Nursing: Thermoregulation
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Body temperature is:
Indicates the difference between production of heat and loss of heat
Heat produced – heat lost = body temperature

Core temperature is normally…
between 36.0C and 37.5C
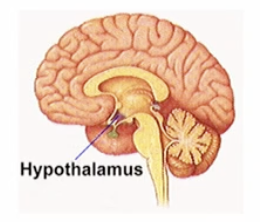
body tempeture is maintained by…
the thermoregulatory centre in the hypothalamus
What are the four main processes heat energy can be transferred by - RECC
RADIATION, EVAPORATION, CONVECTION AND CONDUCTION
Conduction:
A diffusive process where molecules transmit their kinetic energy to other molecules by colliding with them. Heat energy is tranferred by adjacent molecular collisons inside a material. the medium itself does not move.
what state does Conduction occur in
a solid
Which one of the following is the reaction of the skin when the body becomes very cold?
The arterioles constrict, the hair stands on end and sweat production ceases.
Which of the following describes the blood vessels, sweat glands and temperature of the skin after a period of exercise?
Blood vessels are dilated; sweat glands are active and skin temperature is high.
where is most of the bodies heat lost from?
Skin
Give an example of Conduction
When the molecules in fire vibrate faster it pushes heat energy against the metal rod. OR heat pad on seat. the chocolate in your hand melts cause your hand is warm.

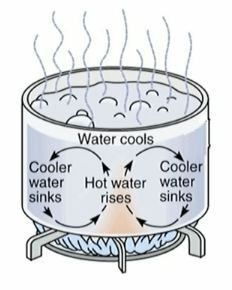
Convection
Transfer of heat through circulating it through liquids or gases. The hot air or liquid rises it becomes less dense, pushing the coldness down.
Convection example:
Boiling water in a pot.
Radiation
Electromagnetic waves carry heat energy form one place to another
Radiation example
If you are sitting next to someone (not touching) with a hot temp, you can sometimes feel their heat.
The principal physical mechanism that accounts for the transfer of heat within the body is what?
Convection
Vaporisation/Evaporation
The change of state from water from a liquid to a vapour (gas) results in the loss of heat from the surrounding structure.
Vaporisation/Evaporation
When we sweat and it evaporate off our skin.
Vasodilation:
Blood vessel dilate, body increases blood flow to the skin. Then skin can lose heat radiating off you. Controlled by autonomic nervous system.
Alot of of heat production is through metabolism. How does this happen?
Thyroxine is secreted from the thyroid, the decrease in thyroxine = the less heat produced by the body
what nervous system is sweat controlled by ?
Sympathetic nervous system
Vasoconstriction
Restricts blood flow to the skin, blood vessel constrict
factors that affect body temp can be
circadian rhythms, exercise, medications, stress, hormone level, age + gender
hyperthermia
when the body can not reduce heat production and promote heat loss.
Hypothermia
when the body can produce heat, excessive heat loss temp is below 35C