U3 AOS2: DP1.1-1.3 Learning (2023)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Operant Conditioning
A learning process in which the consequences that follow a behaviour determine the likelihood that the behaviour will be repeated

Reinforcement
A stimulus that increases the likelihood of a behaviour occurring again in the future

Punishment
A stimulus that decreases the likelihood of a behaviour repeating again in the future

Positive
ADDING a stimulus

Negative
SUBTRACTING/REMOVING a stimulus
Positive Reinforcement
ADDING a pleasant stimulus to INCREASE the likelihood of the behaviour repeating
eg. Ahmed receives pocket money for completing household chores

Negative Reinforcement
REMOVING an unpleasant stimulus to INCREASE the likelihood of the behaviour repeating
eg. Amanda takes a panadol to remove her headache

Positive Punishment
ADDING an unpleasant stimulus to DECREASE the likelihood of the behaviour repeating
eg. 3 year old Eliza received a smack for throwing her food on the ground
Negative Punishment
REMOVING a pleasant stimulus to DECREASE the likelihood of the behaviour repeating
eg. Toby's teacher confiscates his phone for using it during classtime
Maximising the effectiveness of consequences
order of presentation, timing, appropriateness
Three-phase model of operant conditioning
Antecedent, Behaviour, Consequence (ABC model)
Antecedent
the item/stimulus that triggers a behaviour/operant response
Behaviour
response that acts (operates) on the environment
Consequence
the environmental stimulus that follows the operant response that impacts future behaviour
Classical Conditioning
learning that occurs through the repeated (usually) association of two (or more) different stimuli
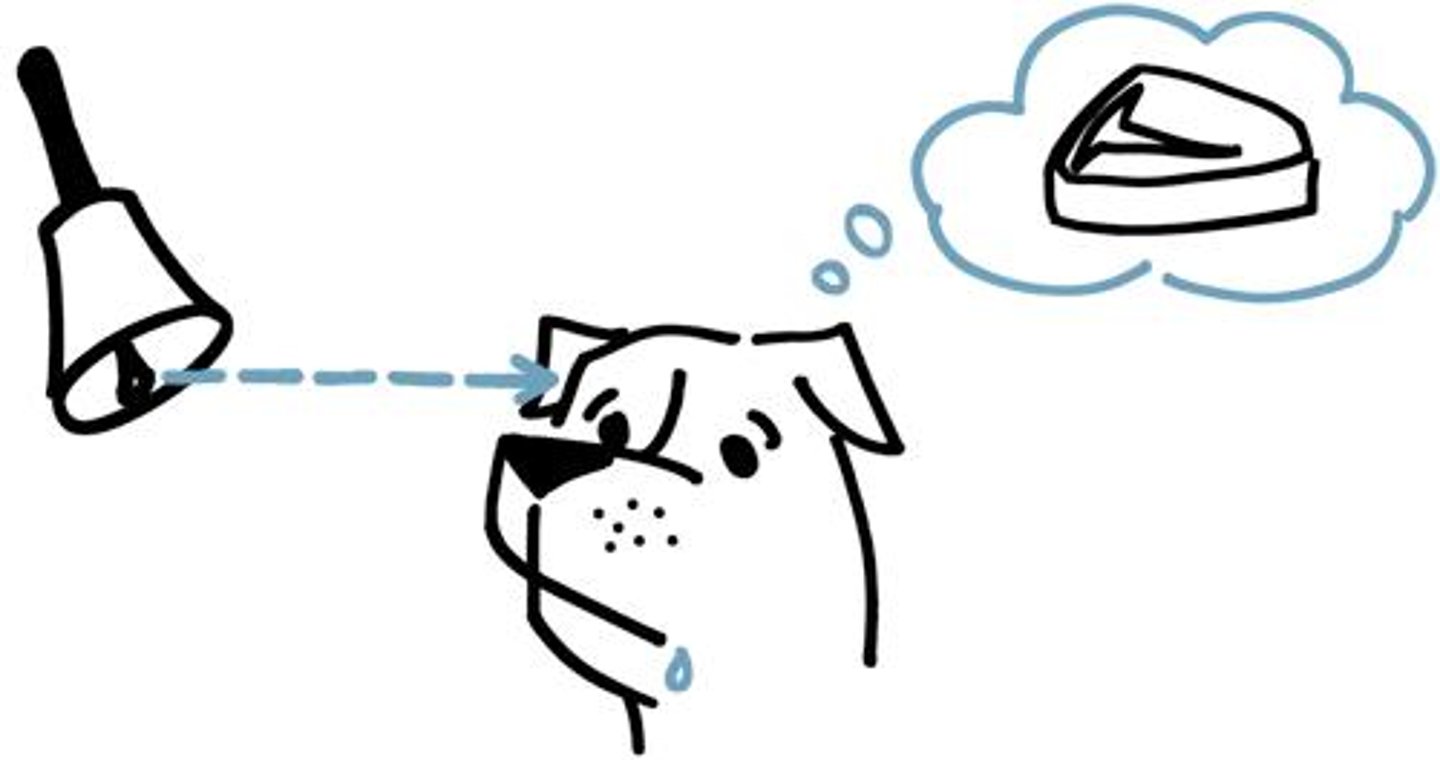
Neutral stimulus (NS)
A stimulus which prior to the conditioning does not evoke a response (e.g. bell, horn, brand, person, people)

Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS)
Any stimulus which produces a (naturally occurring) automatic response (e.g. nice food, good coffee)

Unconditioned Response (UCR)
Occurs automatically when the UCS is presented.
It's reflexive/involuntary (e.g. a physiological change such as salivating when you smell the coffee or food) due to the UCS

Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
originally was the Neutral stimulus (NS) but through repeated (usually) pairings/association with the UCS it now also produces a response

Conditioned Response (CR)
Is a behaviour which is similar but not necessarily the same as the UCR, which is due to (caused/triggered by) the CS after conditioning (eg. dog now salivates to sound of bell)

Three Phase Process of Classical Conditioning
1. Before Conditioning
2. During Conditioning (Acquisition)
3. After Conditioning
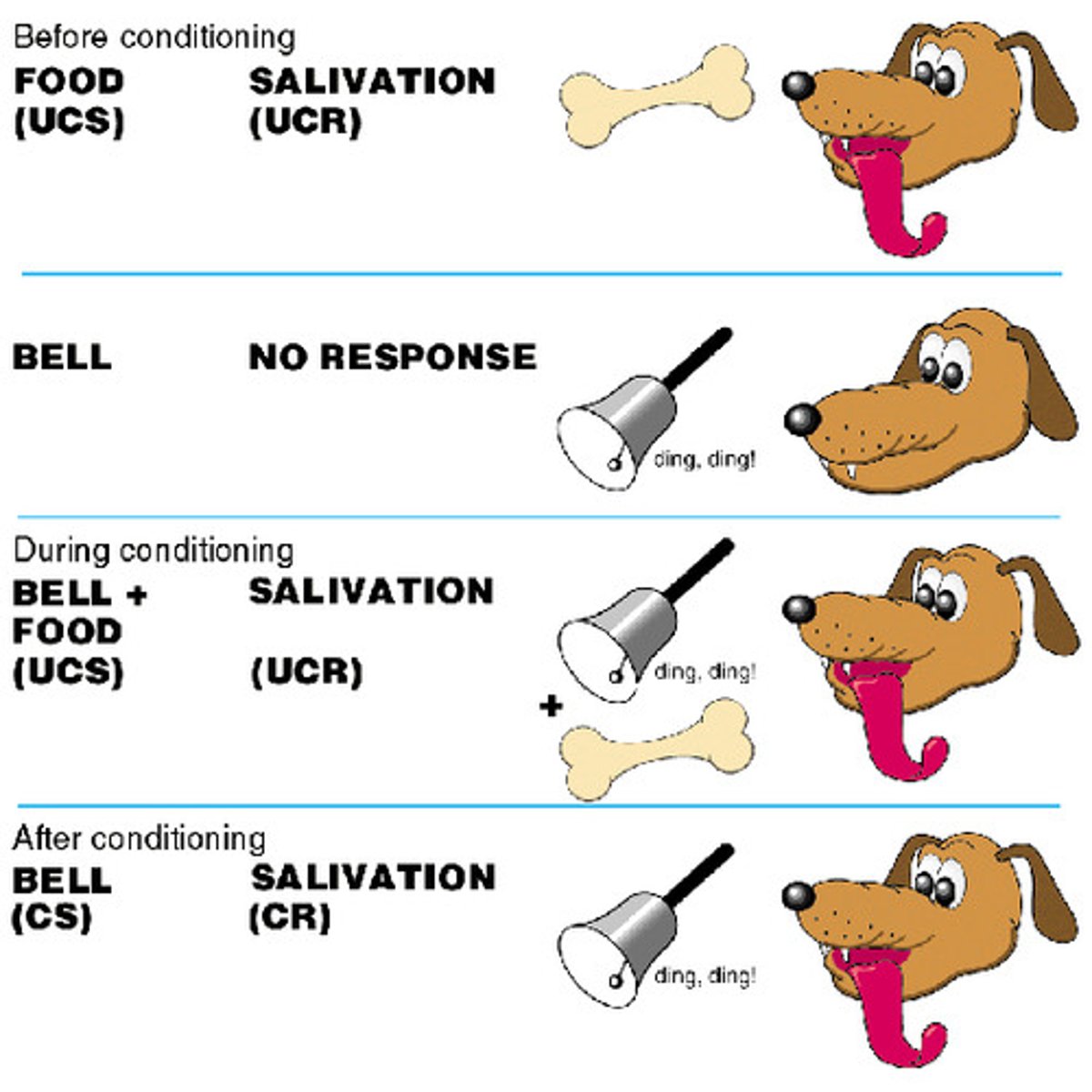
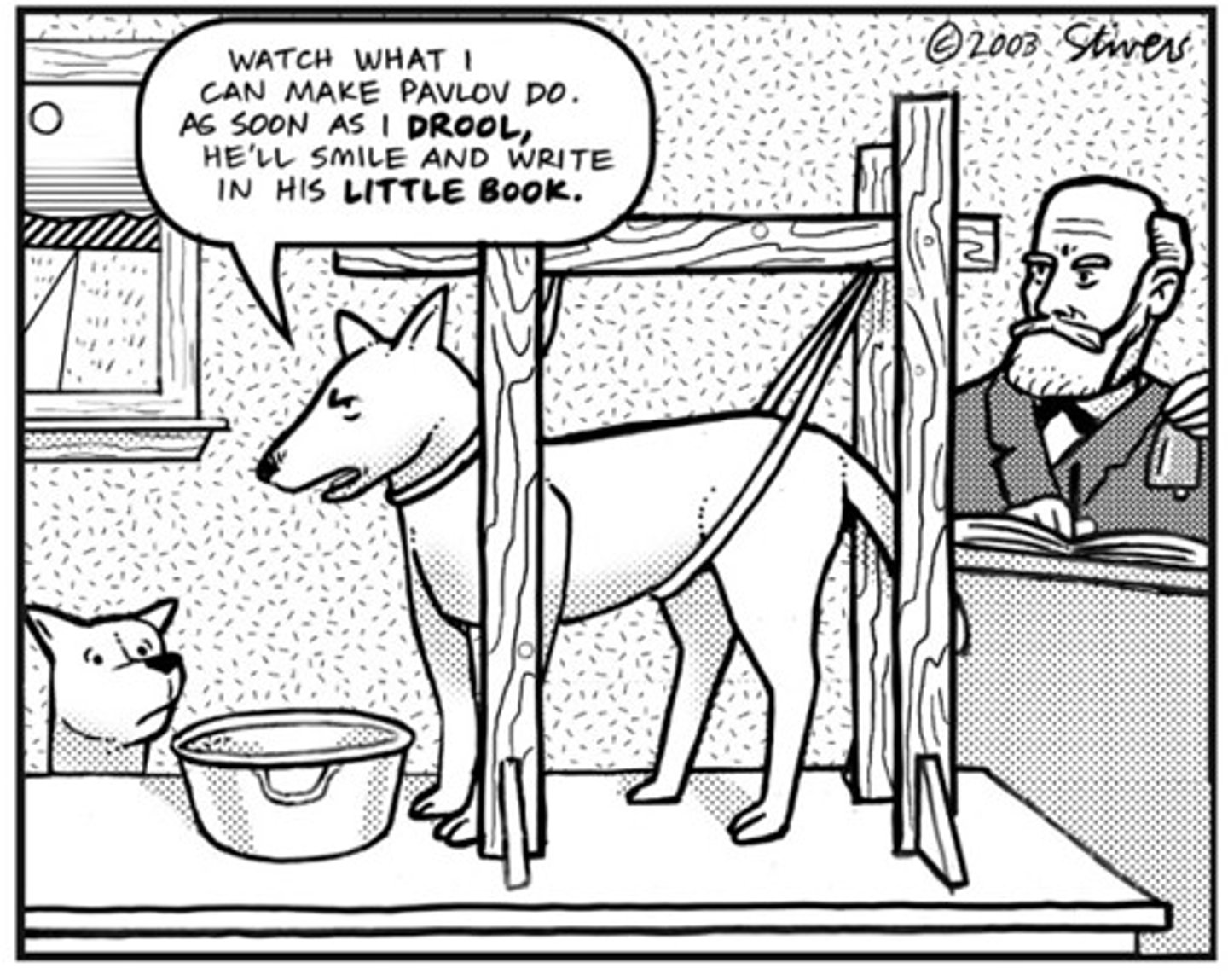
Ivan Pavlov
discovered classical conditioning; trained dogs to salivate at the ringing of a bell

