616 Inclusive Communication and sensory impairments 1/23
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Define social determinants of health
The conditions in the places where people live, learn, work, and play that affect a wide range of health and quality-of-life risks and outcomes

Health disparities vs health care disparities
Health disparities: differences in health status between people related to social or demographic factors such as race, gender, income, geographic region
Health care disparities: differences btwn groups of people in health insurance, access, and use of care, and quality of care
--> both are measures of progress toward achieving health equity
What is unconscious bias?
Social stereotypes about certain groups of people individuals form outside their own conscious awareness
- everyone holds unconscious beliefs about various social and identity groups, and these biases stem from one's tendency to organize social worlds by categorzing
Implicit bias - how it happens
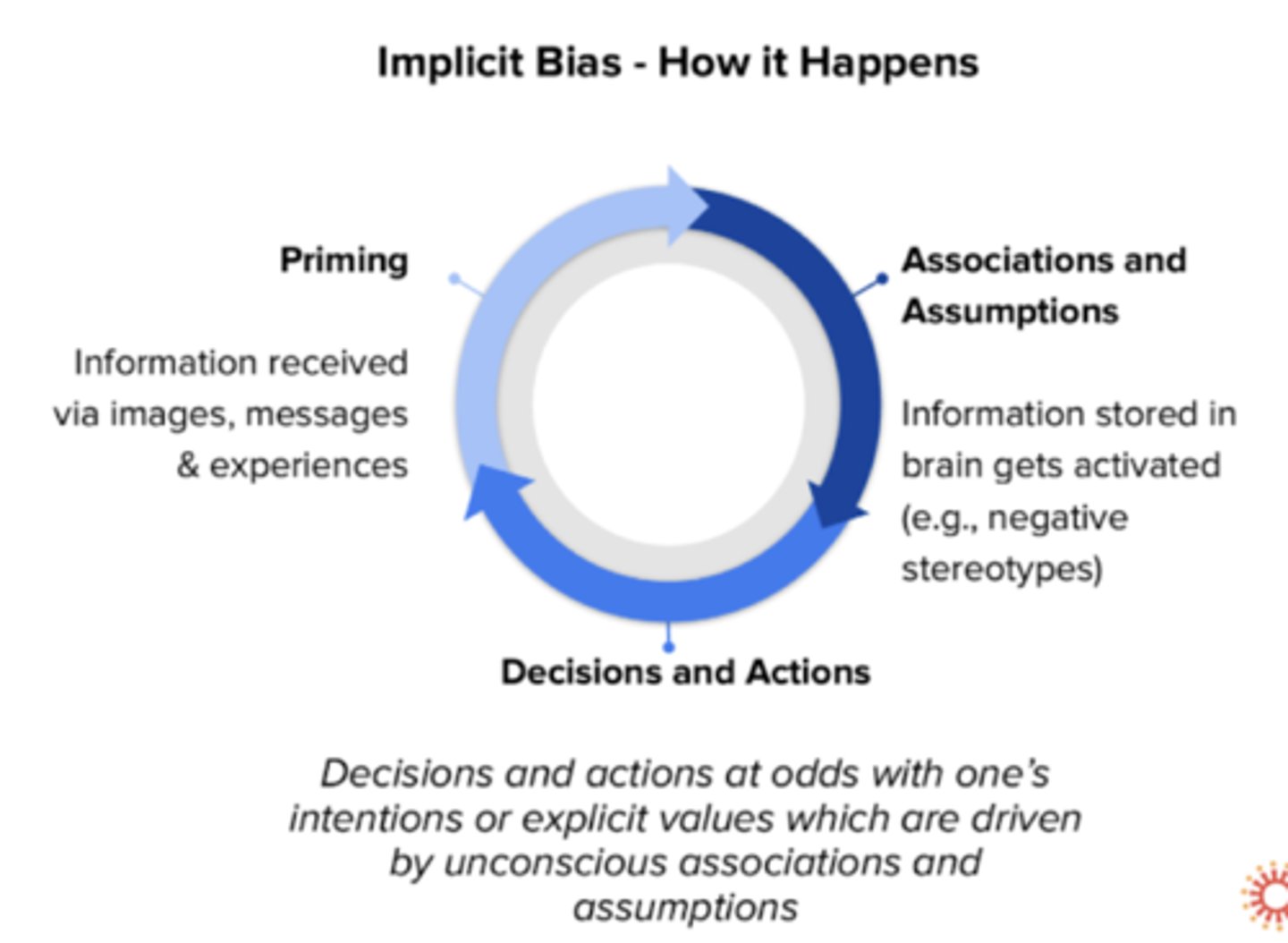
What is priming?
