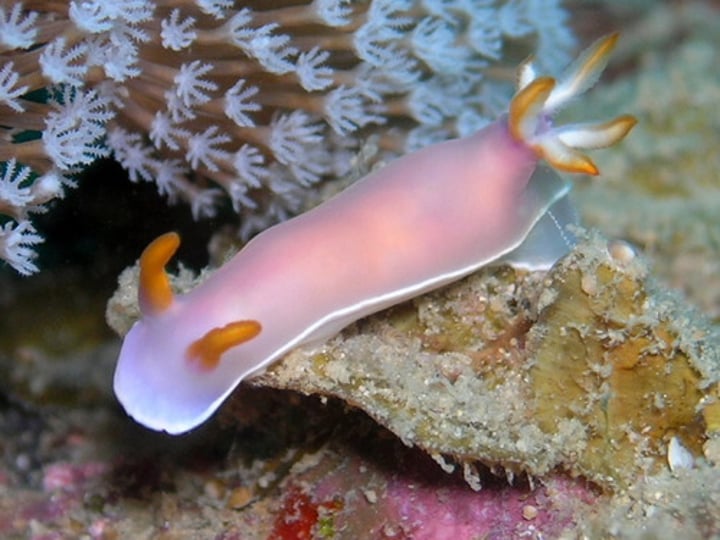
sea slugs and nudibranchs
lack shell at all
some are predators, other feed on sponges
can acquire the nematocysts and use them as a defense mechanism
feed on algae and are able to extract the chloroplasts deriving nutrition from them - kleptoplasty
present warning coloration telling predators not to eat them - aposematism

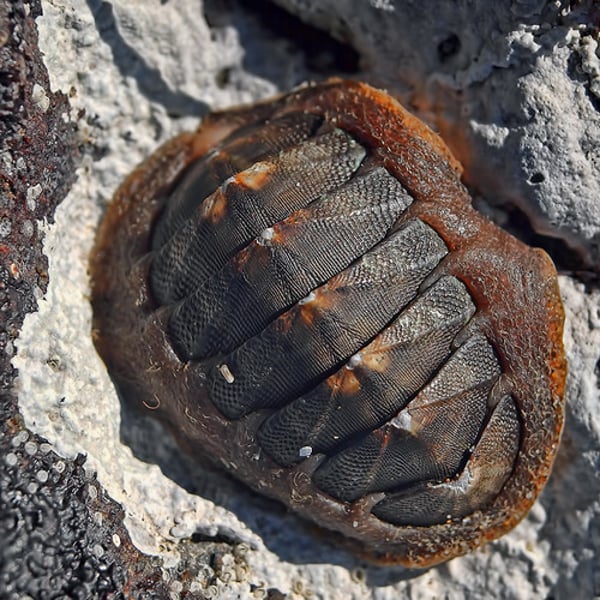
polyplacophora
chitons
common in rocky shore in intertidal and subtidal zones
distinguished by having 8 hard calcium carbonate plates surrounded by a tough mantle
feed on algae that they remove with the radula
while they appear firmly attached to the rock, they actually move around
eyes can distinguish shapes

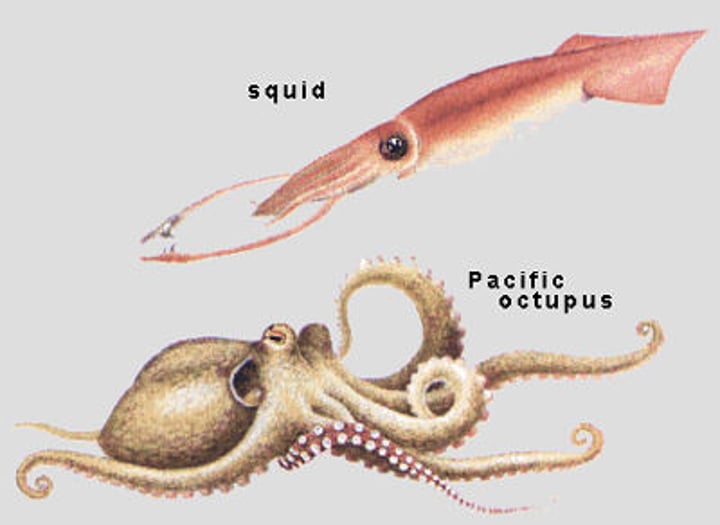
cephalopoda
active swimmers, spend their entire life in the water column
voracious predators with a highly evolve nervous system
excellent eye vision
ex octopuses, squids, cuttlefish
echinodermata
strictly marine, very sensible to change in salinity
radial symmetry
lack a brain and posses a decentralized nervous system
all posses an endoskeleton made of platelike structures called ossicles
adults present a water vascular system with external tube feet

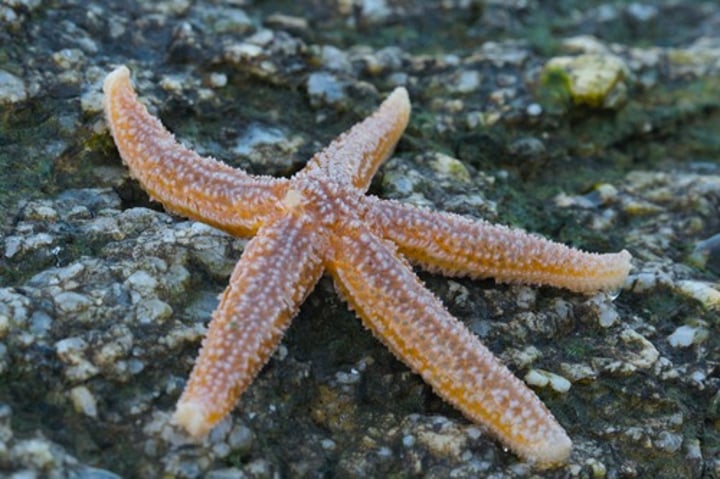
echinodrmata - asteroidea
can digest larger prey externally
able to regenerate missing body parts
apex predators
keystone species in some ecosystems

mesopredators
medium-szied, middle trophic level predator, which both predates and is predated upon
ex raccoons, snakes, small sharks
apex predator
alpha predator, top predator
predator at the top of a food chain, with no natural predators
usually defined in terms of trophic dynamics, meaning that they occupy the highest trophic levels
keystone species
species that substantially affects the structure of communities despite the fact that individuals of the species might not be particularly numerous.