Observational learning
occurs by watching others and noting the positive and negative consequences of their actions before then, if motivated and able, repeating such behaviour.
Attention
The observer must actively watch the model when completing the task and observe distinctive features of the observed behaviour.
Retention
The observer must be able to make mental representations (step by step) of the observed behaviour and its consequences.
Reproduction
The observer must have the (mental and physical) ability to perform the action. Reproduction is restricted by physical limitation, i.e. 'I can't do the splits, no matter how many times you show me'.
Motivation
The learner must want to perform the behaviour. For example, Tom wanted to be polite after watching his older brother get praised for demonstrating the same type of behaviour.
Reinforcement
The learner observes the model receiving positive reinforcement and this increases the likelihood that the observer will repeat the behaviour. (this is vicarious reinforcement).
Characteristics of the MODEL that influence attention
•Characteristics of the model (e.g. personality, attractiveness)
•Model has high status
•The model is distinctive
•Model is perceived to be similar in nature to the observer
•Model is known to the learner
Characteristics of the LEARNER that influence the likelihood of attention
•Motivation and interest of learner
•Importance of behaviour to the learner
•Avoidance of distractors
•Learner is capable of repeating the model's behaviour
Systems of knowledge
(in relation to Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander approaches to learning) refers to knowledge and skills that are based on interconnected social, physical, and spiritual understandings,
and in turn, inform survival and contribute to a strong sense of identity
Country (in relation to Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander cultures)
traditional lands of a particular language or cultural group, including both geographical boundaries and the spiritual, emotional, and intellectual connections to and within it
Multimodal
using a variety of methods
Social-cognitive approaches to learning
theories that propose learning takes place in a social setting and involves various cognitive processes