We are primed to make certain associations based on messages we receive
- begins when we are infants through patterns and associations created based on what we see and hear
- Associations -> unconscious mind makes rapid fire associations (can be pos, neg)
- Building synapses --> the more you see two things together, the faster you associate them
3 parts of counteracting implicit bias
- See: Recognize
- Engage: Interrupt
- Act: Shift

What is person first language?
- ex?
Eliminates generalizations, assumptions, and stereotypes by focusing on the person rather than the disability
- individual first, and the disability second
- Ex: "Person with a hearing impairment," "person with autism" etc
What is identity-first language?
Stating a descriptor of a person's condition first, emphasizing that the condition is an integral part of their identity and community membership
--> the disability plays a role in who the person is and reinforces disability as a positive cultural identifier.
- Generally preferred by self-advocates in the autistic, deaf, and blind communities
- "Deaf person"
What is ableism?
Discrimination of and social prejudice against people with disabilities based on the belief that typical abilities are superior
- rooted in the assumption that disabled people require "fixing" and defines people by their disability
- classifies entire groups as "less than" and that disability is bad, negative, a problem to be fixed, rather than normal, inevitable part of the human experience
Ableism examples

Guiding points for interactions with people with disabilities

Phrases to avoid with people with disabilities

Three responsibilities of clinicians to disability communities
1. Combat ableism
2. Communicate better with pts w disabilities
3. Recognize people w disabilities as experts of their own lives

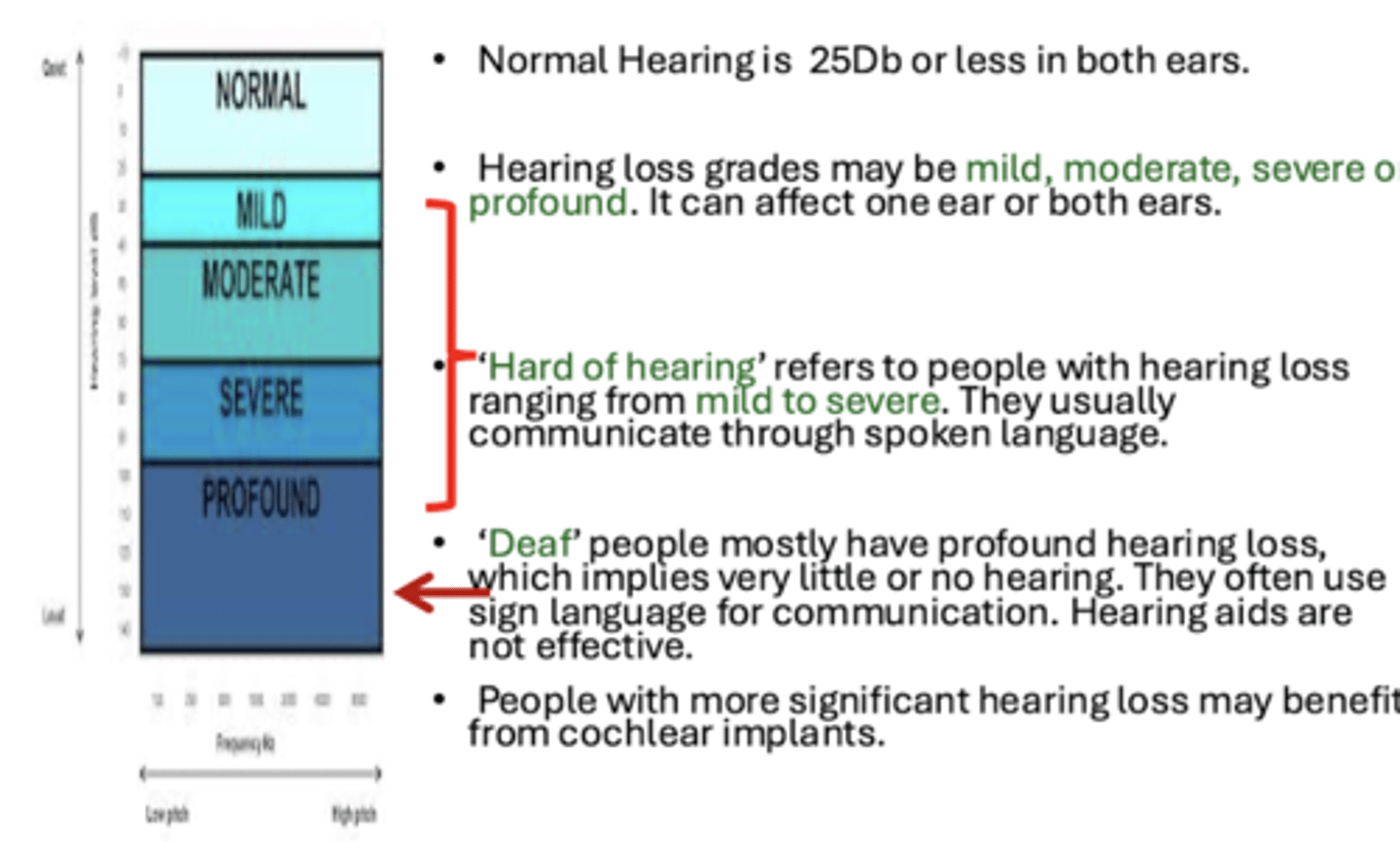
Definition of hearing loss and deafness
- Hard of hearing
- Deaf
- Normal hearing: 25Db or less in both ears
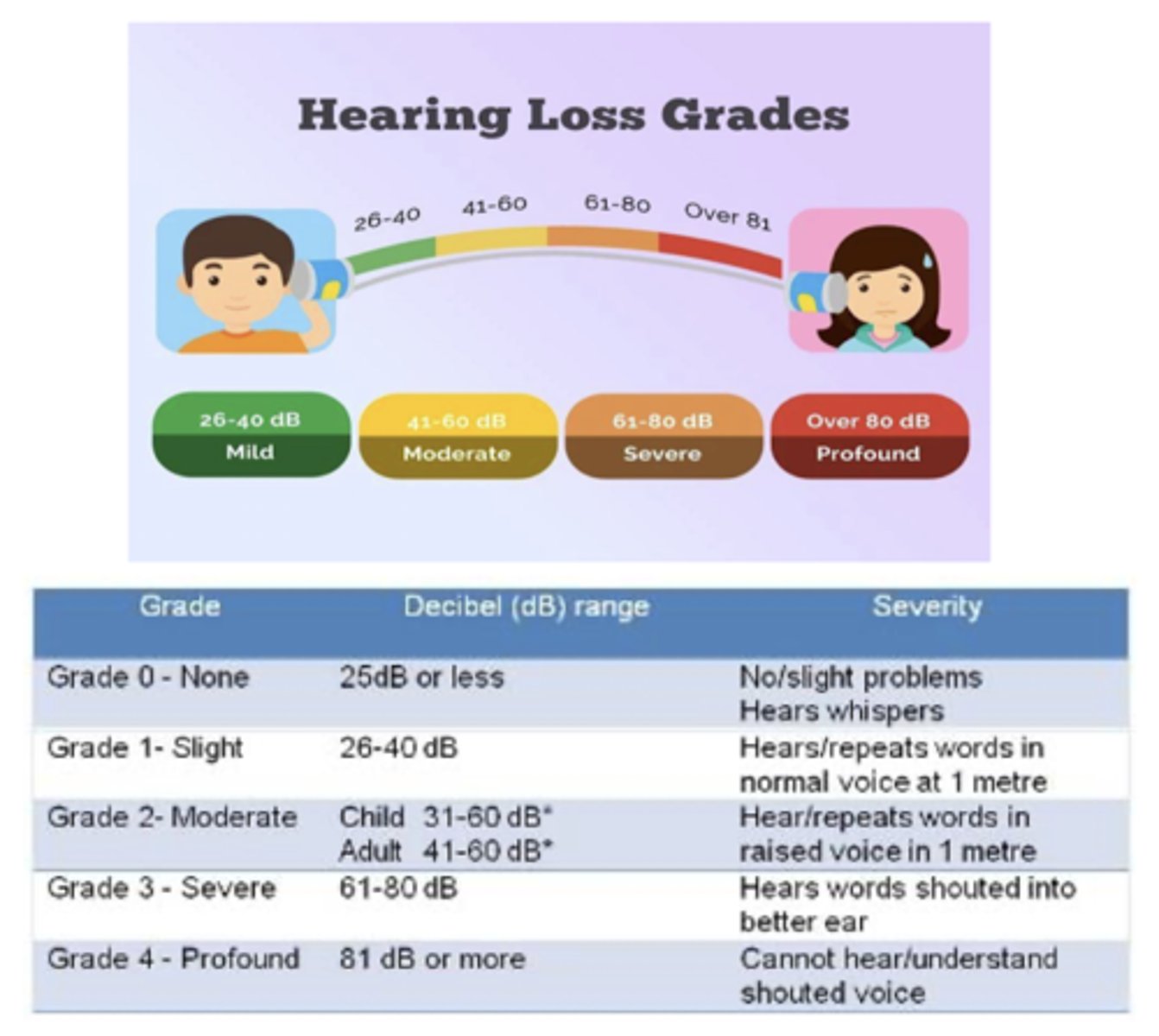
- Hearing loss grades: mild, moderate, severe, or profound
- Hard of hearing: people with hearing loss in range from mild to severe; usually communicate through spoken language
- Deaf: profound hearing loss; little or no hearing; often use sign language for communications, hearing aids are not effective
Hearing loss grades
Causes of hearing loss
Can be caused by many things: viruses and bacteria, disease processes, trauma, certain types of (ototoxic) medications, noise and genetic factors
T/F: Children with hearing loss who begin early intervention earlier have significantly better developmental outcomes
True
- same is true with autism
What is the most important factor in predicting outcomes of newly identified deaf/hard of hearing babies in early intervention?