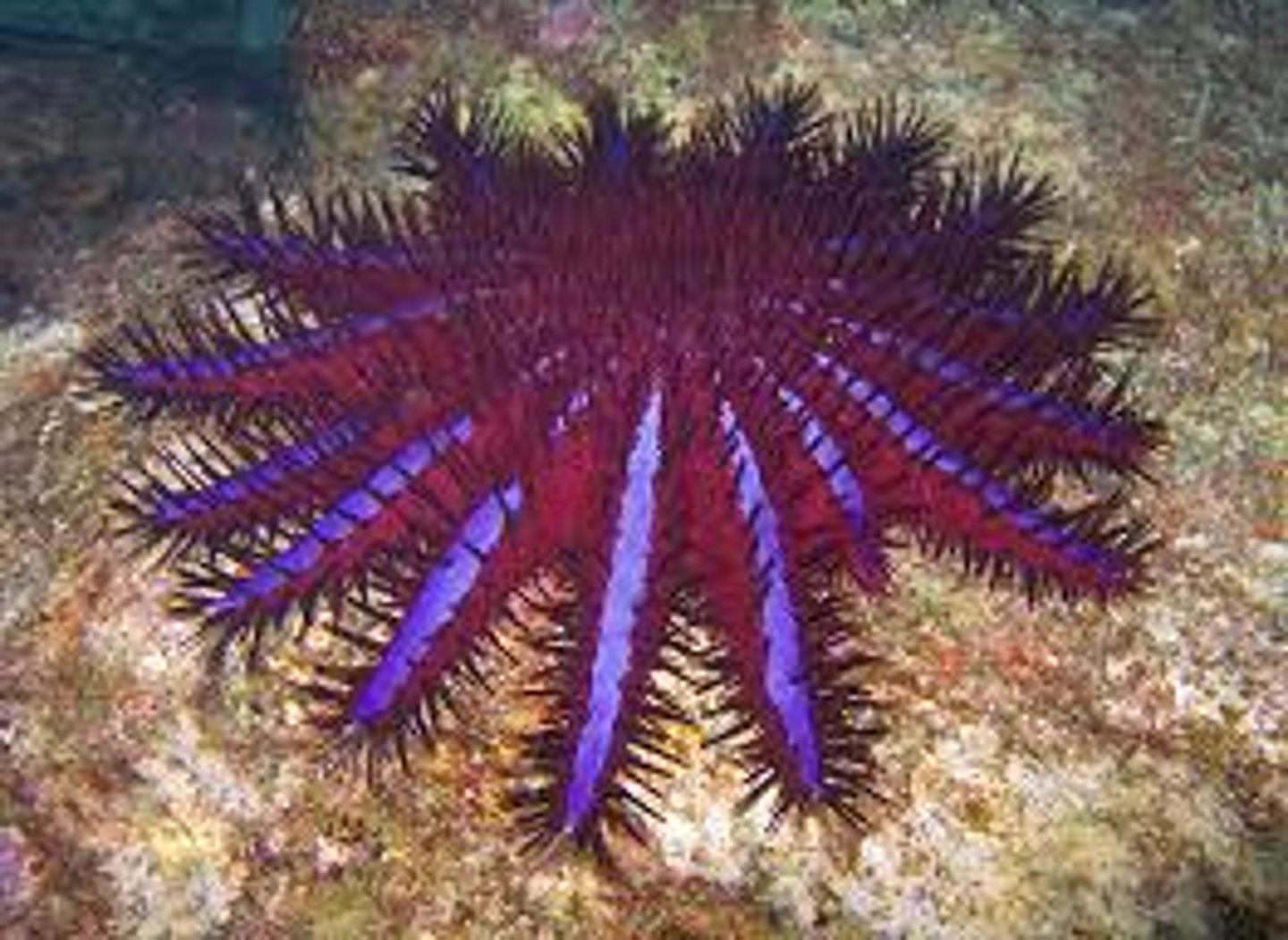
echinodrmata- crown of thorns
active predator feed on coral polyps
responsible for extensive damage to coral reefs
contain toxins in spines
can play an important role in guaranteeing community succession in coral reefs, by not allowing dominant coral species to completely outcompete other coral species