Active participation of their parents
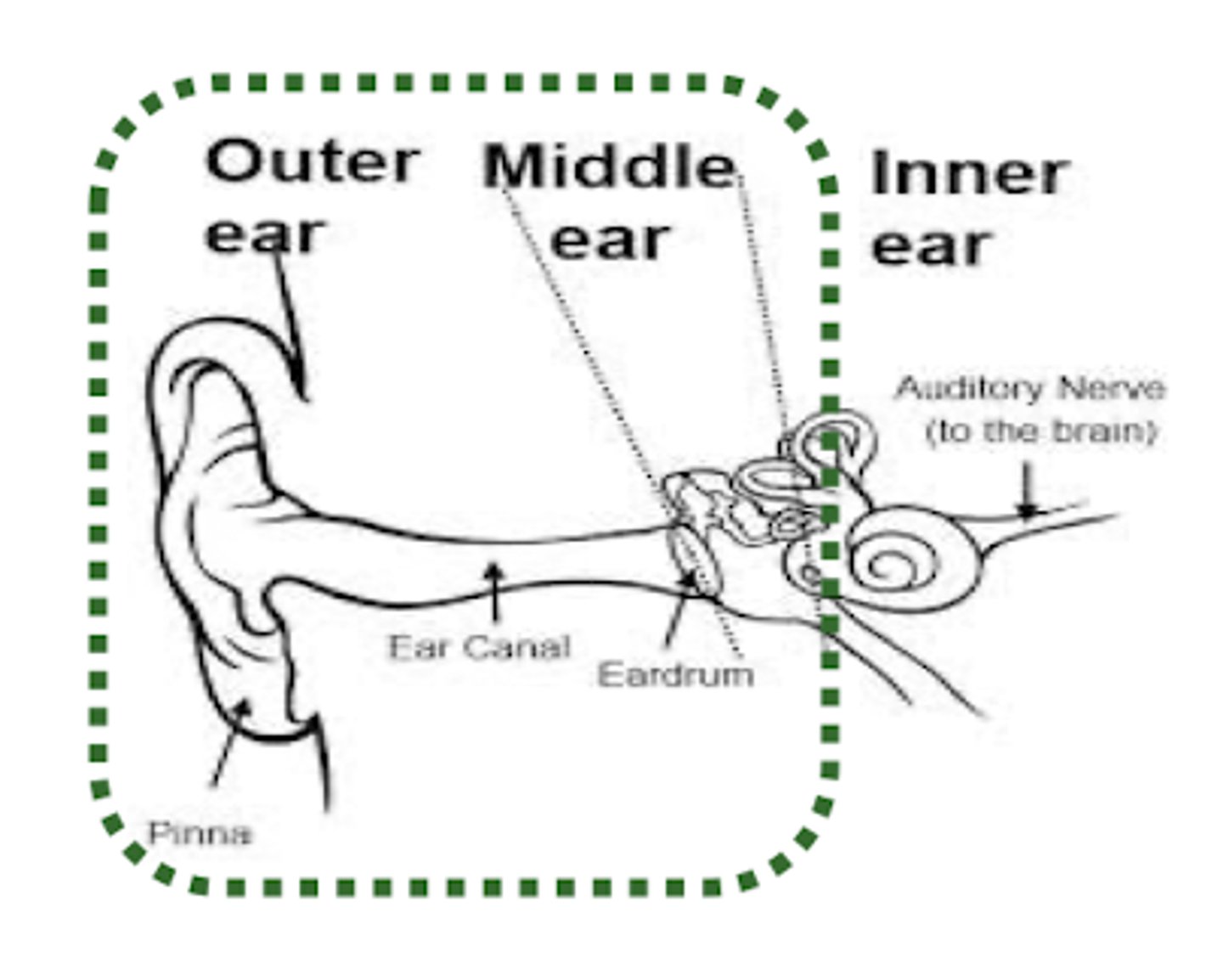
Hearing anatomy
inner ear: malleus, incus, stapes
• cochlea
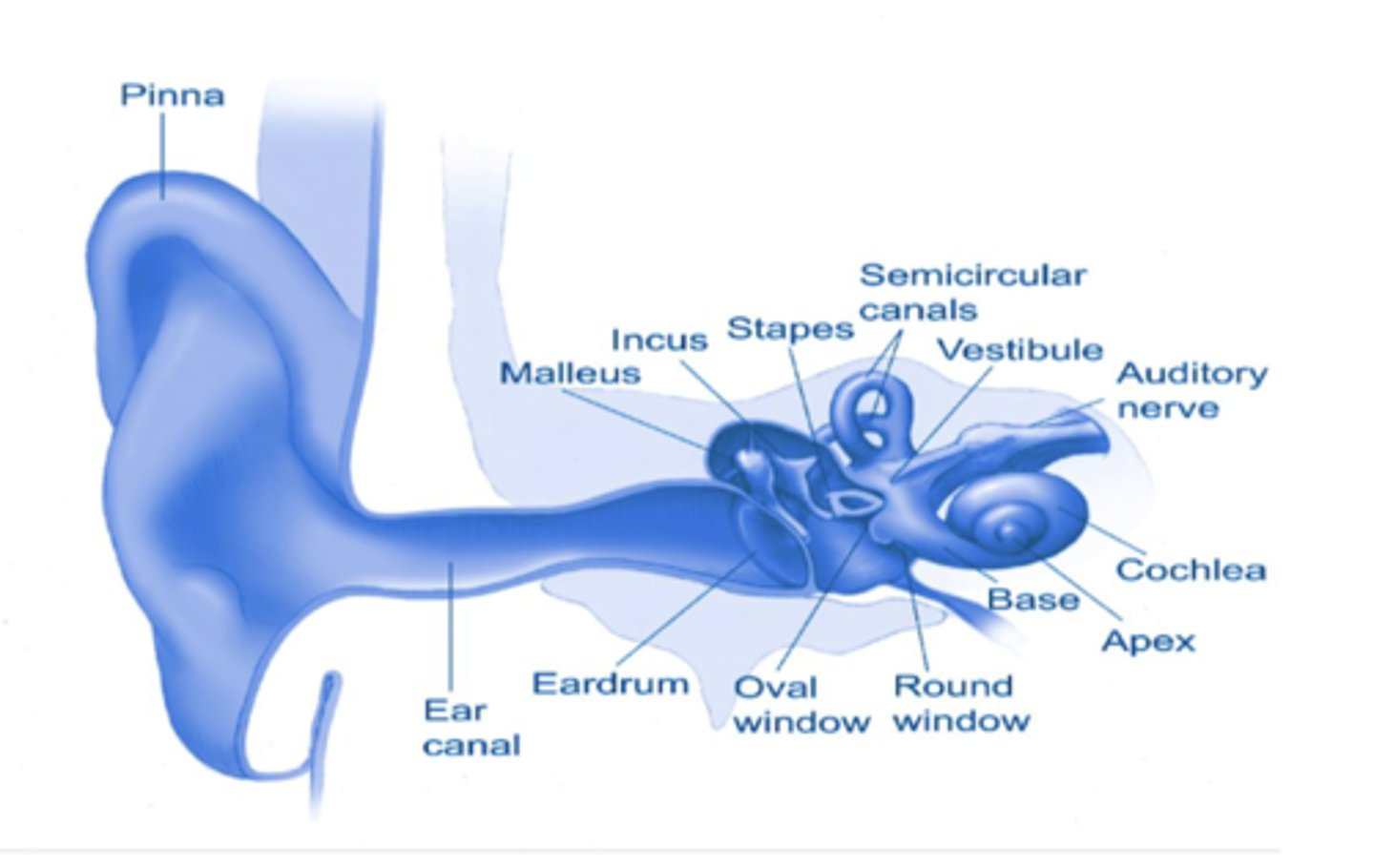
Types of hearing loss (2)
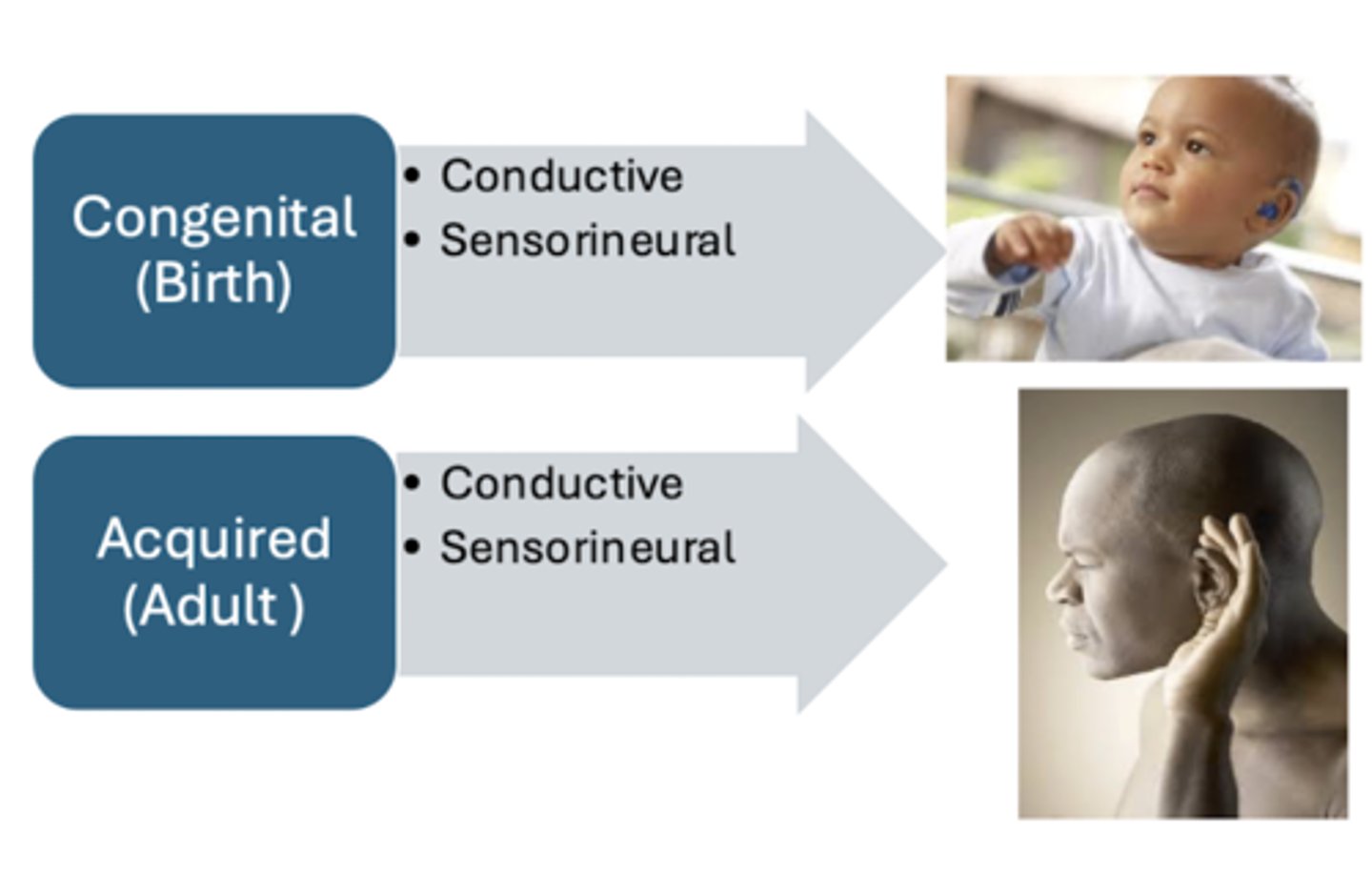
What is conductive hearing loss?
Occurs when something in the outer