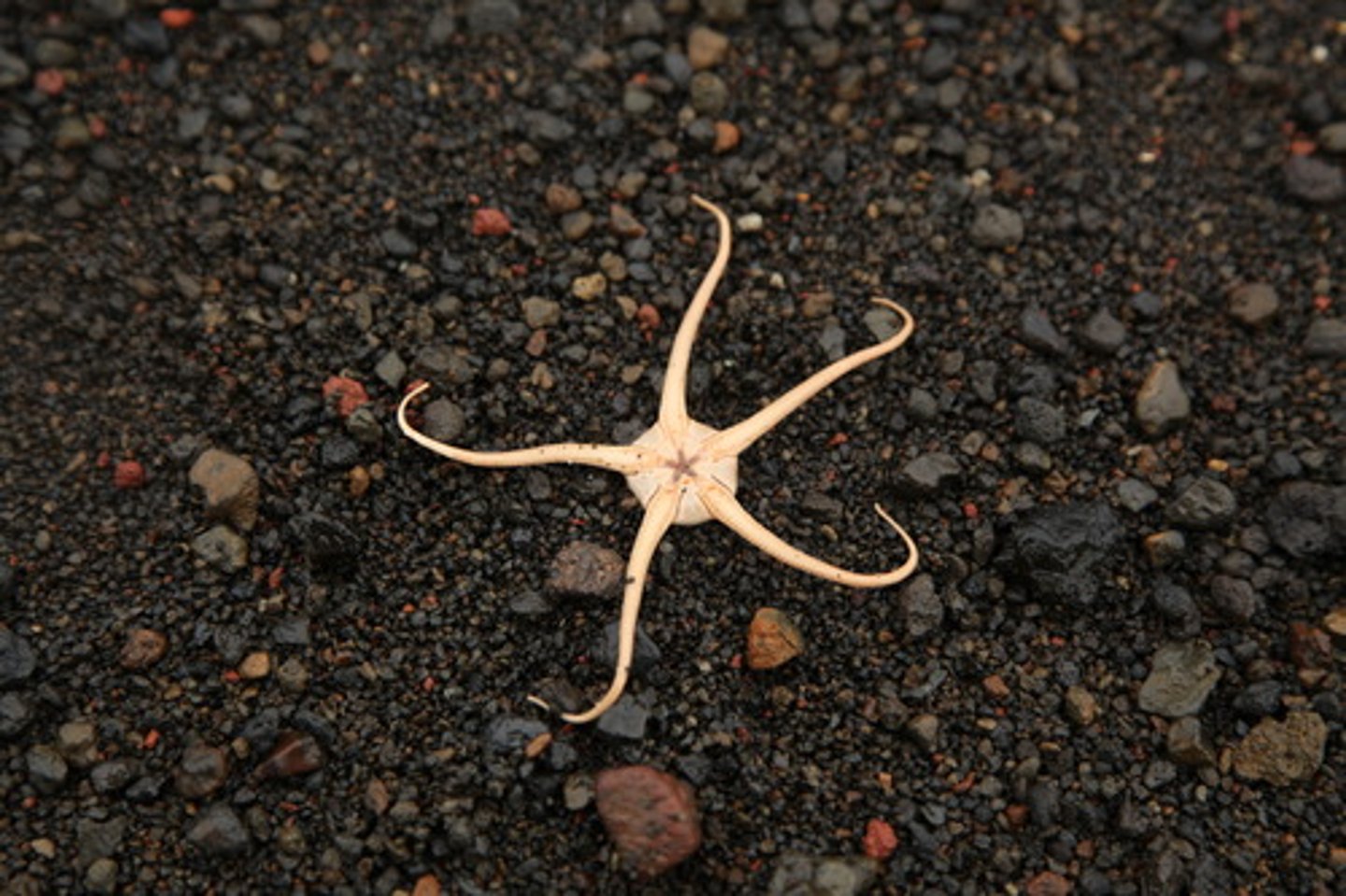
echinodrmata - opiuroidea
similar to starfish
thinner arms
mostly nocturnal
active predators
dominate in deep waters
better crawlers than starfish

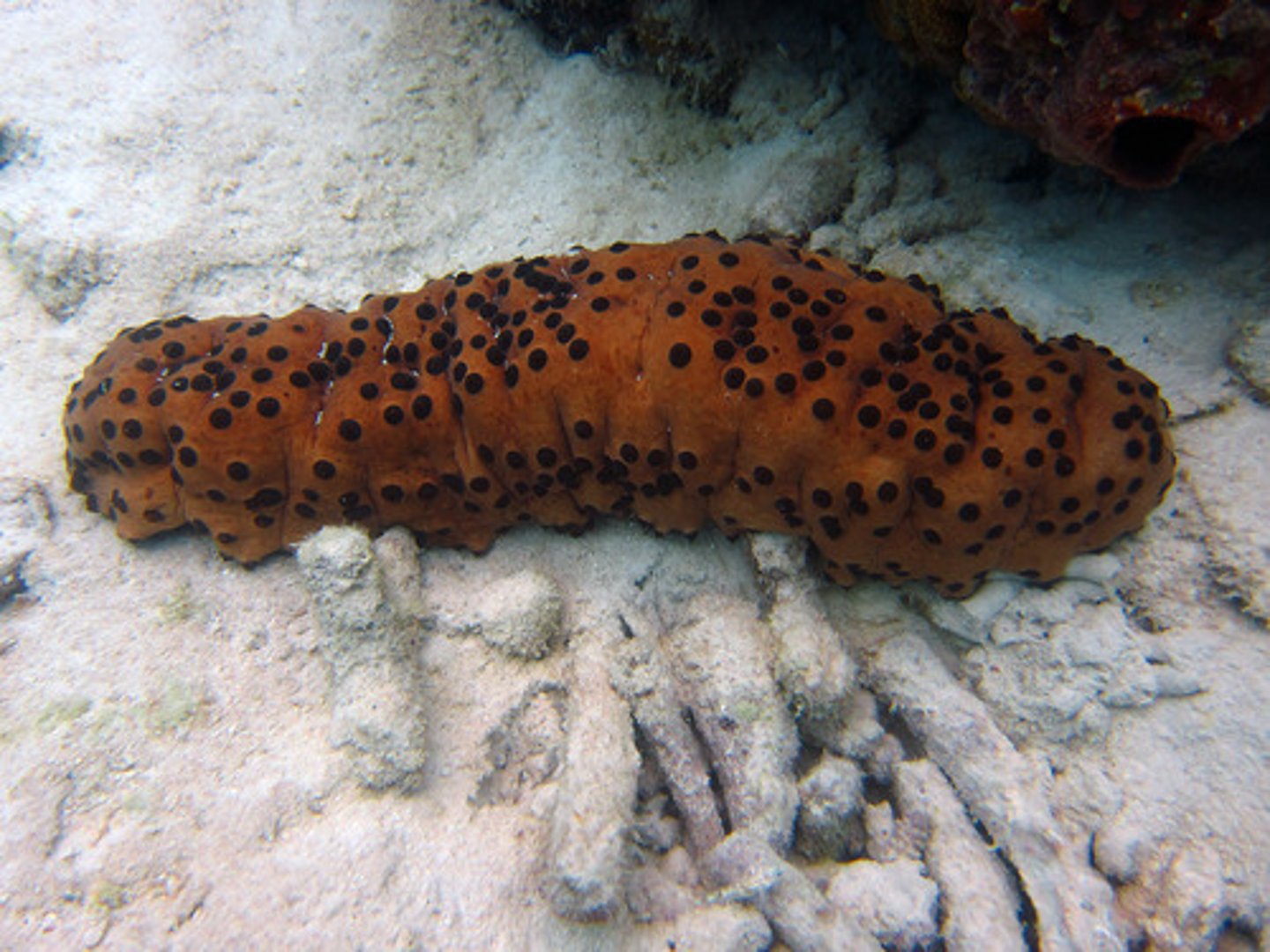
echinodrmata - holothuroidea
look very different than other echnioderms