ear or middle ear blocks or impedes the passage of sound waves ot the inner ear
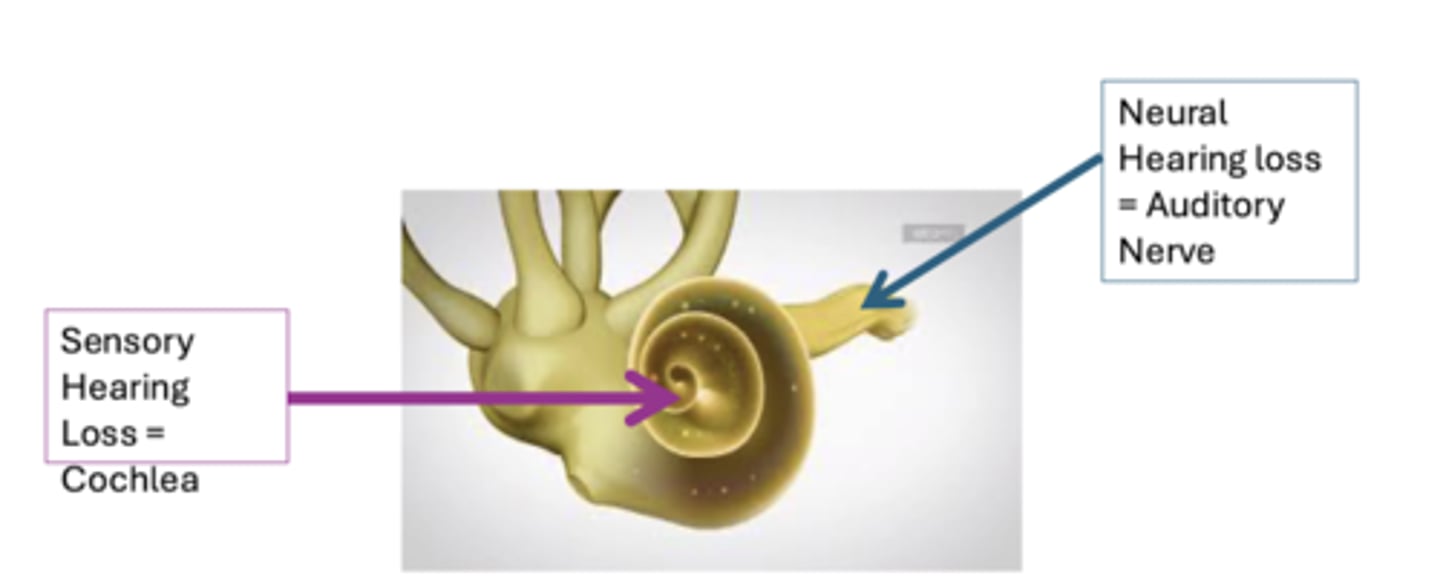
What is sensorineural hearing loss?
Occurs when there is a problem in the inner ear; with either the cochlea (sensory hearing loss) or the auditory nerve (neural hearing loss)
What is the most common cause of sensorineural hearing loss?
Aging
What is the most common loss of sound in sensorineural hearing loss?
in the higher frequencies
T/F: You can have mixed hearing loss with conductive and sensorineural loss.
True
What types of sounds are more difficult to hear with hearing loss?
- Consonants are more difficult to hear ("S", "C")
- Vowels are easier to hear
Treatments for hearing loss (7)

Intensity =
Frequency =
Intensity = loudness
Frequency = pitch
- X = dental equipment

Anything over what decibel is considered hearing loss?
Anything over 30
- normal to not be able to hear under 25-30
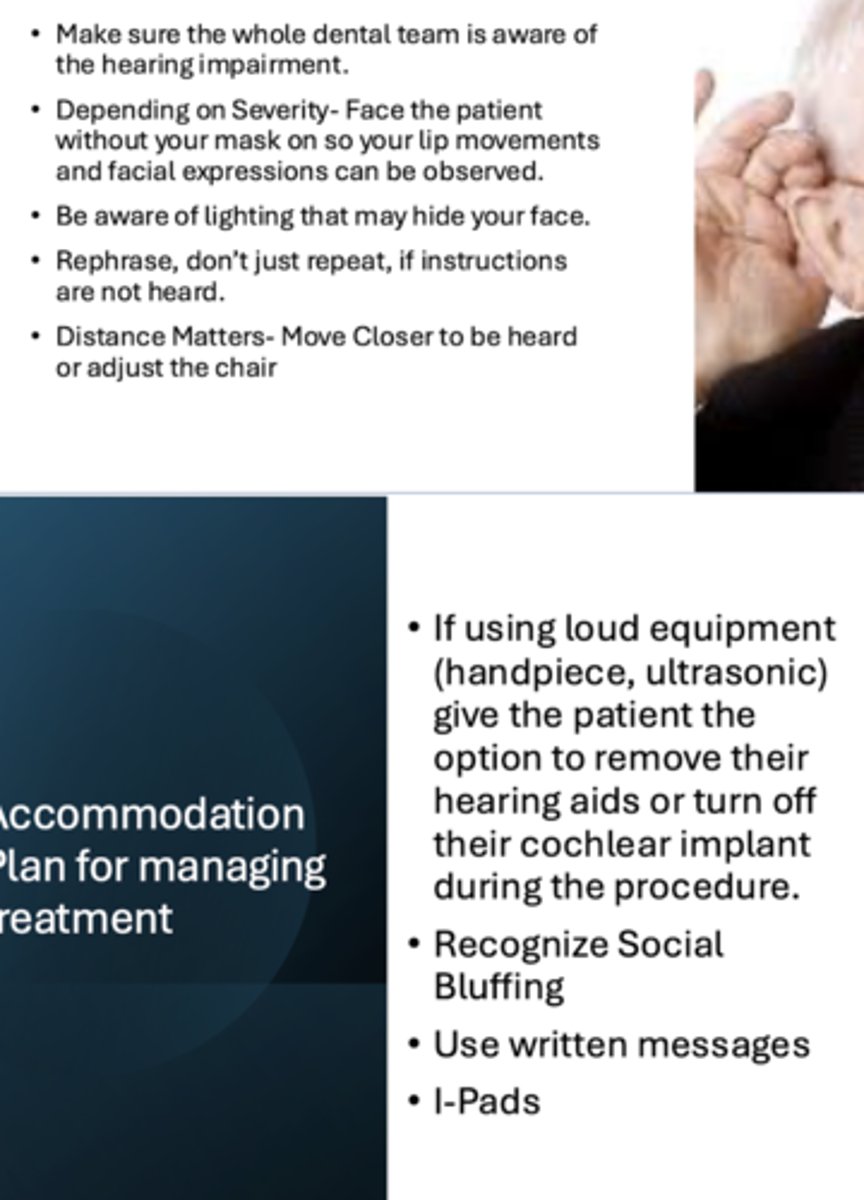
Dental considerations - Accommodations for pts with hearing loss
Misconceptions about people with hearing loss

OSHA guidelines state _____ hours at _______ dB is permissible daily for the dental setting
8 hours, 85dB
Long or repeated exposure to sounds at or above ______ dB can cause hearing loss
85
Definition of legal blindness
The total area an individual can see without moving the eye of 20 degrees or less (tunnel vision) in the better seeing eye

Causes of childhood blindness

Prevention for blindness (3)
- Access to prenatal care
- Primary healthcare
- Good nutrition
What is total blindness?