abundant in shallow waters
dominant in deep waters
deposit feeders

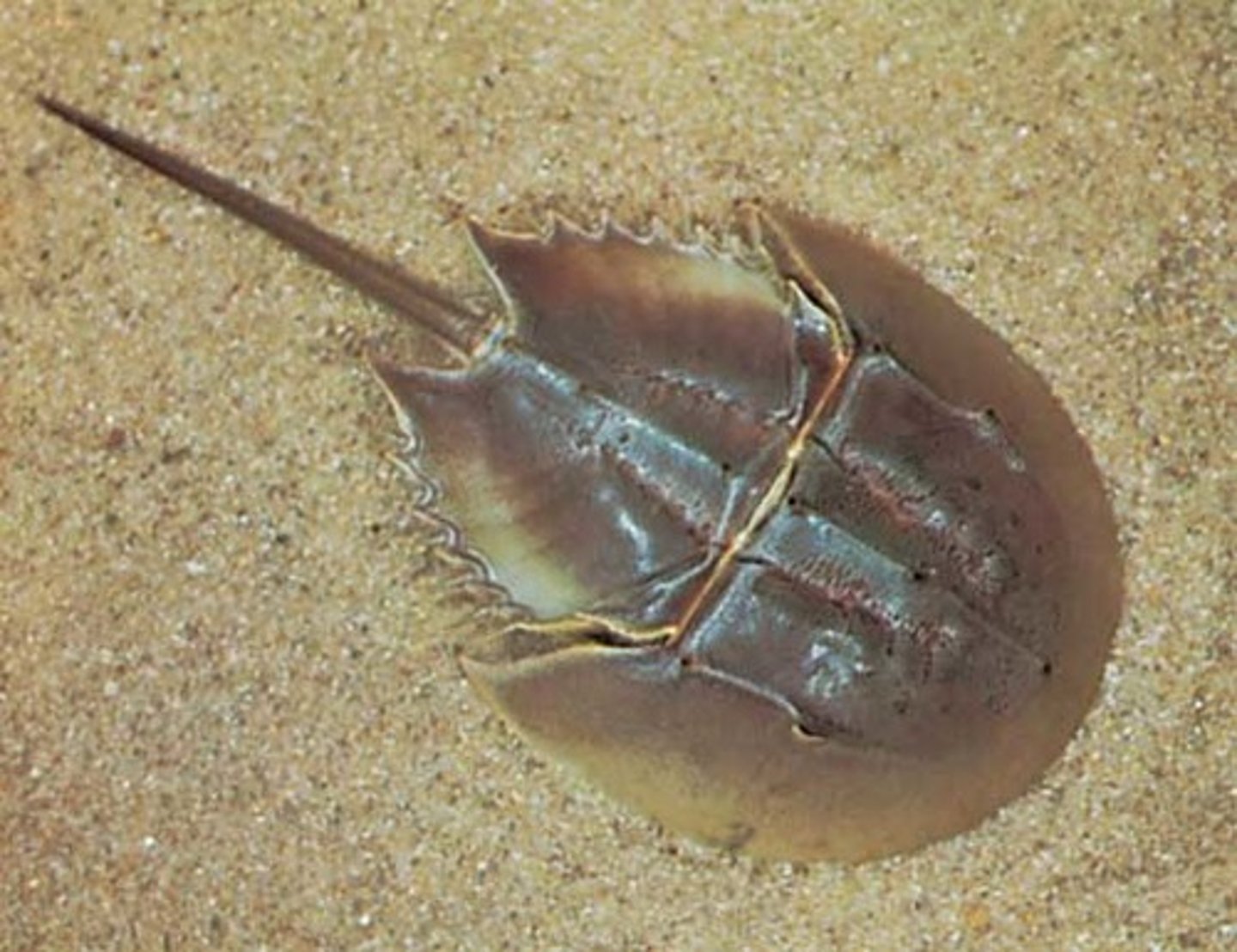
anthropoda - chelicerata
sea spiders and horseshoe crabs
posses two sets of appendages located anterior to their mouth
carnivores, feed on sponges and sea anemones
little know about ecology
economic importance

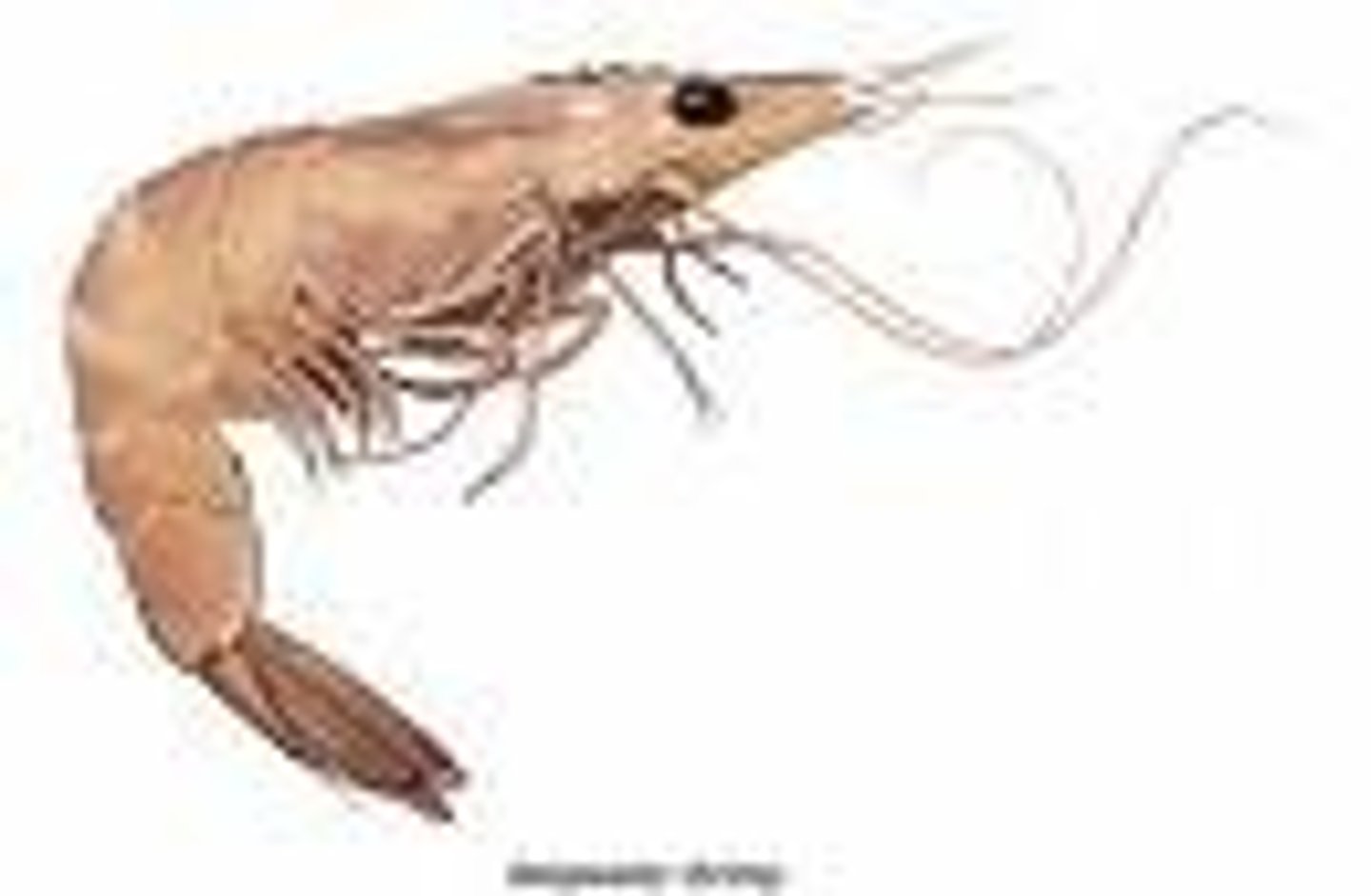
anthropoda - crustacea
very large and important group
all posses an exoskeleton which they molt at part of their growth
exshrimp, isopods, and decapods

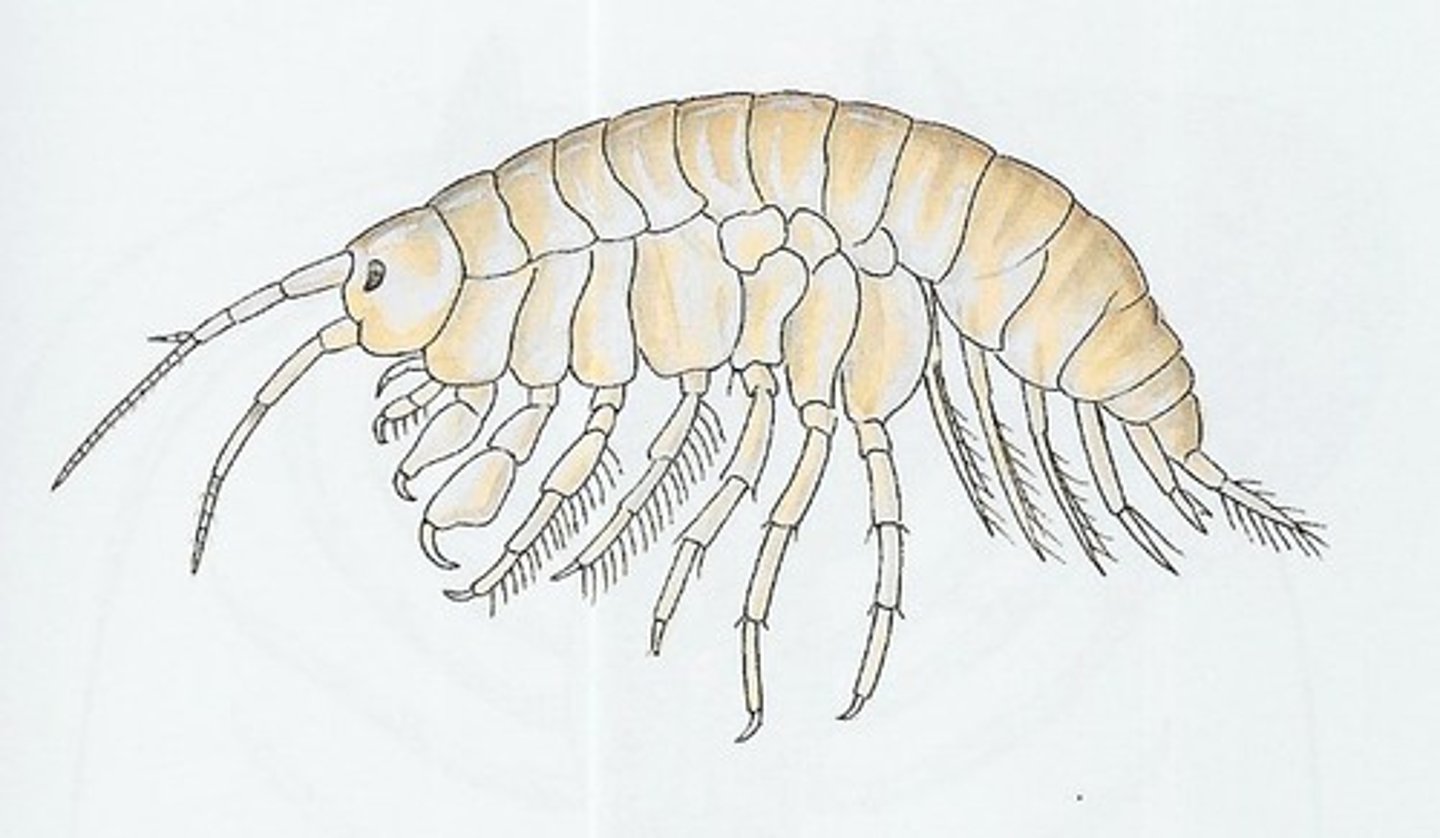
anthropoda- amphipods
extremely abundant
laterally compressed bodies
scavengers