- only what %?
- Complete lack of light perception and form perception
- NLP- No Light Perception
- Only 15% are NLP
Define visually impaired
- Best optical correction is no better than _________
- Best optical correction is no better than 20/70
Define low vision
Having low vision means that even with regular glasses, contact lenses, medication, or surgery, you may find it difficult to perform everyday tasks, such as reading your mail, shopping, preparing meals, and signing your name
- usually caused by age related conditions
Low vision causes (5)

What are some things that may cause acquired low vision and blindness?
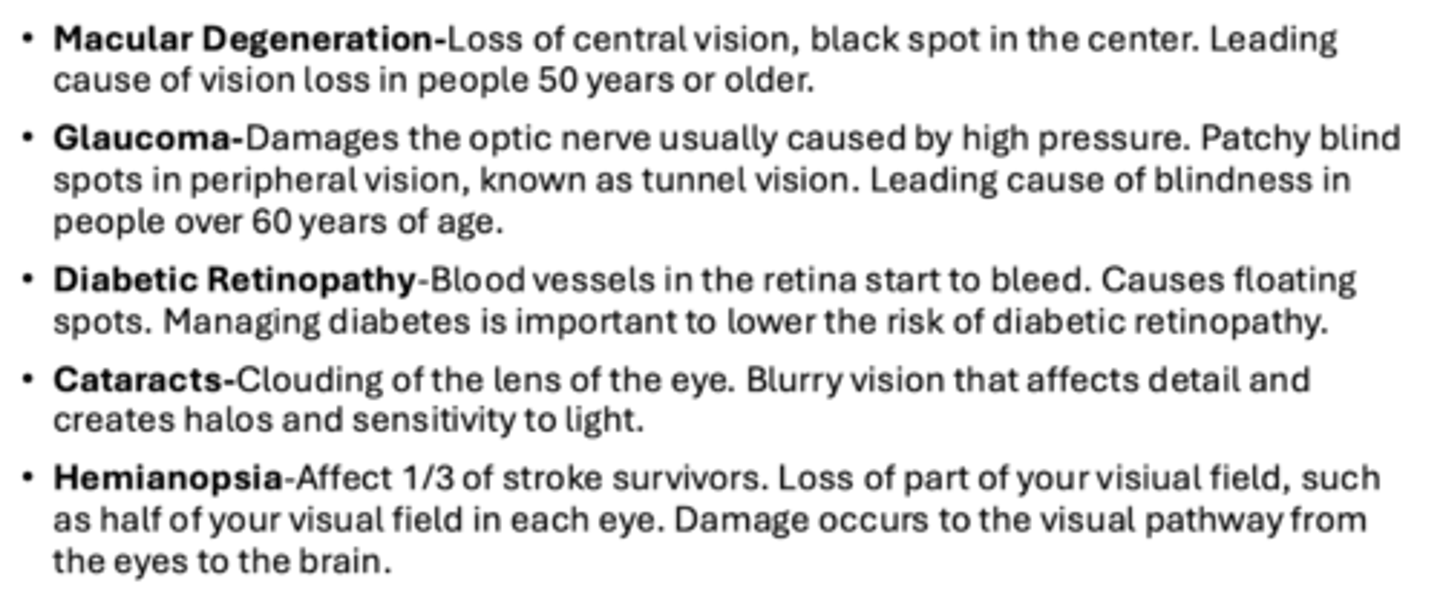
What are some low vision aids?
- less than 10% use braille
- children instead use audio texts, voice-recognition software or other technology
Attitudes and behaviors of society towards low vision and blindness
1. Unsolicited, inappropriate assistance by strangers
2. People talking in a loud voice as if they were deaf
3. Addressing questions to sighted companions
4. Verbalizing pity
Dental office accommodation plan for blind pts
- Avoid loose rugs
- Consider print of materials
- Unwieldy doors
- Slippery floors (changes in surface texture)
- May have assistance by a guide-dog communication with staff
- Children can benefit by a pre-appointment visit prior to their dental exam
- Encourage parents to practice looking in their child's mouth and brushing
- Talk them through the appt
- Introduce all staff that are in the room
- Minimize excess noise-loud music, prolonged suction, ultrasonic cleaners, identify motorized noises and movements