sexual reproduction
prey for many marine spcies
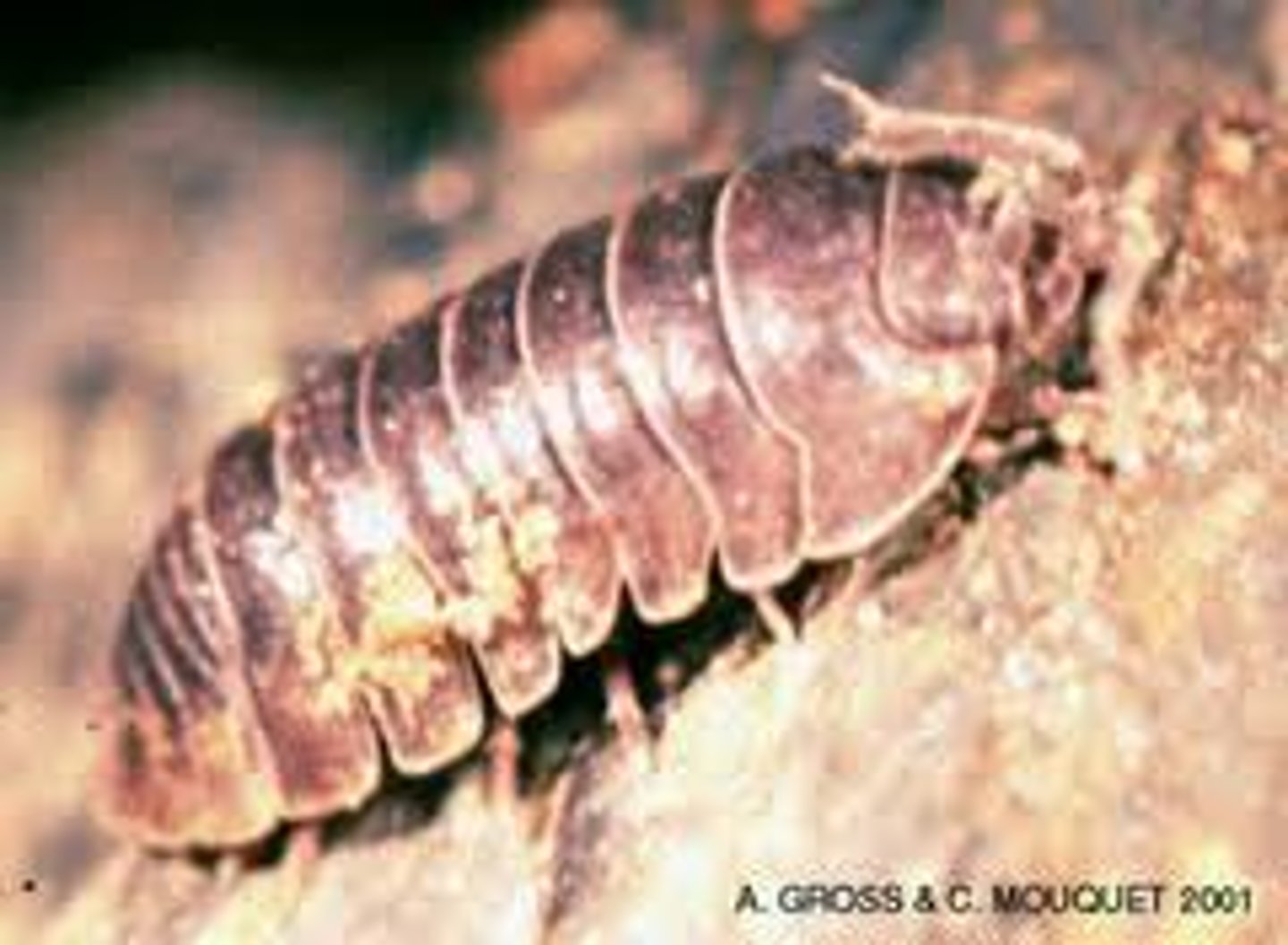
anthropoda- isopods
extremely abundant
dorsal-ventra compressed body
many are parasites
important as a food resource for many other species
some are wood borers
lack a carapace

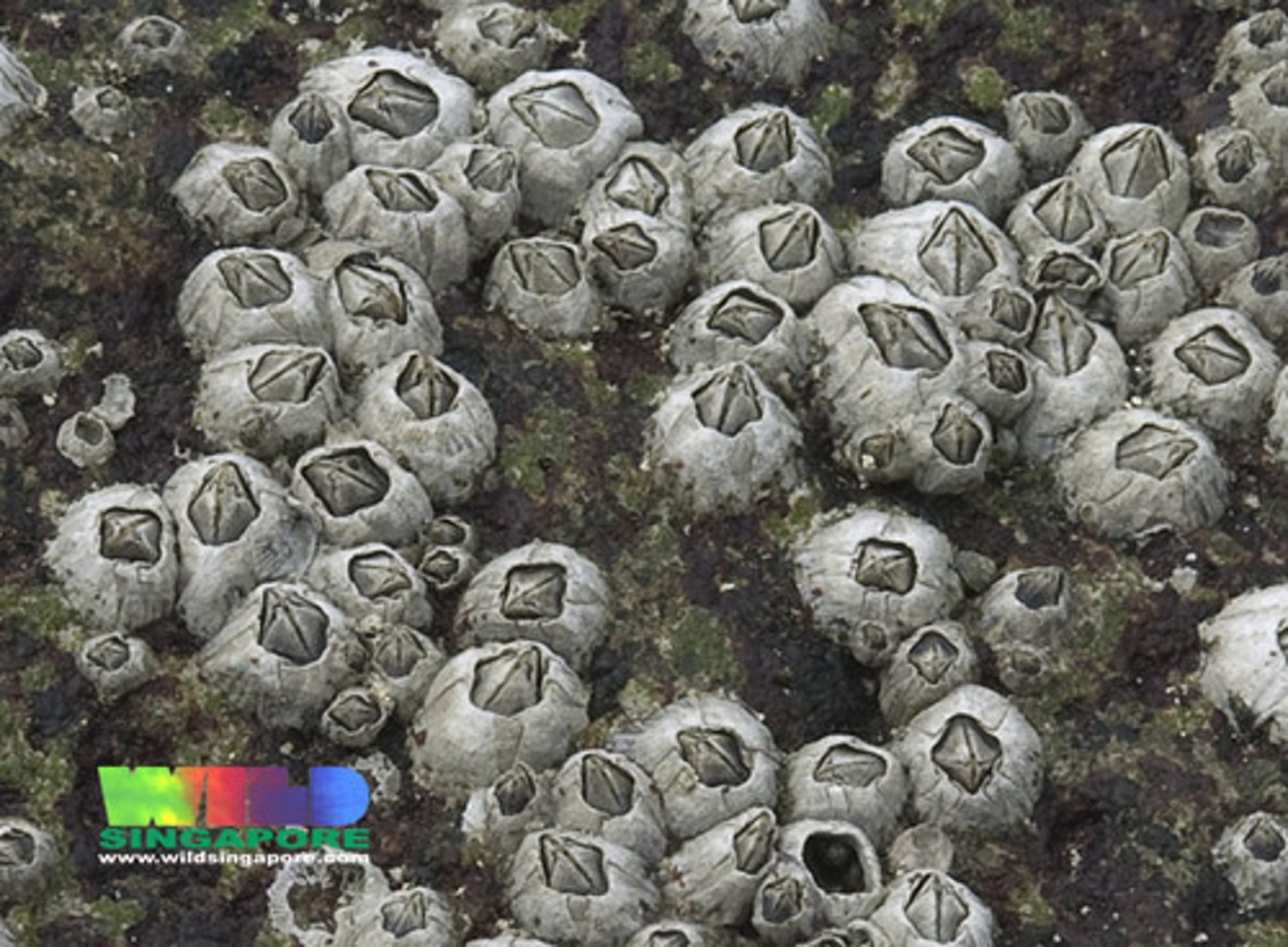
anthropoda- barnacles
extremely abundant
prefor littoral and sublittoral zones
exclusively marine
some are parasites
sessile suspension feeders

anthropoda -decapods
largest and most mobile of all crustacean
economically important
play important ecological roles
marine, freshwater, and some terrestrial
posses carapace
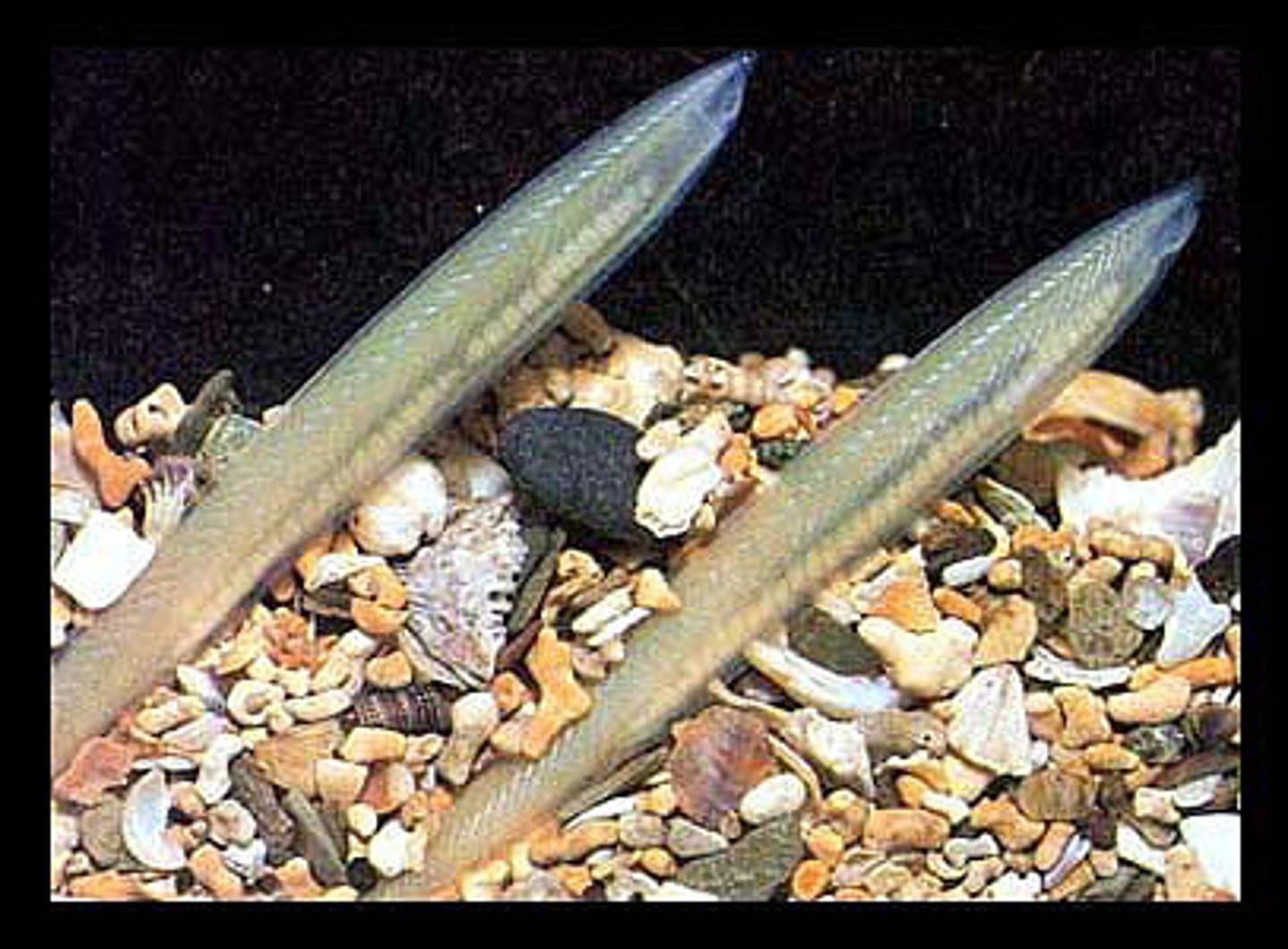
chordata - cephalochordata
found in shallow sandy areas
filter feeders
linked to the vertebrates
dorsal nerve tube

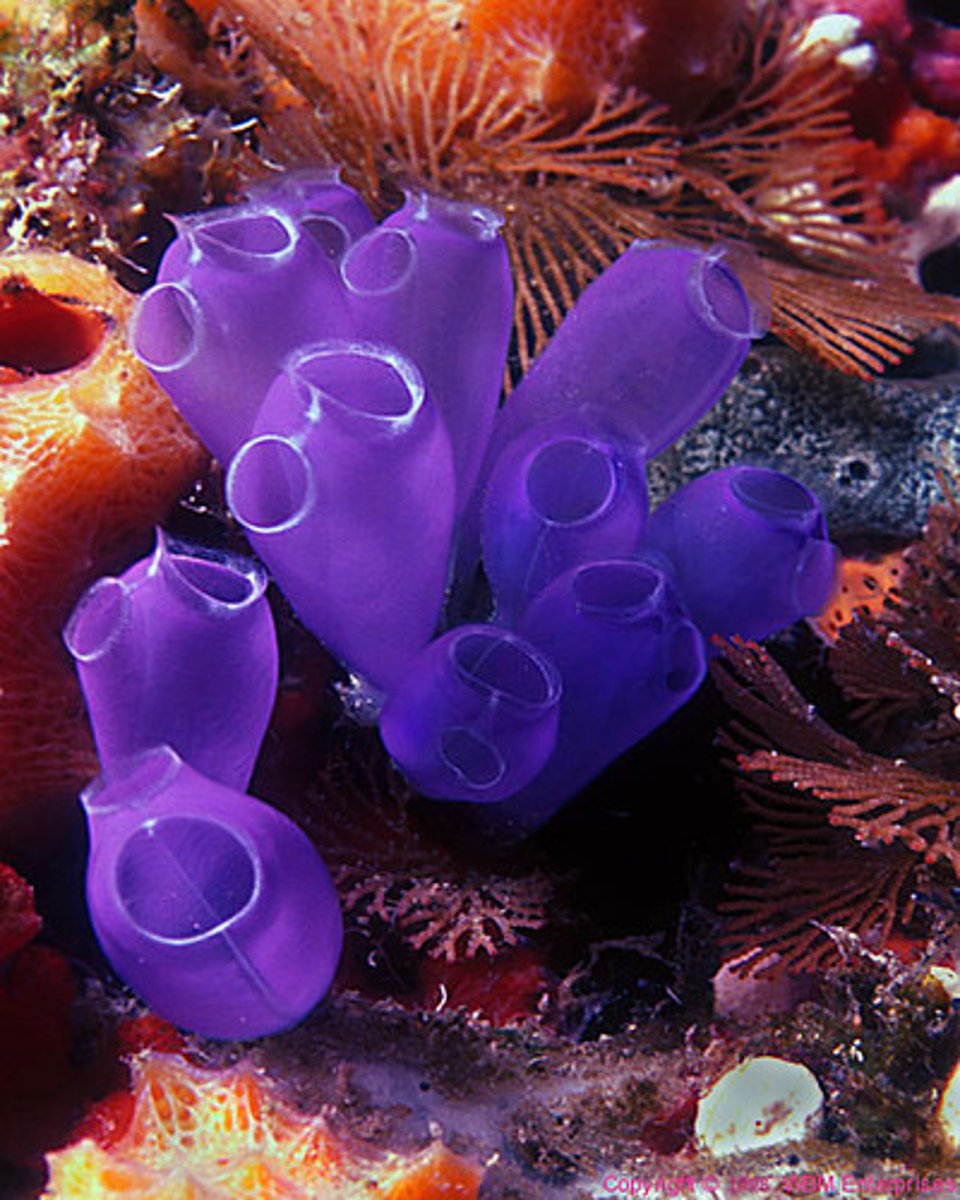
chordata- tunicata
present a rudimentary notochord on their larval development
filter feeders
sessile, some are planktonic
some colonial, other solitary
